INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Materials
Table 1
Cell culture and cell viability assay
Adipocyte differentiation and Oil Red O staining
Lipolysis assay
Animals
Injection
Tissue preparation and histological analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Cytotoxicity of GPC on 3T3-L1 cells
 | Fig. 1Effect of GPC on 3T3-L1 adipocyte viability.3T3-L1 adipocytes were incubated with (A) GPC, (B) PPC and (C) AMPL at indicated concentrations for 96 h. Cell viability was determined by MTS incorporation-based cell proliferation assay. Assays were performed in triplicate for each treatment. (D) Chemical structure of experimental compounds is shown. GPC, glycerophosphocholine; PPC, phosphatidylcholine; AMPL, aminophylline. **p < 0.01 vs. control.
|
GPC suppresses adipogenesis and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
 | Fig. 2Effect of GPC on lipid accumulation and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.(A) Representative photomicrographs show lipid accumulation in the cell treated with GPC. 3T3-L1 cells were induced to differentiate with adipogenic cocktail containing IBMX, dexamethasone and insulin (MDI) in the presence or absence of GPC, PPC or AMPL. Lipid accumulation was visualized with Oil Red O staining. Scale = 100 μm (B) Intracellular lipid content in differentiated adipocytes concomitantly treated with different compounds was quantified by elution of Oil Red O stain. ***p < 0.001 vs. MDI. (C) Differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were incubated for 3 h in the absence of presence of GPC, PPC or AMPL. Lipolysis was quantified by glycerol release in incubation medium. Isoproterenol (Isop) was used as a positive control. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. non-treated cells. GPC, glycerophosphocholine; PPC, phosphatidylcholine; AMPL, aminophylline.
|
GPC enhances basal lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
GPC reduces body weight and food intake in DIO mice
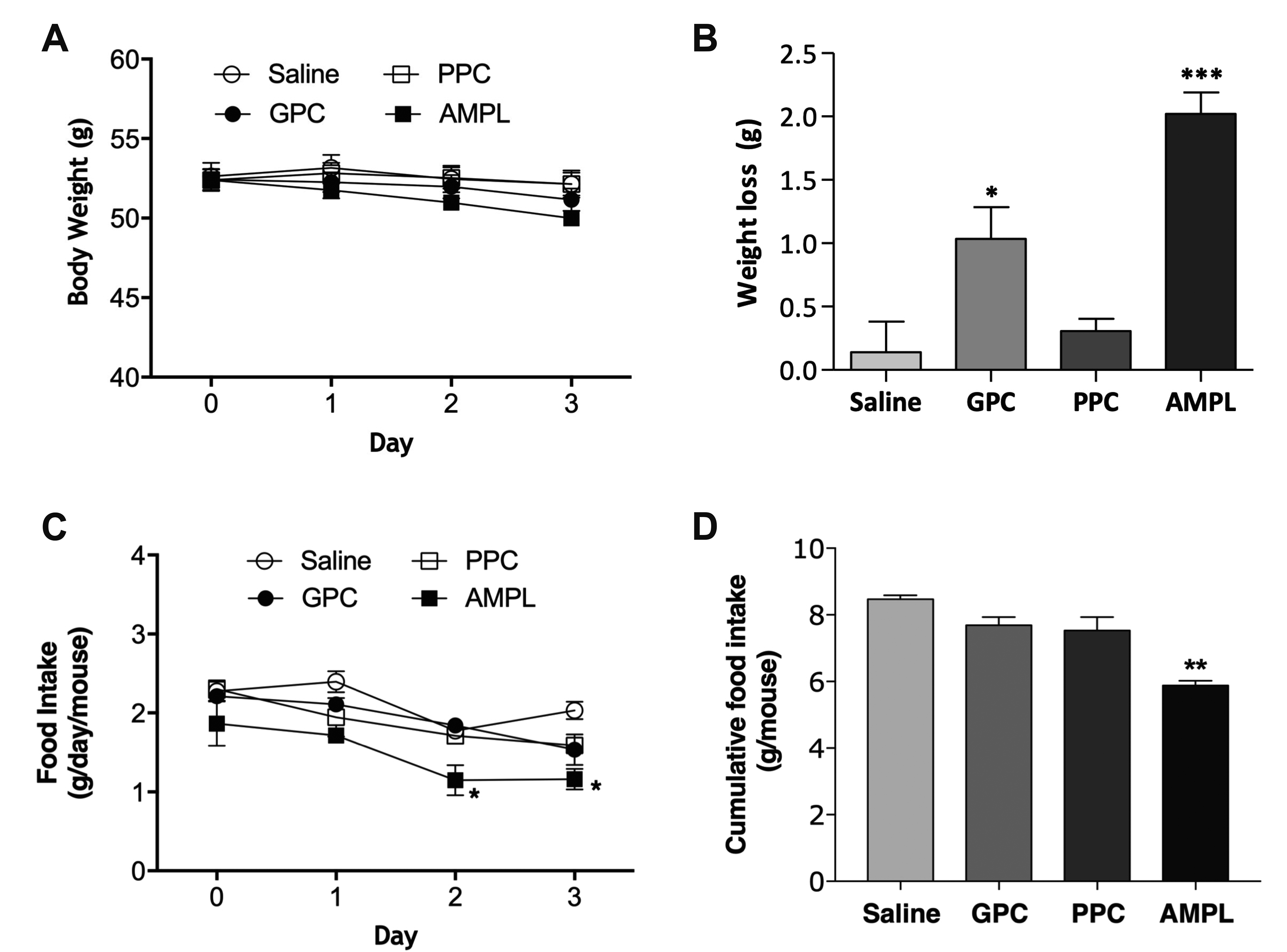 | Fig. 3Effect of GPC on body weight and food intake in DIO mice.(A) Change in body weight of the mice injected with GPC, PPC or AMPL was measured daily. Injection was initiated on day 0 and mice were sacrificed on day 3. (B) Body weight loss after treatment was calculated. (C) Change in food intake of mice injected with GPC, PPC or AMPL was measured daily. (D) Cumulative food intake during injection period was calculated. GPC, glycerophosphocholine; PPC, phosphatidylcholine; AMPL, aminophylline; DIO, diet-induced obesity. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. saline control.
|
GPC reduces inguinal fat mass and adipocyte size
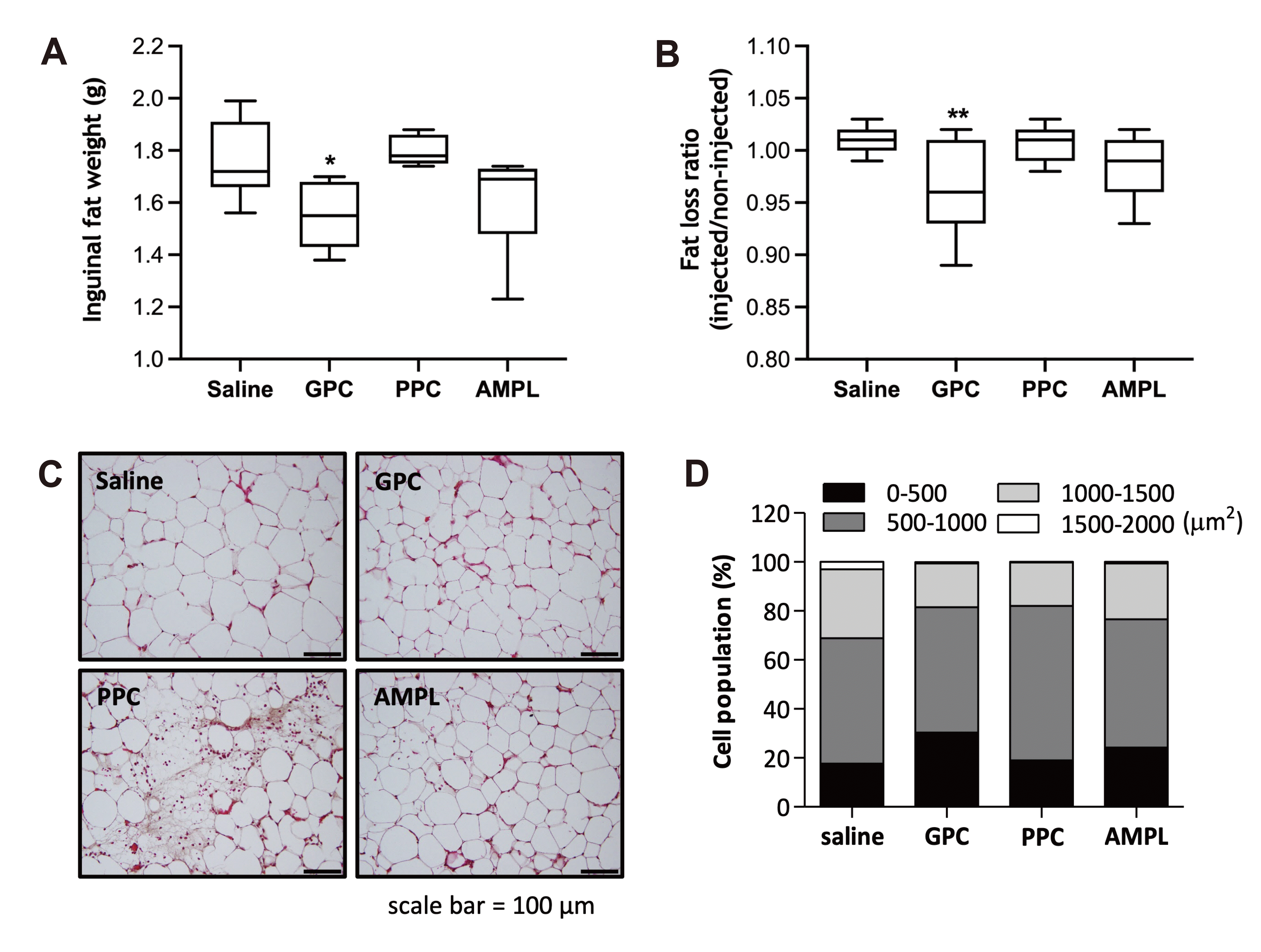 | Fig. 4Effect of GPC on localized fat reduction.(A) Inguinal adipose tissue was dissected and measured after 3 days of GPC, PPC or AMPL injection. *p < 0.05 vs. saline control. (B) Ratio of injected or non-injected mouse inguinal fat pads mass was calculated. **p < 0.01 vs. saline control. (C) Inguinal adipose tissue section was prepared from injection site and stained by H&E. Scale bars indicate 100 μm. (D) Adipocyte area was measured, and the distribution of adipocyte is shown in each size range. GPC, glycerophosphocholine; PPC, phosphatidylcholine; AMPL, aminophylline.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download