1. Forouzanfar MH, Liu P, Roth GA, et al. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA. 2017; 317:165–182. PMID:
28097354.
2. Sullivan PW, Ghushchyan V. Preference-based EQ-5D index scores for chronic conditions in the United States. Med Decis Making. 2006; 26:410–420. PMID:
16855129.

3. Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, et al. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011; 123:933–944. PMID:
21262990.
4. Kim HC, Cho SMJ, Lee H, et al. Korea hypertension fact sheet 2020: analysis of nationwide population-based data. Clin Hypertens. 2021; 27:8. PMID:
33715619.

5. Siu AL. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for high blood pressure in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2015; 163:778–786. PMID:
26458123.

6. Yoo JS, Choe EY, Kim YM, Kim SH, Won YJ. Predictive costs in medical care for Koreans with metabolic syndrome from 2009 to 2013 based on the National Health Insurance claims dataset. Korean J Intern Med. 2020; 35:936–945. PMID:
31422650.

7. Lee SW, Lee HY, Ihm SH, Park SH, Kim TH, Kim HC. Status of hypertension screening in the Korea National General Health Screening Program: a questionnaire survey on 210 screening centers in two metropolitan areas. Clin Hypertens. 2017; 23:23. PMID:
29225914.

8. Nguyen TP, Wright EP, Nguyen TT, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of screening for and managing identified hypertension for cardiovascular disease prevention in Vietnam. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0155699. PMID:
27192051.

9. Lovibond K, Jowett S, Barton P, et al. Cost-effectiveness of options for the diagnosis of high blood pressure in primary care: a modelling study. Lancet. 2011; 378:1219–1230. PMID:
21868086.

10. Briggs A, Sculpher M. An introduction to Markov modelling for economic evaluation. Pharmacoeconomics. 1998; 13:397–409. PMID:
10178664.

11. Seong SC, Kim YY, Khang YH, et al. Data resource profile: the National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:799–800. PMID:
27794523.
12. Kang SH, Kim SH, Cho JH, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in Korea. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:10970. PMID:
31358791.

13. Seong SC, Kim YY, Park SK, et al. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open. 2017; 7:e016640.

14. Law MR, Morris JK, Wald NJ. Use of blood pressure lowering drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of 147 randomised trials in the context of expectations from prospective epidemiological studies. BMJ. 2009; 338:b1665. PMID:
19454737.

15. Neal B, MacMahon S, Chapman N; Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Effects of ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, and other blood-pressure-lowering drugs: results of prospectively designed overviews of randomised trials. Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Lancet. 2000; 356:1955–1964. PMID:
11130523.
16. Kim L, Kim JA, Kim S. A guide for the utilization of health insurance review and assessment service national patient samples. Epidemiol Health. 2014; 36:e2014008. PMID:
25078381.

17. Manns B, Hemmelgarn B, Tonelli M, et al. Population based screening for chronic kidney disease: cost effectiveness study. BMJ. 2010; 341:c5869. PMID:
21059726.

18. Feldman AM, de Lissovoy G, Bristow MR, et al. Cost effectiveness of cardiac resynchronization therapy in the comparison of medical therapy, pacing, and defibrillation in heart failure (COMPANION) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 46:2311–2321. PMID:
16360064.

19. La Puma J, Lawlor EF. Quality-adjusted life-years. Ethical implications for physicians and policymakers. JAMA. 1990; 263:2917–2921. PMID:
2110986.

20. König HH, Barry JC. Cost effectiveness of treatment for amblyopia: an analysis based on a probabilistic Markov model. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:606–612. PMID:
15090409.
21. Weinstein MC, Siegel JE, Gold MR, Kamlet MS, Russell LB. Recommendations of the panel on cost-effectiveness in health and medicine. JAMA. 1996; 276:1253–1258. PMID:
8849754.

22. Shin J, Cho MC. Updated reasons and clinical implications of new Korean hypertension guidelines for cardiologists. Korean Circ J. 2020; 50:476–484. PMID:
32281319.

23. Jung MH, Ihm SH. Improving the quality of hypertension management: multifaceted approach. Korean Circ J. 2019; 49:528–531. PMID:
31074223.

24. Algabbani FM, Algabbani AM. Treatment adherence among patients with hypertension: findings from a cross-sectional study. Clin Hypertens. 2020; 26:18. PMID:
32944283.

25. Kaczorowski J, Chambers LW, Dolovich L, et al. Improving cardiovascular health at population level: 39 community cluster randomised trial of Cardiovascular Health Awareness Program (CHAP). BMJ. 2011; 342:d442. PMID:
21300712.

26. Lin CC, Ko CY, Liu JP, Lee YL, Chie WC. Nationwide periodic health examinations promote early treatment of hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia in adults: experience from Taiwan. Public Health. 2011; 125:187–195. PMID:
21440274.

27. Deng BH, Liu HW, Pan PC, Mau LW, Chiu HC. Cost-effectiveness of elderly health examination program: the example of hypertension screening. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2007; 23:17–24. PMID:
17282981.

28. Wang YC, Cheung AM, Bibbins-Domingo K, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of blood pressure screening in adolescents in the United States. J Pediatr. 2011; 158:257–264.e1-7. PMID:
20850759.

29. Pyun WB. Hypertension control in young population: the earlier, the better. Korean Circ J. 2020; 50:1092–1094. PMID:
33258317.

30. Kweon S, Kim Y, Jang MJ, et al. Data resource profile: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Int J Epidemiol. 2014; 43:69–77. PMID:
24585853.

31. National Health Insurance Service. A report on the in-depth analysis of the Korea Health Panel Survey 2013. Wonju: National Health Insurance Service;2013.
32. Ministry of Employment and Labor. Survey on work status by employment type. Sejong: Ministry of Employment and Labor;2016.
33. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. A report on the Korea Health Panel Survey of 2008. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2009.
34. Bae EY. Guidelines for economic evaluation of pharmaceuticals in Korea. J Prev Med Public Health. 2008; 41:80–83. PMID:
18385547.

35. Manns MP, Woynarowski M, Kreisel W, et al. Budesonide induces remission more effectively than prednisone in a controlled trial of patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2010; 139:1198–1206. PMID:
20600032.

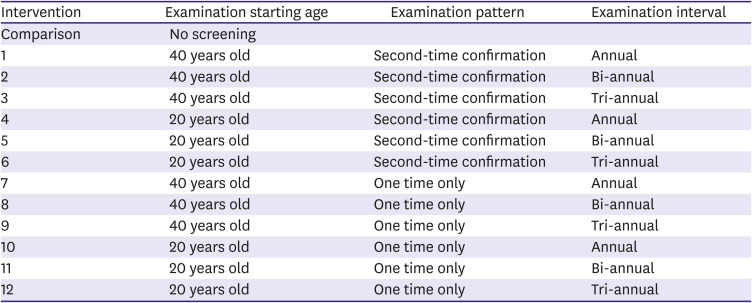
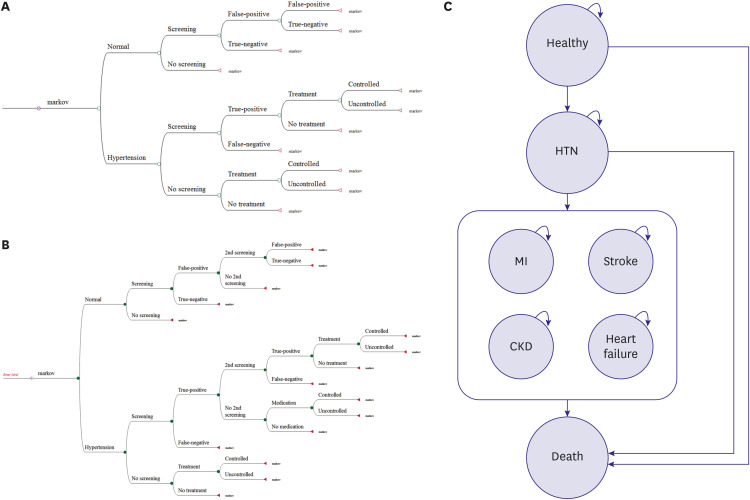
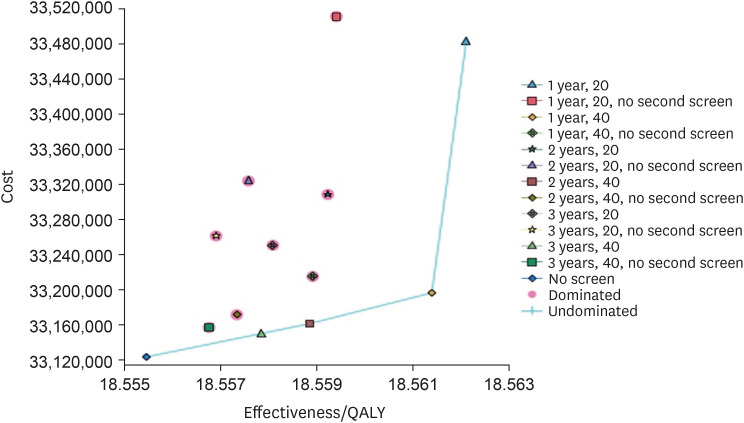




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



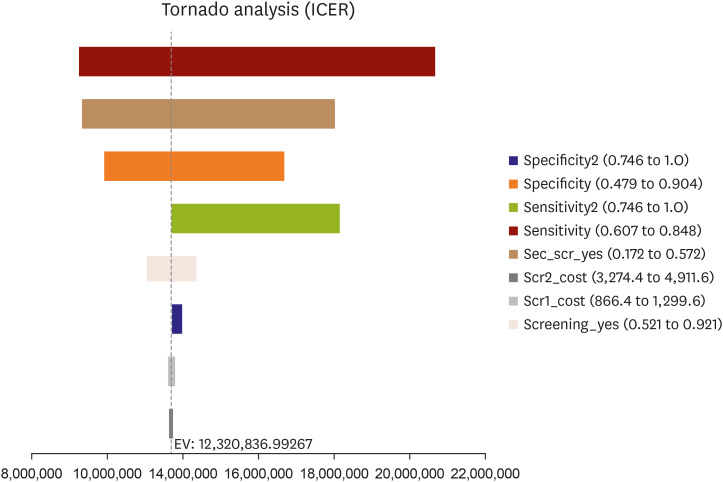
 XML Download
XML Download