서 론
연구대상 및 방법
1. Cell culture and treatment with nicotine
2. Cell viability assay
3. Apoptosis and necrosis assay
4. Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
Table 1
5. Enzyme-liked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
6. Inhibitory effect of nicotine on cell proliferation
7. 통계학적 유의성 검사
연구 성적
1. MTT assay
Table 2
| MTT assay | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | Mean±SD | ||
| Nicotine | Control | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.45±0.01 |
| 0.1 mM | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.44±0.02 | |
| 1 mM | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.44±0.01 | |
| 5 mM | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.21±0.03* | |
| 10 mM | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.12±0.01* | |
2. Investigation of apoptosis and necrosis
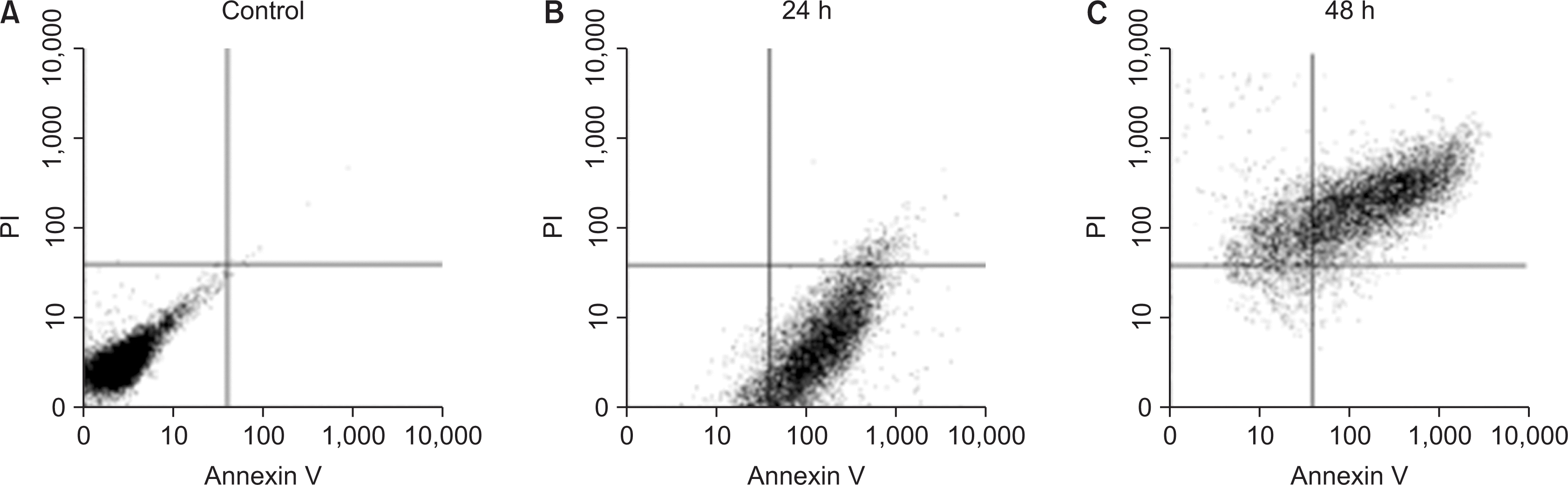 | Fig. 2Investigation of apoptosis and necrosis. Nicotine-treated HGF for 24 h and 48 h was treated with 2 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in PBS to detach from cell culture dish. The cell was washed twice with cold PBS. The cells were reacted 1.25 µl of Annexin V-FITC in Binding buffer (200 µl; 0.1 M HEPES, pH7.4; 1.4 M NaCl; 25 mM CaCl2) for 15 min at RT in the dark and then add 4 µl of propidium iodine (0.05 mg/ml). The cells were analyzed by a fluorescence-activated cell sorter. |
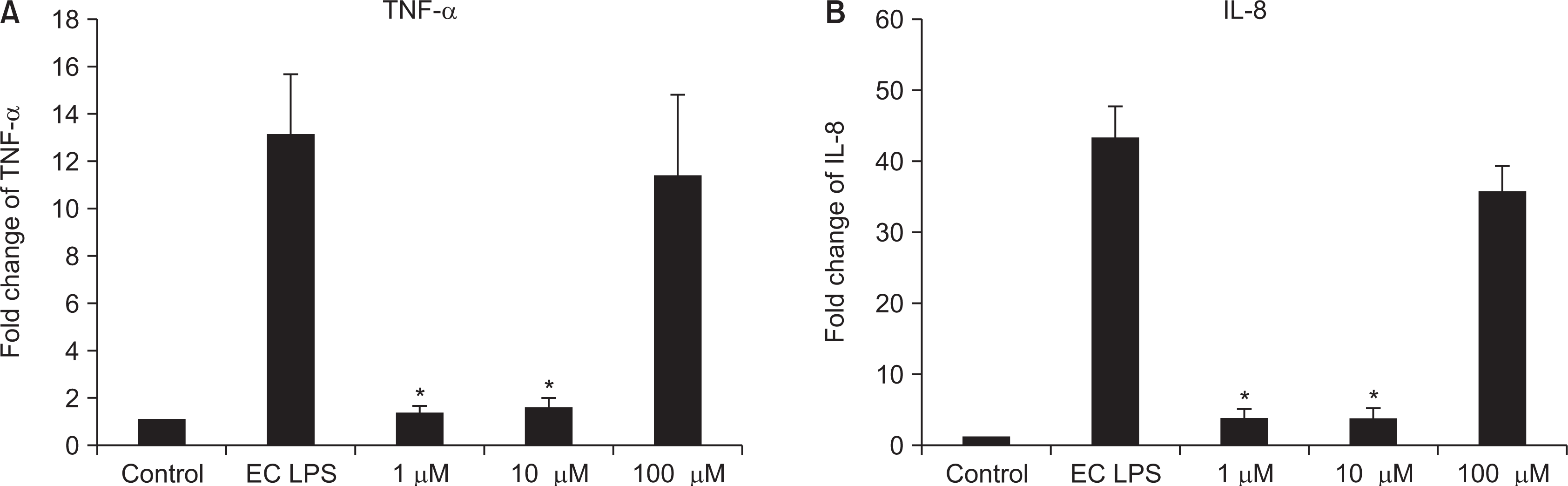
3. Investigation of inflammation cytokines by real-time RT PCR
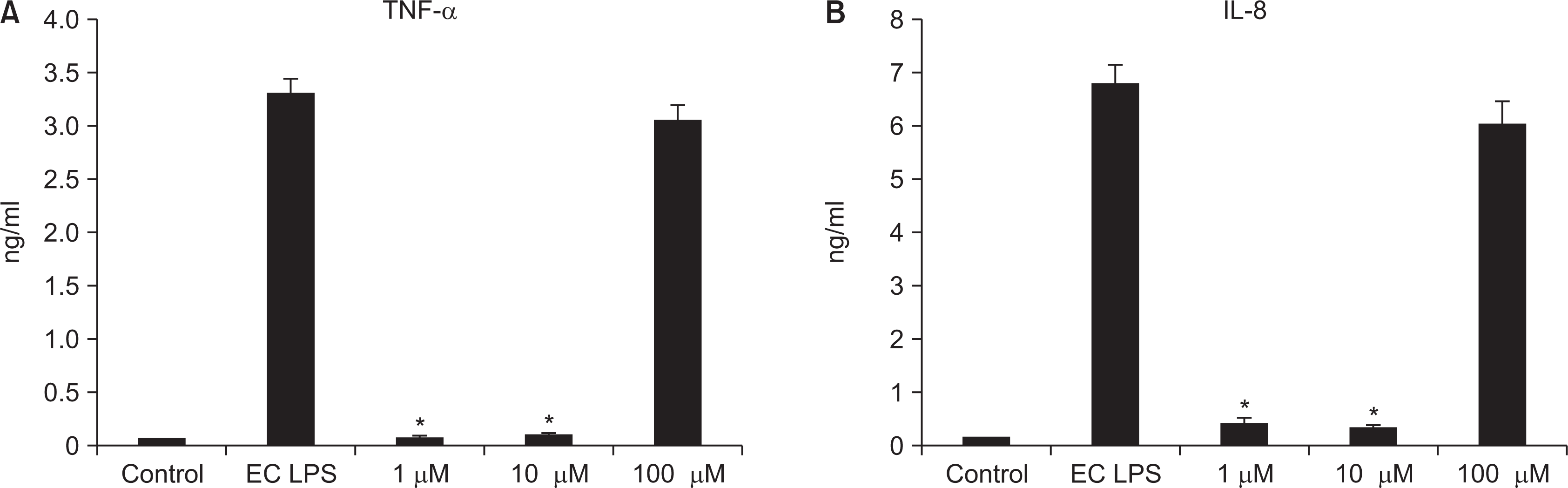
4. Investigation of inflammation cytokines by ELISA
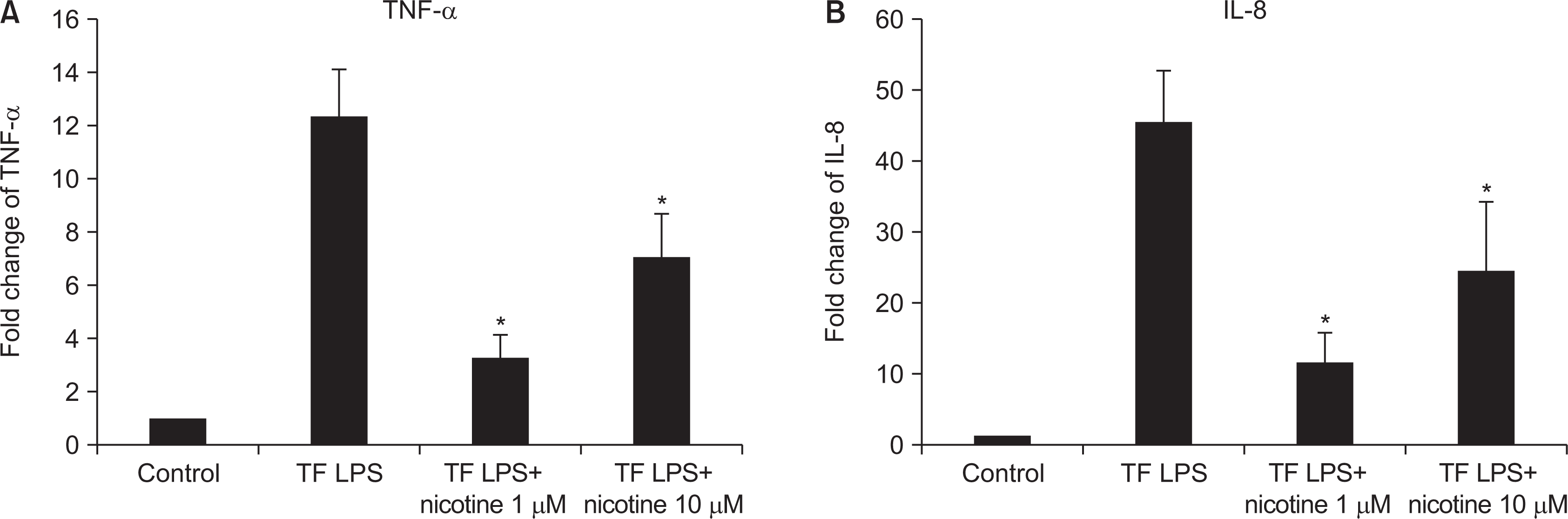
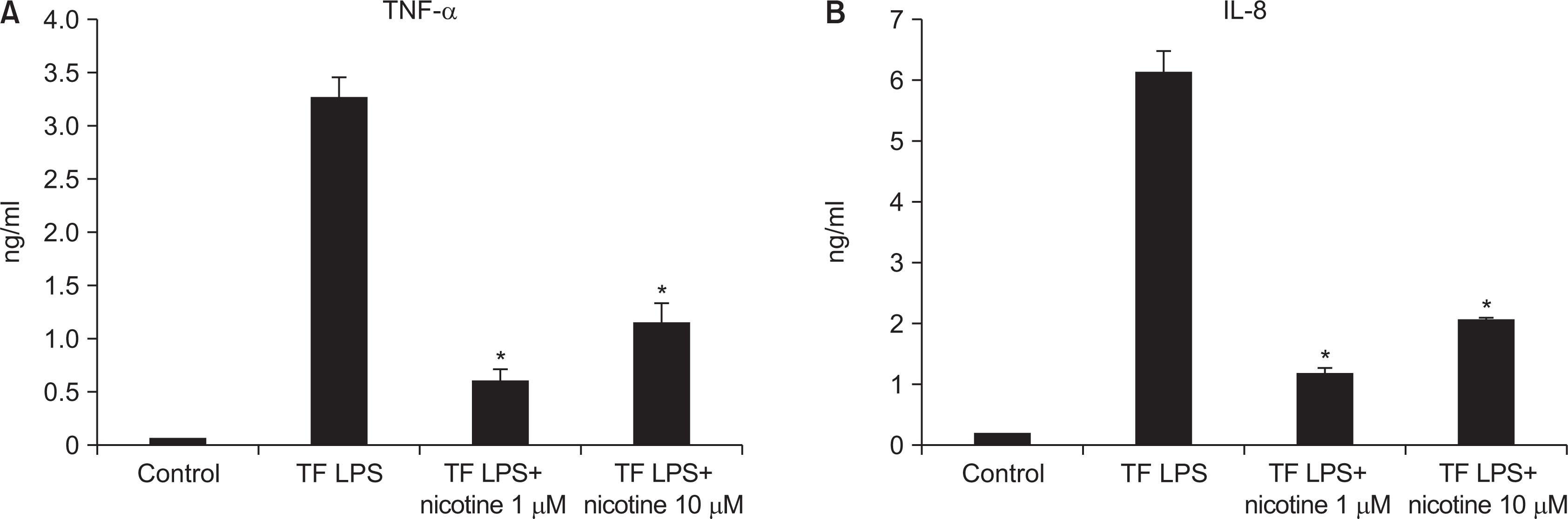 | Fig. 6Investigation of inflammation cytokines by T. forsythia LPS. HGF was treated with T. forsythia LPS in the presence or the absence of nicotine. The cell was used to RT-PCR, and the conditioned media was used to ELISA. *Statistically significant difference compared with T. forsythia LPS (P<0.05). |
5. Inhibitory effect of nicotine on cell proliferation
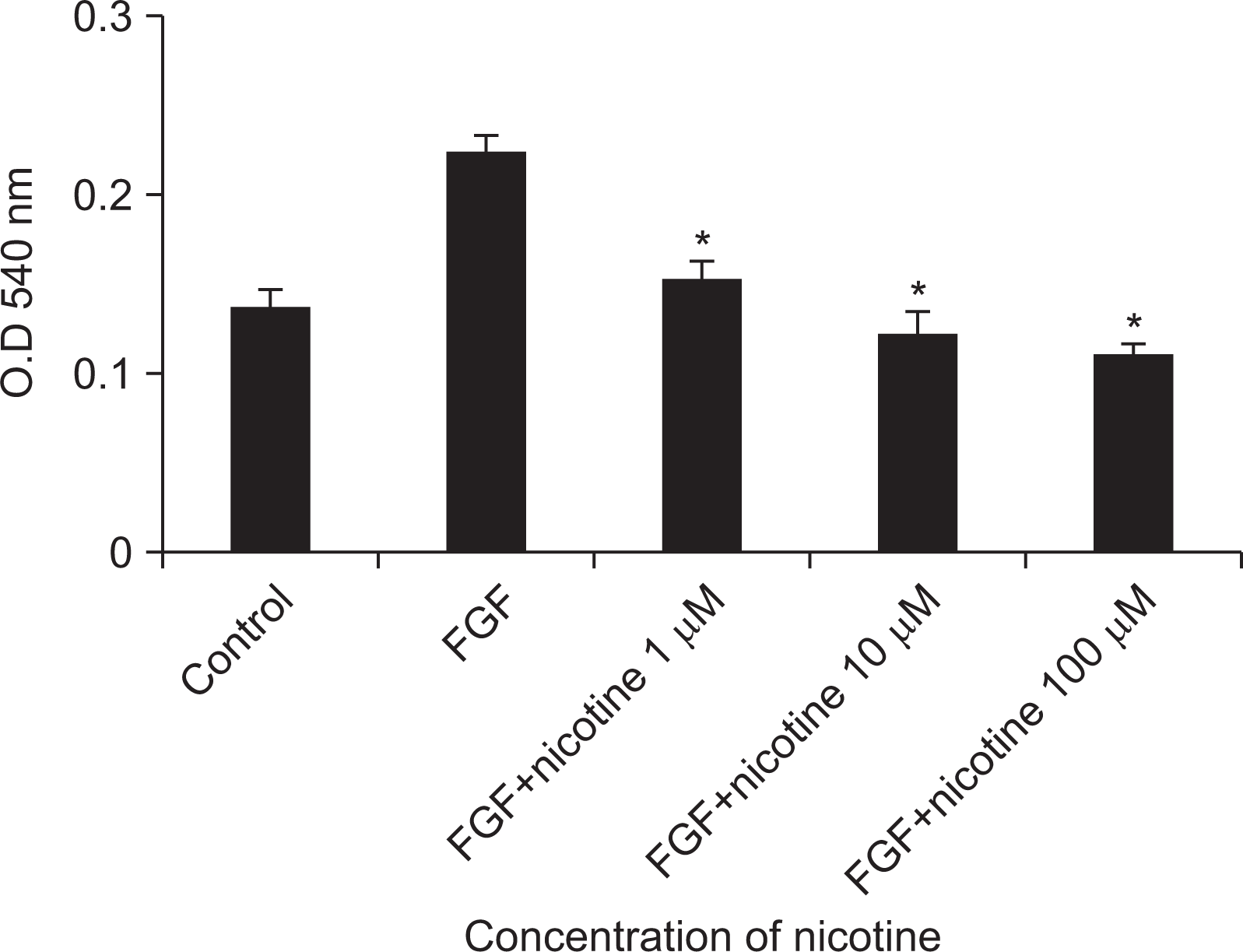 | Fig. 7Inhibitory effect of nicotine on cell proliferation. The gingival fibroblasts were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, and cells were dropped using trypsin-EDTA and dispensed into a 96-well polystyrene culture dish at 1×103 cells/ml at a concentration of 10 ng/ml was added to the culture medium, Of nicotine was added to the culture medium to remove the existing culture medium. After incubation in a 5% CO2 incubator for 12 hours, cell growth was examined using MTT. *Statistically significant difference compared with fibroblast growth factor (P<0.05). FGF, fibroblast growth factor. |
Table 3
| MTT assay | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | Mean±SD | |
| Control | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14±0.01 |
| FGF | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.22±0.00 |
| FGF+nicotine 1 mM | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.15±0.01* |
| FGF+nicotine 10 mM | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.12±0.01* |
| FGF+nicotine 100 µM | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11±0.00* |
The gingival fibroblasts were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, and cells were dropped using trypsin-EDTA and dispensed into a 96-well polystyrene culture dish at 1×103 cells/ml at a concentration of 10 ng/ml was added to the culture medium, Of nicotine was added to the culture medium to remove the existing culture medium. After incubation in a 5% CO2 incubator for 12 hours, cell growth was examined using MTT. *Statistically significant difference compared with fibroblast growth factor (P<0.05).
고 안
결 론
1) 니코틴의 농도가 높아질수록 치은섬유아세포의 생존능력이 감소하였다.
2) 저농도(0.1 mM)의 니코틴을 투여시, 24시간 노출시 치은 섬유아세포의 사멸이 발생하는 것으로 나타났고 48시간 노출시 치은 섬유아세포의 사멸과 괴사가 함께 발생하는 것으로 나타났다.
3) 염증성 사이토카인은 Real-time RT-PCR, ELISA 측정시 니코틴의 농도가 높아질수록 높아졌다.
4) 염증성 사이토카인이 낮았던 저농도(1, 10 µM)의 니코틴에 E. coli LPS, T. forsythia LPS를 추가 처치하였을 때 염증성 사이토카인의 발현을 낮추는 것으로 나타났다.
5) 성장인자(FGF)는 니코틴을 투여시, 농도가 높아질수록 세포의 생존능력이 감소함을 나타냈다.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download