1. Rosse C, Gaddum-Rosse P. 1997. Hollinshead's textbook of anatomy. 5th ed. Lippincott-Raven;Philadelphia: p. 473.
2. Moore KL, Persaud TVN. Moore KL, Persaud TVN, editors. 2003. The cardiovascular system. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology. 7th ed. Saunders;Philadelphia: p. 340–5.
3. Sadler TW. Sadler TW, editor. 2012. Cardiovascular system. Langman's Medical Embryology. 12th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia: p. 162–200.
4. Standring S, Gray H. 2008. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 40th ed. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier;Edinburgh: p. 964.
5. Nashat H, Montanaro C, Li W, Kempny A, Wort SJ, Dimopoulos K, Gatzoulis MA, Babu-Narayan SV. 2018; Atrial septal defects and pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Thorac Dis. 10(Suppl 24):S2953–65. DOI:
10.21037/jtd.2018.08.92. PMID:
30305956. PMCID:
PMC6174141.

6. Schott JJ, Benson DW, Basson CT, Pease W, Silberbach GM, Moak JP, Maron BJ, Seidman CE, Seidman JG. 1998; Congenital heart disease caused by mutations in the transcription factor NKX2-5. Science. 281:108–11. DOI:
10.1126/science.281.5373.108. PMID:
9651244.


8. Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R, Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS, Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, Matsuoka R, Cohen JC, ivastava D Sr. 2003; GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature. 424:443–7. DOI:
10.1038/nature01827. PMID:
12845333.


9. Davison P, Clift PF, Steeds RP. 2010; The role of echocardiography in diagnosis, monitoring closure and post-procedural assessment of patent foramen ovale. Eur J Echocardiogr. 11:i27–34. DOI:
10.1093/ejechocard/jeq120. PMID:
21078836.

10. Mirzaali M, Dooley M, Wynne D, Cooter N, Lee L, Haworth P, Saha R, Gainsborough N, Hildick-Smith D. 2015; Patent foramen ovale closure following cryptogenic stroke or transient ischaemic attack: long-term follow-up of 301 cases. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 86:1078–84. DOI:
10.1002/ccd.26080. PMID:
26105198.


11. Nighoghossian N, Perinetti M, Barthelet M, Adeleine P, Trouillas P. 1996; Potential cardioembolic sources of stroke in patients less than 60 years of age. Eur Heart J. 17:590–4. DOI:
10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a014913. PMID:
8733093.


12. Milev I, Zafirovska P, Zimbakov Z, Idrizi S, Ampova-Sokolov V, Gorgieva E, Ilievska L, Tosheski G, Hristov N, Georgievska-Ismail L, Anguseva T, Mitrev Z. 2016; Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale: a single center experience. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 4:613–8. DOI:
10.3889/oamjms.2016.113. PMID:
28028400. PMCID:
PMC5175508.



13. Overell JR, Bone I, Lees KR. 2000; Interatrial septal abnormalities and stroke: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Neurology. 55:1172–9. DOI:
10.1212/WNL.55.8.1172. PMID:
11071496.


14. Nietlispach F, Meier B. 2015; Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale: safe and effective but underutilized. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 13:121–3. DOI:
10.1586/14779072.2015.1000305. PMID:
25556896.


15. Rigatelli G, Magro B, Oliva L. 2011; Anatomo-functional characterization of interatrial septum for catheter-based interventions. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 1:227–35. PMID:
22254200. PMCID:
PMC3253514.


16. Marelli AJ, Mackie AS, Ionescu-Ittu R, Rahme E, Pilote L. 2007; Congenital heart disease in the general population: changing prevalence and age distribution. Circulation. 115:163–72. DOI:
10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.627224. PMID:
17210844.

17. Rigatelli G, Rigatelli G. 2005; Congenital heart diseases in aged patients: clinical features, diagnosis, and therapeutic indications based on the analysis of a twenty five-year Medline search. Cardiol Rev. 13:293–6. DOI:
10.1097/01.crd.0000145928.08280.ef. PMID:
16230886.

18. Reig J, Mirapeix R, Jornet A, Petit M. 1997; Morphologic characteristics of the fossa ovalis as an anatomic basis for transseptal catheterization. Surg Radiol Anat. 19:279–82. DOI:
10.1007/BF01637589. PMID:
9413071.


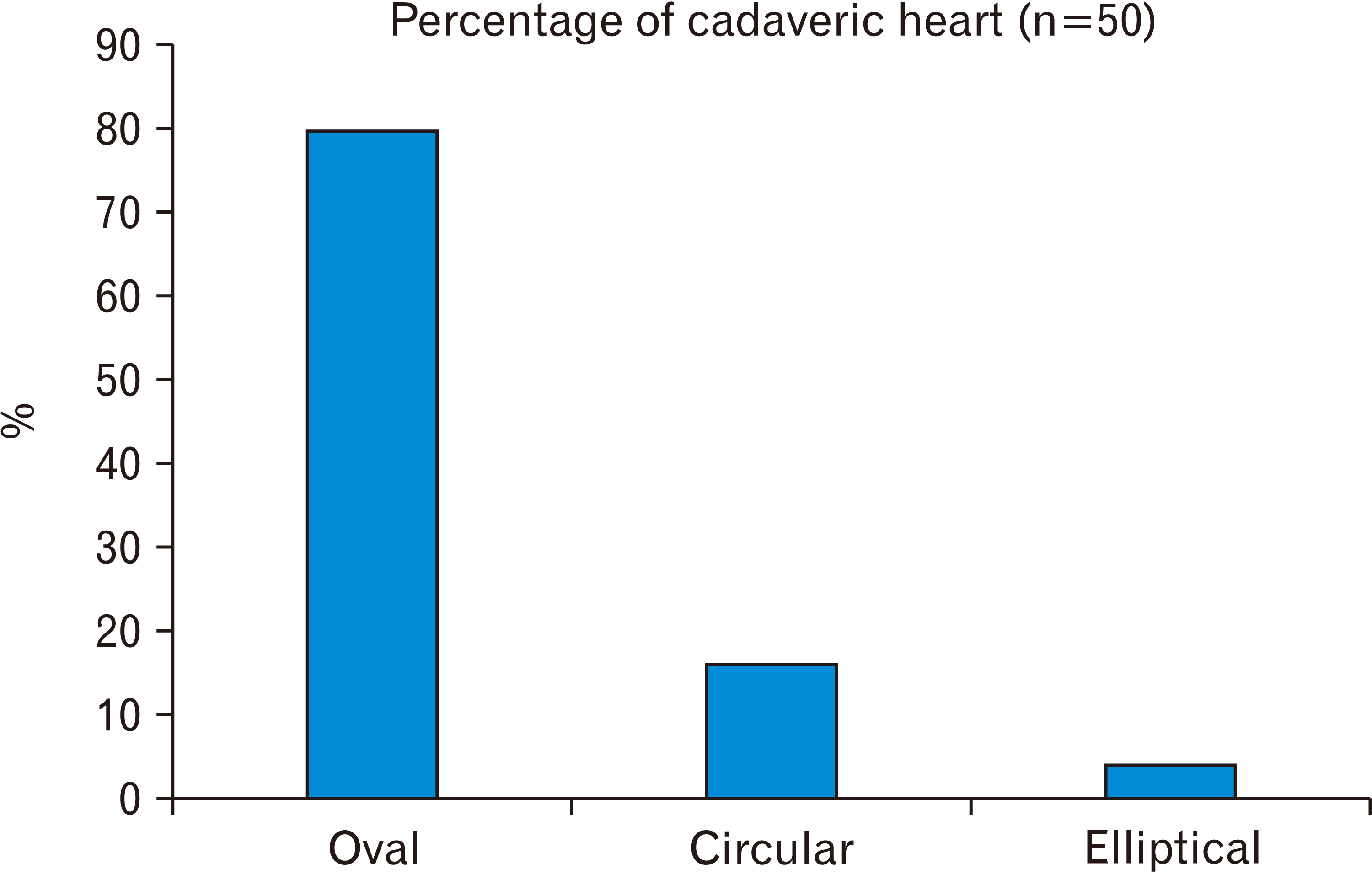
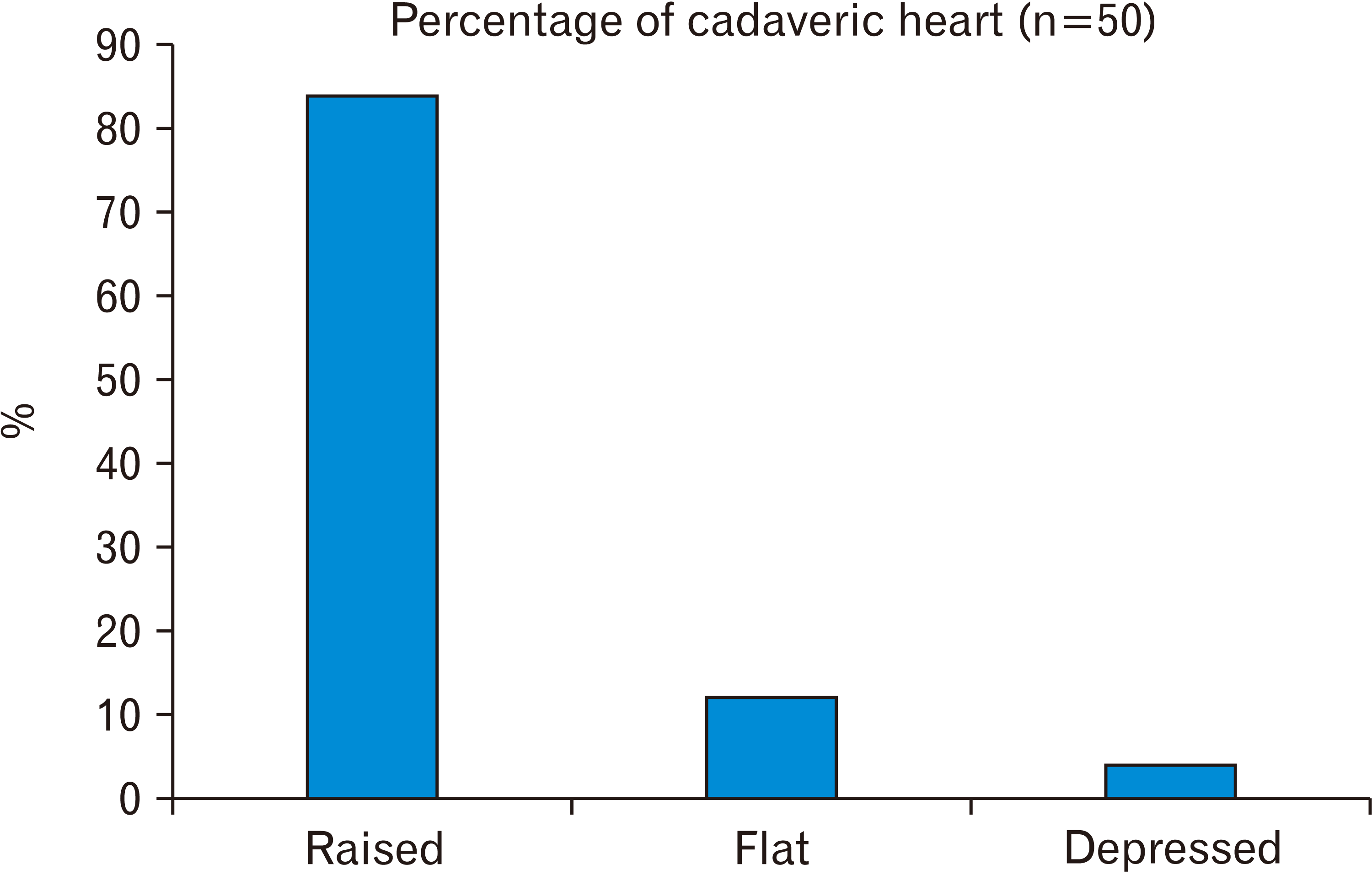
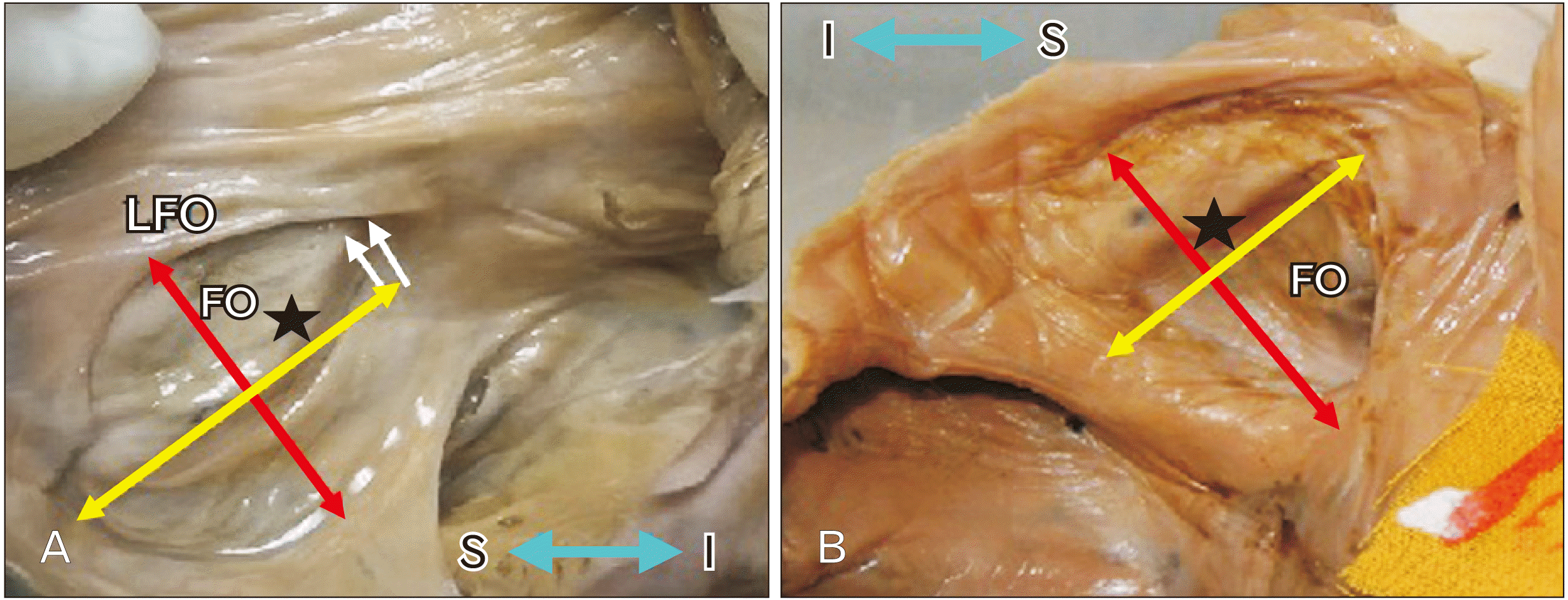
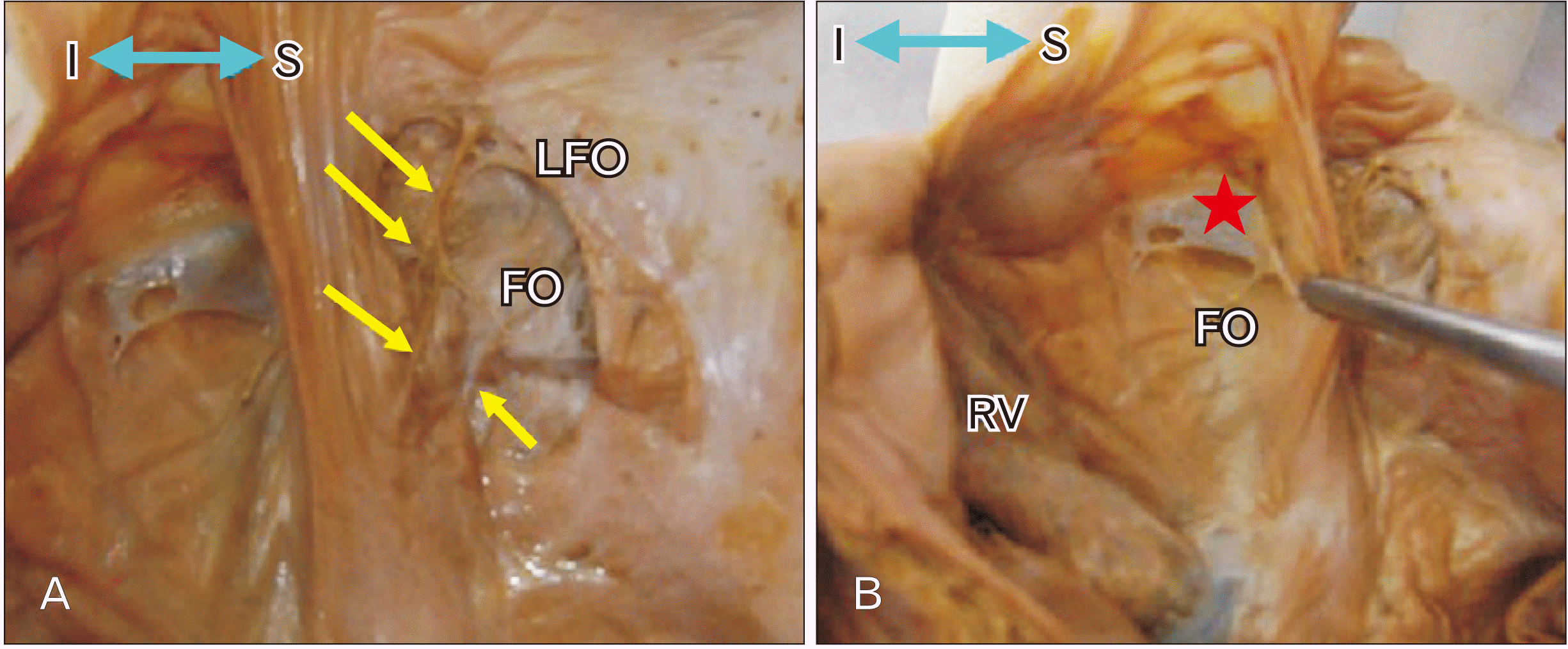
19. Kanani SD, Tank K, Patil DS, Nirvan AB, Dave RV. 2014; Cadaveric study of fossa ovalis. BJKines-NJBAS. 6:1–4.
20. Fraisse A, Latchman M, Sharma SR, Bayburt S, Amedro P, di Salvo G, Baruteau AE. 2018; Atrial septal defect closure: indications and contra-indications. J Thorac Dis. 10(Suppl 24):S2874–81. DOI:
10.21037/jtd.2018.08.111. PMID:
30305947. PMCID:
PMC6174144.

21. Chan KC, Godman MJ. 1993; Morphological variations of fossa ovalis atrial septal defects (secundum): feasibility for transcutaneous closure with the clam-shell device. Br Heart J. 69:52–5. DOI:
10.1136/hrt.69.1.52. PMID:
8457395. PMCID:
PMC1024917.

23. Kydd AC, Das P, Hoole S, Shapiro LM, Rana BS. 2013; Defining patent foramen ovale morphology using three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography and relationship to shunt size. Heart. 99(Suppl S2):A72. DOI:
10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304019.119.
25. Rana BS, Shapiro LM, McCarthy KP, Ho SY. 2010; Three-dimensional imaging of the atrial septum and patent foramen ovale anatomy: defining the morphological phenotypes of patent foramen ovale. Eur J Echocardiogr. 11:i19–25. DOI:
10.1093/ejechocard/jeq122. PMID:
21078835.

26. Kim JS, Virágh S, Moorman AF, Anderson RH, Lamers WH. 2001; Development of the myocardium of the atrioventricular canal and the vestibular spine in the human heart. Circ Res. 88:395–402. DOI:
10.1161/01.RES.88.4.395. PMID:
11230106.


28. Teo KS, Disney PJ, Dundon BK, Worthley MI, Brown MA, Sanders P, Worthley SG. 2010; Assessment of atrial septal defects in adults comparing cardiovascular magnetic resonance with transoesophageal echocardiography. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 12:44. DOI:
10.1186/1532-429X-12-44. PMID:
20663157. PMCID:
PMC2912273.



29. Klimek-Piotrowska W, Hołda MK, Koziej M, Piątek K, Hołda J. 2016; Anatomy of the true interatrial septum for transseptal access to the left atrium. Ann Anat. 205:60–4. DOI:
10.1016/j.aanat.2016.01.009. PMID:
26879344.


30. Bhatnagar KP, Nettleton GS, Campbell FR, Wagner CE, Kuwabara N, Muresian H. 2006; Chiari anomalies in the human right atrium. Clin Anat. 19:510–6. DOI:
10.1002/ca.20195. PMID:
16258973.


31. Krishnan SC, Salazar M. 2010; Septal pouch in the left atrium: a new anatomical entity with potential for embolic complications. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 3:98–104. DOI:
10.1016/j.jcin.2009.07.017. PMID:
20129577.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download