Abstract
Background
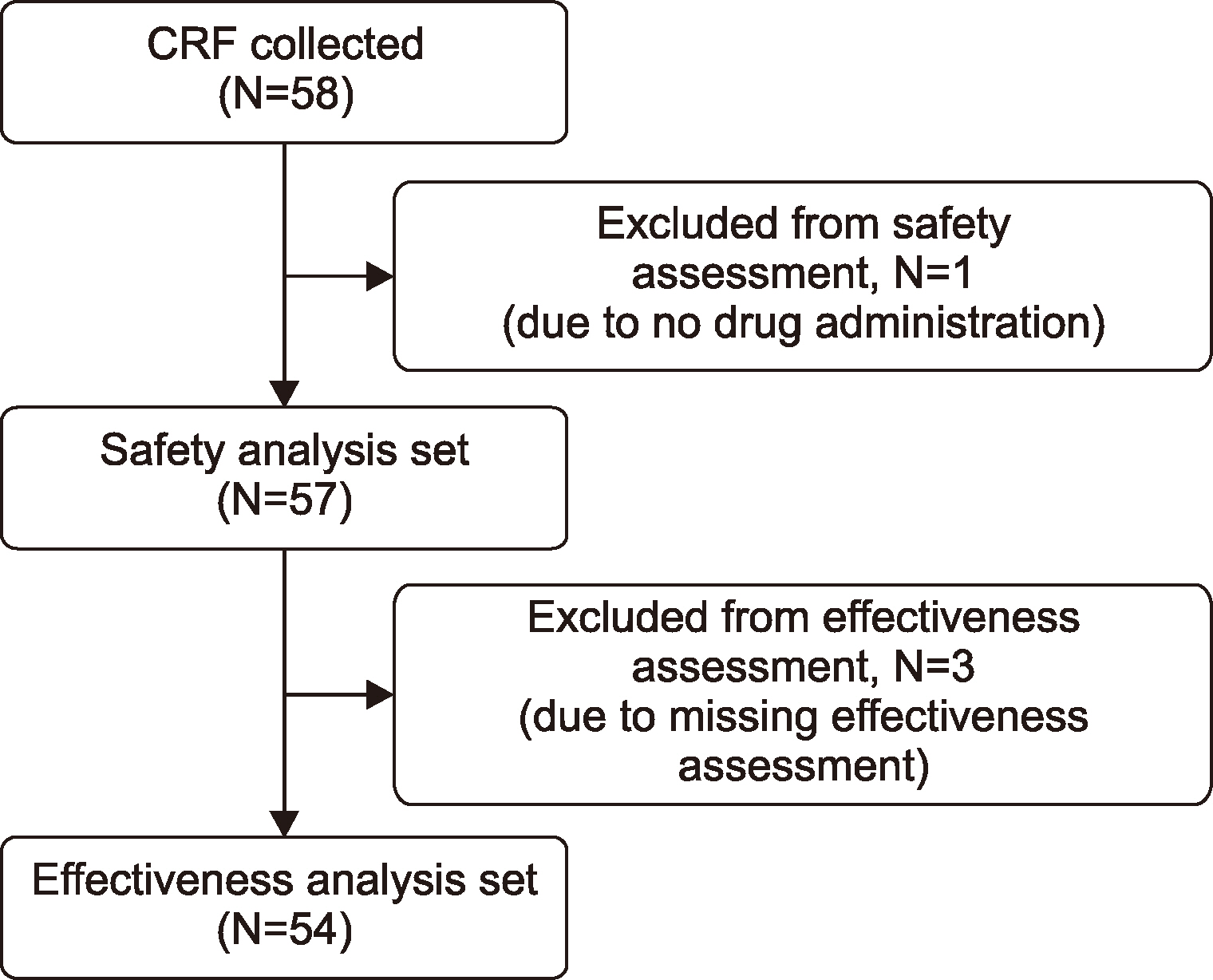
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
E.J. Choi, T.J. Hwang, Y.M. Choi, H.C. Kim, and M.C. Yoo collected and interpreted data, and reviewed, edited, and approved the manuscript; H. Song developed the publication plan and interpreted and reviewed the data; K.A. Badejo developed the study plan and evaluated the data, reviewed, and approved the manuscript.
REFERENCES
Table 1
| Characteristics | N=57 |
|---|---|
| Sex, N (%) | |
| Male | 57 (100.0) |
| Age, mean±SD | 34.6±19.0 |
| Age group (yr), N (%) | |
| <6 | 3 (5.3) |
| ≥6 to <12 | 6 (10.5) |
| ≥12 to <19 | 4 (7.0) |
| ≥19 | 44 (77.2) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean±SDa) | 24.0±3.7 |
| Hepatic impairment, N (%) | |
| Yes | 6 (10.5) |
| No | 51 (89.5) |
| History of allergic reactions, N (%) | |
| Yes | 1 (1.8) |
| No | 55 (96.5) |
| Unknown | 1 (1.8) |
| Family history of inhibitor development, N (%) | |
| Yes | 3 (5.3) |
| No | 51 (89.5) |
| Unknown | 3 (5.3) |
| Bleeding episodes by severity (number) within the last 12 mo (mean±SD) | |
| Minor (N=41) | 22.4±24.8 |
| Moderate (N=14) | 2.5±3.1 |
| Major (N=4) | 1.3±0.5 |
| Use of FIX before Rixubis treatment, N (%) | |
| Yes | 54 (94.7) |
| No | 3 (5.3) |
| Total number of days of FIX product use after hemophilia B diagnosis, N (%)b) | |
| 1–4 days | 4 (7.4) |
| 5–20 days | 4 (7.4) |
| 21–50 days | 4 (7.4) |
| 51–100 days | 16 (29.6) |
| 101–150 days | 1 (1.9) |
| >150 days | 24 (44.4) |
| Current medical status, N (%) | |
| Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome | 3 (5.3) |
| Chronic hepatitis C | 3 (5.3) |
| Chronic hepatitis B | 2 (3.5) |
| Hepatitis C | 1 (1.8) |
| Hypertension | 4 (7.0) |
| Arthralgia | 1 (1.8) |
| Hemophilic arthropathy | 1 (1.8) |
| Osteonecrosis | 1 (1.8) |
| Arthroscopy | 1 (1.8) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1 (1.8) |
| Bronchitis chronic | 1 (1.8) |
| Rehabilitation therapy | 1 (1.8) |
| Duration of hemophilia B (yr), mean±SDb) | 18.1±10.2 |
Table 2
Prophylaxis:
-
Total treatment dose (IU/kg)=sum of [(total number of infusions)×(total dose per infusion/body weight)]
✓ Total number of infusions=(actual Dosing interval)×integer of {(stop date of treatment regimen-start date of treatment regimen+1)/7} +[7×decimal of {(stop date of treatment regimen-start date of treatment regimen+1)/7}]/(dosing interval)
✓ Actual dosing interval=stop date of treatment regimen-start date of treatment regimen
Average treatment dose (IU/kg)=(total treatment dose/body weight)/total number of infusions
Table 3
| AEs (PTa)) | N of patients (%) | N of AEs | Unexpected AEs | Serious AEs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemophilic arthropathy | 2 (3.5) | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Cataract | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Upper abdominal pain | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Aspergillus infection | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Tinea pedis | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Procedural pain | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Anti-factor IX antibody increasedb) | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Hyperuricemia | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Insomnia | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Hematuria | 1 (1.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 8 (14.0) | 11 | 11 | 3 |
Table 4
| Treatment type | N of assessments (%) | N of patients (%)b) |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment of bleedinga) | ||
| Total | 66 | 25c) |
| None | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Fair | 11 (16.7) | 7 (28.0) |
| Good | 50 (75.8) | 17 (68.0) |
| Excellent | 5 (7.6) | 4 (16.0) |
| Effective (excellent+good) | 55 (83.3) | 18 (72.0) |
| Prophylaxisa) | ||
| Total | 76 | 40c) |
| None | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Fair | 8 (10.5) | 5 (12.5) |
| Good | 47 (61.8) | 32 (80.0) |
| Excellent | 21 (27.6) | 17 (42.5) |
| Effective (excellent+good) | 68 (89.5) | 35 (87.5) |
| Overall treatment typea) | ||
| Total | 142 | 54c) |
| None | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Fair | 19 (13.4) | 12 (22.2) |
| Good | 97 (68.3) | 43 (79.6) |
| Excellent | 26 (18.3) | 20 (37.0) |
| Effective (excellent+good) | 123 (86.6) | 42 (77.8) |
a)In case an assessment is performed by the patient as well as by the physician, then the worst-case assessment is considered. b)For the ratings “None,” “Fair,” “Good,” or “Excellent,” each patient could rate more often. For the rating “Good” or “Excellent,” in case a patient had more than one assessment, the worst-case assessment is considered for this patient. c)Number of unique patients with an effectiveness assessment available in the respective “Treatment type/Assessor.”




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download