INTRODUCTION
METHODS
The curriculum development and implementation
Table 1
Two-week schedule of the IPE program in 2018
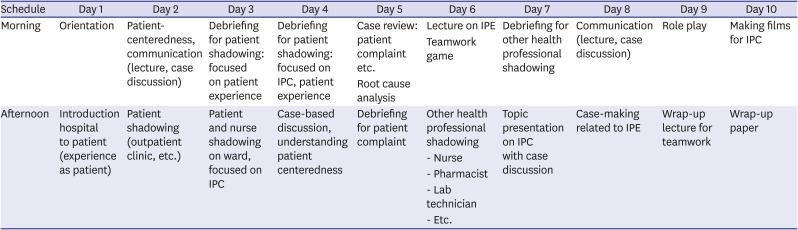
Table 2
Two-week schedule of the IPE program in 2019

- Human centeredness/Patient centeredness
- Patient experience
- Patient safety
- Values/Ethics for Interprofessional Practice
- Roles/Responsibilities
- Communication with patients
- Communication with other professionals
- Teams and teamwork
- Respect
Subjects
Outcome measures
Level 1 – Reaction: After the training, we asked all students to describe their satisfaction with the IPE program. We asked them to each write a reflection paper and to make a video clip describing their experiences, lessons learned, and feelings during the program.
Level 2 – Modification of attitudes/perceptions & acquisition of knowledge/skills: To analyze perceptual changes of students related to readiness for interprofessional learning, we asked all students to complete a readiness for interprofessional learning scale (RIPLS) 19-item questionnaire (see Table 3 for items) before, immediately after, and 4 months after the training. The RIPLS is a commonly used tool for evaluating attitudes and perceptions of students regarding IPE that was developed by Parsell and Bligh.21 We used the 2009 version of the RIPLS that was adapted by Latrobe Health Service and the Health & Social Care Interprofessional Network and consists of 19 questions and 4 subscales including teamwork and collaboration, negative professional identity, positive professional identity, and roles and responsibilities.222324 In order to help students understand it, the questionnaire was written in both Korean and English. Students gave responses to the statements using a five-point scale (5 = strongly agree; 1 = strongly disagree).
Table 3
Results of the RIPLS surveys before and after IPE training in 2018 and 2019

Levels 3 and 4 – Behavioral change and change in organizational practice & benefit to patients: By the end of the medical internships of the medical graduates who first participated in the IPE program, we obtained 360° evaluation by diverse health professionals during the medical internships one year after the training. During 1 year of their internship, we received feedback repeatedly from senior doctors and nurses. At the end of each year, nurses have scored satisfaction with interns as team members using 5-point Likert scale (5 = very satisfied, 1 = very dissatisfied), and we compared satisfaction scores before and after IPE training. As for improvement of patient outcome and benefit to patients, we are planning a long-term follow-up comparative investigation to see if there was any change in patient outcomes after the IPE training.
Data analysis
RESULTS
Participant satisfaction with the education program
- I'm glad I could participate in this curriculum before my clinical clerkship.
- I was surprised to see that there are so many different jobs in the hospital that I had not heard of before.
- It was only a few days' program, but as I toured various facilities in wards and hospitals, I realized that hospitals could never be run by doctors alone.
- It was good chance for me to see the system of the hospital as a whole before my clinical clerkship.
- I really enjoyed shadowing. After visiting various departments and experiencing other jobs indirectly through friends' presentations, I could feel that so many people were working together in the hospital. When I asked my seniors who are currently in practice, they said they didn't know there was such a department in the hospital after a year of practice.
- I now understand that the hospital needs a wide variety of other jobs besides doctor or nurse to function.
- It was an opportunity to feel how hard nurses were working and realize that patient care is not something that doctors can do without their cooperation.
- The simulation session with nursing students was so fun, and I couldn't help but admire the professionalism of the nursing students.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download