Highlights
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design and population
Definition of diabetic microvascular complications
Anthropometric and biochemical measurements
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Characteristics of study population
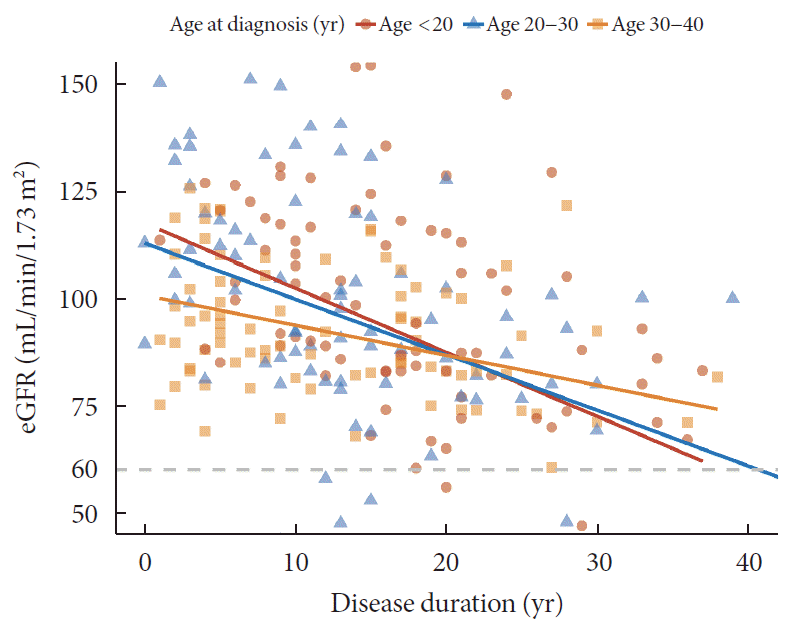
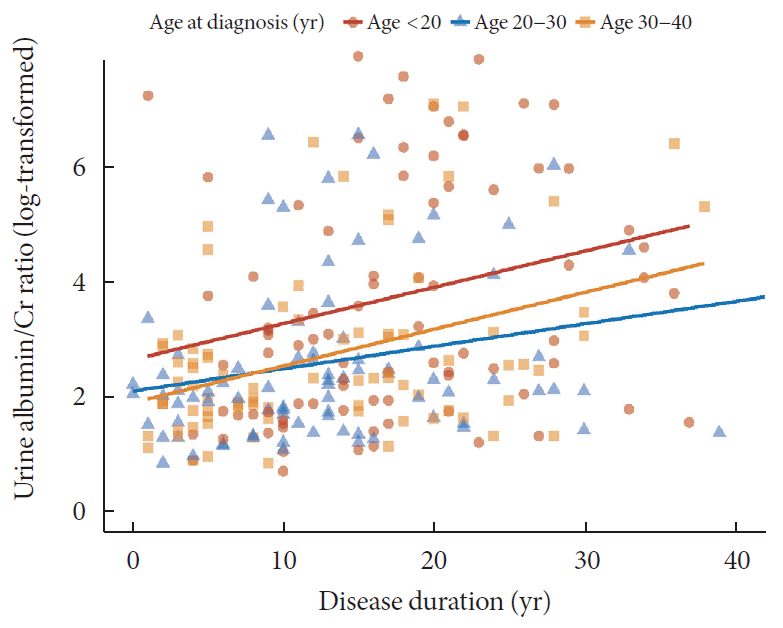
Different patterns of the progression of CKD and albuminuria according to age at diagnosis
Risk factors of diabetic microvascular complications in patients with T1DM
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Total | <20 years of age | 20–29 years of age | 30–40 years of age | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 255 | 87 | 85 | 83 | |
| Age of onset, yr | 25 (18–32) | 16 (13–18) | 26 (23–27) | 33 (32–37) | <0.001 |
| Age of registration, yr | 36 (31–44) | 31 (26–36) | 37 (31–42) | 45 (38–52) | <0.001 |
| Disease duration, yr | 14 (8–20) | 16 (11–22) | 13 (7–19) | 11 (5–19) | 0.001 |
| Male sex | 126 (49.4) | 37 (42.5) | 45 (52.9) | 44 (53.0) | 0.286 |
| FHx. of diabetes | 63 (24.7) | 27 (31.0) | 18 (21.2) | 18 (21.7) | 0.418 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.3 (20.5–24.5) | 21.4 (19.4–23.8) | 22.9 (20.7–24.6) | 22.5 (20.9–24.6) | 0.022 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 118 (110–128) | 115 (107–125) | 118 (111–127) | 121 (110–135) | 0.019 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 70 (64–79) | 70 (63–78) | 71 (64–78) | 70 (65–80) | 0.609 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 167 (148–190) | 164 (149–193) | 168 (148–186) | 168 (147–195) | 0.897 |
| TG, mg/dL | 76 (55–105) | 73 (53–107) | 76 (57–100) | 79 (56–111) | 0.833 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 61 (50–75) | 60 (49–74) | 63 (50–76) | 59 (50–73) | 0.639 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 91 (76–109) | 93 (77–108) | 90 (73–109) | 90 (75–109) | 0.781 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 14.8 (12.0–19.5) | 15.0 (11.2–20.1) | 16.1 (12.5–21.1) | 14.0 (12.0–16.9) | 0.172 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.8 (0.7–1.1) | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.858 |
| uACR, mg/g | 9.7 (4.7–47.0) | 20.7 (4.9–59.4) | 7.3 (3.7–14.7) | 9.2 (4.8–20.7) | 0.002 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m² | 91.8 (80.1–110.7) | 90.1 (75.5–114.2) | 95.0 (80.0–115.7) | 90.3 (82.0–102.4) | 0.524 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 150 (102–186) | 132 (102–190) | 131 (100–175) | 140 (97–195) | 0.704 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.9 (7.0–9.0) | 7.6 (7.0–8.9) | 7.8 (7.0–8.8) | 8.2 (7.0–9.1) | 0.419 |
| Fasting C-peptide, ng/mL | 0.07 (0.02–0.43) | 0.02 (0.01–0.16) | 0.08 (0.02–0.43) | 0.19 (0.02–0.48) | 0.094 |
| Stimulated C-peptide, ng/mL | 0.10 (0.02–0.60) | 0.02 (0.01–0.38) | 0.19 (0.02–0.63) | 0.27 (0.02–0.68) | 0.047 |
| Presence of autoantibodya | 87 (51.8) | 27 (52.9) | 37 (59.7) | 23 (41.8) | 0.152 |
| Anti-GAD Ab | 82 (94.3) | 24 (88.9) | 36 (97.3) | 22 (95.7) | |
| Other autoantibodies | 5 (5.7) | 3 (11.1) | 1 (2.7) | 1 (4.3) | |
| Intensive insulin treatment | 170 (66.7) | 71 (81.6) | 51 (60.0) | 48 (57.8) | 0.001 |
| Total daily insulin dose, IU/kg | 0.64 (0.52–0.79) | 0.7 (0.6–0.9) | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.001 |
| Medication use | |||||
| Oral glucose lowering drugs | 60 (23.5) | 14 (16.1) | 20 (23.5) | 26 (31.3) | 0.065 |
| Antihypertensive drugs | 67 (26.3) | 28 (32.2) | 19 (22.4) | 20 (24.1) | 0.294 |
| Statins | 66 (25.9) | 24 (27.6) | 19 (22.4) | 23 (27.7) | 0.661 |
| Smoking | 0.008 | ||||
| Current smoker | 31 (12.2) | 6 (7.4) | 7 (9.6) | 18 (24.0) | |
| Ex-smoker | 39 (15.3) | 10 (12.3) | 16 (21.9) | 13 (17.3) | |
| Non-smoker | 159 (62.4) | 65 (80.2) | 50 (68.5) | 44 (58.7) | |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 109 (42.7) | 52 (61.9) | 24 (28.9) | 33 (40.2) | <0.001 |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 43 (16.9) | 22 (25.3) | 13 (15.3) | 8 (9.6) | 0.022 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). Intensive insulin treatment, multiple daily injection or continuous subcutaneous insulin injection; Diabetic retinopathy, the presence of mild non-proliferative retinopathy or more; Diabetic nephropathy, uACR ≥300 mg/g or eGFR ≤60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
FHx, family history; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; uACR, urine albumin-creatinine ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration ratio; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; anti-GAD Ab, anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download