Abstract
Hydatid cysts are caused by an infestation with larval tapeworms of the genus Echinococcus. The disease is endemic in developing countries but has rarely been reported from immigrant workers in Korea. This paper reports a case of hepatic hydatid cyst in a 27-year-old female. She was referred with abdominal pain that had persisted for the past 2 months. The patient was a foreign worker from Mongolia. The physical examination was unremarkable, and blood tests showed peripheral blood eosinophilia and elevated liver enzymes. Abdominal ultrasonography showed a well-circumscribed cystic mass with septation in the liver. A surgical resection was performed for complete removal. After uncomplicated postoperative recovery, the patient was discharged with albendazole 400 mg twice daily. The hydatid cyst is an important disease that should be considered in the differential diagnosis of cystic lesions in the liver, particularly in those who have lived in endemic areas. A correct early diagnosis based on the typical image findings is important for early treatment before the rupture of the cyst, which is associated with low morbidity and mortality. A current surgical resection combined albendazole are effective treatments for hepatic hydatid cysts, associated with low recurrence rates.
간 포충낭(hepatic hydatid cyst)은 단방 조충(echinococcus granulosus)이나 다방 조충(echinococcus multilocularis) 유충에 의한 감염에 의해 발생한다. 단방 조충에 의한 감염은 질환의 경과가 느리고 수년간 무증상으로 지내는 경우가 많으나 다방 조충에 의한 감염은 더 드물게 발생하지만 빠르게 진행하고 예후가 불량한 것으로 알려져 있다. 포충증은 간을 가장 흔히 침범하지만(50-60%), 폐(10-30%), 신장, 비장, 뇌 등 인체 어느 부위도 침범 가능하다.
이 질환은 과거 우리나라 제주도 등지의 일부 가축에서 유행한 일이 있었으나 지금은 거의 소멸된 것으로 알려져 있다. 대체로 지중해 연안, 호주, 뉴질랜드, 북아프리카, 동유럽, 발칸 반도, 중동 및 남미에서 주로 발견된다고 알려져 있으며 국내에서는 매우 드문 질환으로 여겨지고 있다. 그러나 현재 한국은 다문화 국가가 되었으며 외국인의 유입도 많고 한국인의 해외여행 또한 지속적으로 증가하고 있다. 그러므로 국내에서 흔하지 않았던 포충증과 같은 질병이 앞으로 증가할 수 있으므로 이에 대한 임상의사들의 관심이 필요하다. 저자들은 27세 여성에서 진단된 단방 조충에 의한 간포충증 증례를 문헌고찰과 함께 보고하고자 한다.
27세 여자 환자가 약 2달 전부터 발생한 배꼽 주변의 복통을 주소로 내원하였다. 환자는 몽골 국적의 외국인 노동자였고 내원 당시 혈압은 120/70 mmHg, 맥박 64회/분, 호흡 20회/분, 체온 36.6℃로 특이 소견이 없었으나 말초 혈액 검사에서 백혈구 6,900/mm3 (호산구 18.0%), 혈색소 11.3 g/dL, 혈소판 223,000/mm3로 호산구 증가 소견이 있었다. 약물력 및 천식과 같은 알레르기 질환 병력을 확인하였으나 호산구 증가를 일으킬 수 있는 특이 소견은 없었다. 혈청 생화학 검사에서는 AST 18 U/L, ALT 16 U/L, 총 빌리루빈 0.5 mg/dL, 혈액요소질소 11.5 mg/dL, 크레아티닌 0.5 mg/dL로 특이 소견은 없었다. 태아 알파 단백, CA 19-9 등 종양 표지자 검사는 모두 정상이었다. 단순 흉부 촬영에서 특이 소견은 관찰되지 않았다.
복부 초음파 검사에서 약 7.5 cm 크기의 큰 낭종이 관찰되었고 내부에 불규칙한 에코성 및 격막이 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 복부 전산화단층촬영 결과 우측 간엽에서 7.5 cm 크기의 내부에 격막이 있는 낭성 덩어리가 발견되었다(Fig. 2). 임상적으로 기생충 감염에 의한 호산구 증가의 가능성이 높다고 생각되어 시행한 echinococcal IgG에 대한 혈청학적 검사 결과 양성이었다. 결론적으로 환자의 초음파 및 복부 CT에서 일부 격벽이 있으면서 비균질한 초음파 음영이 있는 낭종이 확인되었으며 이병변은 World Health Organization 분류 CE3인 과도기 상태의 간포충증으로 진단되어 확진 및 수술적 치료를 위하서 외과로 전과 되었다.
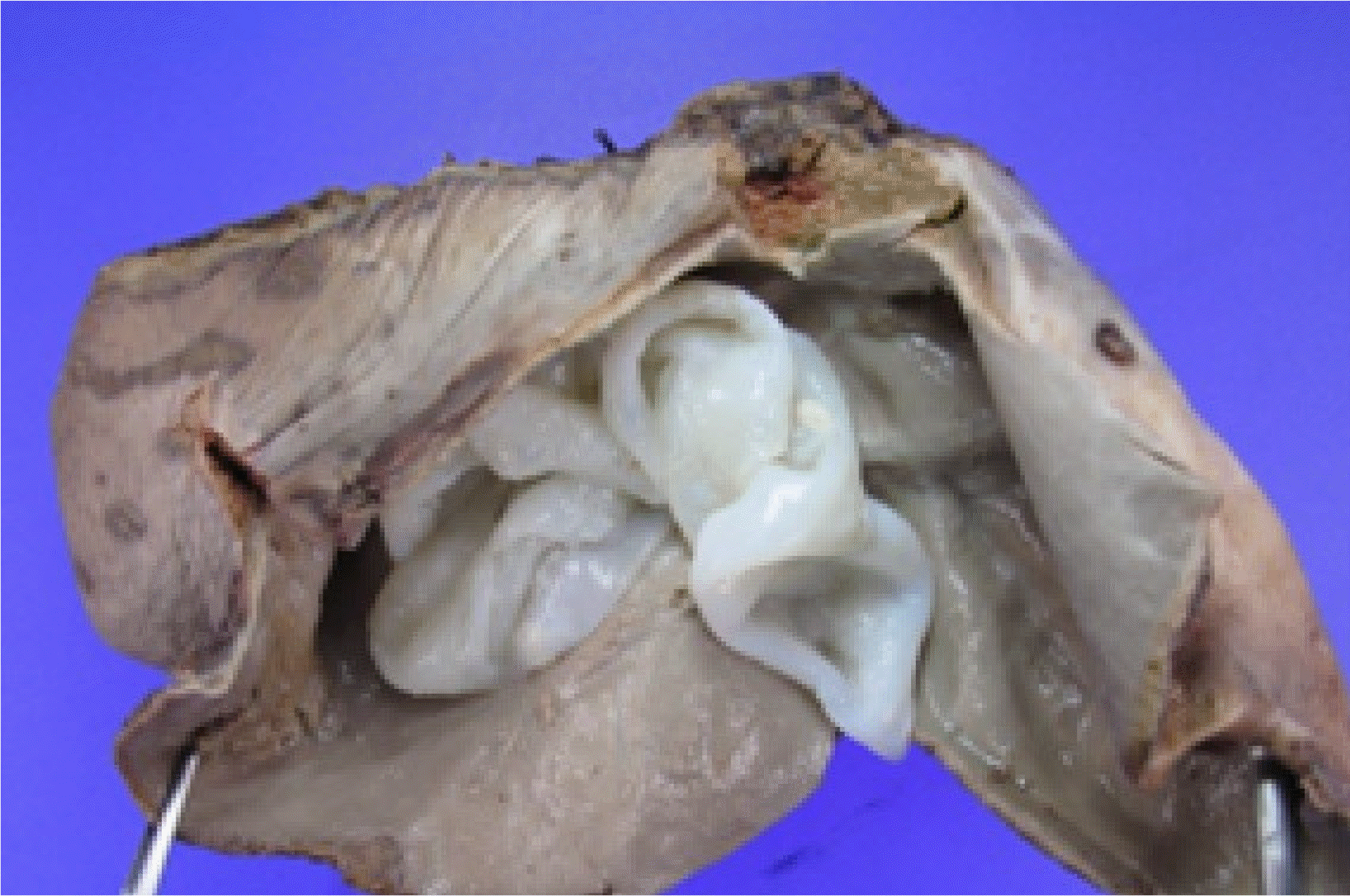
환자는 수술 전 1주일 동안 몸무게 1 kg 당 하루 10 mg, 알벤다졸 총 400 mg을 투여하였다. 수술은 우선 복강쪽 낭종 벽의 일부를 절개하여 낭종 내의 액체를 흡입하였으며, 이후 내부의 내막을 제거한 뒤 20% 알코올 액으로 낭종 내부를 채우고 15분간 기다린 후에 이 알코올 액을 모두 배액하였다. 이후 낭종 전체와 주변부 간실질을 포함한 간절제술을 시행하였다. 낭종의 크기는 9×9 cm였으며 완전 절제가 되었고 유착의 증거나 특별한 합병증은 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 3). 조직 소견에서 포충낭 외면의 층판층(laminated layer)과 내면의 배아층(germinal layer)이 관찰되었다(Fig. 4). 환자는 입원 13일째 특별한 문제없이 퇴원하였으며, 현재 알벤다졸 400 mg을 복용하면서 외래에서 추적 관찰하고 있다.
포충증은 단방조충(Echinococcus granulosus)과 다방조충(Echinococcus multilocularis)에 의해 흔히 발생하고 각각 cystic echinococcosis (CE)와 alveolar echinococcosis (AE)의 원인이 된다.1 다른 2종류인 Echinococcus vogeli 와 Echinococcus oligarthrus 는 다낭성 조충(polycystic echinococcosis)이 발생 가능하지만 인간 감염과는 거의 관련이 없다. 단방 조충의 종숙주는 개, 여우 등이며 중간 숙주는 양, 염소, 낙타, 돼지 등이고 인간은 우연숙주에 해당된다.2 다방 조충의 경우는 여우가 중요한 종숙주이다.
종숙주에 기생하고 있던 단방 조충의 성충에서 배출된 충란이 중간 숙주에 먹히게 되면 육우유충이 탈각하고 소장을 뚫고 혈액이나 림프계를 따라서 간이나 폐, 신장, 비장 등 다른 장기로 이행하여 낭종성 병변을 유발한다. 낭포는 서서히 자라기 때문에 대부분의 사람들이 감염 후 오랜 기간 무증상 상태로 지내다가 대부분 성인이 되어서 증상이 나타난다.3 침범 장기에 따라서 증상은 다양한데, 간에 침범한 경우는 복부 불편감 및 식욕 부진이 가장 흔한 증상이며, 낭포의 크기가 증가함에 따라서 복통, 낭포 파열로 인한 아나필락시스 반응, 복수 등이 생길 수 있다. 폐에 침범한 경우는 기침이나 흉통, 객혈 등의 증상이 발생하기도 한다.4 일반적으로 간 포충증의 진단 및 치료는 World Health Organization 분류 기준을 따른다. CE는 활동기인 CE1과 CE2, 과도기인 CE3 그리고 비활동기인 CE4, CE5로 분류된다. CE1은 단반낭 형태로 순수 낭액이 있는 경우고 CE2는 격막과 낭액이 있으면서 벌집 모양(honeycomb pattern)을 띄고 있다. 간 포충증의 치료는 수술, 경피적 치료, 약물 치료 등 세 가지 방법이 있다. 현재까지 이 세 가지 치료법을 비교한 무작위 대조 연구는 없다. 그러므로 임상에서 간 포충증을 치료하는 방법은 환자의 전신적 상태, 간 포충증의 상태, 현실적 치료 여건 등을 고려하여 선택하게 된다.
이 질환은 국내에서 1970년대 총 2건의 가축 감염의 보고5,6가 있으며 1983년 국내에 처음으로 폐 감염이 보고되었고 이후 간 감염 그리고 간과 폐에 동시에 발생한 감염 등의 다양한 보고가 있었다. 지금까지 인체 감염은 총 38건의 보고가 있었는데 간에 침범한 경우가 총 22건(57.9%)으로 가장많았고 다음으로 폐에 침범한 경우가 11건(28.9%), 그 외 다른 장기(신장 및 방광, 안구, 비장, 뇌)에 침범한 것은 5건(13.2%)이었다. 국내에서 발표된 논문 중 간에 침범한 보고중 10건을 좀 더 자세히 분석해 보았을 때(Table 1) 한국인이총 6명이었고 우즈베키스탄인이 총 4명이었다. 복통을 주소로 온 경우가 5건으로 가장 많았고 무증상이 2건, 의식 저하가 2건, 소화불량이 1건 있었다. 간에만 단독으로 침범한 경우는 6건 있었고 간을 포함한 2개 이상의 장기에 침범한 경우가 총 4건 있었다. 9건의 경우는 수술로 치료하였고 한 건은 비수술적 방법으로 치료하였다. 2009년에 의식 소실을 동반한 간포층증으로 진단된 30세 우즈베키스탄인을 국내에서최초로 PAIR, 즉 경피 흡인(percutaneuos aspiration), 두절박멸 약제 주입(scolicidal agent injection), 재흡인(re-aspi-ration)을 이용하여 치료한 케이스가 있었다.7
1990년대 중반까지만 해도 우리나라의 포충증은 대개 중동에서 감염되어 국내로 들어온 환자들이 대부분이었다.8-10 우리나라 노동자들이 포충증 유행지인 중동에 가서 감염이 되고 우리나라에 돌아온 후에 증상이 나타났었다. 하지만 우리나라의 소득 수준이 증가하던 1990년대 후반부터는 우리나라 노동자가 외국에서 감염된 증례는 거의 사라졌지만 반대로 외국인 노동자가 자기 나라에서 감염되어 국내로 입국한 뒤 진단된 증례가 보고되고 있다.11-14 따라서 국내에서도 포충증이 다시 유행할 수 있으므로 외국인 노동자들에 대한 정밀한 건강 검진이 필요할 것으로 생각된다. 최근 국제 결혼이 증가하면서 외국 국적의 여성 비율이 많이 증가하고 있으므로 젊은 여성이 복통이나 기침, 흉통 등 증상이 있을 때 포충증에 의한 증상도 염두해야 할 것이다.
이번 증례는 크기가 5 cm 이상인 CE3 포충낭을 수술로 완전히 제거한 후 알벤다졸을 하루 10 mg/kg, 총 8주 동안 투여하여 치료하였다. 수술 후 약 2개월 뒤 시행한 복부 CT에서 재발의 증거는 관찰되지 않았으며 향후 지속적인 추적 관찰을 시행할 예정이다. 우리는 간포층증 감염에 의한 의한 복통과 간의 낭종으로 내원한 환자의 드문 증례를 보고하였다. 포충증은 조기에 진단될 경우 알벤다졸만으로 치료 가능하지만, 진단이 늦어져 간낭종이 커질 경우 수술적 치료가 병행되어야 하고 때에 따라 치명적일 수 있으므로 초기에 의심하여 진단, 치료하는 것이 중요하겠다.
REFERENCES
1. Frider B, Larrieu E, Odriozola M. 1999; Long-term outcome of asymptomatic liver hydatidosis. J Hepatol. 30:228–231. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(99)80066-X. PMID: 10068100.


2. Nunnari G, Pinzone MR, Gruttadauria S, et al. 2012; Hepatic echinococcosis: clinical and therapeutic aspects. World J Gastroenterol. 18:1448–1458. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1448. PMID: 22509076. PMCID: PMC3319940.



3. Moro P, Schantz PM. 2009; Echinococcosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis. 13:125–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.037. PMID: 18938096.


4. Santivanez S, Garcia HH. 2010; Pulmonary cystic echinococcosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 16:257–261. DOI: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e3283386282. PMID: 20216420. PMCID: PMC3362862.



5. Jang HJ, Oh MU. 1974; Epizootiological study of echinococcus granulosus( Batsch, 1786) Rudolphi, 1805. in Jeju-do. 1. Incidences of bovine hydatid cyst and its speciation. Korean J Vet. 14:73–76.
6. Seo BS, Oh MY, Cho SY. 1975; An echinococcal cyst found inlung of cattle in Cheju-do. Korean J Parasitol. 13:85.
7. Park KH, Jung SI, Jang HC, Shin JH. 2009; First successful puncture, aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration of hydatid cyst in the liver presenting with anaphylactic shock in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 50:717–720. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.717. PMID: 19881979. PMCID: PMC2768250.

8. Chai JY, Seo M, Suh KS, Lee SH. 1995; An imported case of hepatic unilocular hydatid disease. Korean J Parasitol. 33:125–130. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.1995.33.2.125. PMID: 7551803.


9. Jung BH, Kim TH, Kang JS, et al. 1993; A case of pulmonary and hepatic hydatid cystic disease. Korean J Med. 45:550–556.
10. Chae GR, Ann HS, Soo BJ, Chae KM. 1996; A clinical case report of hydatid disease of the liver and lung caused by Echino-coccus granulosus. J Korean Surg Soc. 50:285–290.
11. Kim IK, Kim DY, Moon IS, et al. 2004; A case of echinococcal hydatid cyst as misdiagnosed to the bladder cancer. Korean J Urol. 45:1292–1295.
12. Ryou JY, Kim KH, Kim SY. 2006; Hydatid cyst of the orbit. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 47:484–488. PMID: 29622837. PMCID: PMC5870786.
13. Kang MJ, Lee SH, Kim SJ, et al. 2007; A case of multiple intraperitoneal cysts from ruptured hepatic hydatid cysts. Korean J Gastroenterol. 50:203–206. PMID: 17885288.

14. Kim IY, Kim SW, Shin HC, Han JK. 2009; US and CT findings of splenic hydatid cyst: a case report. J Korean Soc Ultrasound Med. 28:39–42.
15. Kim JM, Choi KW, Lee HJ. 2001; A clinical case report of hydatid cyst of liver. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 18:138–143. DOI: 10.12701/yujm.2001.18.1.138.

16. Byun SJ, Moon KC, Suh KS, Han JK, Chai JY. 2010; An imported case of echinococcosis of the liver in a Korean who traveled to Western and Central Europe. Korean J Parasitol. 48:161–165. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2010.48.2.161. PMID: 20585534. PMCID: PMC2892573.



17. Ahn KS, Hong ST, Kang YN, et al. 2012; An imported case of cystic echinococcosis in the liver. Korean J Parasitol. 50:357–360. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2012.50.4.357. PMID: 23230336. PMCID: PMC3514430.



18. Kim AR, Park SJ, Gu MJ, Choi JH, Kim HJ. 2013; Fine needle aspiration cytology of hepatic hydatid cyst: a case study. Korean J Pathol. 47:395–398. DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.395. PMID: 24009638. PMCID: PMC3759642.



19. Shin DH, Jo HC, Kim JH, et al. 2019; An imported case of disseminated echinococcosis in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 57:429–434. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.4.429. PMID: 31533411. PMCID: PMC6753304.



20. Cho E, Shin SS, Kim GE. 2019; Hepatic hydatid disease causing gastric ulcer as a rare complication. J Korean Soc Radiol. 80:987–991. DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2019.80.5.987.

Fig. 1
Abdominal ultrasonography findings, it shows the large cystic lesion has intracystic irregular echogenicities of inner cyst wall infoldings with separation of the hydatid membrane.
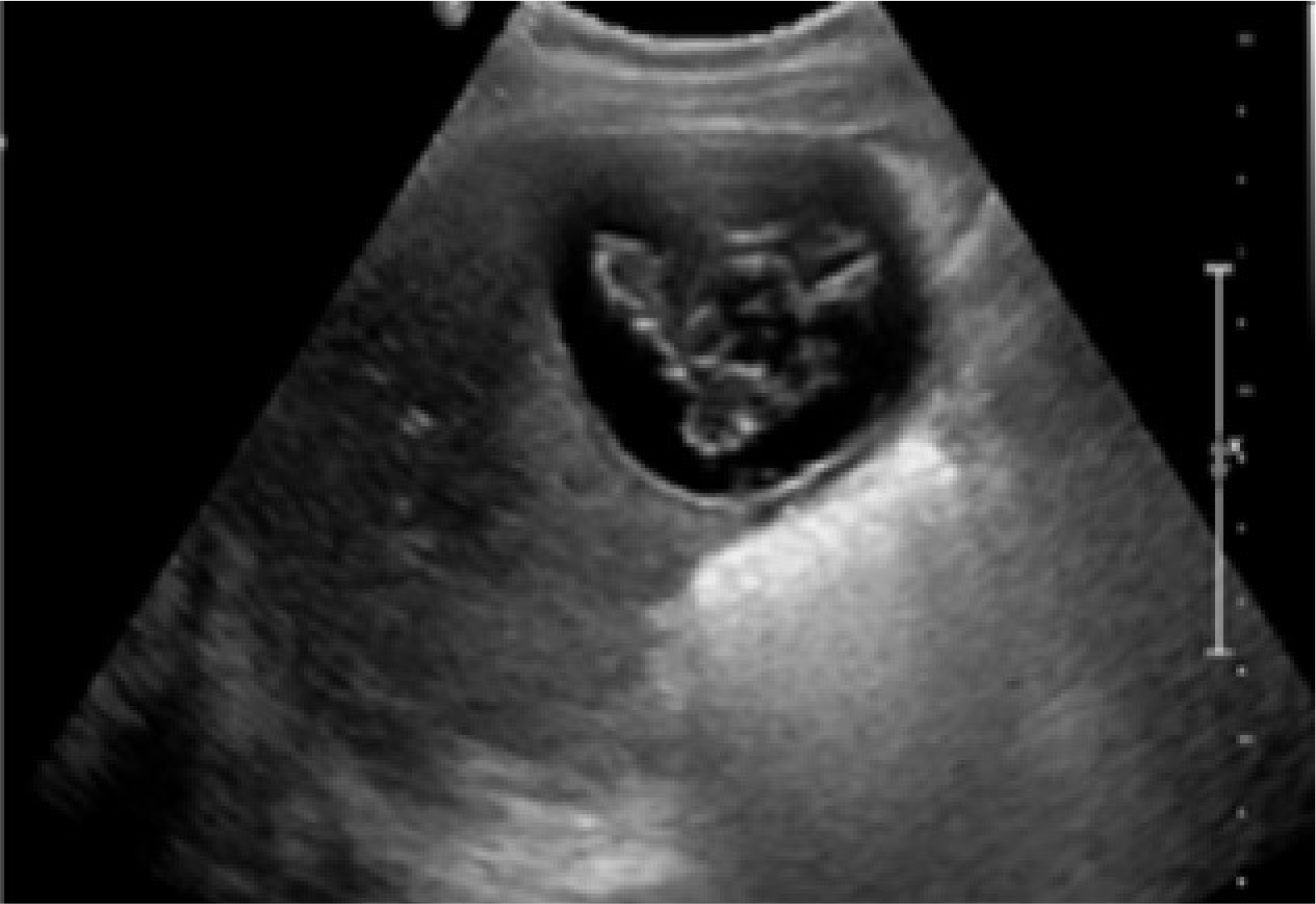
Fig. 2
Abdominal computed tomography scan. It shows a cystic mass with internal septation is present in the right hepatic lobe.
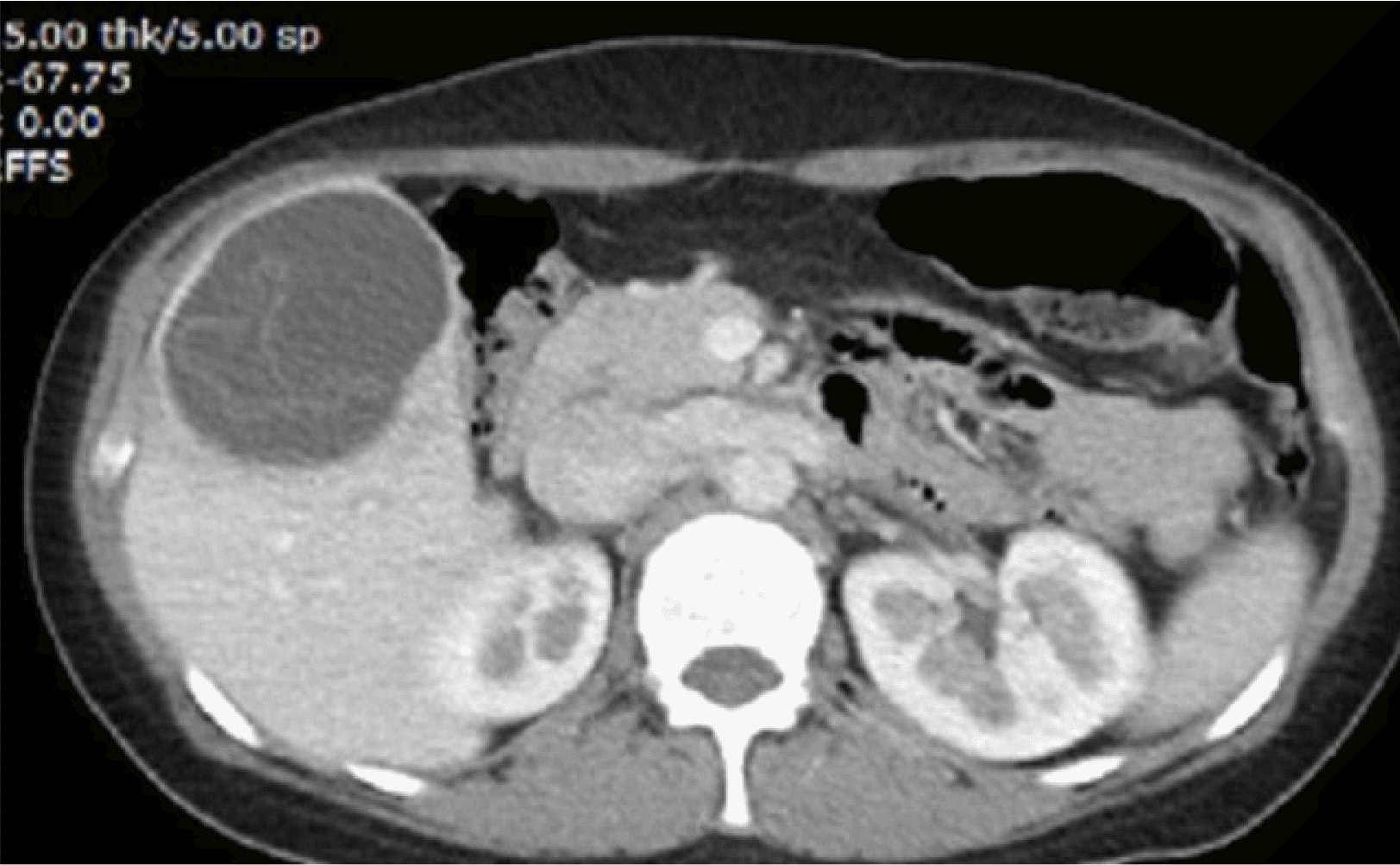
Fig. 4
Micropic finding of resected cyst, it shows outer thick laminate menbrane (black arrow) and inner germinal layer is seen (yellow arrow) (H-E stain, ×200).
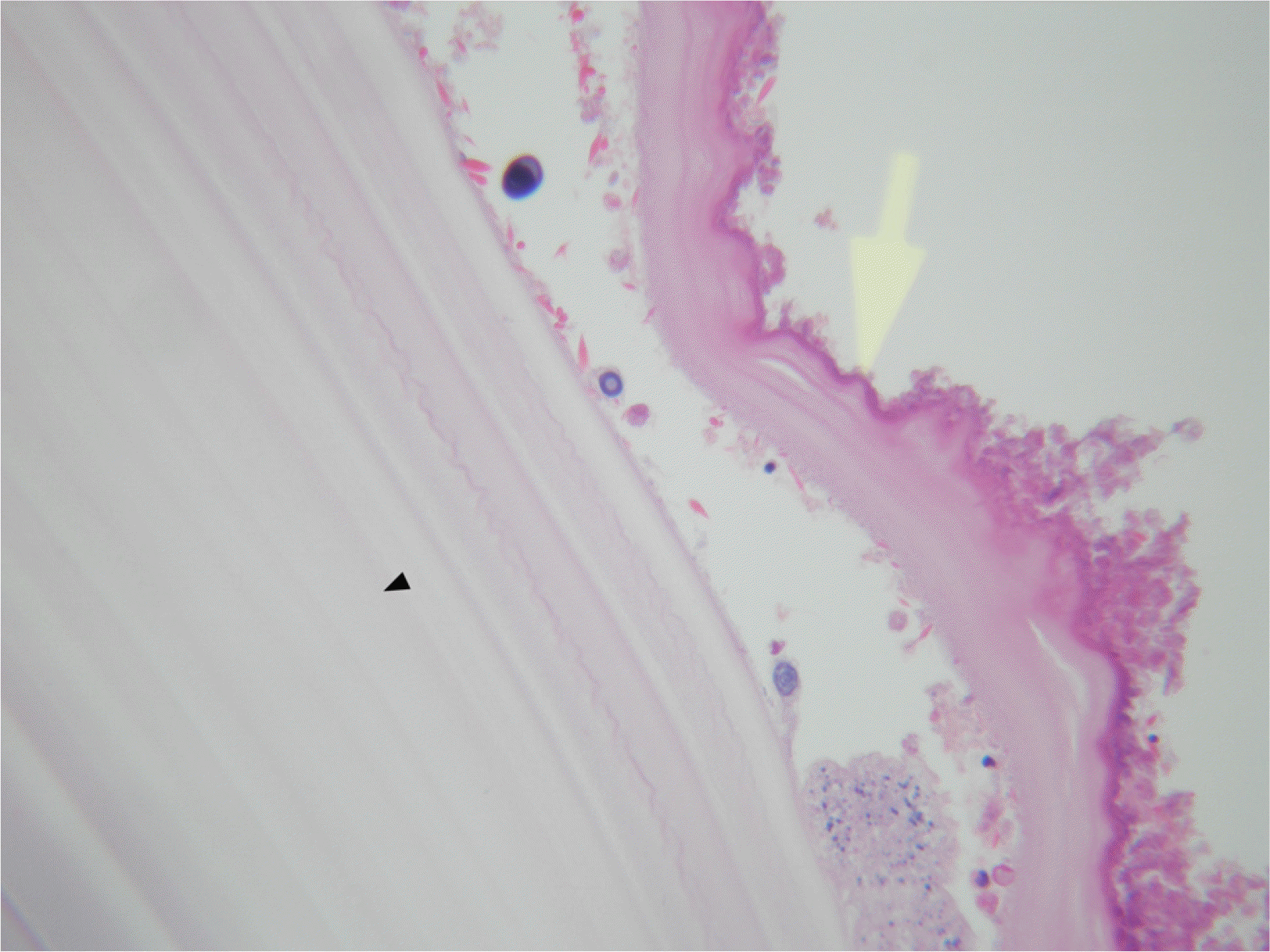
Table 1
Summary of Recent Hepatic Hydatid Cysts Reported in Korea
| Study | Age/gender | Nationality | Travel history | Symptom | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jung et al. (1993)9 | 50/M | Korean | Saudi Arabia, Iraq | Abdominal discomfort | Surgery |
| Chai et al. (1995)8 | 38/M | Korean | Saudi Arabia | Indigestion | Surgery |
| Kim et al. (2001)15 | 53/M | Korean | Vietnam | Asymptomatic | Surgery |
| Kang et al. (2007)13 | 35/M | Uzbekistan | Uzbekistan | Abdominal pain | Surgery |
| Park et al. (2009)7 | 30/M | Uzbekistan | Uzbekistan | Syncope | Non-surgical (PAIR) |
| Byun et al. (2010)16 | 61/M | Korean | Europe (France, German, Italy, Spain, Switzerland) | Asymptomatic | Surgery |
| Ahn et al. (2012)17 | 25/M | Uzbekistan | Uzbekistan | Abdominal pain | Surgery |
| Kim et al. (2013)18 | 28/M | Uzbekistan | Uzbekistan | Abdominal pain | Surgery |
| Shin et al. (2019)19 | 53/M | Korean | China, Russia, Kazakhstan | Dizziness and dysarthria | Surgery |
| Cho et al. (2019)20 | 49/M | Korean | Uzbekistan | Abdominal pain | Surgery |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download