INTRODUCTION
Since the first report of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Hubei Province, China, in December 2019, it has been spreading rapidly worldwide, and the World Health Organization had declared the disease a pandemic on March 11, 2020.
12 Studies on a small sample of patients with COVID-19 in China reported that preexisting cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs) or cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) increase the risk of COVID-19.
23456 However, studies on a large sample of patients with COVID-19 in China presented that the prevalence rate of preexisting CVRFs or CVDs in patients with COVID-19 is not higher than those in the general population.
789 Therefore, it remains unclear whether CVRFs or known CVDs are causally linked to COVID-19.
101112 Furthermore, it is uncertain whether patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs are more likely to progress to severe disease requiring intensive care and invasive mechanical ventilation (MV). Moreover, although several studies have reported on the association between preexisting CVRFs or CVDs and mortality,
234567 a comprehensive analysis considering the demographic characteristics, initial presentation, and multiple comorbidities has not yet been conducted. Therefore, this study investigated the impact of preexisting CVRFs or CVDs on the outcomes of patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in a Korean healthcare system.
METHODS
Study population
The Daegu COVID-19 Research Project is an observational multicenter registry of patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in a Korean healthcare system in Daegu City. All data about the patients and management details were obtained at each hospital.
Between February 15, 2020, and April 24, 2020, 2,269 consecutive patients (814 male; mean age, 55.5 ± 20.2 years) admitted to 10 hospitals (viz., Kyungpook National University Hospital, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Yeungnam University Hospital, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University Daegu Dongsan Hospital, Daegu Catholic University Hospital, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu Medical Center, Daegu Veterans Hospital, and Korea Workers' Compensation and Welfare Service Daegu Hospital in Daegu City) for confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) based on the positive results on polymerase chain reaction testing of nasopharyngeal samples were included. The data obtained included patient demographic information, initial vital signs, presenting symptoms, comorbidities, and history of medical illnesses, laboratory findings at baseline and during hospitalization, radiological findings, daily clinical course, inpatient medications, treatments (including intensive care unit [ICU] admission, invasive MV, hemodialysis, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation), and outcomes (including the length of stay, readmission, and mortality). All variables were available for all admitted patients except for presenting symptoms and laboratory findings (available in 9 of the 10 hospitals). Baseline comorbidities were available for all patients in the 10 hospitals. Among the comorbidities, CVRF was defined as a history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and current smoking. Known CVD was defined as a history of coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular accidents, and other chronic cardiac diseases. Moreover, chronic cardiac disease was defined as other cardiac conditions excluding coronary artery disease and congestive heart failure.
Statistical analysis
The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and as percentages for categorical variables. Comparisons between the baseline variables were performed using Student's
t-test for continuous variables and Pearson's χ
2 test for categorical variables. The patients were categorized into two groups: group with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs and group without preexisting CVRFs or CVDs. Demographics, vital signs at admission, clinical presentation at admission, comorbidities, laboratory findings, treatment, and outcomes were compared between the two groups. Moreover, the prevalence rates of preexisting CVRFs or CVDs in hospitalized patients, treatments, and outcomes were compared by 10-year age intervals. We compared the prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus and hypertension between patients with COVID-19 and general population. The data regarding prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus and hypertension in general population were collected from Korea National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2018. In addition, data regarding prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus and hypertension in general population of Daegu Metropolitan City were collected from Community Health Survey (CHS) 2019. The data are available in Korean Statistical Information Service (
https://kosis.kr) and Community Health Survey (
https://chs.cdc.go.kr), respectively. To determine the predictors of in-hospital death, multivariate logistic regression models were used to provide adjusted odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Variables with
P < 0.05 in univariate analyses were included in the multivariate model analysis. For all analyses, a two-sided
P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Ethics statement
The Joint Institutional Review Board in Daegu City approved this study (No. 2020-07-003) as minimal-risk research using data collected for routine clinical practice and waived the requirement for informed consent.
RESULTS
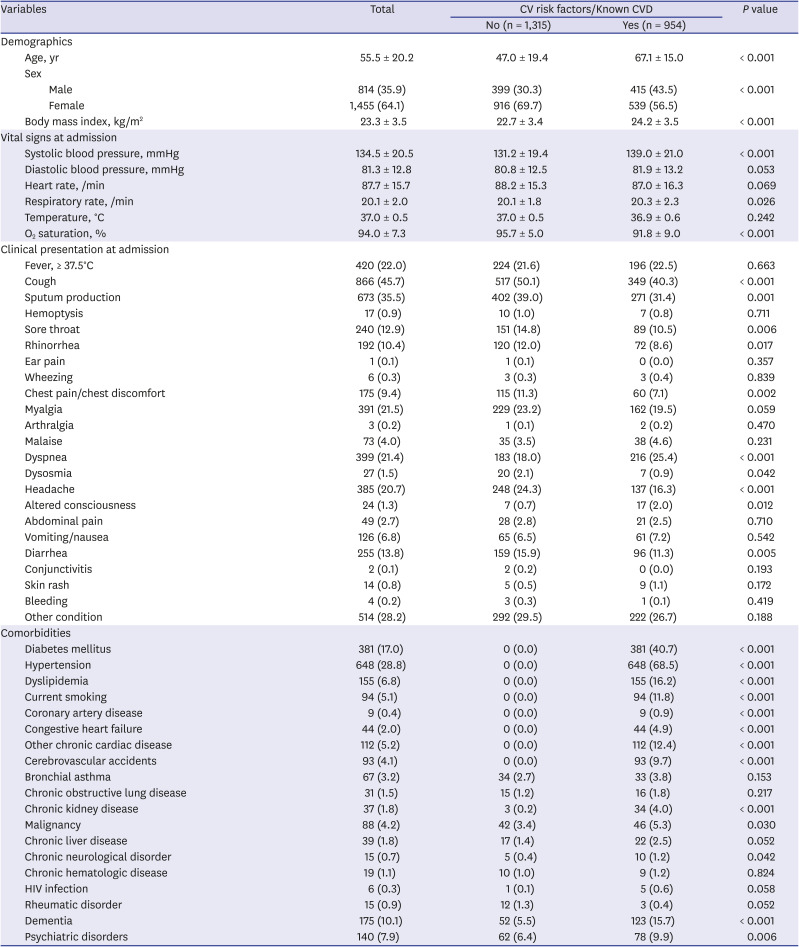
Table 1 presents the patients' baseline characteristics. Overall, the mean age was 55.5 ± 20.2 years, and 814 patients were male. Of all the patients, 954 (42.0%) had preexisting CVRFs or CVDs upon admission. Patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs were older and more likely to be male. Compared with those without preexisting CVRFs or CVDs, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, and respiratory rate were significantly higher in patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs, whereas O
2 saturation at admission was significantly lower. Respiratory symptoms such as cough, sputum production, sore throat, and rhinorrhea; chest discomfort; dysosmia; headache; and diarrhea were less frequent in patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs than those without, whereas dyspnea and altered consciousness were more frequent. Among the comorbidities, the most common were hypertension (28.8%) and diabetes mellitus (17.0%).
Supplementary Fig. 1 presents the prevalence rates of hypertension and diabetes mellitus among the patients. The prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus and hypertension in patients with COVID-19 were comparable with those in the general population of in the KNHANES 2018. The prevalence rate of diabetes mellitus was numerically higher in COVID-19 patients compared with those in the general population of Daegu Metropolitan City in the CHS 2019. Chronic kidney disease, malignancy, chronic neurologic disorder, dementia, and psychiatric disorders were more frequent in patients with preexisting CVRF or CVD than in those without.
Table 1
Baseline characteristics of study subject
|
Variables |
Total |
CV risk factors/Known CVD |
P value |
|
No (n = 1,315) |
Yes (n = 954) |
|
Demographics |
|
|
|
|
|
Age, yr |
55.5 ± 20.2 |
47.0 ± 19.4 |
67.1 ± 15.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Male |
814 (35.9) |
399 (30.3) |
415 (43.5) |
< 0.001 |
|
|
Female |
1,455 (64.1) |
916 (69.7) |
539 (56.5) |
|
|
Body mass index, kg/m2
|
23.3 ± 3.5 |
22.7 ± 3.4 |
24.2 ± 3.5 |
< 0.001 |
|
Vital signs at admission |
|
|
|
|
|
Systolic blood pressure, mmHg |
134.5 ± 20.5 |
131.2 ± 19.4 |
139.0 ± 21.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg |
81.3 ± 12.8 |
80.8 ± 12.5 |
81.9 ± 13.2 |
0.053 |
|
Heart rate, /min |
87.7 ± 15.7 |
88.2 ± 15.3 |
87.0 ± 16.3 |
0.069 |
|
Respiratory rate, /min |
20.1 ± 2.0 |
20.1 ± 1.8 |
20.3 ± 2.3 |
0.026 |
|
Temperature, °C |
37.0 ± 0.5 |
37.0 ± 0.5 |
36.9 ± 0.6 |
0.242 |
|
O2 saturation, % |
94.0 ± 7.3 |
95.7 ± 5.0 |
91.8 ± 9.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Clinical presentation at admission |
|
|
|
|
|
Fever, ≥ 37.5°C |
420 (22.0) |
224 (21.6) |
196 (22.5) |
0.663 |
|
Cough |
866 (45.7) |
517 (50.1) |
349 (40.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Sputum production |
673 (35.5) |
402 (39.0) |
271 (31.4) |
0.001 |
|
Hemoptysis |
17 (0.9) |
10 (1.0) |
7 (0.8) |
0.711 |
|
Sore throat |
240 (12.9) |
151 (14.8) |
89 (10.5) |
0.006 |
|
Rhinorrhea |
192 (10.4) |
120 (12.0) |
72 (8.6) |
0.017 |
|
Ear pain |
1 (0.1) |
1 (0.1) |
0 (0.0) |
0.357 |
|
Wheezing |
6 (0.3) |
3 (0.3) |
3 (0.4) |
0.839 |
|
Chest pain/chest discomfort |
175 (9.4) |
115 (11.3) |
60 (7.1) |
0.002 |
|
Myalgia |
391 (21.5) |
229 (23.2) |
162 (19.5) |
0.059 |
|
Arthralgia |
3 (0.2) |
1 (0.1) |
2 (0.2) |
0.470 |
|
Malaise |
73 (4.0) |
35 (3.5) |
38 (4.6) |
0.231 |
|
Dyspnea |
399 (21.4) |
183 (18.0) |
216 (25.4) |
< 0.001 |
|
Dysosmia |
27 (1.5) |
20 (2.1) |
7 (0.9) |
0.042 |
|
Headache |
385 (20.7) |
248 (24.3) |
137 (16.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Altered consciousness |
24 (1.3) |
7 (0.7) |
17 (2.0) |
0.012 |
|
Abdominal pain |
49 (2.7) |
28 (2.8) |
21 (2.5) |
0.710 |
|
Vomiting/nausea |
126 (6.8) |
65 (6.5) |
61 (7.2) |
0.542 |
|
Diarrhea |
255 (13.8) |
159 (15.9) |
96 (11.3) |
0.005 |
|
Conjunctivitis |
2 (0.1) |
2 (0.2) |
0 (0.0) |
0.193 |
|
Skin rash |
14 (0.8) |
5 (0.5) |
9 (1.1) |
0.172 |
|
Bleeding |
4 (0.2) |
3 (0.3) |
1 (0.1) |
0.419 |
|
Other condition |
514 (28.2) |
292 (29.5) |
222 (26.7) |
0.188 |
|
Comorbidities |
|
|
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
381 (17.0) |
0 (0.0) |
381 (40.7) |
< 0.001 |
|
Hypertension |
648 (28.8) |
0 (0.0) |
648 (68.5) |
< 0.001 |
|
Dyslipidemia |
155 (6.8) |
0 (0.0) |
155 (16.2) |
< 0.001 |
|
Current smoking |
94 (5.1) |
0 (0.0) |
94 (11.8) |
< 0.001 |
|
Coronary artery disease |
9 (0.4) |
0 (0.0) |
9 (0.9) |
< 0.001 |
|
Congestive heart failure |
44 (2.0) |
0 (0.0) |
44 (4.9) |
< 0.001 |
|
Other chronic cardiac disease |
112 (5.2) |
0 (0.0) |
112 (12.4) |
< 0.001 |
|
Cerebrovascular accidents |
93 (4.1) |
0 (0.0) |
93 (9.7) |
< 0.001 |
|
Bronchial asthma |
67 (3.2) |
34 (2.7) |
33 (3.8) |
0.153 |
|
Chronic obstructive lung disease |
31 (1.5) |
15 (1.2) |
16 (1.8) |
0.217 |
|
Chronic kidney disease |
37 (1.8) |
3 (0.2) |
34 (4.0) |
< 0.001 |
|
Malignancy |
88 (4.2) |
42 (3.4) |
46 (5.3) |
0.030 |
|
Chronic liver disease |
39 (1.8) |
17 (1.4) |
22 (2.5) |
0.052 |
|
Chronic neurological disorder |
15 (0.7) |
5 (0.4) |
10 (1.2) |
0.042 |
|
Chronic hematologic disease |
19 (1.1) |
10 (1.0) |
9 (1.2) |
0.824 |
|
HIV infection |
6 (0.3) |
1 (0.1) |
5 (0.6) |
0.058 |
|
Rheumatic disorder |
15 (0.9) |
12 (1.3) |
3 (0.4) |
0.052 |
|
Dementia |
175 (10.1) |
52 (5.5) |
123 (15.7) |
< 0.001 |
|
Psychiatric disorders |
140 (7.9) |
62 (6.4) |
78 (9.9) |
0.006 |

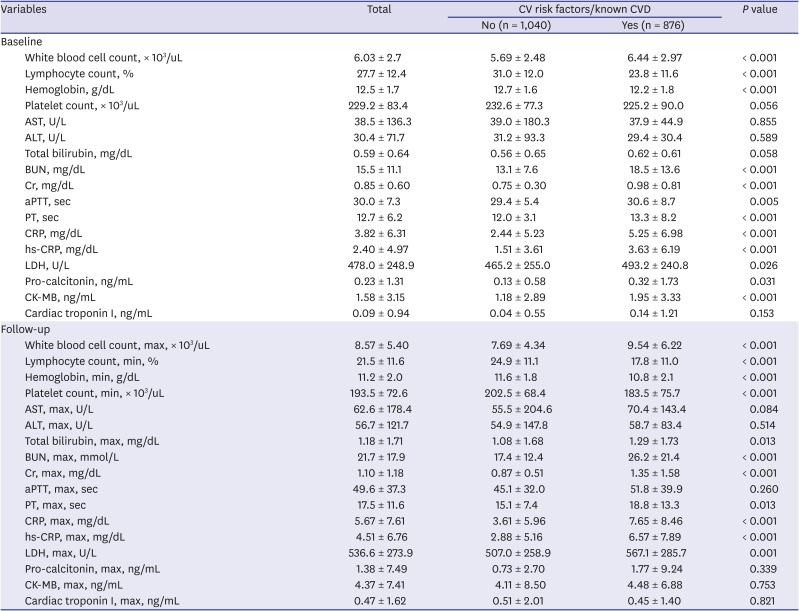
Table 2 presents the laboratory findings. White blood cell (WBC) count, C-reactive protein (CRP), high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP), lactate dehydrogenase, pro-calcitonin, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine were significantly higher in patients with preexisting CVRFs or known CVDs than those without, whereas hemoglobin and lymphocyte counts at baseline were significantly lower. Moreover, these results were consistent with the laboratory findings during the follow-up.
Table 2
Laboratory findings of study subject
|
Variables |
Total |
CV risk factors/known CVD |
P value |
|
No (n = 1,040) |
Yes (n = 876) |
|
Baseline |
|
|
|
|
|
White blood cell count, × 103/uL |
6.03 ± 2.7 |
5.69 ± 2.48 |
6.44 ± 2.97 |
< 0.001 |
|
Lymphocyte count, % |
27.7 ± 12.4 |
31.0 ± 12.0 |
23.8 ± 11.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
Hemoglobin, g/dL |
12.5 ± 1.7 |
12.7 ± 1.6 |
12.2 ± 1.8 |
< 0.001 |
|
Platelet count, × 103/uL |
229.2 ± 83.4 |
232.6 ± 77.3 |
225.2 ± 90.0 |
0.056 |
|
AST, U/L |
38.5 ± 136.3 |
39.0 ± 180.3 |
37.9 ± 44.9 |
0.855 |
|
ALT, U/L |
30.4 ± 71.7 |
31.2 ± 93.3 |
29.4 ± 30.4 |
0.589 |
|
Total bilirubin, mg/dL |
0.59 ± 0.64 |
0.56 ± 0.65 |
0.62 ± 0.61 |
0.058 |
|
BUN, mg/dL |
15.5 ± 11.1 |
13.1 ± 7.6 |
18.5 ± 13.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
Cr, mg/dL |
0.85 ± 0.60 |
0.75 ± 0.30 |
0.98 ± 0.81 |
< 0.001 |
|
aPTT, sec |
30.0 ± 7.3 |
29.4 ± 5.4 |
30.6 ± 8.7 |
0.005 |
|
PT, sec |
12.7 ± 6.2 |
12.0 ± 3.1 |
13.3 ± 8.2 |
< 0.001 |
|
CRP, mg/dL |
3.82 ± 6.31 |
2.44 ± 5.23 |
5.25 ± 6.98 |
< 0.001 |
|
hs-CRP, mg/dL |
2.40 ± 4.97 |
1.51 ± 3.61 |
3.63 ± 6.19 |
< 0.001 |
|
LDH, U/L |
478.0 ± 248.9 |
465.2 ± 255.0 |
493.2 ± 240.8 |
0.026 |
|
Pro-calcitonin, ng/mL |
0.23 ± 1.31 |
0.13 ± 0.58 |
0.32 ± 1.73 |
0.031 |
|
CK-MB, ng/mL |
1.58 ± 3.15 |
1.18 ± 2.89 |
1.95 ± 3.33 |
< 0.001 |
|
Cardiac troponin I, ng/mL |
0.09 ± 0.94 |
0.04 ± 0.55 |
0.14 ± 1.21 |
0.153 |
|
Follow-up |
|
|
|
|
|
White blood cell count, max, × 103/uL |
8.57 ± 5.40 |
7.69 ± 4.34 |
9.54 ± 6.22 |
< 0.001 |
|
Lymphocyte count, min, % |
21.5 ± 11.6 |
24.9 ± 11.1 |
17.8 ± 11.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Hemoglobin, min, g/dL |
11.2 ± 2.0 |
11.6 ± 1.8 |
10.8 ± 2.1 |
< 0.001 |
|
Platelet count, min, × 103/uL |
193.5 ± 72.6 |
202.5 ± 68.4 |
183.5 ± 75.7 |
< 0.001 |
|
AST, max, U/L |
62.6 ± 178.4 |
55.5 ± 204.6 |
70.4 ± 143.4 |
0.084 |
|
ALT, max, U/L |
56.7 ± 121.7 |
54.9 ± 147.8 |
58.7 ± 83.4 |
0.514 |
|
Total bilirubin, max, mg/dL |
1.18 ± 1.71 |
1.08 ± 1.68 |
1.29 ± 1.73 |
0.013 |
|
BUN, max, mmol/L |
21.7 ± 17.9 |
17.4 ± 12.4 |
26.2 ± 21.4 |
< 0.001 |
|
Cr, max, mg/dL |
1.10 ± 1.18 |
0.87 ± 0.51 |
1.35 ± 1.58 |
< 0.001 |
|
aPTT, max, sec |
49.6 ± 37.3 |
45.1 ± 32.0 |
51.8 ± 39.9 |
0.260 |
|
PT, max, sec |
17.5 ± 11.6 |
15.1 ± 7.4 |
18.8 ± 13.3 |
0.013 |
|
CRP, max, mg/dL |
5.67 ± 7.61 |
3.61 ± 5.96 |
7.65 ± 8.46 |
< 0.001 |
|
hs-CRP, max, mg/dL |
4.51 ± 6.76 |
2.88 ± 5.16 |
6.57 ± 7.89 |
< 0.001 |
|
LDH, max, U/L |
536.6 ± 273.9 |
507.0 ± 258.9 |
567.1 ± 285.7 |
0.001 |
|
Pro-calcitonin, max, ng/mL |
1.38 ± 7.49 |
0.73 ± 2.70 |
1.77 ± 9.24 |
0.339 |
|
CK-MB, max, ng/mL |
4.37 ± 7.41 |
4.11 ± 8.50 |
4.48 ± 6.88 |
0.753 |
|
Cardiac troponin I, max, ng/mL |
0.47 ± 1.62 |
0.51 ± 2.01 |
0.45 ± 1.40 |
0.821 |

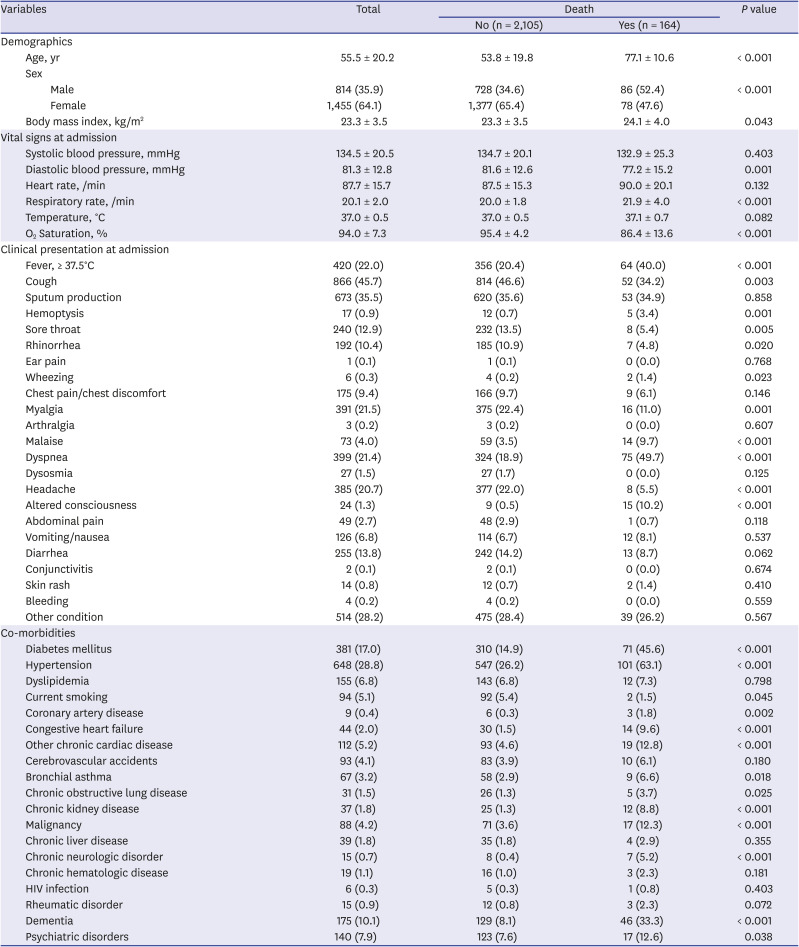
Table 3 shows the univariate analysis for in-hospital death. In total, 164 (7.2%) patients died in the hospital. In the demographic findings, deceased patients were older and more likely to be male and obese. Regarding the vital signs at admission, the deceased patients had higher respiratory rates, lower O
2 saturation, and lower diastolic blood pressures at baseline. Patients with fever upon admission (
P < 0.001) and systemic symptoms such as body malaise (
P < 0.001) and myalgia (
P = 0.001) had higher in-hospital mortality. Among the respiratory symptoms, hemoptysis (
P = 0.001) and dyspnea (
P < 0.001) were lower in the survivors than in the deceased patients, whereas cough, sore throat, and rhinorrhea were higher. Altered consciousness was higher (
P < 0.001) and headache was lower (
P < 0.001) in the deceased patients than in the survivors. Among the comorbidities, patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs such as diabetes mellitus (
P < 0.001), hypertension (
P < 0.001), coronary artery disease (
P = 0.002), congestive heart failure (
P < 0.001), and chronic cardiac disease (
P < 0.001) had a higher in-hospital mortality. Among the other comorbidities, patients with bronchial asthma (
P = 0.018), chronic obstructive lung disease (
P = 0.025), chronic kidney disease (
P < 0.001), malignancy (
P < 0.001), chronic neurologic disease (
P < 0.001), dementia (
P < 0.001), and psychiatric disorders (
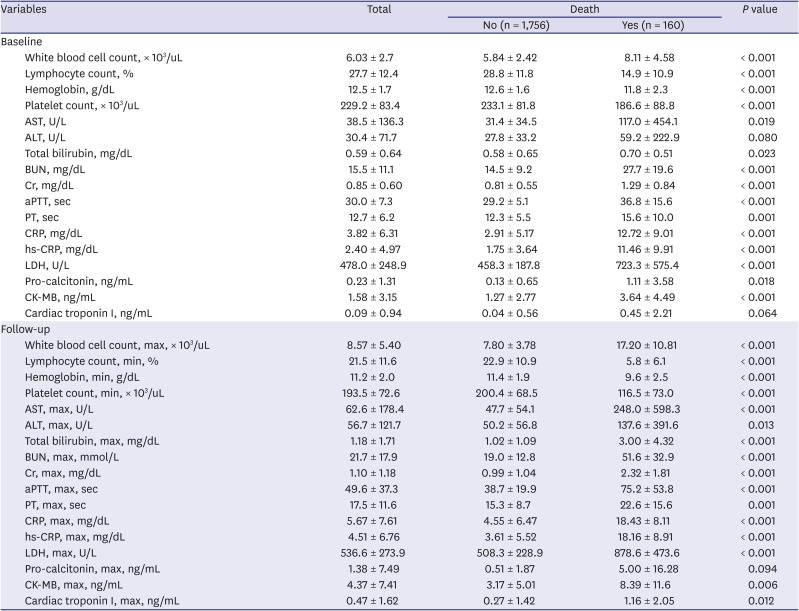
P = 0.038) had higher in-hospital mortality. Among the laboratory findings, the inflammatory markers such as WBC count, CRP, hs-CRP, and pro-calcitonin; hepatic function markers such as aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and lactate dehydrogenase; renal function markers such as blood urea nitrogen and creatinine; and creatine kinase myocardial band (CK-MB) were higher in patients with in-hospital death at baseline and during follow-up, whereas lymphocyte and platelet counts and hemoglobin were lower (
Table 4). WBC count, CRP, hs-CRP, and pro-calcitonin were statistically significantly higher in patients requiring intensive care and invasive MV at baseline and during follow-up (
Supplementary Fig. 2). Pulmonary infiltration on chest X-ray was presented in 44.3% (n = 989) and 55.6% (n = 1,240) of the patients at the time of admission and during hospitalization, respectively. The use of invasive MV was significantly greater in patients with pulmonary infiltration at the time of admission (0.9% vs. 5.2%,
P < 0.001) and during hospitalization (0.5% vs. 4.6%,
P < 0.001).
Table 3
Univariate analysis for death
|
Variables |
Total |
Death |
P value |
|
No (n = 2,105) |
Yes (n = 164) |
|
Demographics |
|
|
|
|
|
Age, yr |
55.5 ± 20.2 |
53.8 ± 19.8 |
77.1 ± 10.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Male |
814 (35.9) |
728 (34.6) |
86 (52.4) |
< 0.001 |
|
|
Female |
1,455 (64.1) |
1,377 (65.4) |
78 (47.6) |
|
|
Body mass index, kg/m2
|
23.3 ± 3.5 |
23.3 ± 3.5 |
24.1 ± 4.0 |
0.043 |
|
Vital signs at admission |
|
|
|
|
|
Systolic blood pressure, mmHg |
134.5 ± 20.5 |
134.7 ± 20.1 |
132.9 ± 25.3 |
0.403 |
|
Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg |
81.3 ± 12.8 |
81.6 ± 12.6 |
77.2 ± 15.2 |
0.001 |
|
Heart rate, /min |
87.7 ± 15.7 |
87.5 ± 15.3 |
90.0 ± 20.1 |
0.132 |
|
Respiratory rate, /min |
20.1 ± 2.0 |
20.0 ± 1.8 |
21.9 ± 4.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Temperature, °C |
37.0 ± 0.5 |
37.0 ± 0.5 |
37.1 ± 0.7 |
0.082 |
|
O2 Saturation, % |
94.0 ± 7.3 |
95.4 ± 4.2 |
86.4 ± 13.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
Clinical presentation at admission |
|
|
|
|
|
Fever, ≥ 37.5°C |
420 (22.0) |
356 (20.4) |
64 (40.0) |
< 0.001 |
|
Cough |
866 (45.7) |
814 (46.6) |
52 (34.2) |
0.003 |
|
Sputum production |
673 (35.5) |
620 (35.6) |
53 (34.9) |
0.858 |
|
Hemoptysis |
17 (0.9) |
12 (0.7) |
5 (3.4) |
0.001 |
|
Sore throat |
240 (12.9) |
232 (13.5) |
8 (5.4) |
0.005 |
|
Rhinorrhea |
192 (10.4) |
185 (10.9) |
7 (4.8) |
0.020 |
|
Ear pain |
1 (0.1) |
1 (0.1) |
0 (0.0) |
0.768 |
|
Wheezing |
6 (0.3) |
4 (0.2) |
2 (1.4) |
0.023 |
|
Chest pain/chest discomfort |
175 (9.4) |
166 (9.7) |
9 (6.1) |
0.146 |
|
Myalgia |
391 (21.5) |
375 (22.4) |
16 (11.0) |
0.001 |
|
Arthralgia |
3 (0.2) |
3 (0.2) |
0 (0.0) |
0.607 |
|
Malaise |
73 (4.0) |
59 (3.5) |
14 (9.7) |
< 0.001 |
|
Dyspnea |
399 (21.4) |
324 (18.9) |
75 (49.7) |
< 0.001 |
|
Dysosmia |
27 (1.5) |
27 (1.7) |
0 (0.0) |
0.125 |
|
Headache |
385 (20.7) |
377 (22.0) |
8 (5.5) |
< 0.001 |
|
Altered consciousness |
24 (1.3) |
9 (0.5) |
15 (10.2) |
< 0.001 |
|
Abdominal pain |
49 (2.7) |
48 (2.9) |
1 (0.7) |
0.118 |
|
Vomiting/nausea |
126 (6.8) |
114 (6.7) |
12 (8.1) |
0.537 |
|
Diarrhea |
255 (13.8) |
242 (14.2) |
13 (8.7) |
0.062 |
|
Conjunctivitis |
2 (0.1) |
2 (0.1) |
0 (0.0) |
0.674 |
|
Skin rash |
14 (0.8) |
12 (0.7) |
2 (1.4) |
0.410 |
|
Bleeding |
4 (0.2) |
4 (0.2) |
0 (0.0) |
0.559 |
|
Other condition |
514 (28.2) |
475 (28.4) |
39 (26.2) |
0.567 |
|
Co-morbidities |
|
|
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
381 (17.0) |
310 (14.9) |
71 (45.6) |
< 0.001 |
|
Hypertension |
648 (28.8) |
547 (26.2) |
101 (63.1) |
< 0.001 |
|
Dyslipidemia |
155 (6.8) |
143 (6.8) |
12 (7.3) |
0.798 |
|
Current smoking |
94 (5.1) |
92 (5.4) |
2 (1.5) |
0.045 |
|
Coronary artery disease |
9 (0.4) |
6 (0.3) |
3 (1.8) |
0.002 |
|
Congestive heart failure |
44 (2.0) |
30 (1.5) |
14 (9.6) |
< 0.001 |
|
Other chronic cardiac disease |
112 (5.2) |
93 (4.6) |
19 (12.8) |
< 0.001 |
|
Cerebrovascular accidents |
93 (4.1) |
83 (3.9) |
10 (6.1) |
0.180 |
|
Bronchial asthma |
67 (3.2) |
58 (2.9) |
9 (6.6) |
0.018 |
|
Chronic obstructive lung disease |
31 (1.5) |
26 (1.3) |
5 (3.7) |
0.025 |
|
Chronic kidney disease |
37 (1.8) |
25 (1.3) |
12 (8.8) |
< 0.001 |
|
Malignancy |
88 (4.2) |
71 (3.6) |
17 (12.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Chronic liver disease |
39 (1.8) |
35 (1.8) |
4 (2.9) |
0.355 |
|
Chronic neurologic disorder |
15 (0.7) |
8 (0.4) |
7 (5.2) |
< 0.001 |
|
Chronic hematologic disease |
19 (1.1) |
16 (1.0) |
3 (2.3) |
0.181 |
|
HIV infection |
6 (0.3) |
5 (0.3) |
1 (0.8) |
0.403 |
|
Rheumatic disorder |
15 (0.9) |
12 (0.8) |
3 (2.3) |
0.072 |
|
Dementia |
175 (10.1) |
129 (8.1) |
46 (33.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Psychiatric disorders |
140 (7.9) |
123 (7.6) |
17 (12.6) |
0.038 |

Table 4
Laboratory findings of study subjects
|
Variables |
Total |
Death |
P value |
|
No (n = 1,756) |
Yes (n = 160) |
|
Baseline |
|
|
|
|
|
White blood cell count, × 103/uL |
6.03 ± 2.7 |
5.84 ± 2.42 |
8.11 ± 4.58 |
< 0.001 |
|
Lymphocyte count, % |
27.7 ± 12.4 |
28.8 ± 11.8 |
14.9 ± 10.9 |
< 0.001 |
|
Hemoglobin, g/dL |
12.5 ± 1.7 |
12.6 ± 1.6 |
11.8 ± 2.3 |
< 0.001 |
|
Platelet count, × 103/uL |
229.2 ± 83.4 |
233.1 ± 81.8 |
186.6 ± 88.8 |
< 0.001 |
|
AST, U/L |
38.5 ± 136.3 |
31.4 ± 34.5 |
117.0 ± 454.1 |
0.019 |
|
ALT, U/L |
30.4 ± 71.7 |
27.8 ± 33.2 |
59.2 ± 222.9 |
0.080 |
|
Total bilirubin, mg/dL |
0.59 ± 0.64 |
0.58 ± 0.65 |
0.70 ± 0.51 |
0.023 |
|
BUN, mg/dL |
15.5 ± 11.1 |
14.5 ± 9.2 |
27.7 ± 19.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
Cr, mg/dL |
0.85 ± 0.60 |
0.81 ± 0.55 |
1.29 ± 0.84 |
< 0.001 |
|
aPTT, sec |
30.0 ± 7.3 |
29.2 ± 5.1 |
36.8 ± 15.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
PT, sec |
12.7 ± 6.2 |
12.3 ± 5.5 |
15.6 ± 10.0 |
0.001 |
|
CRP, mg/dL |
3.82 ± 6.31 |
2.91 ± 5.17 |
12.72 ± 9.01 |
< 0.001 |
|
hs-CRP, mg/dL |
2.40 ± 4.97 |
1.75 ± 3.64 |
11.46 ± 9.91 |
< 0.001 |
|
LDH, U/L |
478.0 ± 248.9 |
458.3 ± 187.8 |
723.3 ± 575.4 |
< 0.001 |
|
Pro-calcitonin, ng/mL |
0.23 ± 1.31 |
0.13 ± 0.65 |
1.11 ± 3.58 |
0.018 |
|
CK-MB, ng/mL |
1.58 ± 3.15 |
1.27 ± 2.77 |
3.64 ± 4.49 |
< 0.001 |
|
Cardiac troponin I, ng/mL |
0.09 ± 0.94 |
0.04 ± 0.56 |
0.45 ± 2.21 |
0.064 |
|
Follow-up |
|
|
|
|
|
White blood cell count, max, × 103/uL |
8.57 ± 5.40 |
7.80 ± 3.78 |
17.20 ± 10.81 |
< 0.001 |
|
Lymphocyte count, min, % |
21.5 ± 11.6 |
22.9 ± 10.9 |
5.8 ± 6.1 |
< 0.001 |
|
Hemoglobin, min, g/dL |
11.2 ± 2.0 |
11.4 ± 1.9 |
9.6 ± 2.5 |
< 0.001 |
|
Platelet count, min, × 103/uL |
193.5 ± 72.6 |
200.4 ± 68.5 |
116.5 ± 73.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
AST, max, U/L |
62.6 ± 178.4 |
47.7 ± 54.1 |
248.0 ± 598.3 |
< 0.001 |
|
ALT, max, U/L |
56.7 ± 121.7 |
50.2 ± 56.8 |
137.6 ± 391.6 |
0.013 |
|
Total bilirubin, max, mg/dL |
1.18 ± 1.71 |
1.02 ± 1.09 |
3.00 ± 4.32 |
< 0.001 |
|
BUN, max, mmol/L |
21.7 ± 17.9 |
19.0 ± 12.8 |
51.6 ± 32.9 |
< 0.001 |
|
Cr, max, mg/dL |
1.10 ± 1.18 |
0.99 ± 1.04 |
2.32 ± 1.81 |
< 0.001 |
|
aPTT, max, sec |
49.6 ± 37.3 |
38.7 ± 19.9 |
75.2 ± 53.8 |
< 0.001 |
|
PT, max, sec |
17.5 ± 11.6 |
15.3 ± 8.7 |
22.6 ± 15.6 |
0.001 |
|
CRP, max, mg/dL |
5.67 ± 7.61 |
4.55 ± 6.47 |
18.43 ± 8.11 |
< 0.001 |
|
hs-CRP, max, mg/dL |
4.51 ± 6.76 |
3.61 ± 5.52 |
18.16 ± 8.91 |
< 0.001 |
|
LDH, max, U/L |
536.6 ± 273.9 |
508.3 ± 228.9 |
878.6 ± 473.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
Pro-calcitonin, max, ng/mL |
1.38 ± 7.49 |
0.51 ± 1.87 |
5.00 ± 16.28 |
0.094 |
|
CK-MB, max, ng/mL |
4.37 ± 7.41 |
3.17 ± 5.01 |
8.39 ± 11.6 |
0.006 |
|
Cardiac troponin I, max, ng/mL |
0.47 ± 1.62 |
0.27 ± 1.42 |
1.16 ± 2.05 |
0.012 |

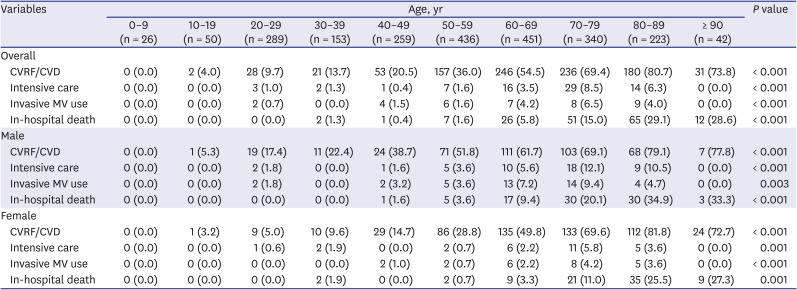
The prevalence rates of preexisting CVRFs or CVDs increased with age (
P < 0.001) (
Table 5). Moreover, the number of patients requiring intensive care (
P < 0.001) and invasive MV (
P < 0.001) increased with age. In-hospital death was significantly higher in the elderly (
P < 0.001). During hospitalization, the need for intensive care (5.3% vs. 1.6%;
P < 0.001) and invasive MV (4.3% vs. 1.7%;
P < 0.001) was significantly greater in patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs than those without. Moreover, in-hospital mortality (12.9% vs. 3.1%;
P < 0.001) was significantly higher in patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs. Among the CVRFs, diabetes mellitus (
P < 0.001) and hypertension (
P < 0.001) were associated with increased requirement of intensive care and invasive MV and in-hospital death (
Fig. 1). Among the CVDs, coronary artery disease (22.2% vs. 2.7%;
P < 0.001) was associated with invasive MV. Coronary artery disease (33.3% vs. 7.1%;
P = 0.002) and congestive heart failure (31.8% vs. 6.3%;
P < 0.001) were associated with in-hospital death. Based on the multivariate analysis, preexisting CVRFs or CVDs (OR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.07–3.01;
P = 0.027) were independent predictors of in-hospital death after adjusting for confounding variables. Among the individual CVRF or CVD components, diabetes mellitus (OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.51–3.90;
P < 0.001) and congestive heart failure (OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.06–5.87;
P = 0.049) were independent predictors of in-hospital death (
Table 6). Moreover, advanced age, male gender, respiratory rate > 20/min, fever ≥ 37.5°C, altered consciousness, hemoptysis, and chronic neurologic disorders were independent predictors of in-hospital death.
Fig. 1
Frequency according to the presence (“yes”) or absence (“no”) of preexisting cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease. Frequency of intensive care unit utilization (A), invasive mechanical ventilator utilization (B), and in-hospital death (C) according to the presence (“yes”) or absence (“no”) of preexisting cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease.
ICU = intensive care unit, CV = cardiovascular, CVD = cardiovascular disease, DM = diabetes mellitus, HTN = hypertension, DL = dyslipidemia, CAD = coronary artery disease, HF = heart failure, CVA = cerebrovascular accidents, CCD = chronic cardiac disease, MV = mechanical ventilator.
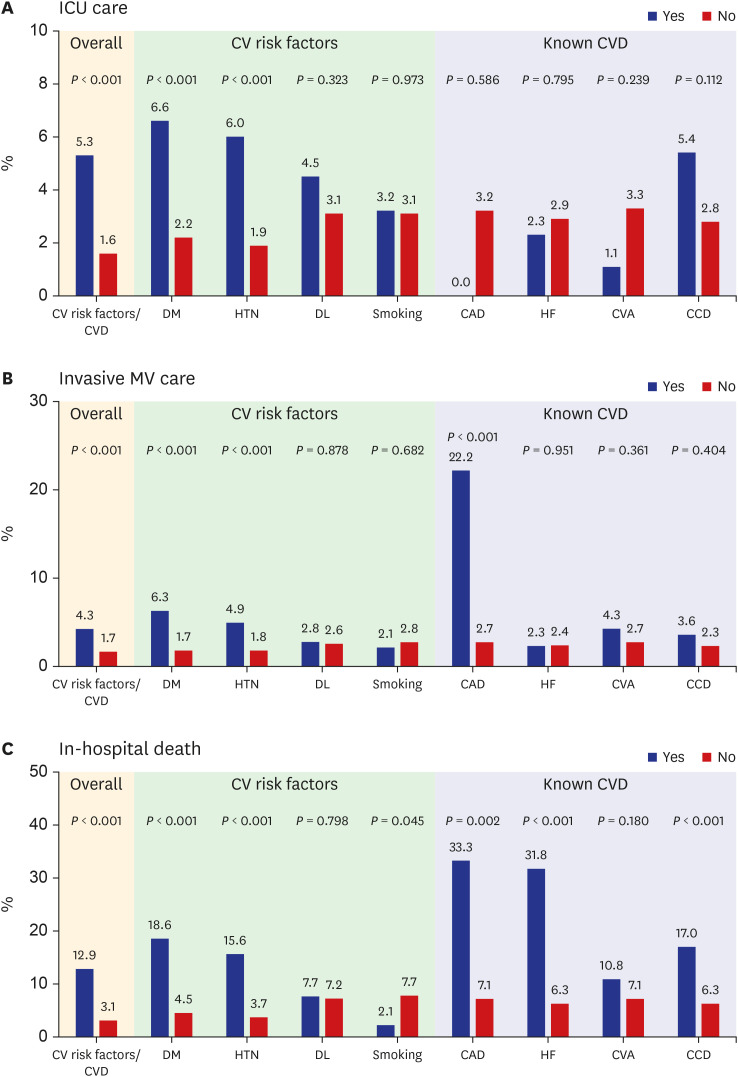

Table 5
Clinical measures and outcomes by 10-year intervals of patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019
|
Variables |
Age, yr |
P value |
|
0–9 (n = 26) |
10–19 (n = 50) |
20–29 (n = 289) |
30–39 (n = 153) |
40–49 (n = 259) |
50–59 (n = 436) |
60–69 (n = 451) |
70–79 (n = 340) |
80–89 (n = 223) |
≥ 90 (n = 42) |
|
Overall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CVRF/CVD |
0 (0.0) |
2 (4.0) |
28 (9.7) |
21 (13.7) |
53 (20.5) |
157 (36.0) |
246 (54.5) |
236 (69.4) |
180 (80.7) |
31 (73.8) |
< 0.001 |
|
Intensive care |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
3 (1.0) |
2 (1.3) |
1 (0.4) |
7 (1.6) |
16 (3.5) |
29 (8.5) |
14 (6.3) |
0 (0.0) |
< 0.001 |
|
Invasive MV use |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (0.7) |
0 (0.0) |
4 (1.5) |
6 (1.6) |
7 (4.2) |
8 (6.5) |
9 (4.0) |
0 (0.0) |
< 0.001 |
|
In-hospital death |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (1.3) |
1 (0.4) |
7 (1.6) |
26 (5.8) |
51 (15.0) |
65 (29.1) |
12 (28.6) |
< 0.001 |
|
Male |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CVRF/CVD |
0 (0.0) |
1 (5.3) |
19 (17.4) |
11 (22.4) |
24 (38.7) |
71 (51.8) |
111 (61.7) |
103 (69.1) |
68 (79.1) |
7 (77.8) |
< 0.001 |
|
Intensive care |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (1.8) |
0 (0.0) |
1 (1.6) |
5 (3.6) |
10 (5.6) |
18 (12.1) |
9 (10.5) |
0 (0.0) |
< 0.001 |
|
Invasive MV use |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (1.8) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (3.2) |
5 (3.6) |
13 (7.2) |
14 (9.4) |
4 (4.7) |
0 (0.0) |
0.003 |
|
In-hospital death |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
1 (1.6) |
5 (3.6) |
17 (9.4) |
30 (20.1) |
30 (34.9) |
3 (33.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Female |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CVRF/CVD |
0 (0.0) |
1 (3.2) |
9 (5.0) |
10 (9.6) |
29 (14.7) |
86 (28.8) |
135 (49.8) |
133 (69.6) |
112 (81.8) |
24 (72.7) |
< 0.001 |
|
Intensive care |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
1 (0.6) |
2 (1.9) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (0.7) |
6 (2.2) |
11 (5.8) |
5 (3.6) |
0 (0.0) |
0.001 |
|
Invasive MV use |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (1.0) |
2 (0.7) |
6 (2.2) |
8 (4.2) |
5 (3.6) |
0 (0.0) |
< 0.001 |
|
In-hospital death |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (1.9) |
0 (0.0) |
2 (0.7) |
9 (3.3) |
21 (11.0) |
35 (25.5) |
9 (27.3) |
0.001 |

Table 6
Multivariate analysis for in-hospital death
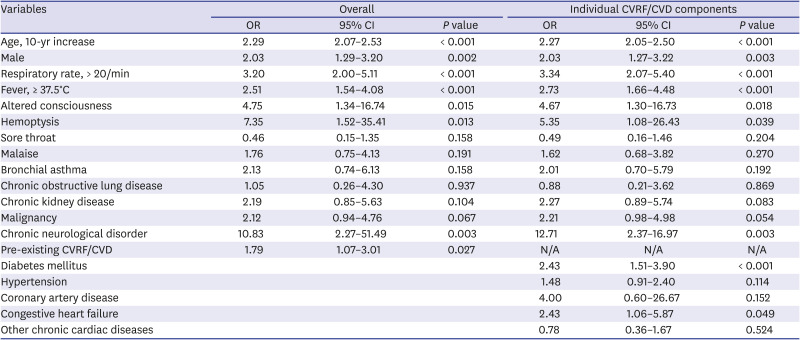
|
Variables |
Overall |
Individual CVRF/CVD components |
|
OR |
95% CI |
P value |
OR |
95% CI |
P value |
|
Age, 10-yr increase |
2.29 |
2.07–2.53 |
< 0.001 |
2.27 |
2.05–2.50 |
< 0.001 |
|
Male |
2.03 |
1.29–3.20 |
0.002 |
2.03 |
1.27–3.22 |
0.003 |
|
Respiratory rate, > 20/min |
3.20 |
2.00–5.11 |
< 0.001 |
3.34 |
2.07–5.40 |
< 0.001 |
|
Fever, ≥ 37.5°C |
2.51 |
1.54–4.08 |
< 0.001 |
2.73 |
1.66–4.48 |
< 0.001 |
|
Altered consciousness |
4.75 |
1.34–16.74 |
0.015 |
4.67 |
1.30–16.73 |
0.018 |
|
Hemoptysis |
7.35 |
1.52–35.41 |
0.013 |
5.35 |
1.08–26.43 |
0.039 |
|
Sore throat |
0.46 |
0.15–1.35 |
0.158 |
0.49 |
0.16–1.46 |
0.204 |
|
Malaise |
1.76 |
0.75–4.13 |
0.191 |
1.62 |
0.68–3.82 |
0.270 |
|
Bronchial asthma |
2.13 |
0.74–6.13 |
0.158 |
2.01 |
0.70–5.79 |
0.192 |
|
Chronic obstructive lung disease |
1.05 |
0.26–4.30 |
0.937 |
0.88 |
0.21–3.62 |
0.869 |
|
Chronic kidney disease |
2.19 |
0.85–5.63 |
0.104 |
2.27 |
0.89–5.74 |
0.083 |
|
Malignancy |
2.12 |
0.94–4.76 |
0.067 |
2.21 |
0.98–4.98 |
0.054 |
|
Chronic neurological disorder |
10.83 |
2.27–51.49 |
0.003 |
12.71 |
2.37–16.97 |
0.003 |
|
Pre-existing CVRF/CVD |
1.79 |
1.07–3.01 |
0.027 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Diabetes mellitus |
|
|
|
2.43 |
1.51–3.90 |
< 0.001 |
|
Hypertension |
|
|
|
1.48 |
0.91–2.40 |
0.114 |
|
Coronary artery disease |
|
|
|
4.00 |
0.60–26.67 |
0.152 |
|
Congestive heart failure |
|
|
|
2.43 |
1.06–5.87 |
0.049 |
|
Other chronic cardiac diseases |
|
|
|
0.78 |
0.36–1.67 |
0.524 |

DISCUSSION
The principal findings of this large observational study are as follows. First, it is uncertain whether diabetes mellitus and hypertension increase the risk of COVID-19 infection. Second, patients with COVID-19 with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs were more likely to have severe disease progression. Third, preexisting CVRFs or CVDs increased the mortality of patients with COVID-19.
Furthermore, three important clinical questions regarding the association between preexisting CVRFs or CVDs and COVID-19 infection should be considered. Our study provided important findings to address these important questions through a comprehensive analysis.
The first clinical question is whether diabetes mellitus and hypertension increase the risk of COVID-19 infection. SARS-CoV-2 binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors in the lungs which are also associated with heart function, high blood pressure, and diabetes mellitus.
13 In animal studies, the expression of ACE2 is markedly increased in patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and failing heart as an adaptive response to counteract the elevated level of angiotensin II.
14 Therefore, theoretically, diabetes mellitus and hypertension could increase the risk of COVID-19 infection. In studies from China that enrolled a small sample of patients with COVID-19 (200 or less), the prevalence rates of hypertension, diabetes, and CVD were comparable to those of the general population in 2018.
23456 However, the prevalence rate of CVRFs in patients with COVID-19 was less than that in the general population based on the findings of studies with a large sample of patients with COVID-19 (more than 1,000).
789 However, these results are inconsistent with those in western countries. Based on the data from New York City, patients with COVID-19 had higher prevalence rates of hypertension (56.6% vs. 45%) and diabetes (33.8% vs. 10.5%) than the general population.
15 In the present study, the prevalence rates of hypertension and diabetes mellitus in patients with COVID-19 were comparable to those in the general population in the KNHANES 2018. However, the prevalence rate of diabetes mellitus in patients with COVID-19 showed numerically higher trend compared with those in the general population of Daegu Metropolitan City in the CHS 2019. Therefore, it is still uncertain whether diabetes mellitus and hypertension increase the risk of COVID-19 infection.
The second clinical question is whether patients with COVID-19 with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs are more likely to have severe disease. SARS-CoV-2 infection is a mild disease in most patients, but in some patients, it progresses to a serious respiratory disease causing hyper-inflammation, multi-organ failure, and death.
16 Although a study from China reported that in patients with COVID-19, the requirement of invasive MV was greater in those with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs, this result was inconsistent with another study from China.
23 However, in the latest study, patients with COVID-19 with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs were more likely to progress to severe disease.
7 In our study, in patients with COVID-19, the requirement for intensive care and invasive MV was significantly greater in those with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs. In particular, preexisting coronary artery disease was associated with the use of invasive MV. Although the effect of preexisting coronary artery disease on the clinical course of COVID-19 has not been fully investigated, it has been known that severe respiratory failure and multi-organ failure might be directly or indirectly related with coronary artery disease.
17 COVID-19 is an infectious disease. Therefore, severe inflammatory response is associated with disease progression and poor prognosis. In this study, surrogate markers of severe inflammatory reaction such as WBC count, CRP, hs-CRP, and pro-calcitonin were greater in patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs at baseline and during the follow-up. Moreover, these surrogate markers were statistically significantly higher in patients requiring intensive care and invasive MV and in deceased patients. Although multiple possible explanations regarding the clear association between preexisting CVRFs or CVDs and COVID-19 severity exist, the greater inflammatory response in patients with preexisting CVRF or CVD is an important reason why patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs are more likely to have severe COVID-19.
The third clinical question is whether preexisting CVRFs or CVDs increase the mortality of patients with COVID-19. Studies from China reported that CVRFs or known CVDs are associated with increased in-hospital mortality.
456 However, a study from a Western country reported that diabetes mellitus was associated with in-hospital death in patients with COVID-19 requiring intensive care and invasive MV, but hypertension was not.
15 It can be assumed that patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs are more likely to be older than those without. Advanced age has consistently been shown to be associated with poor prognosis in patients with COVID-19. However, most of the aforementioned studies did not adjust for age. Moreover, some studies showed that female were more resistant to viral infections than male, which is consistent with the results of this study. In animal models, male mice showed a higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-1 infection.
18 Moreover, initial vital signs and presenting characteristics reflected the severity of COVID-19 infection. Furthermore, patients with multiple comorbidities were more likely to have severe disease and subsequent mortality. Nonetheless, a comprehensive analysis considering age, sex, vital signs at admission, presenting characteristics, and comorbidities has not yet been conducted. The present study clearly demonstrated that preexisting CVRFs or CVDs were an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality after adjusting for the confounding variables. In particular, diabetes mellitus, among the CVRFs, and congestive heart failure, among the CVDs, were independent predictors of in-hospital morality after adjusting for all variables.
However, this study has several limitations to consider. First, since the Daegu COVID-19 Research Project was an observational study, we cannot exclude the possibility of having residual confounding factors. Therefore, our results should only be regarded as hypothesis generating. Second, the study population only included patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in a Korean healthcare system in Daegu Metropolitan City. Third, history taking, and laboratory findings were not available in some patients. Moreover, some of the patients had missing laboratory data. Fourth, since this analysis was performed based on chart review without external prospective ascertainment, the results need to be interpreted with caution. Fifth, although the use of invasive MV might be related with the severity of pneumonia, the status of pneumonia was not obtained in our registry. Sixth, the frequency of ICU utilization in patients with coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular accidents was too small to explain the differences between patients with coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular accidents and those without. Further studies are required to clarify these associations. However, the limitations should not undermine the strength of this study including the overall consecutive patients with COVID-19 encountered in day-to-day clinical practice during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In conclusion, it remains uncertain whether patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension are more causally vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. However, the patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs had worse clinical COVID-19 outcomes, mainly driven by a severe inflammatory reaction. Therefore, we should emphasize that appropriate risk stratification at triage for patients with preexisting CVRFs or CVDs is necessary for the patients' survival especially during this COVID-19 pandemic.











 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download