1. Kelley AS, Morrison RS. Palliative care for the seriously Ill. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373(8):747–755. PMID:
26287850.

2. Wachterman MW, Pilver C, Smith D, Ersek M, Lipsitz SR, Keating NL. Quality of end-of-life care provided to patients with different serious illnesses. JAMA Intern Med. 2016; 176(8):1095–1102. PMID:
27367547.

3. Kavalieratos D, Corbelli J, Zhang D, Dionne-Odom JN, Ernecoff NC, Hanmer J, et al. Association between palliative care and patient and caregiver outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016; 316(20):2104–2114. PMID:
27893131.
4. Gómez-Batiste X, Caja C, Espinosa J, Bullich I, Martínez-Muñoz M, Porta-Sales J, et al. The Catalonia World Health Organization demonstration project for palliative care implementation: quantitative and qualitative results at 20 years. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 43(4):783–794. PMID:
22265127.

5. Gomes B, Calanzani N, Curiale V, McCrone P, Higginson IJ. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of home palliative care services for adults with advanced illness and their caregivers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013; (6):CD007760. PMID:
23744578.

6. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Colvin MM, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 70(6):776–803. PMID:
28461007.
7. Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37(27):2129–2200. PMID:
27206819.
8. Selecky PA, Eliasson CA, Hall RI, Schneider RF, Varkey B, McCaffree DR, et al. Palliative and end-of-life care for patients with cardiopulmonary diseases: American College of Chest Physicians position statement. Chest. 2005; 128(5):3599–3610. PMID:
16304319.
9. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Dementia: Assessment, Management and Support for People Living with Dementia and Their Carers. NICE Guideline, No. 97. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence;2018.
11. Holloway RG, Arnold RM, Creutzfeldt CJ, Lewis EF, Lutz BJ, McCann RM, et al. Palliative and end-of-life care in stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014; 45(6):1887–1916. PMID:
24676781.
12. Mataqi M, Aslanpour Z. Factors influencing palliative care in advanced dementia: a systematic review. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2019; 10(2):145–156.

13. Siouta N, van Beek K, Preston N, Hasselaar J, Hughes S, Payne S, et al. Towards integration of palliative care in patients with chronic heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic literature review of European guidelines and pathways. BMC Palliat Care. 2016; 15(1):18. PMID:
26872741.

14. Steigleder T, Kollmar R, Ostgathe C. Palliative care for stroke patients and their families: barriers for implementation. Front Neurol. 2019; 10:164. PMID:
30894836.

15. Carter G, van der Steen JT, Galway K, Brazil K. General practitioners' perceptions of the barriers and solutions to good-quality palliative care in dementia. Dementia. 2017; 16(1):79–95. PMID:
25888620.

16. Dening KH, Greenish W, Jones L, Mandal U, Sampson EL. Barriers to providing end-of-life care for people with dementia: a whole-system qualitative study. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2012; 2(2):103–107.

17. Thuné-Boyle IC, Sampson EL, Jones L, King M, Lee DR, Blanchard MR. Challenges to improving end of life care of people with advanced dementia in the UK. Dementia. 2010; 9(2):259–284.

18. Creutzfeldt CJ, Holloway RG. Treatment decisions after severe stroke: uncertainty and biases. Stroke. 2012; 43(12):3405–3408. PMID:
23150658.
19. Weeks JC, Cook EF, O'Day SJ, Peterson LM, Wenger N, Reding D, et al. Relationship between cancer patients' predictions of prognosis and their treatment preferences. JAMA. 1998; 279(21):1709–1714. PMID:
9624023.

20. Enzinger AC, Zhang B, Schrag D, Prigerson HG. Outcomes of prognostic disclosure: associations with prognostic understanding, distress, and relationship with physician among patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33(32):3809–3816. PMID:
26438121.

21. Beauchamp TL, Childress JF. Principles of Biomedical Ethics. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;2009.
22. Yun YH, Kim KN, Sim JA, Kang E, Lee J, Choo J, et al. Priorities of a “good death” according to cancer patients, their family caregivers, physicians, and the general population: a nationwide survey. Support Care Cancer. 2018; 26(10):3479–3488. PMID:
29682690.

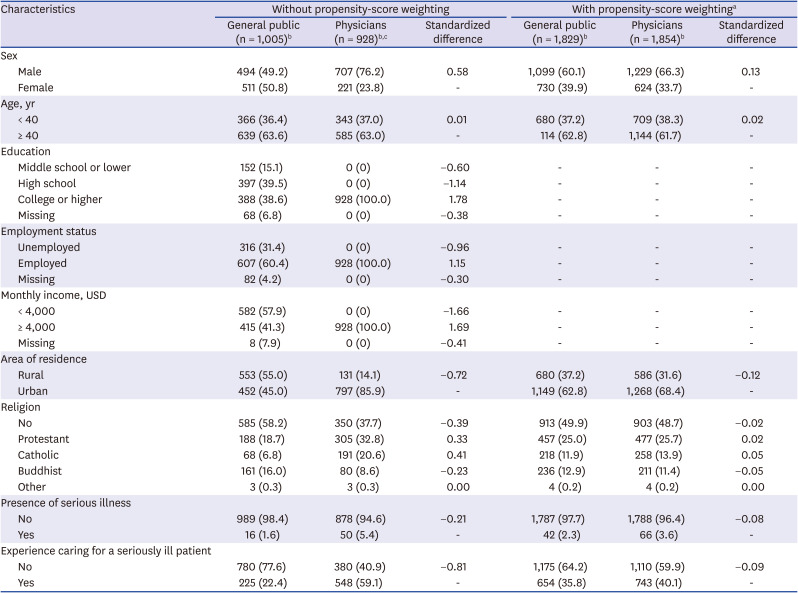
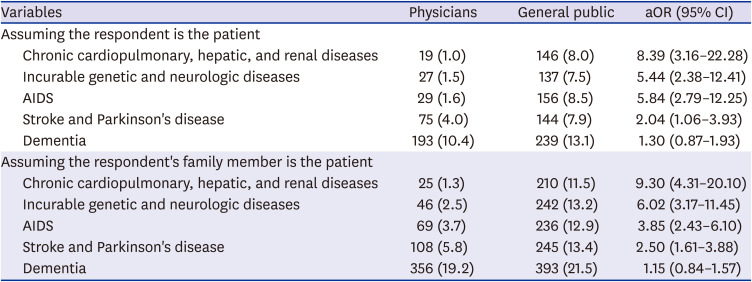
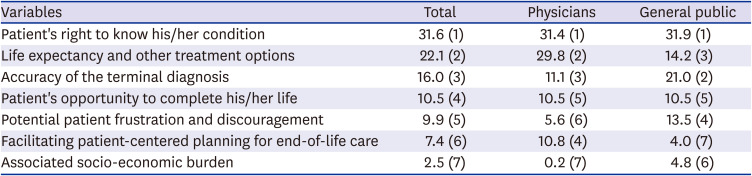
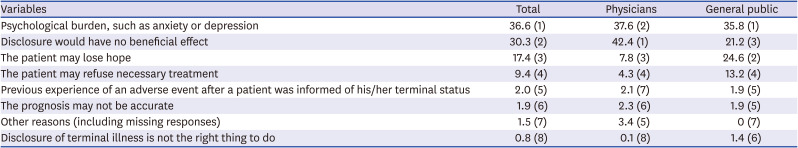
23. Korean Medical Association. Annual Report Membership Statistics Korean Medical Association. Seoul: Korean Medical Association;2015.
24. Austin PC, Stuart EA. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat Med. 2015; 34(28):3661–3679. PMID:
26238958.

25. Linden A, Samuels SJ. Using balance statistics to determine the optimal number of controls in matching studies. J Eval Clin Pract. 2013; 19(5):968–975. PMID:
23910956.

26. Yun YH, Lee CG, Kim SY, Lee SW, Heo DS, Kim JS, et al. The attitudes of cancer patients and their families toward the disclosure of terminal illness. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22(2):307–314. PMID:
14722040.

27. Yun YH, Kwon YC, Lee MK, Lee WJ, Jung KH, Do YR, et al. Experiences and attitudes of patients with terminal cancer and their family caregivers toward the disclosure of terminal illness. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28(11):1950–1957. PMID:
20212258.

28. Lee IH, Sohn MS, Kim SY, Park JY, Lee EY. Developing Medical Decision-Making Process in the End-of-Life Care. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2013.
29. Kim MS, Lee J, Sim JA, Kwon JH, Kang EJ, Kim YJ, et al. Discordance between physician and the general public perceptions of prognostic disclosure to children with serious illness: a Korean nationwide study. J Korean Med Sci. 2018; 33(49):e327. PMID:
30505258.

30. Epstein AS, Prigerson HG, O'Reilly EM, Maciejewski PK. Discussions of life expectancy and changes in illness understanding in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34(20):2398–2403. PMID:
27217454.

31. Nipp RD, Greer JA, El-Jawahri A, Moran SM, Traeger L, Jacobs JM, et al. Coping and prognostic awareness in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35(22):2551–2557. PMID:
28574777.

32. Mack JW, Wolfe J, Cook EF, Grier HE, Cleary PD, Weeks JC. Hope and prognostic disclosure. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25(35):5636–5642. PMID:
18065734.

33. Ouchi K, Wu M, Medairos R, Grudzen CR, Balsells H, Marcus D, et al. Initiating palliative care consults for advanced dementia patients in the emergency department. J Palliat Med. 2014; 17(3):346–350. PMID:
24387752.

34. Hill E, Savundranayagam MY, Zecevic A, Kloseck M. Staff perspectives of barriers to access and delivery of palliative care for persons with dementia in long-term care. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2018; 33(5):284–291. PMID:
29554814.

35. Andrews S, McInerney F, Toye C, Parkinson CA, Robinson A. Knowledge of dementia: do family members understand dementia as a terminal condition? Dementia. 2017; 16(5):556–575. PMID:
26394629.

36. Davies N, Maio L, van Riet Paap J, Mariani E, Jaspers B, Sommerbakk R, et al. Quality palliative care for cancer and dementia in five European countries: some common challenges. Aging Ment Health. 2014; 18(4):400–410. PMID:
24131061.

37. Ryan T, Gardiner C, Bellamy G, Gott M, Ingleton C. Barriers and facilitators to the receipt of palliative care for people with dementia: the views of medical and nursing staff. Palliat Med. 2012; 26(7):879–886. PMID:
21969310.

38. Lum HD, Jordan SR, Brungardt A, Ayele R, Katz M, Miyasaki JM, et al. Framing advance care planning in Parkinson disease: patient and care partner perspectives. Neurology. 2019; 92(22):e2571–9. PMID:
31028124.
39. Walter HA, Seeber AA, Willems DL, de Visser M. The role of palliative care in chronic progressive neurological diseases-a survey amongst neurologists in the Netherlands. Front Neurol. 2019; 9:1157. PMID:
30692960.

40. Tuck KK, Brod L, Nutt J, Fromme EK. Preferences of patients with Parkinson's disease for communication about advanced care planning. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2015; 32(1):68–77. PMID:
24052430.

41. Mitchell SL, Teno JM, Kiely DK, Shaffer ML, Jones RN, Prigerson HG, et al. The clinical course of advanced dementia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361(16):1529–1538. PMID:
19828530.

42. Mack JW, Cronin A, Keating NL, Taback N, Huskamp HA, Malin JL, et al. Associations between end-of-life discussion characteristics and care received near death: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30(35):4387–4395. PMID:
23150700.

43. Murray SA, Kendall M, Boyd K, Sheikh A. Illness trajectories and palliative care. BMJ. 2005; 330(7498):1007–1011. PMID:
15860828.

44. Sangarlangkarn A, Merlin JS, Tucker RO, Kelley AS. Advance care planning and HIV infection in the era of antiretroviral therapy: a review. Top Antivir Med. 2016; 23(5):174–180. PMID:
27398771.
45. Evans LR, Boyd EA, Malvar G, Apatira L, Luce JM, Lo B, et al. Surrogate decision-makers' perspectives on discussing prognosis in the face of uncertainty. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 179(1):48–53. PMID:
18931332.

46. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Hospice & Palliative Care in Korea: Facts & Figures 2017. Goyang: Central Hospice Center, National Cancer Center;2019.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download