INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Mice
Sensitization and antigen challenge protocol
Isolation of hADSCs and hBMSCs
Administration of hADSCs or hBMSCs
Measurement of AHR
Cell counts of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining
Statistical analyses
Ethics statement
RESULTS
Double injection of hMSCs leads to greater improvement of AHR
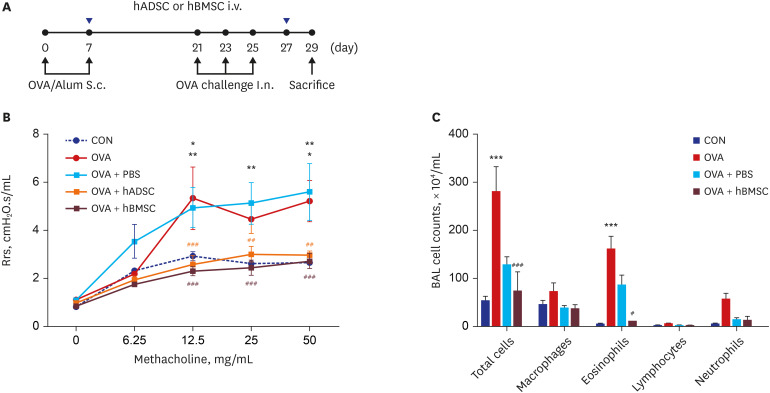 | Fig. 1Double injection of human mesenchymal stem cells inhibited airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation. (A) Schematic diagram of the mouse model of acute asthma and treatment with hADSCs or hBMSCs. Mice were sensitized on days 0 and 7 by subcutaneous injection of OVA and challenged intranasally on days 21, 23, and 25 (black dots). Aliquots of 2.5 × 107/kg hADSCs or hBMSCs were injected via the tail vein on days 7 and 27 (blue triangles). Samples were harvested on day 29. (B) Rrs was used to measure airway hyperresponsiveness with increasing concentration of nebulized methacholine. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to the CON group; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared to the OVA+PBS group. (C) BALF cells were isolated by centrifugation and stained with Diff-Quik. Total numbers of macrophages, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophils in the BALF were counted. ***P < 0.001 compared to the CON group; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 compared to the OVA group.hADSC = human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell, hBMSC = human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell, OVA = ovalbumin, Alum = aluminum, Rrs = airway resistance, CON = control, PBS = phosphate buffered saline, BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage, BALF = bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, S.c.= subcutaneous, I.n.= intranasal.
|
Airway inflammation is attenuated by hMSC double injection in BALF cells
Double injection of hMSCs further increases lung inflammation
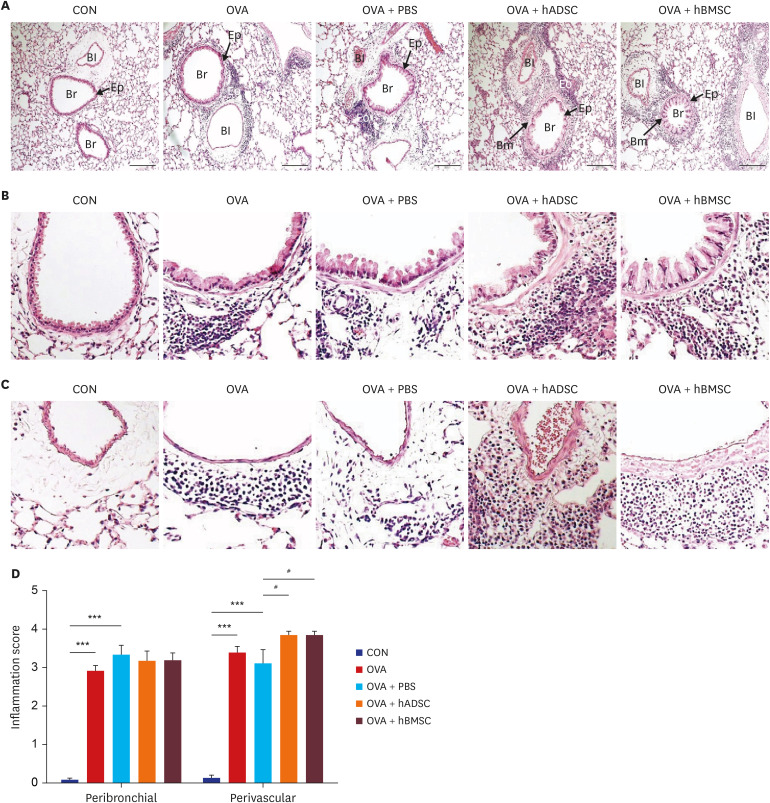 | Fig. 2Double injection of hMSCs led to more severe airway inflammation. (A–C) Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections. (A) The lungs in the mouse model of acute asthma showing airways and blood vessels surrounded by alveoli (×100). (B) Airway (×400). Black arrows indicate smooth muscle, and black stars indicate goblet cell metaplasia. (C) Blood vessel (×400). (D) Histological quantification of peribronchial and perivascular inflammation in the lung. ***P < 0.001 compared to the CON group; #P < 0.05 compared to the OVA+PBS group.CON = control, OVA = ovalbumin, PBS = phosphate buffered saline, hADSC = human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell, hBMSC = human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell, Br = bronchus, Bm = basement membrane, Bl = blood vessel, Eo = eosinophil, Ep = epithelium.
|
Double injection of hMSCs increases TH2 cytokine production in BALF
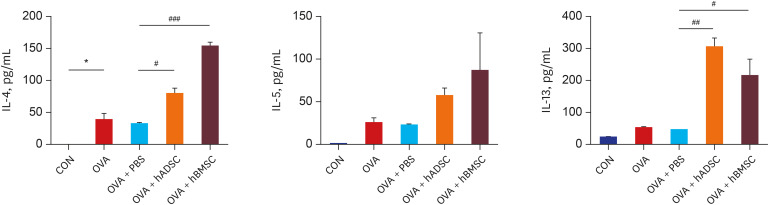 | Fig. 3Double injection of human mesenchymal stem cells exacerbated levels of T-helper 2 cytokine. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was obtained from the mouse model of acute asthma with and without treatment with hADSCs or hBMSCs and the levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 were measured.IL = interleukin, CON = control, OVA = ovalbumin, PBS = phosphate buffered saline, hADSC = human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell, hBMSC = human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
*P < 0.05 compared to the CON group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared to the OVA+PBS group.
|
Single injection of hMSCs also reduces AHR
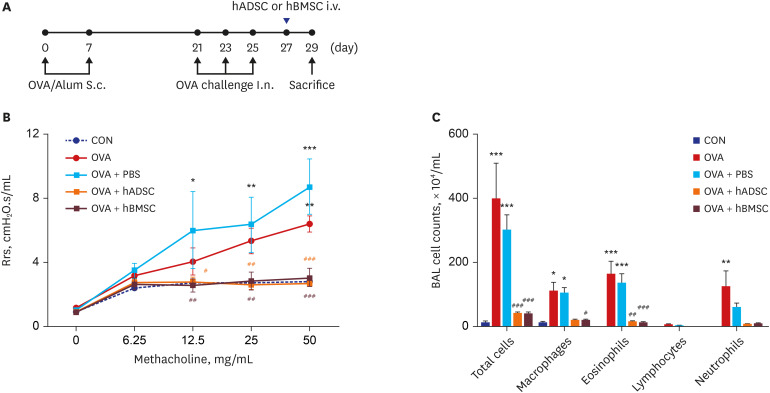 | Fig. 4Single injection of human mesenchymal stem cells reduced airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation. (A) Schematic diagram of the mouse model of acute asthma and treatment with hADSCs or hBMSCs. Mice were sensitized on days 0 and 7 by subcutaneous injection of OVA and challenged intranasally on days 21, 23, and 25 (black dots). Aliquots of 2.5 × 107/kg hADSCs or hBMSCs were injected via the tail vein on day 27 (blue triangles). Samples were harvested on day 29. (B) Rrs was used to measure airway hyperresponsiveness with increasing concentration of nebulized methacholine. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to the CON group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared to the OVA+PBS group. (C) BAL cells were isolated by centrifugation and stained with Diff-Quik. Total numbers of macrophages, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophils in the BAL fluid were counted. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to the CON group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared to the OBA+PBS group.hADSC = human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell, hBMSC = human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell, OVA = ovalbumin, Alum = aluminum, Rrs = airway resistance, CON = control, PBS = phosphate buffered saline, BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage, S.c= subcutaneous, I.n.= intranasal.
|
Single hMSC injection is more effective for reducing airway inflammation
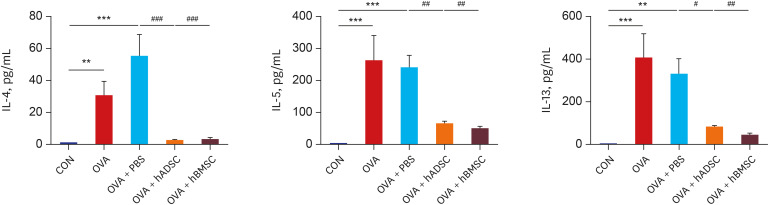 | Fig. 5Single injection with human mesenchymal stem cells attenuated levels of T-helper 2 cytokine. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was obtained from the mouse model of acute asthma with and without hADSC or hBMSC treatment and levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 were measured.IL = interleukin, CON = control, OVA = ovalbumin, PBS = phosphate buffered saline, hADSC = human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell, hBMSC = human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to the CON group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared to the OVA or OVA+PBS group.
|
Single hMSC injection inhibits eosinophilic lung inflammation
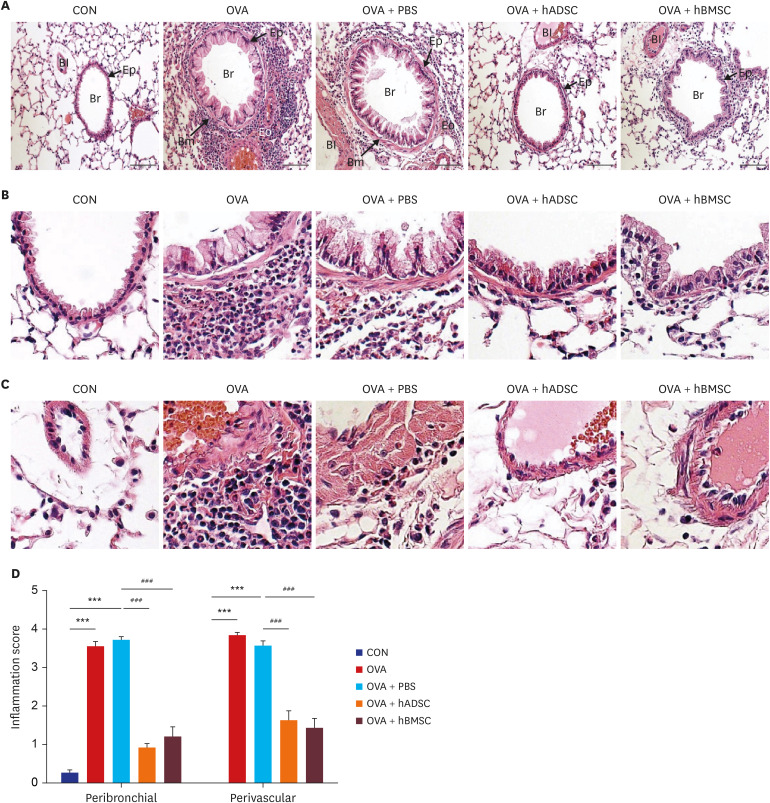 | Fig. 6Single injection with human mesenchymal stem cells reduced eosinophil infiltration and lung inflammation. (A) Paraffin-embedded lung tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (original magnification: ×200). (B) Airway (× 400). Black arrows indicate smooth muscle, and black stars indicate goblet cell metaplasia. (C) Blood vessel (× 400). (D) Histological quantification of peribronchial and perivascular inflammation in the lung.CON = control, OVA = ovalbumin, PBS = phosphate buffered saline, hADSC = human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell, hBMSC = human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell, Br = bronchus, Bm = basement membrane, Bl = blood vessel, Eo = eosinophil, Ep = epithelium.
***P < 0.001 compared to the CON group; ###P < 0.001 compared to the OVA+PBS group.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download