TO THE EDITOR
A 65-year-old Japanese woman with a 2-week history of fever, whole-body lymph node swelling, and abdominal swelling caused by splenomegaly was admitted to our hospital. Results of complete blood count (CBC) on admission were as follows: white blood cell (WBC) count, 25×109/L; hemoglobin (Hb) level, 7.4 g/dL; and platelet count, 128×109/L. Liver function and renal function test results were normal; however, elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (1,407 U/L) was noted. The patient was diagnosed with peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS) based on histopathological analysis of lymph nodes. Bone marrow biopsy revealed proliferating CD3+ CD4- CD8+ lymphocytes and bone marrow invasion of the lymphoma. Because the patient had a clinical stage IVB lymphoma with an International Prognostic Index score of 5 (high risk), she received six cycles of EPOCH (cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine, etoposide, and prednisone) chemotherapy. Although she achieved complete remission (CR), confirmed using positron emission tomography, she again developed fever and splenomegaly after 1 month; spleen and bone marrow biopsies showed PTCL recurrence (Fig. 1A). We thus administered ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin) chemotherapy as a salvage treatment; however, her general condition progressively exacerbated with persistent fever, anorexia, peripheral edema, and a performance status of 4. During chemotherapy, her peripheral blood lymphocyte count markedly increased (WBC count, 15.9×109/L; lymphocyte count, 87.1%; Hb, 6.1 g/dL; and platelet count, 11×109/L), indicating a progression to the leukemic phase (Fig. 1C–G). The LDH and creatinine levels were 474 U/L and 1.49 mg/dL, respectively. Therefore, we initiated weekly administration of intravenous romidepsin at a dose of 14 mg/m2 for 4 hours. A significant improvement was observed after one treatment course, and after two courses, her bone marrow condition and splenomegaly also improved, and she achieved CR (Fig. 1B). In total, we administered six courses of romidepsin. However, we believed that the risk of recurrence after romidepsin administration was high, and thus, she received an allogeneic transplant and has maintained CR. She underwent a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen that comprised total body irradiation, 4 Gy; fludarabine, 25 mg/m2 for 5 days; and melpharan, 70 mg/m2 for 2 days, as well as an allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from an HLA-2-locus-mismatched cord blood donor containing 2.8×107 cells/kg and 3.34×106 CD34 cells/kg. Following this treatment, she did not develop grade 3–4 acute or chronic graft versus host disease, and she has completed 1 year without lymphoma recurrence.
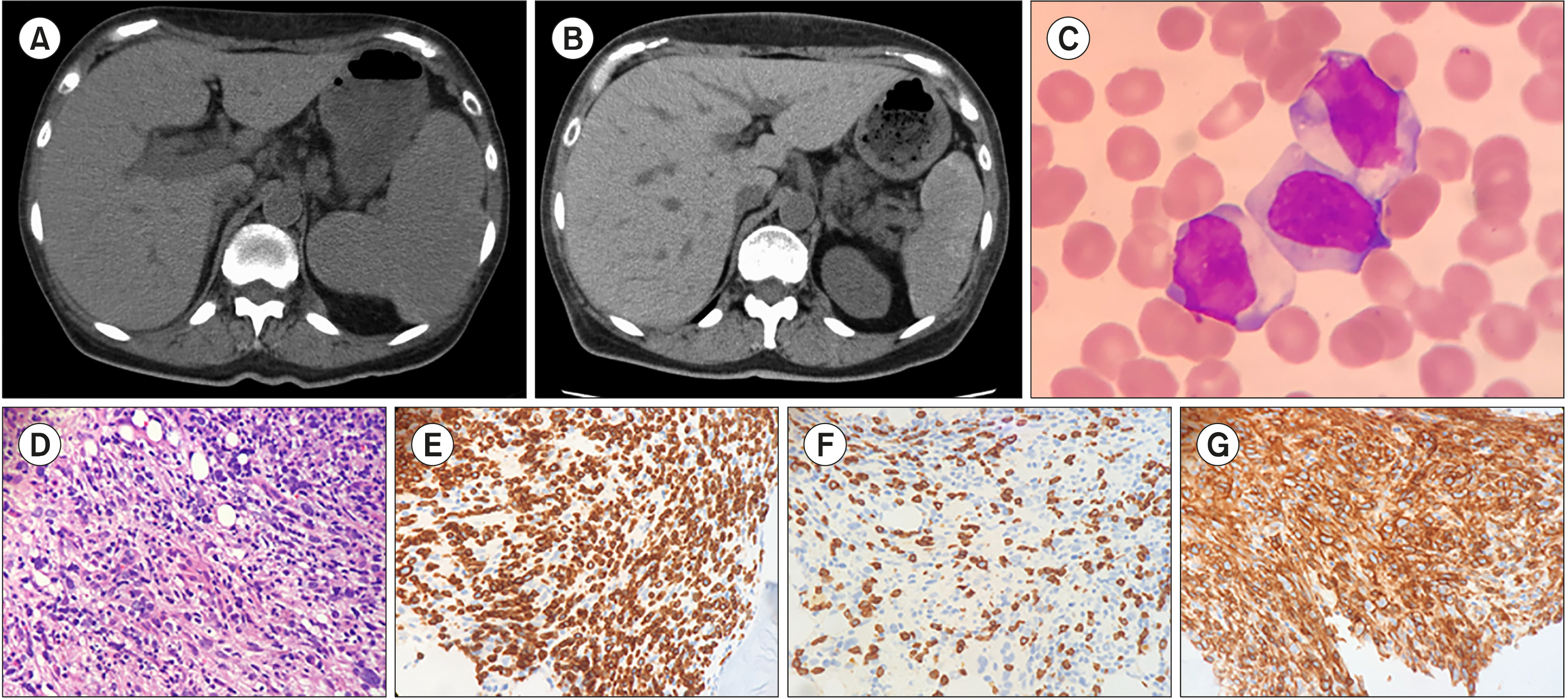 | Fig. 1Computed tomography (CT) findings at relapse showing splenomegaly (A). CT after 2 courses of romidepsin showing that the splenomegaly improved (B). Peripheral blood smear with May–Giemsa staining (C) and histopathological findings from bone marrow biopsy showing diffuse proliferation of medium-sized lymphoid cells (hematoxylin-eosin staining, ×20) (D), indicating a leukemic-phase peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Immunohistochemical staining expressed (E) CD3, (F) CD4 (weakly), and (G) CD8 lymphocytes. |
PTCL is a heterogeneous category of predominantly nodal lymphomas and represents the most common mature T-cell lymphoma subtype [1]. Although PTCL has an aggressive clinical course, leukemic presentation is uncommon [1, 2]. When our patient progressed to the leukemic phase, most of peripheral leukocytes were neoplastic cells, which is a rare presentation. The leukemic phase of PTCL indicates poor prognosis [3, 4], revealing that lymphoma cells refractory to various chemotherapies survived and could have transformed into more aggressive lymphoma cells.
Because PTCL exhibits varying forms of recurrence and many second-line therapy options are available, there is often uncertainty regarding the choice of treatment. There is currently no standard of care for treating most PTCL subtypes. Romidepsin, a structurally unique, potent, bicyclic class-1 selective histone deacetylase inhibitor, was approved in 2011 for treating patients with PTCL who received at least one prior therapy [5]. Romidepsin was recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines as a second-line and subsequent therapy for PTCL patients, regardless of the intention to proceed to high-dose therapies or stem cell transplantation [6]. We summarized the results of clinical studies on romidepsin in Table 1. In phase II studies of romidepsin for relapsed or refractory PTCL, the overall response rate to romidepsin was 25–44%, which included 15–23% with CR. Additionally, romidepsin induced durable responses with manageable toxicity [5, 7-9]. In our case, romidepsin was selected because of its potential for minimal toxicity when administered after chemotherapy for refractory PTCL. However, the median duration of romidepsin response has been reported to be as short as 8.9–28 months [5, 7-9]. Our patient had no adverse event with romidepsin, and she underwent allogenic transplantation after her general condition sufficiently improved.
Table 1
Studies of romidepsin as a single agent for treating mature T-cell lymphomas.
| Studies | Setting | Study design | N | PTCL subtypes | Median N of prior therapies | ORR | CR rate | PFS | Median duration of response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coiffeir et al. [5, 7] | RR | Phase 2, multicenter | 130 | PTCL NOS (N=69, 53%) | 2 (1–8) | 25% | 15% | 4 mo | 28 (1–48+) mo |
| PTCL | AITL (N=27, 21%) | ||||||||
| Piekarz et al. [8] | RR | Phase 2, multicenter | 47 | PTCL NOS (N=27, 59%) | 3 (1–11) | 38% | 18% | 8.9 mo | 8.9 (2–74) mo |
| PTCL | AITL (N=7, 15%) | ||||||||
| Maruyama et al. [9] | RR | Phase 1/2 multicenter | 50 | PTCL NOS (N=20, 42%) | 7.1 (1.2–82.9) | 44% | 23% | 5.6 mo | 11.1 mo |
| PTCL | AITL (N=21, 44%) | ||||||||
| CTCL |
Although there are relatively limited preclinical and clinical data, the combination of romidepsin and a hypomethylating agent has previously resulted in CR, not only for T-cell lymphoma but also for relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [10-12]. However, in a pivotal trial, patients who had inadequate bone marrow function were ineligible [5]. Our case demonstrates the possibility of rescue from an aggressive leukemic phase of PTCL by a romidepsin-only therapy. Because effective therapies for aggressive-relapse PTCL are limited, further investigation of romidepsin is warranted.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download