INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Chemicals and drugs
Experimental animal and ethical approval
Induction of psoriasis
Experimental animals grouping
Sample collection and processing
Lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants
Inflammatory markers/mediators
Western blot
Histopathological analysis
Data analysis
RESULTS
Impact of SAB/MTX on spleen index
Impact of SAB/MTX on PASI, erythema, scaling and skin thickness
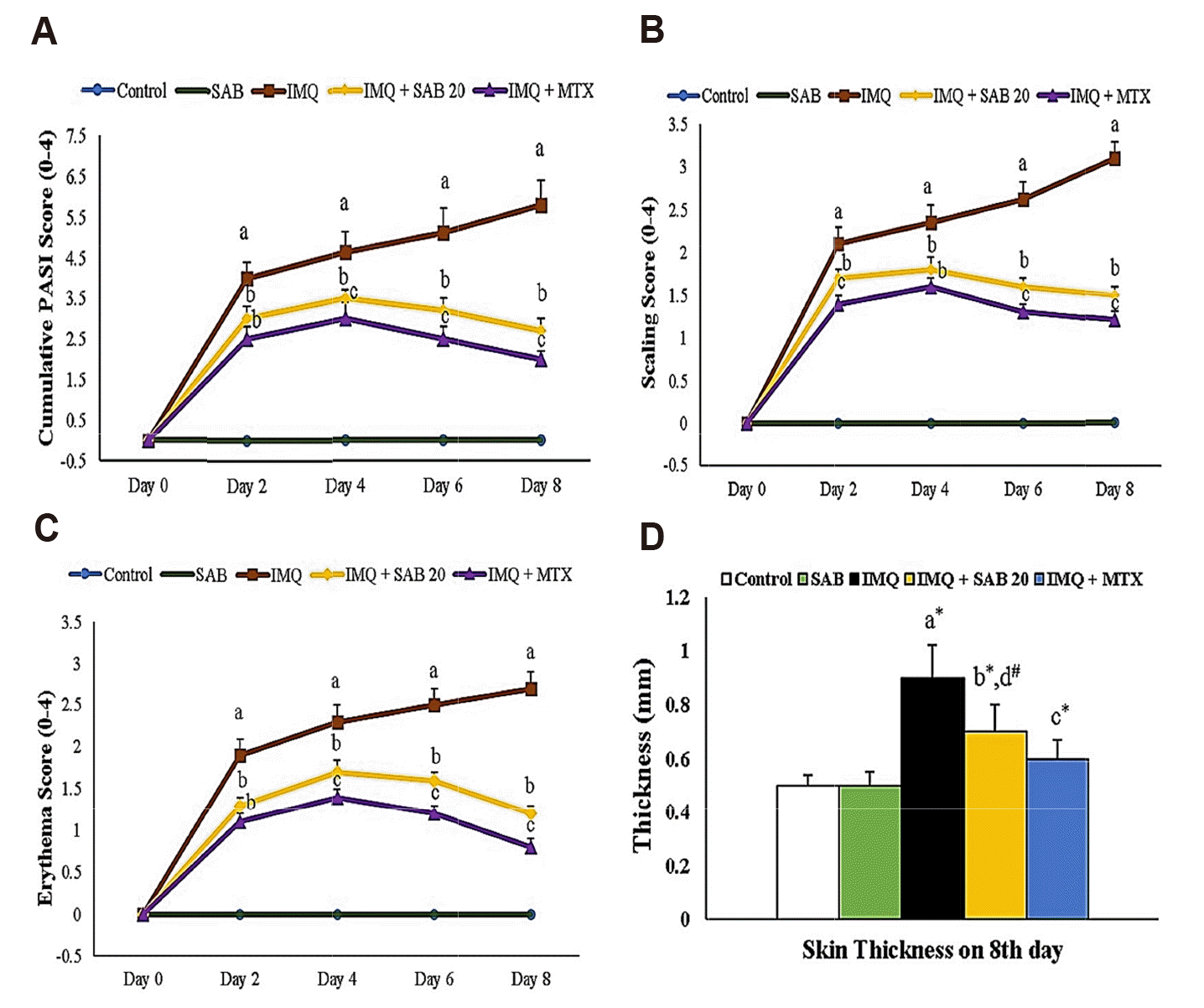 | Fig. 1Illustrate the skin PASI (A), scaling (B), erythema (C) and thickness (D) (only on 8th day) in control and IMQ-induced mice.Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. IMQ, imiquimod; SAB, salvianolic acid B; MTX, methotrexate; PASI, psoriasis area severity index. p-value (#p < 0.05, *p < 0.01): where ‘a’ denotes the comparison between IMQ vs. Control, ‘b’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ, ‘c’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + MTX vs. IMQ, ‘d’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ + MTX.
|
Impact of SAB/MTX on lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants
Table 1
| Parameters | MDA (nmol/mg protein) | CAT (U/mg protein) | SOD (U/mg protein) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 10.64 ± 1.80 | 21.50 ± 2.40 | 39.22 ± 4.50 |
| SAB | 11.02 ± 1.75 | 21.00 ± 2.25 | 38.85 ± 4.09 |
| IMQ | 28.95 ± 3.70a* | 09.88 ± 1.10a* | 20.40 ± 2.20a* |
| IMQ + SAB | 18.61 ± 2.35b*,d# | 17.10 ± 3.00b*,d# | 33.68 ± 3.80b*,d# |
| IMQ + MTX | 20.05 ± 2.03c* | 14.75 ± 2.05c# | 29.79 ± 3.15c* |
Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. IMQ, imiquimod; MDA, malondialdehyde; CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; SAB, salvianolic acid B; MTX, methotrexate. p-value (#p < 0.05, *p < 0.01): where ‘a’ denotes the comparison between IMQ vs. Control, ‘b’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ, ‘c’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + MTX vs. IMQ, ‘d’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ + MTX.
Impact of SAB/MTX on inflammatory markers/mediators
Table 2
| Parameters | IL-23 (pg/mg protein) | IL-22 (pg/mg protein) | IL-17A (pg/mg protein) | IL-1β (ng/mg protein) | TNF-α (ng/mg protein) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 15.80 ± 1.75 | 1.10 ± 0.15 | 7.55 ± 0.75 | 7.42 ± 0.71 | 5.10 ± 0.50 |
| SAB | 16.00 ± 2.10 | 1.05 ± 0.10 | 7.40 ± 0.58 | 7.45 ± 0.80 | 4.97 ± 0.52 |
| IMQ | 41.25 ± 4.60a* | 3.87 ± 0.40a* | 13.98 ± 1.80a* | 25.10 ± 2.45a* | 15.04 ± 1.85a* |
| IMQ + SAB | 23.50 ± 3.00b*,d# | 2.02 ± 0.20b*,d,NS | 9.75 ± 1.10b*,d,NS | 11.21 ± 1.35b*,d# | 7.14 ± 0.97b*,d# |
| IMQ + MTX | 25.18 ± 2.10c* | 2.22 ± 0.22c* | 9.50 ± 1.12c* | 13.76 ± 1.50c* | 8.95 ± 0.88c* |
Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. IMQ, imiquimod; IL-23/22/17A/1β, interleukins 23/22/17A/1beta; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor alpha; SAB, salvianolic acid B; MTX, methotrexate; NS, non-significant. p-value (#p < 0.05, *p < 0.01): where ‘a’ denotes the comparison between IMQ vs. Control, ‘b’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ, ‘c’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + MTX vs. IMQ, ‘d’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ + MTX.
Impact of SAB/MTX on the protein expression of keratin markers and PI3K/Akt signaling molecules
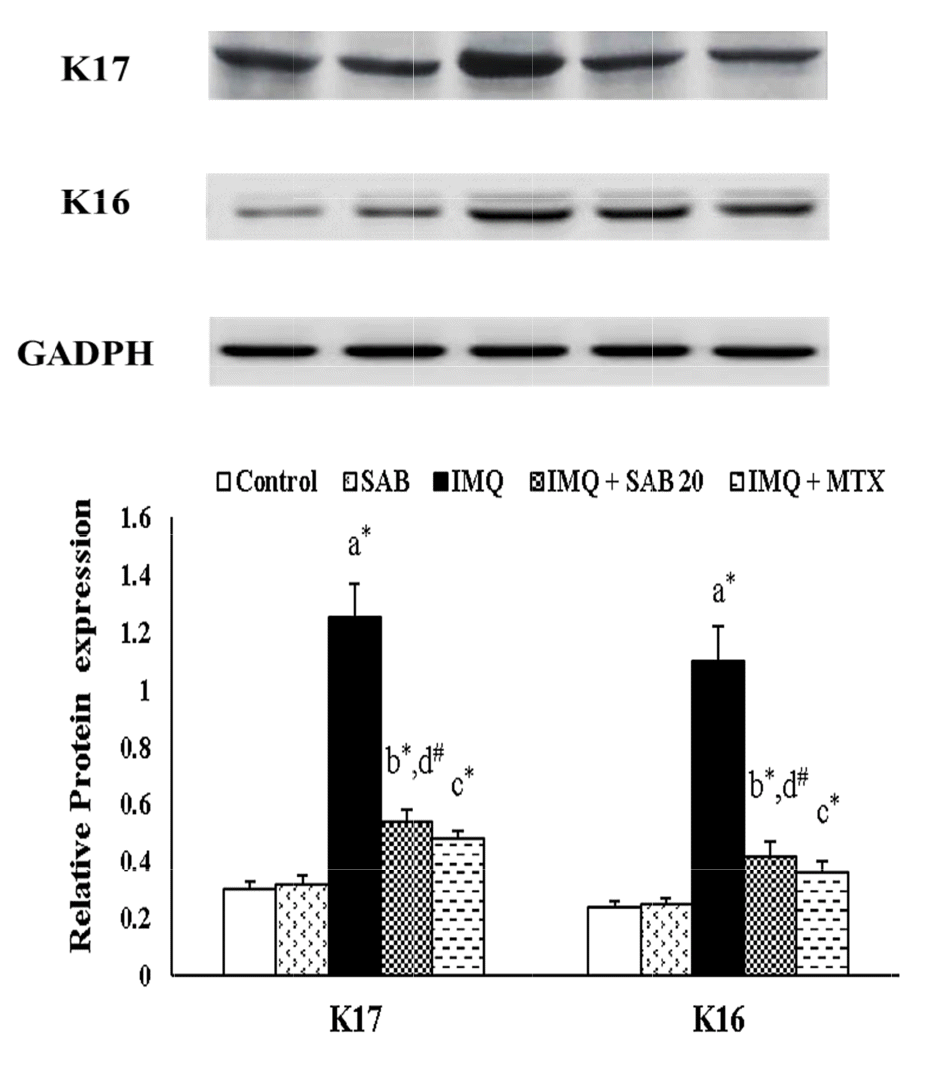 | Fig. 2Illustrate the protein expression of skin keratin markers (K16 and K17) in control and IMQ-induced mice.Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. IMQ, imiquimod; SAB, salvianolic acid B; MTX, methotrexate; K16 and K17, keratin 16/17. p-value (#p < 0.05, *p < 0.01): where ‘a’ denotes the comparison between IMQ vs. Control, ‘b’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ, ‘c’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + MTX vs. IMQ, ‘d’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ + MTX.
|
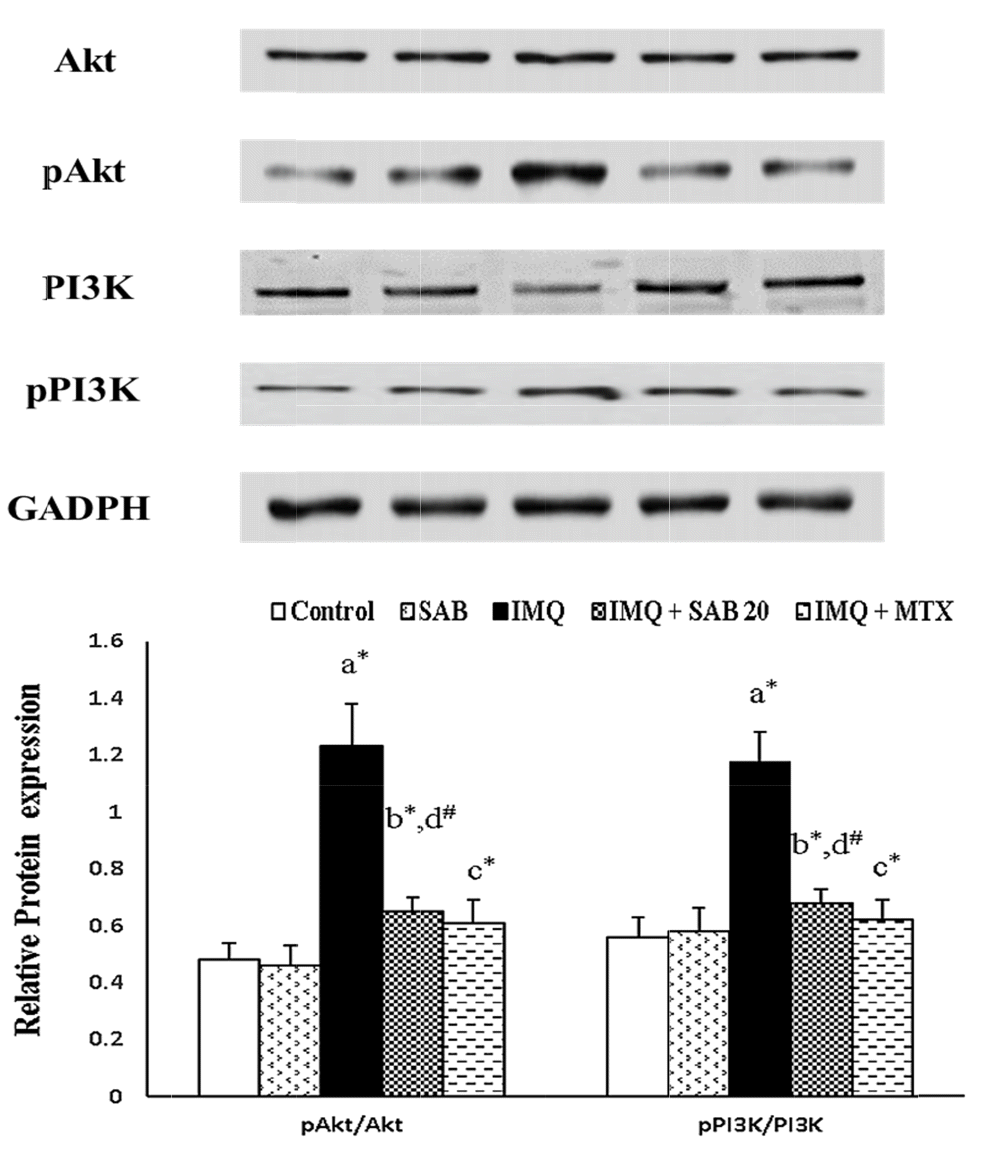 | Fig. 3Illustrate the protein expression of skin PI3K/Akt signaling molecules in control and IMQ-induced mice.Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. IMQ, imiquimod; SAB, salvianolic acid B; MTX, methotrexate; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; Akt: protein kinase B. p-value (#p < 0.05, *p < 0.01): where ‘a’ denotes the comparison between IMQ vs. Control, ‘b’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ, ‘c’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + MTX vs. IMQ, ‘d’ denotes the comparison between IMQ + SAB vs. IMQ + MTX.
|
Impact of SAB/MTX on histopathological changes in dermal tissue
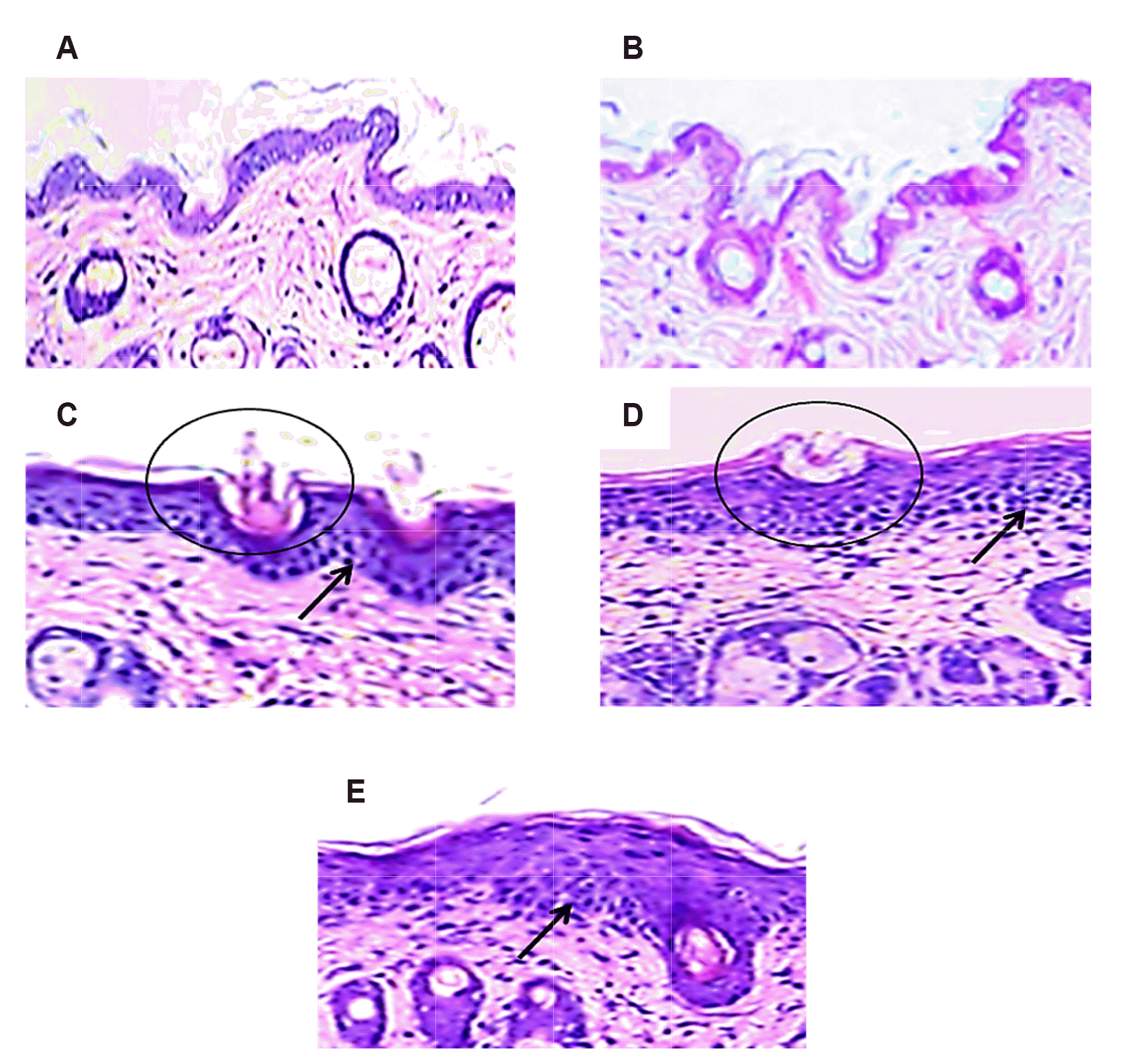 | Fig. 4Illustrates the histopathological changes in dermal tissue upon staining with H&E (100× magnification) in control and IMQ-induced mice.Control (A) and SAB (B) mice dermal tissue slide display normal smoother epidermis without any inflammation or lesion. The IMQ induced mice dermal section (C) showed thickened epidermis (hyperplasia and acanthosis-circle) with elevated immune cell infiltration (arrow mark). Nevertheless, the mice dermal section treated with SAB (D) and MTX (E) portrait lesser thick epidermis (circle) with decreased immune cell infiltration (arrow mark) than IMQ-induced mice section. Scale bar:100 μm. IMQ, imiquimod; SAB, salvianolic acid B.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download