2. Banchereau J, Pascual V. 2006; Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity. 25:383–92.

3. Korman BD, Kastner DL, Gregersen PK, Remmers EF. 2008; STAT4: genetics, mechanisms, and implications for auto-immunity. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 8:398–403. DOI:
10.1007/s11882-008-0077-8. PMID:
18682104. PMCID:
PMC2562257.

4. Korman BD, Kastner DL, Gregersen PK, Remmers EF. 2008; STAT4: genetics, mechanisms, and implications for auto-immunity. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 8:398. DOI:
10.1007/s11882-008-0077-8. PMID:
18682104. PMCID:
PMC2562257.

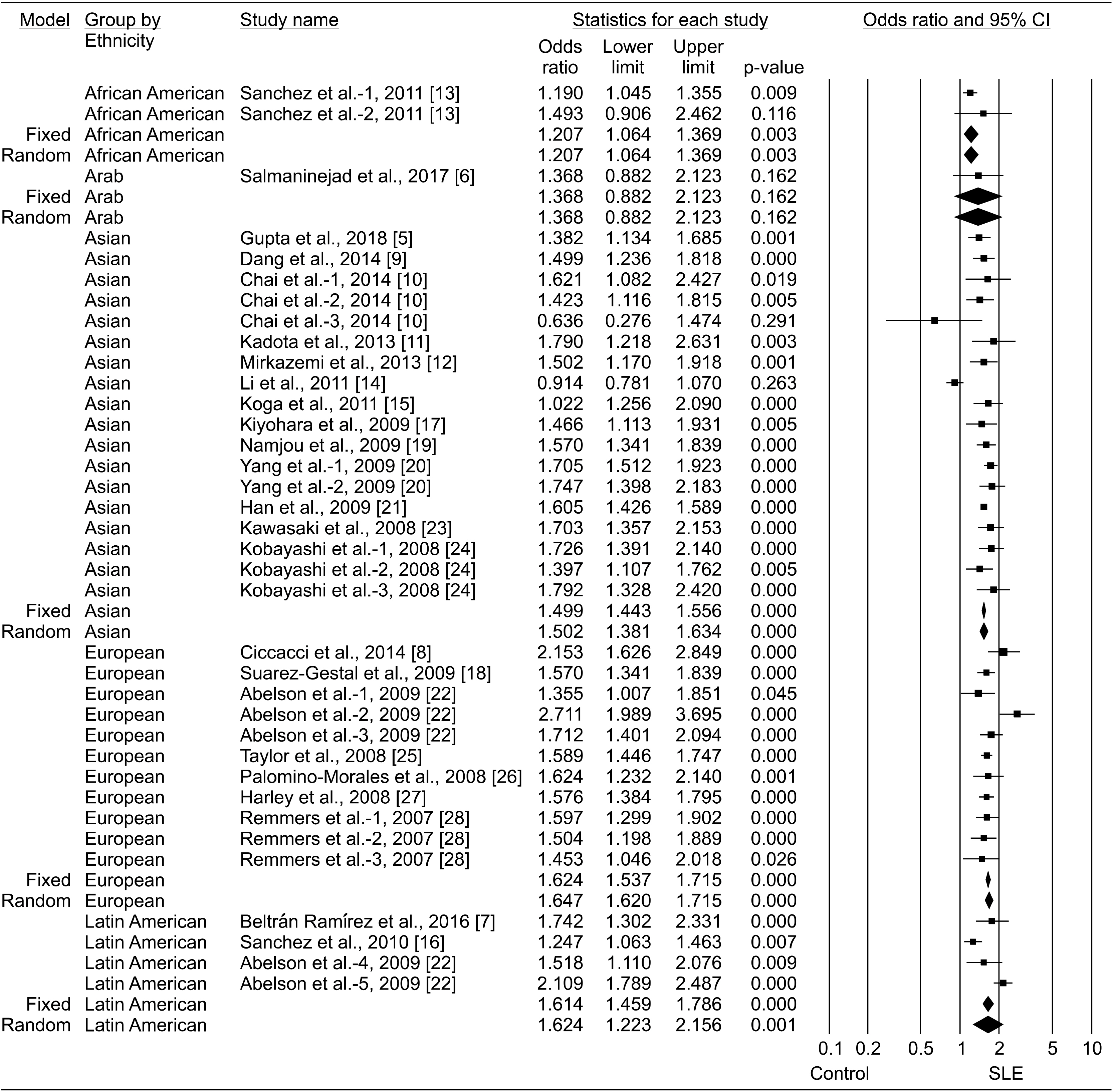
5. Gupta V, Kumar S, Pratap A, Singh R, Kumari R, Kumar S, et al. 2018; Association of ITGAM, TNFSF4, TNFAIP3 and STAT4 gene polymorphisms with risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in a North Indian population. Lupus. 27:1973–9. DOI:
10.1177/0961203318786432. PMID:
30041578.

6. Salmaninejad A, Mahmoudi M, Aslani S, Poursani S, Ziaee V, Rezaei N. 2017; Association of STAT4 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with Iranian juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Turk J Pediatr. 59:144–9. DOI:
10.24953/turkjped.2017.02.005. PMID:
29276866.

7. Beltrán Ramírez O, Mendoza Rincón JF, Barbosa Cobos RE, Alemán Ávila I, Ramírez Bello J. 2016; STAT4 confers risk for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Mexican patients. Immunol Lett. 175:40–3. DOI:
10.1016/j.imlet.2016.05.003. PMID:
27178308.

8. Ciccacci C, Perricone C, Ceccarelli F, Rufini S, Di Fusco D, Alessandri C, et al. 2014; A multilocus genetic study in a cohort of Italian SLE patients confirms the association with STAT4 gene and describes a new association with HCP5 gene. PLoS One. 9:e111991. DOI:
10.1371/journal.pone.0111991. PMID:
25369137. PMCID:
PMC4219822.

9. Dang J, Shan S, Li J, Zhao H, Xin Q, Liu Y, et al. 2014; Gene-gene interactions of IRF5, STAT4, IKZF1 and ETS1 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens. 83:401–8. DOI:
10.1111/tan.12349. PMID:
24697319.

10. Chai HC, Chua KH, Lim SK, Phipps ME. 2014; Insight into gene polymorphisms involved in toll-like receptor/interferon signalling pathways for systemic lupus erythematosus in South East Asia. J Immunol Res. 2014:529167. DOI:
10.1155/2014/529167. PMID:
24741605. PMCID:
PMC3987947.

11. Kadota K, Mori M, Yanagimachi M, Miyamae T, Hara T, Kanetaka T, et al. 2013; Analysis of gender differences in genetic risk: association of TNFAIP3 polymorphism with male childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus in the Japanese population. PLoS One. 8:e72551. DOI:
10.1371/journal.pone.0072551. PMID:
24023622. PMCID:
PMC3758304.

12. Mirkazemi S, Akbarian M, Jamshidi AR, Mansouri R, Ghoroghi S, Salimi Y, et al. 2013; Association of STAT4 rs7574865 with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Iranian population. Inflammation. 36:1548–52. DOI:
10.1007/s10753-013-9698-8. PMID:
23912645.

13. Sánchez E, Comeau ME, Freedman BI, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM, Langefeld CD, et al. 2011; Identification of novel genetic susceptibility loci in African American lupus patients in a candidate gene association study. Arthritis Rheum. 63:3493–501. DOI:
10.1002/art.30563. PMID:
21792837. PMCID:
PMC3205224.

14. Li P, Cao C, Luan H, Li C, Hu C, Zhang S, et al. 2011; Association of genetic variations in the STAT4 and IRF7/KIAA1542 regions with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Northern Han Chinese population. Hum Immunol. 72:249–55. DOI:
10.1016/j.humimm.2010.12.011. PMID:
21167895.

15. Koga M, Kawasaki A, Ito I, Furuya T, Ohashi J, Kyogoku C, et al. 2011; Cumulative association of eight susceptibility genes with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese female population. J Hum Genet. 56:503–7. DOI:
10.1038/jhg.2011.49. PMID:
21562514.

16. Sanchez E, Webb RD, Rasmussen A, Kelly JA, Riba L, Kaufman KM, et al. 2010; Genetically determined Amerindian ancestry correlates with increased frequency of risk alleles for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 62:3722–9. DOI:
10.1002/art.27753. PMID:
20848568. PMCID:
PMC3078084.

17. Kiyohara C, Washio M, Horiuchi T, Tada Y, Asami T, Ide S, et al. 2009; Cigarette smoking, STAT4 and TNFRSF1B polymorphisms, and systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population. J Rheumatol. 36:2195–203. DOI:
10.3899/jrheum.090181. PMID:
19684152.
18. Suarez-Gestal M, Calaza M, Dieguez-Gonzalez R, Perez-Pampin E, Pablos JL, Navarro F, et al. 2009; Rheumatoid arthritis does not share most of the newly identified systemic lupus erythematosus genetic factors. Arthritis Rheum. 60:2558–64.

19. Namjou B, Sestak AL, Armstrong DL, Zidovetzki R, Kelly JA, Jacob N, et al. 2009; High-density genotyping of STAT4 reveals multiple haplotypic associations with systemic lupus erythematosus in different racial groups. Arthritis Rheum. 60:1085–95. DOI:
10.1002/art.24387. PMID:
19333953. PMCID:
PMC2776081.

20. Yang W, Ng P, Zhao M, Hirankarn N, Lau CS, Mok CC, et al. 2009; Population differences in SLE susceptibility genes: STAT4 and BLK, but not PXK, are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun. 10:219–26. DOI:
10.1038/gene.2009.1. PMID:
19225526.

21. Han JW, Zheng HF, Cui Y, Sun LD, Ye DQ, Hu Z, et al. 2009; Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 41:1234–7. DOI:
10.1038/ng.472. PMID:
19838193.
22. Abelson AK, Delgado-Vega AM, Kozyrev SV, Sánchez E, Velázquez-Cruz R, Eriksson N, et al. 2009; STAT4 associates with systemic lupus erythematosus through two independent effects that correlate with gene expression and act additively with IRF5 to increase risk. Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1746–53. DOI:
10.1136/ard.2008.097642. PMID:
19019891. PMCID:
PMC3878433.

23. Kawasaki A, Ito I, Hikami K, Ohashi J, Hayashi T, Goto D, et al. 2008; Role of STAT4 polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population: a case-control association study of the STAT1-STAT4 region. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R113. DOI:
10.1186/ar2516. PMID:
18803832. PMCID:
PMC2592800.

24. Kobayashi S, Ikari K, Kaneko H, Kochi Y, Yamamoto K, Shimane K, et al. 2008; Association of STAT4 with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in the Japanese population. Arthritis Rheum. 58:1940–6. DOI:
10.1002/art.23494. PMID:
18576330.
25. Taylor KE, Remmers EF, Lee AT, Ortmann WA, Plenge RM, Tian C, et al. 2008; Specificity of the STAT4 genetic association for severe disease manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet. 4:e1000084. DOI:
10.1371/journal.pgen.1000084. PMID:
18516230. PMCID:
PMC2377340.

26. Palomino-Morales RJ, Rojas-Villarraga A, González CI, Ramírez G, Anaya JM, Martín J. 2008; STAT4 but not TRAF1/C5 variants influence the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Colombians. Genes Immun. 9:379–82.

27. Harley JB, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, et al. International Consortium for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Genetics (SLEGEN). 2008; Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet. 40:204–10. DOI:
10.1038/ng.81. PMID:
18204446. PMCID:
PMC3712260.

28. Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW, et al. 2007; STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 357:977–86. DOI:
10.1056/NEJMoa073003. PMID:
17804842. PMCID:
PMC2630215.
29. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. 2009; Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 6:e1000097. DOI:
10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. PMID:
19621072. PMCID:
PMC2707599.

30. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. 2002; Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–58. DOI:
10.1002/sim.1186. PMID:
12111919.

33. Watford WT, Hissong BD, Bream JH, Kanno Y, Muul L, O'Shea JJ. 2004; Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the immunoregulatory roles of STAT4. Immunol Rev. 202:139–56. DOI:
10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00211.x. PMID:
15546391.

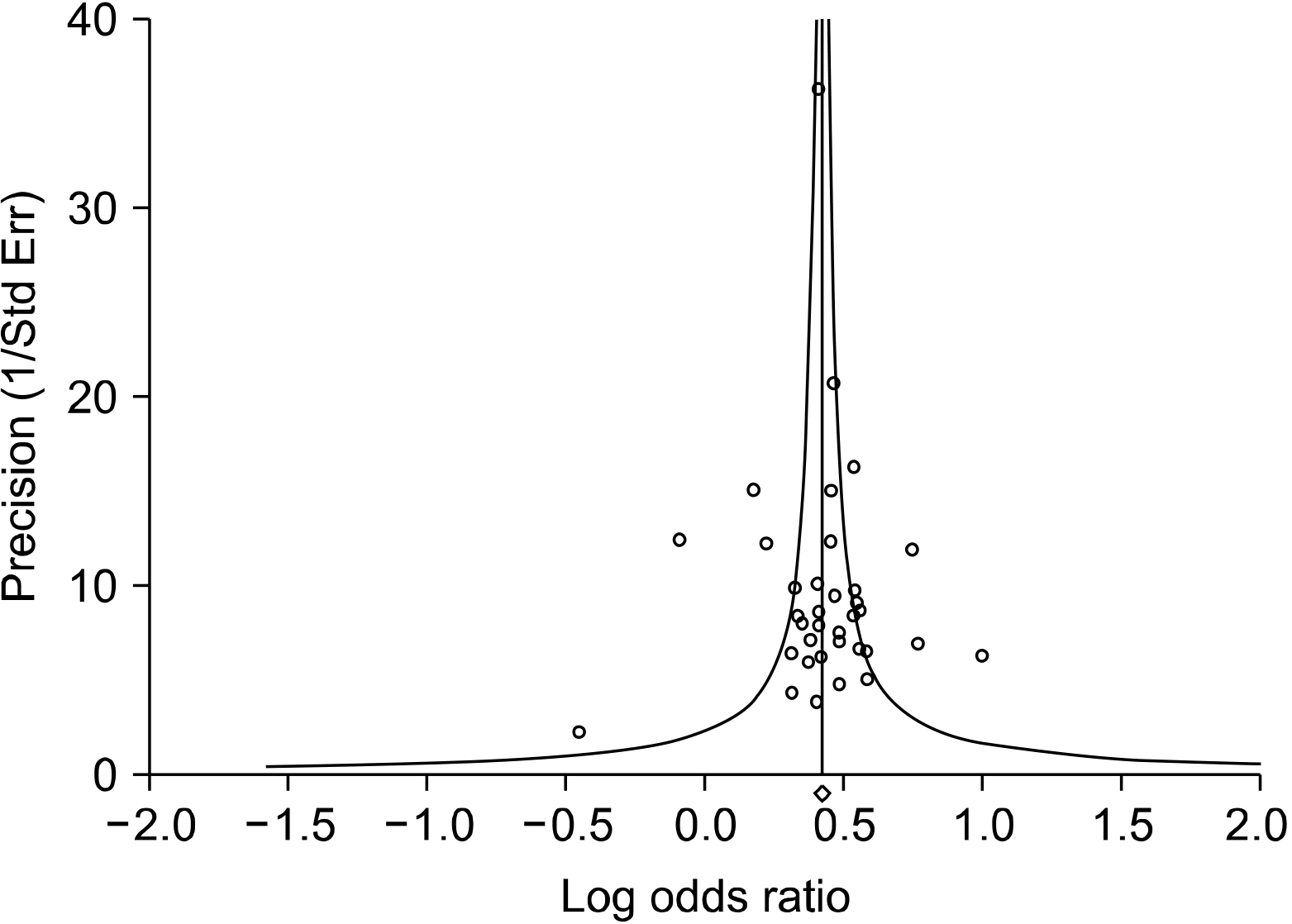
34. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. 1997; Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 315:629–34. PMID:
9492690. PMCID:
PMC2665616.

35. Chitnis T, Najafian N, Benou C, Salama AD, Grusby MJ, Sayegh MH, et al. 2001; Effect of targeted disruption of STAT4 and STAT6 on the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Invest. 108:739–47. DOI:
10.1172/JCI12563. PMID:
11544280. PMCID:
PMC209380.

36. Kariuki SN, Kirou KA, MacDermott EJ, Barillas-Arias L, Crow MK, Niewold TB. 2009; Cutting edge: autoimmune disease risk variant of STAT4 confers increased sensitivity to IFN-alpha in lupus patients in vivo. J Immunol. 182:34–8. DOI:
10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.34. PMID:
19109131. PMCID:
PMC2716754.
37. Zheng J, Yin J, Huang R, Petersen F, Yu X. 2013; Meta-analysis reveals an association of STAT4 polymorphisms with systemic autoimmune disorders and anti-dsDNA antibody. Hum Immunol. 74:986–92. DOI:
10.1016/j.humimm.2013.04.034. PMID:
23628400.

38. Yuan H, Feng JB, Pan HF, Qiu LX, Li LH, Zhang N, et al. 2010; A meta-analysis of the association of STAT4 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod Rheumatol. 20:257–62. DOI:
10.1007/s10165-010-0275-9. PMID:
20169389.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download