Introduction
Materials and Methods
Animals
Experimental protocol
Group I (Control group): included seven rats that were left untreated.
Group II (Short-term Red Bull group): included seven rats which received Red Bull at a dose of 3.75 ml/kg/day orally using gastric tube for four consecutive weeks [24]. This dose (3.75 ml) contains (1.13 mg) of caffeine.
Group III (Long-term Red Bull group): included seven rats which received Red Bull at a dose of 3.75 ml/kg/day orally using gastric tube for eight consecutive weeks [24]. This dose (3.75 ml) contains (1.13 mg) of caffeine.
Methods
Histological studies
Morphometric study and statistical analysis
1) Thickness of pyramidal cell layer was measured using digital micrographs taken by an Olympus CX31 microscope equipped with digital camera. Pixels were calibrated for actual measurements in micrometer using stage micrometer for the objective lens of 40×.
2) Cell count was done by using point selection at the objective lens of 40×.
3) Mean area percentage of GFAP immunoreactivity was done after image splitting. Images were converted into RGB stacks then red stack was adjusted to threshold to mark it with a binary mask. Then the percent area in relation to the field was calculated at the objective lens of 40×. The area percentage was measured in five fields, from five serial sections, from five animals, from each group [29].
Results
Histological results
Group I (control group)
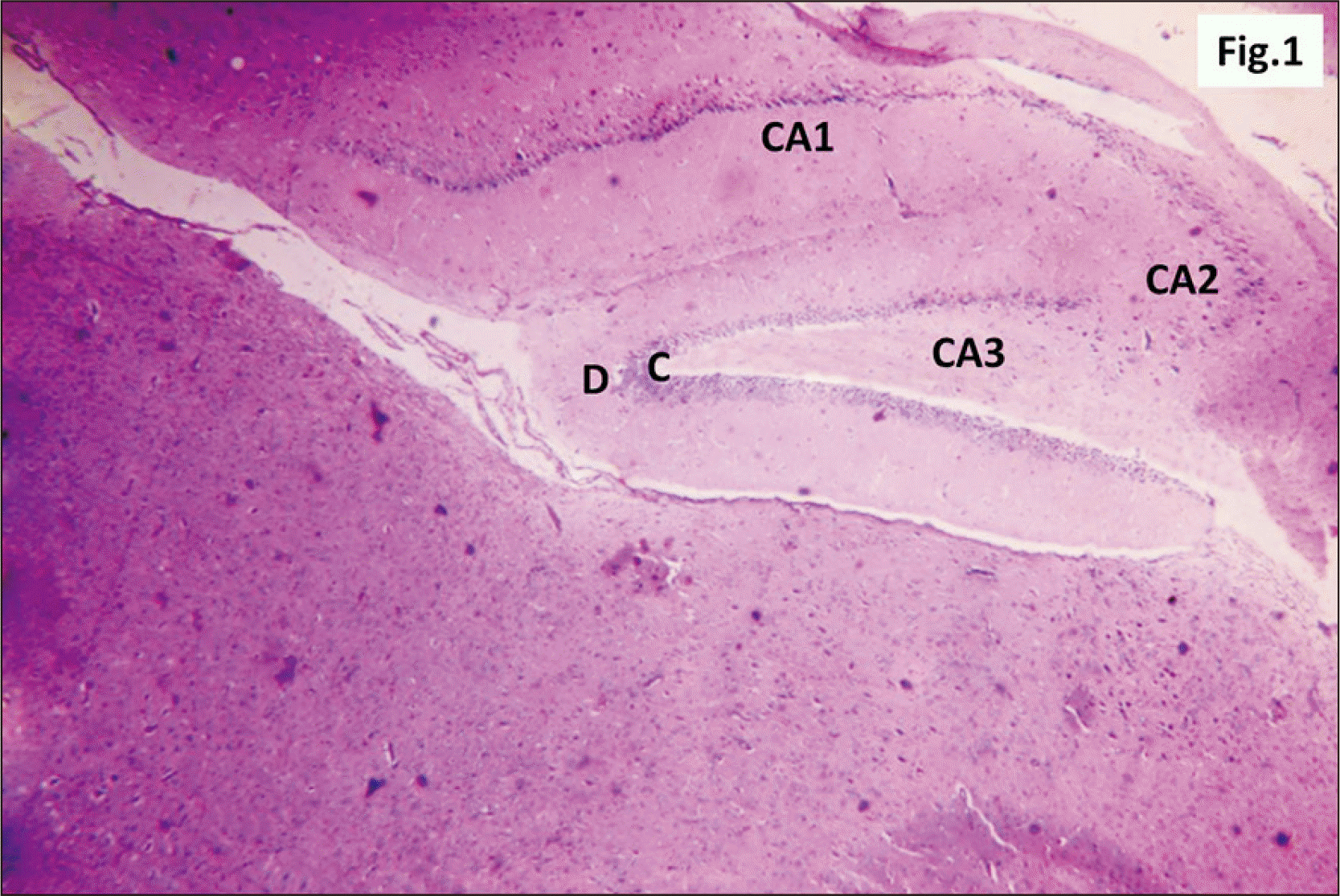
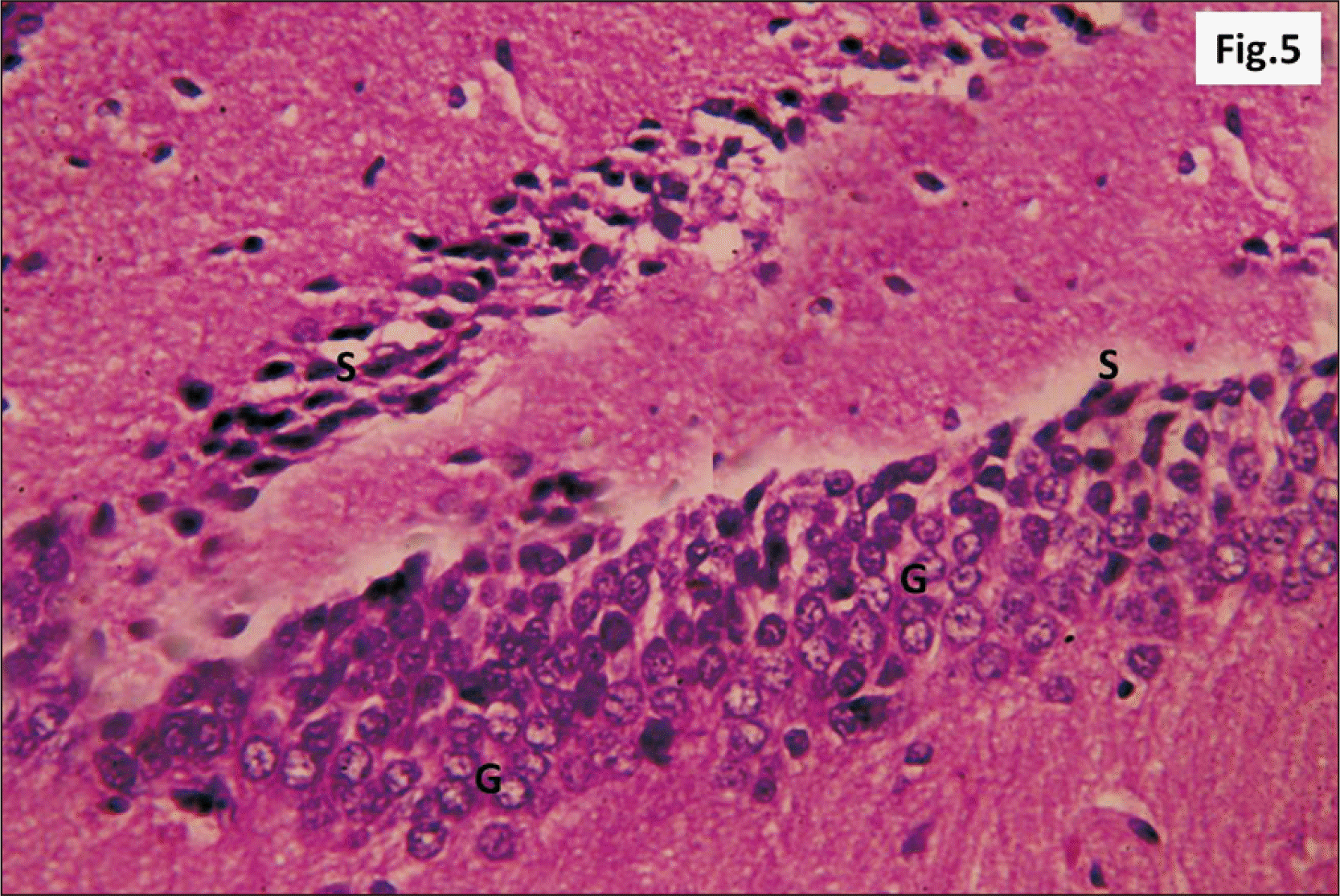
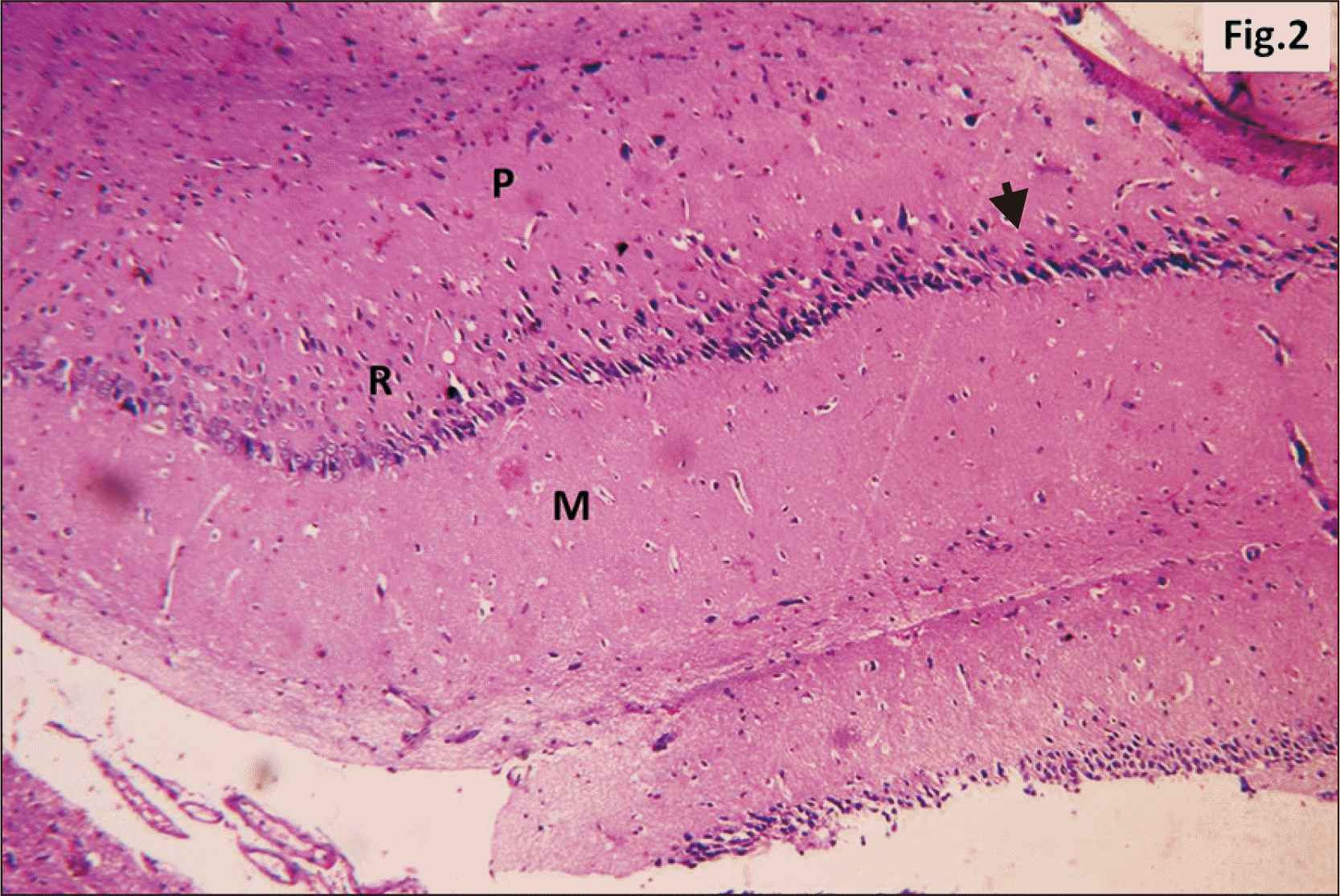 | Fig. 2A photomicrograph of a parasagittal section of control hippocampus showing CA1, with three layers of cells, P, R, and M (H&E, ×200). P layer is seen as a clear narrow zone with widely spaced small deeply stained oligodendroglia cells (arrowhead). R cell layer contains closely packed cells (arrow). The M layer contains widely spaced cells. CA1, cornu ammonis 1; M, molecular; P, polymorphic; R, pyramidal. |
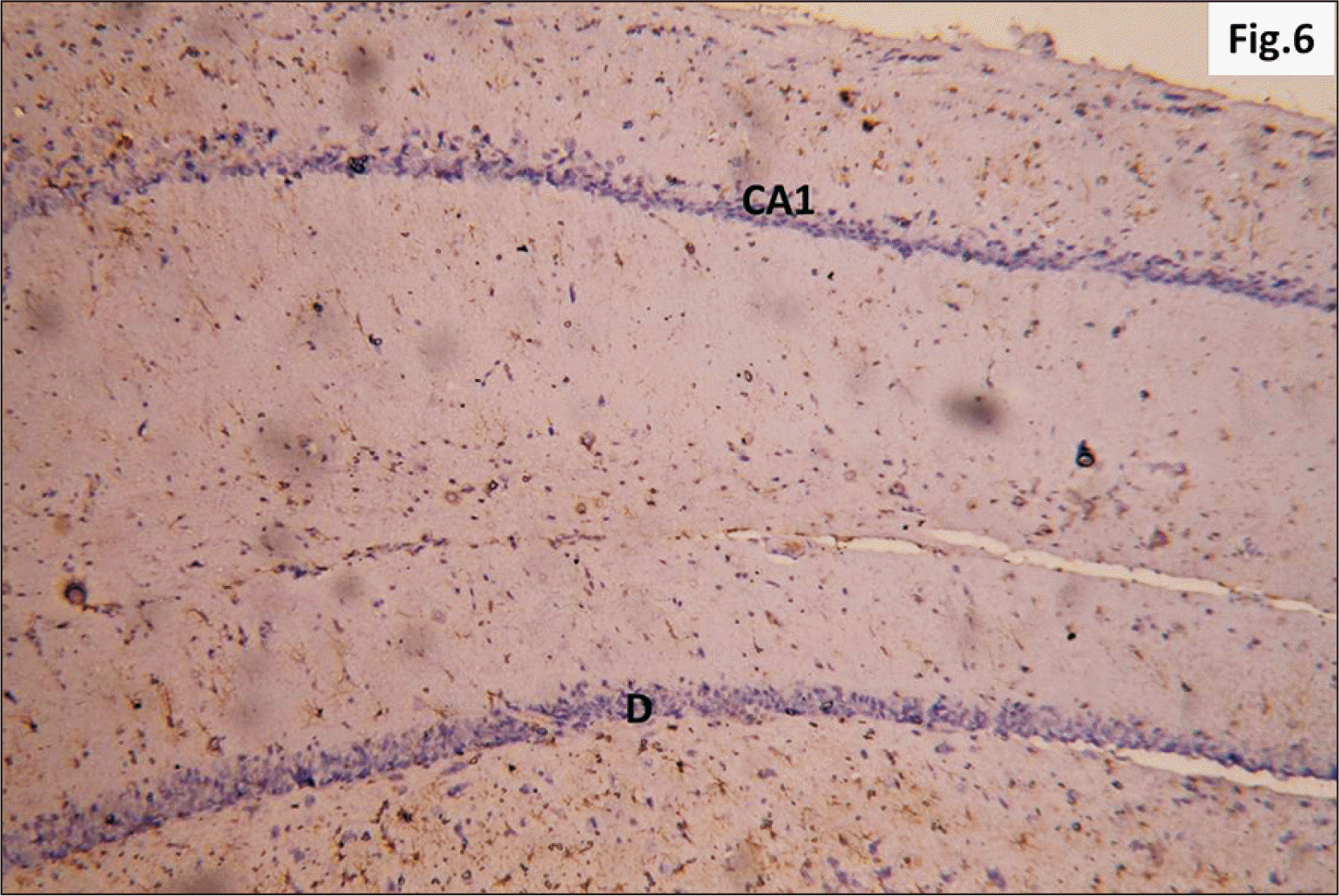 | Fig. 6A photomicrograph of a GFAP immunostaining of hippocampus of adult male control rat showing the normal distribution of apparently few brownish star shaped astrocytes in CA1 and D (GFAP, ×200). CA1, cornu ammonis 1; DG, dentate gyrus; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |
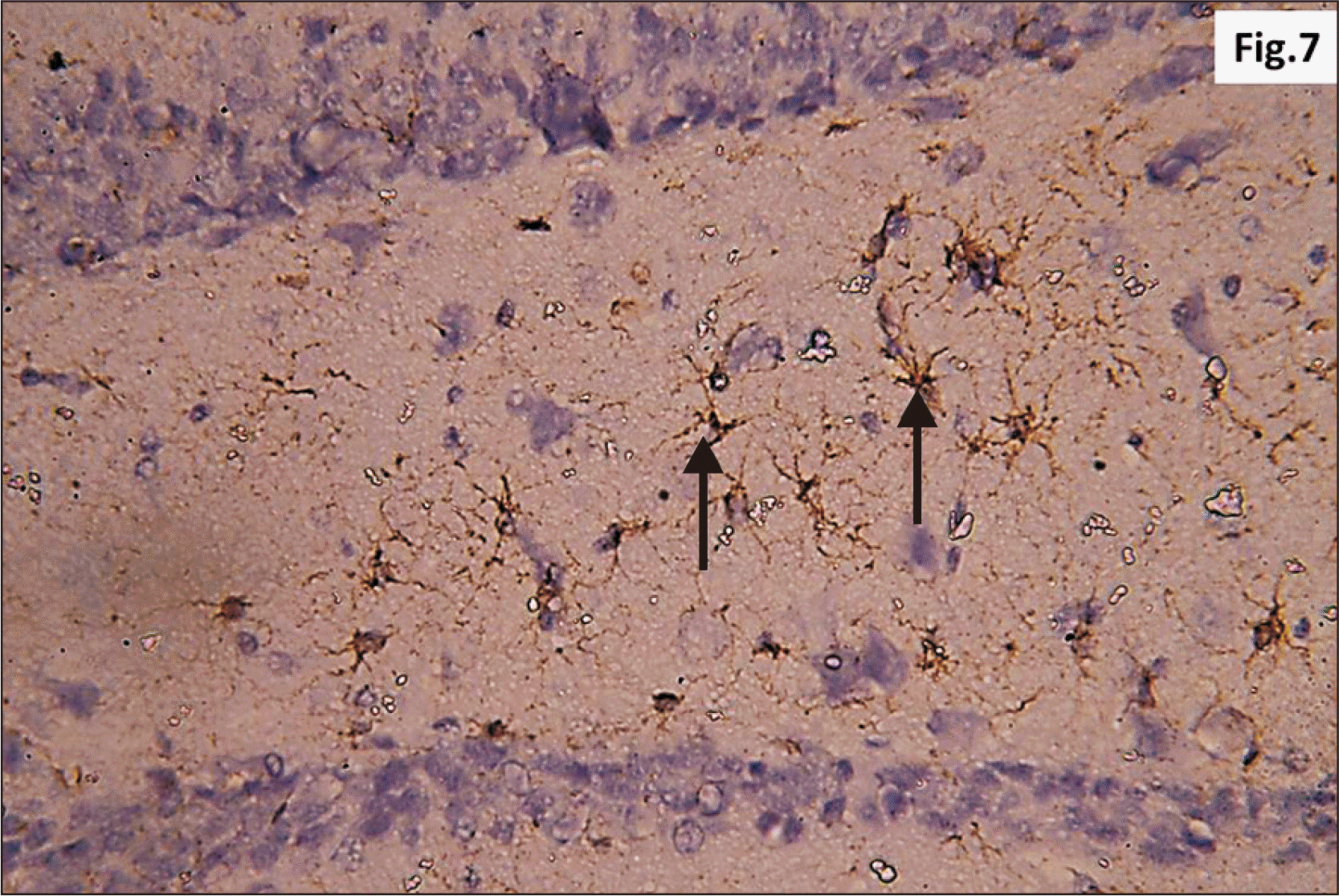 | Fig. 7Higher magnification of a GFAP immunostaining of hippocampus of adult male control rat showing the normal distribution of brown star shaped astrocytes (arrow) within the junctional zone between molecular layers of CA1 and DG (GFAP, ×400). CA1, cornu ammonis 1; DG, dentate gyrus; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |
Group II (Short-term Red Bull group)
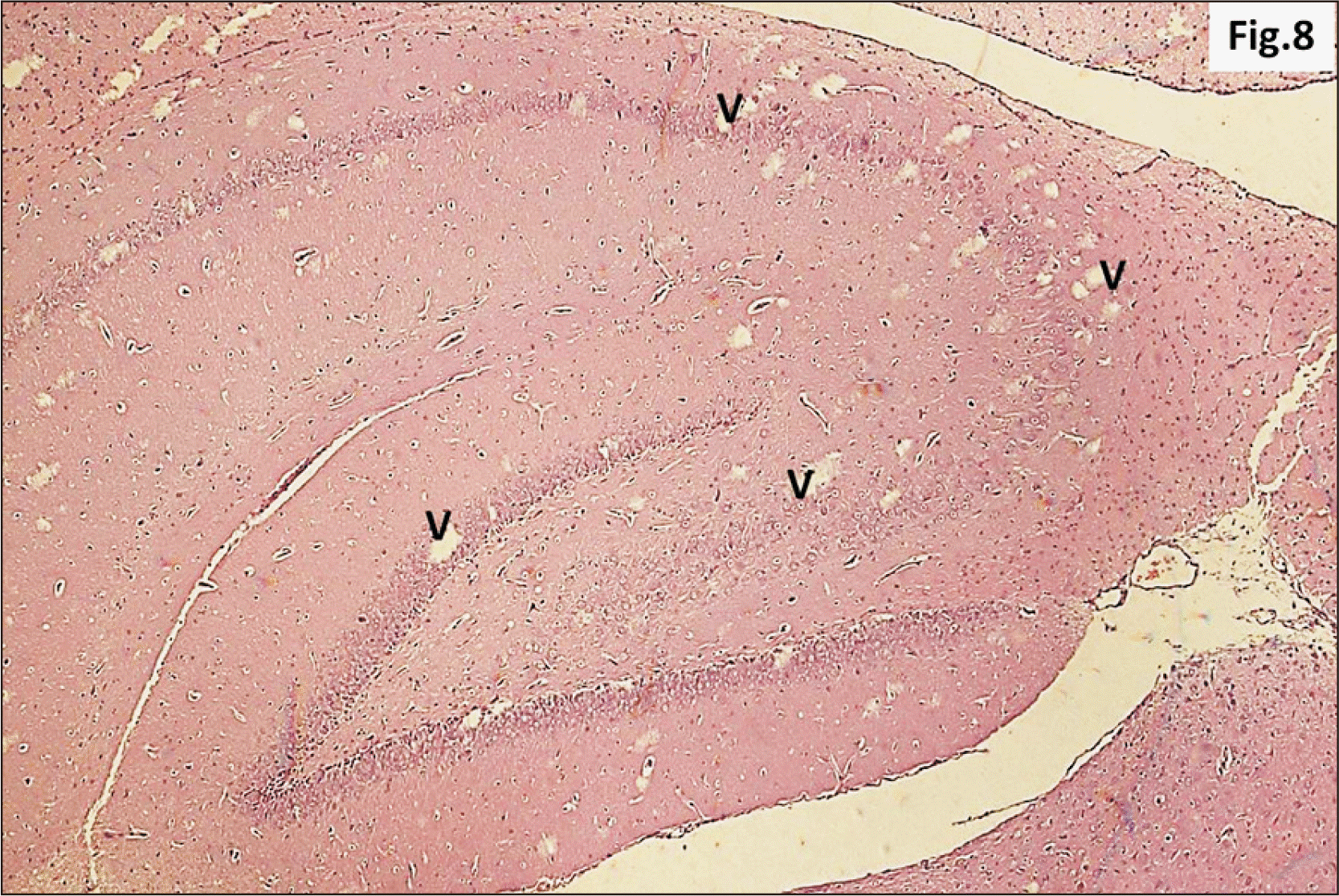 | Fig. 8A photomicrograph of a parasagittal section of hippocampus from group II showing apparent preservation of general architecture with diffuse v in all its regions (H&E, ×100). v, vacuolation. |
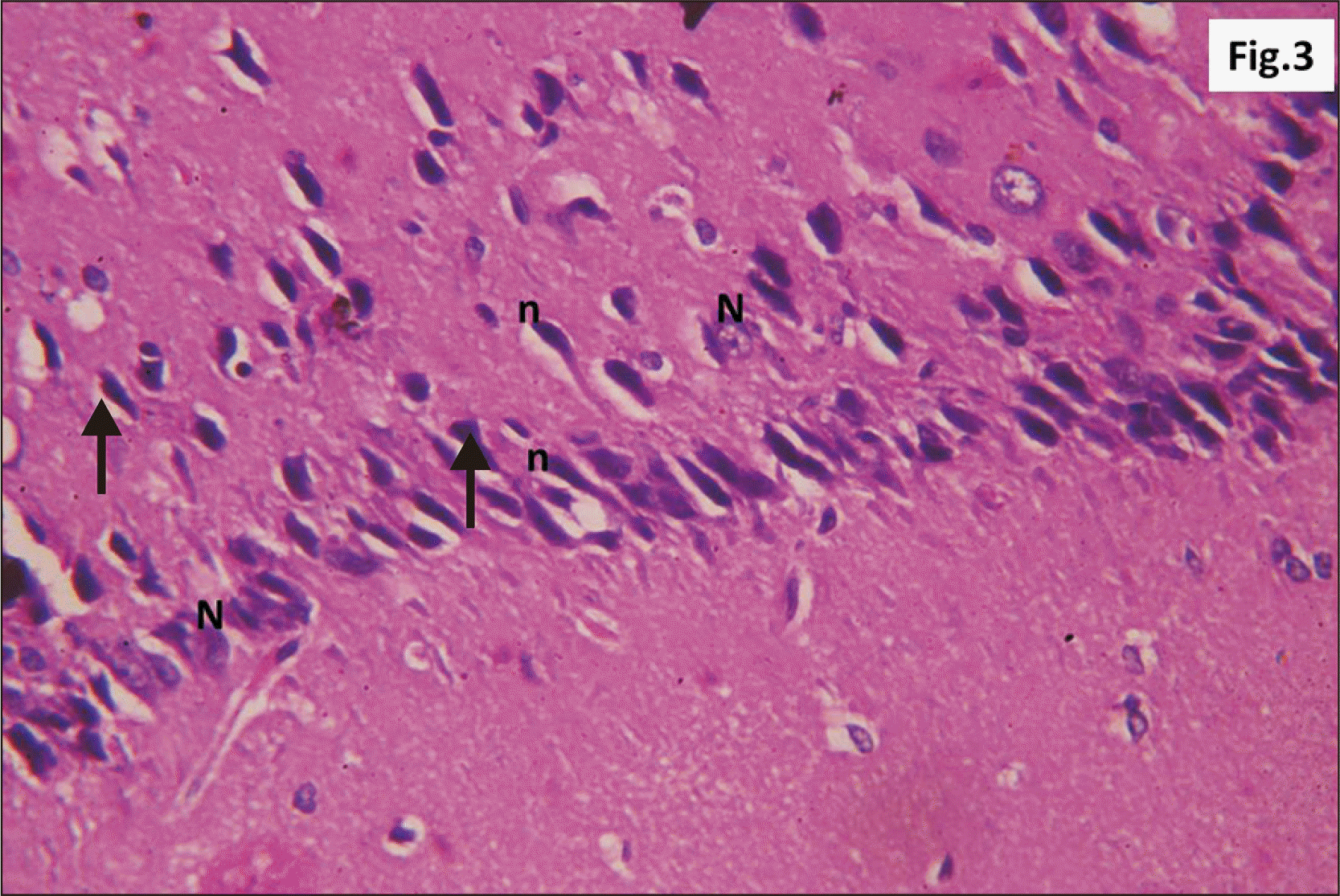
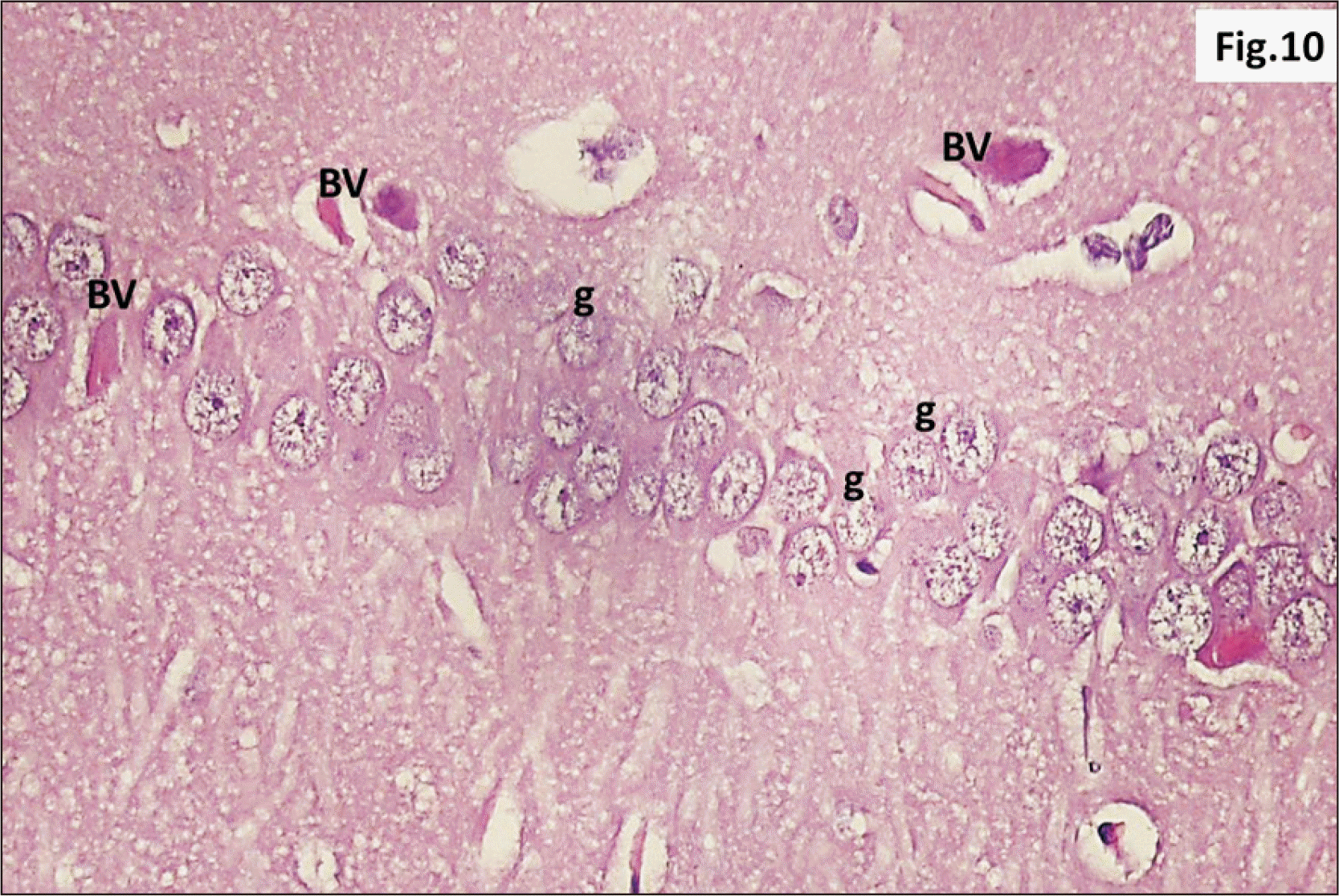
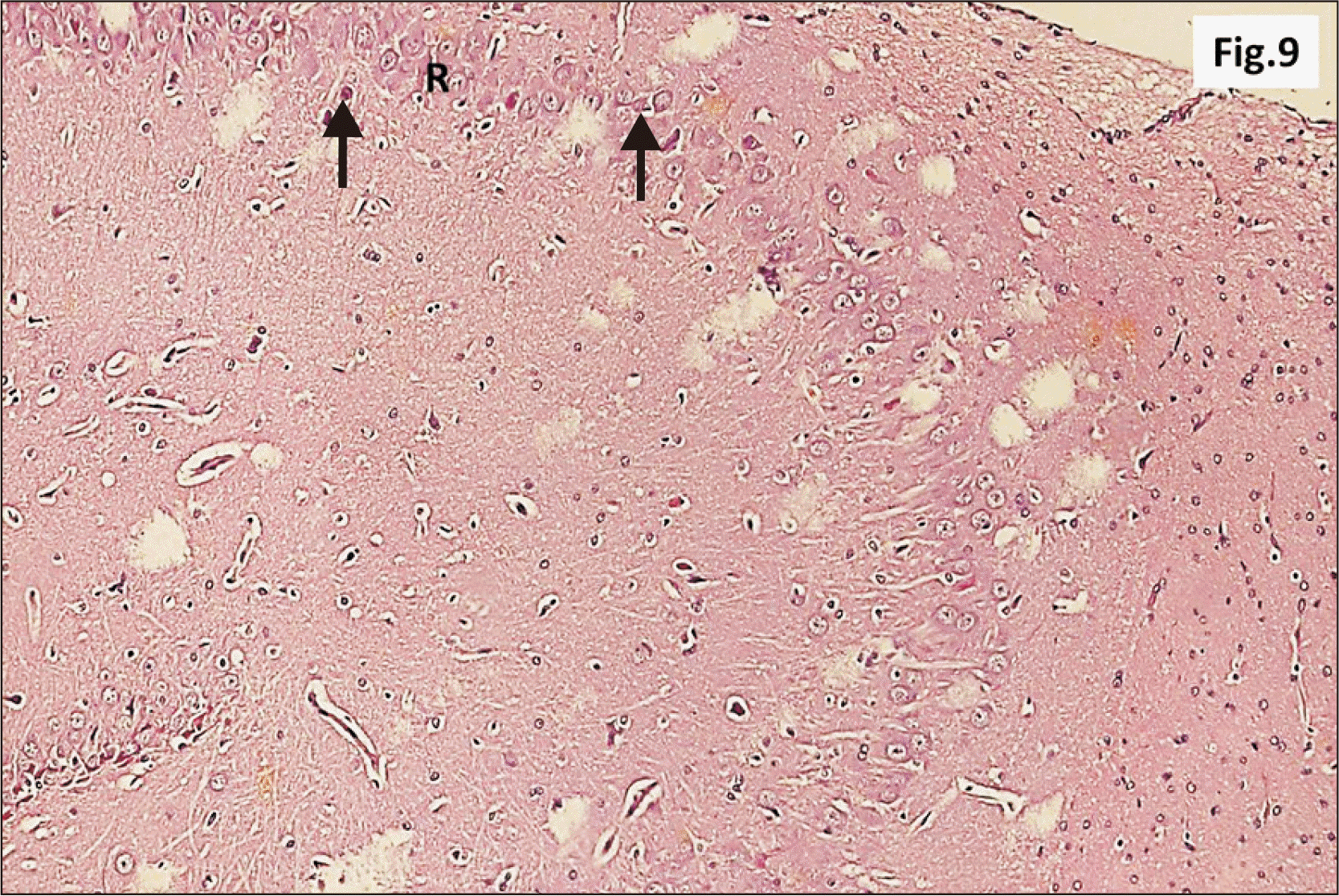 | Fig. 9Higher magnification of a parasagittal section of hippocampus from group II showing an apparent decreased thickness of principal neuronal cell layer of CA1 (R) (H&E, ×200). Note some neurons with dark nuclei and wide pericellular space (arrow). CA1, cornu ammonis 1; R, pyramidal cell layer. |
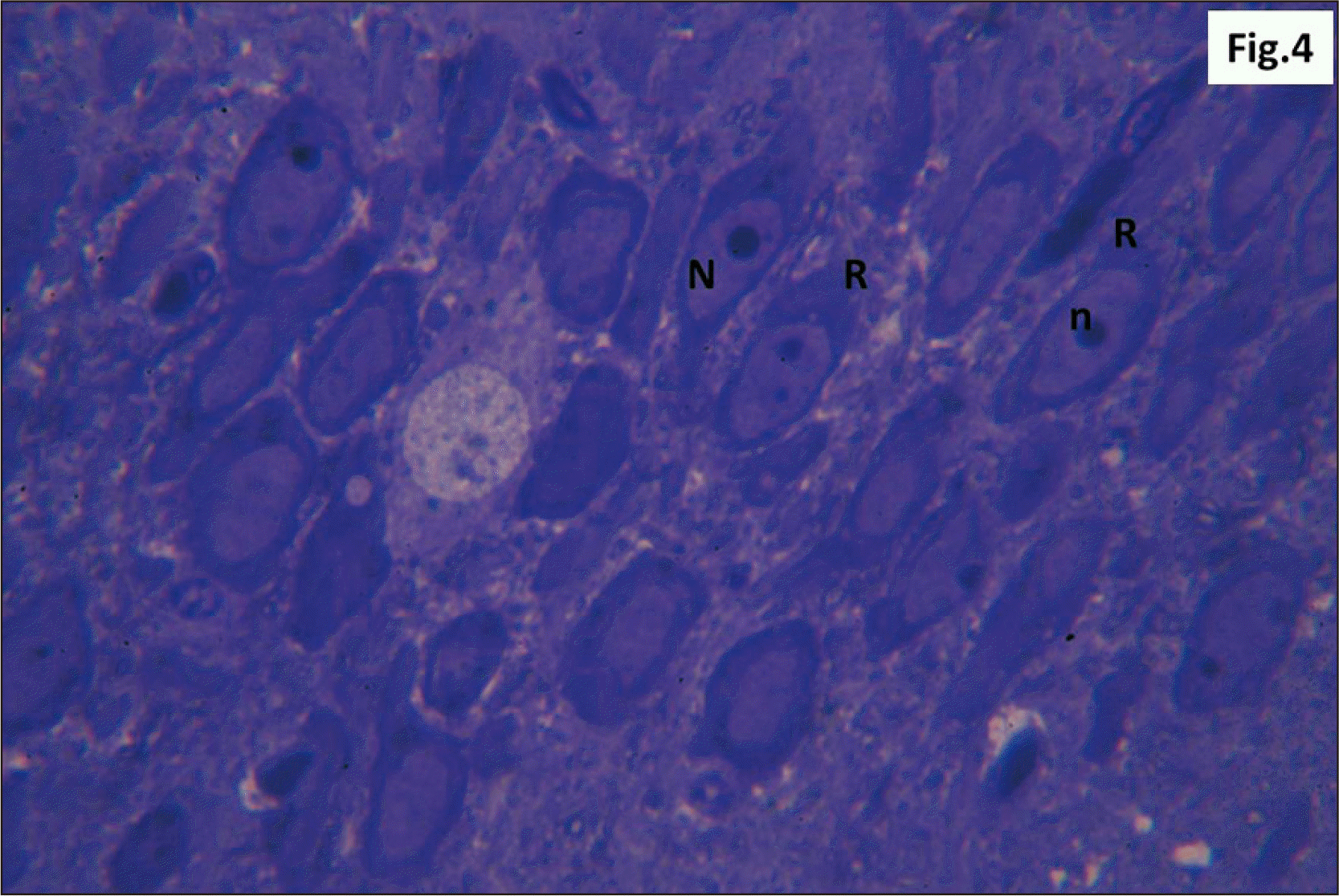
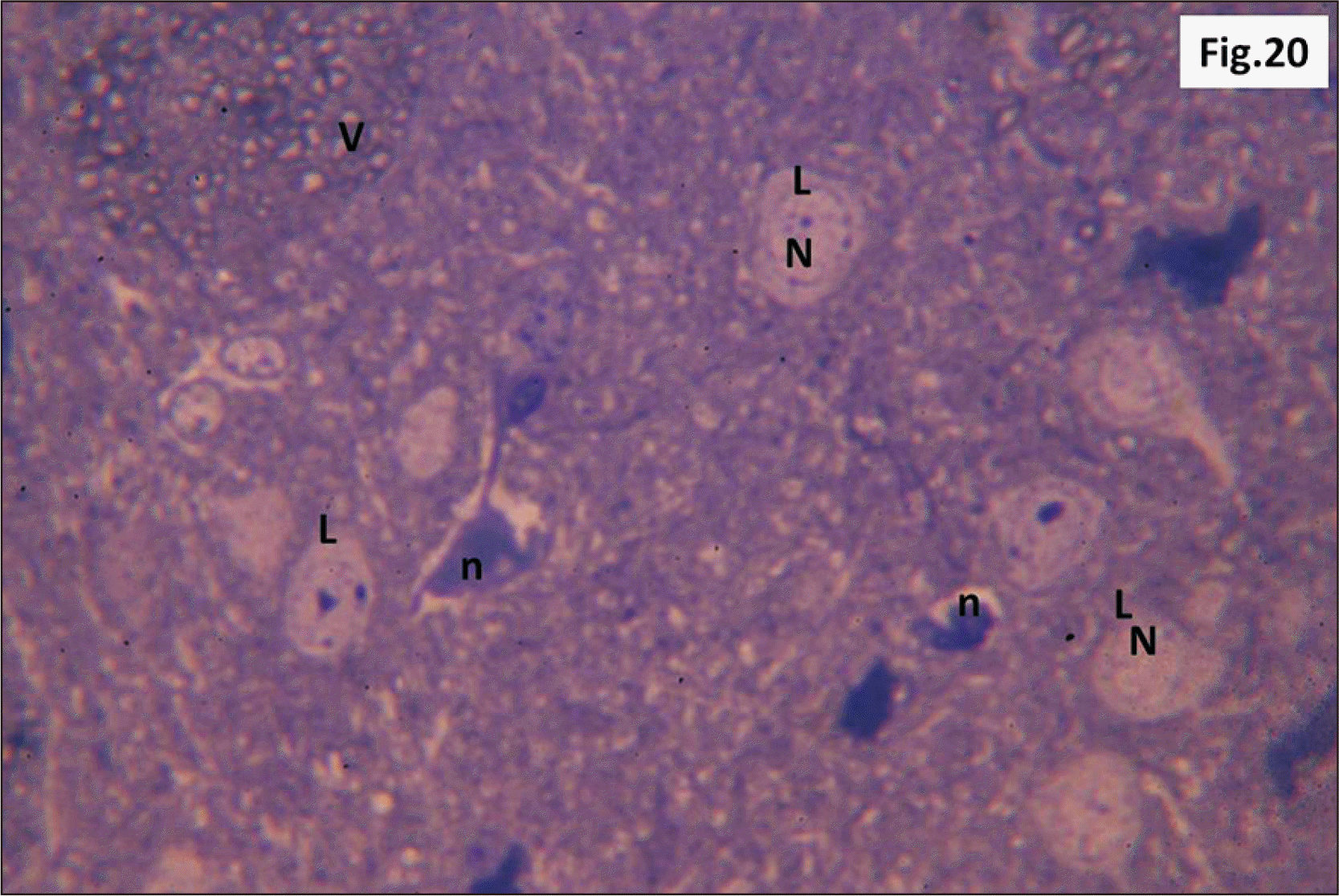
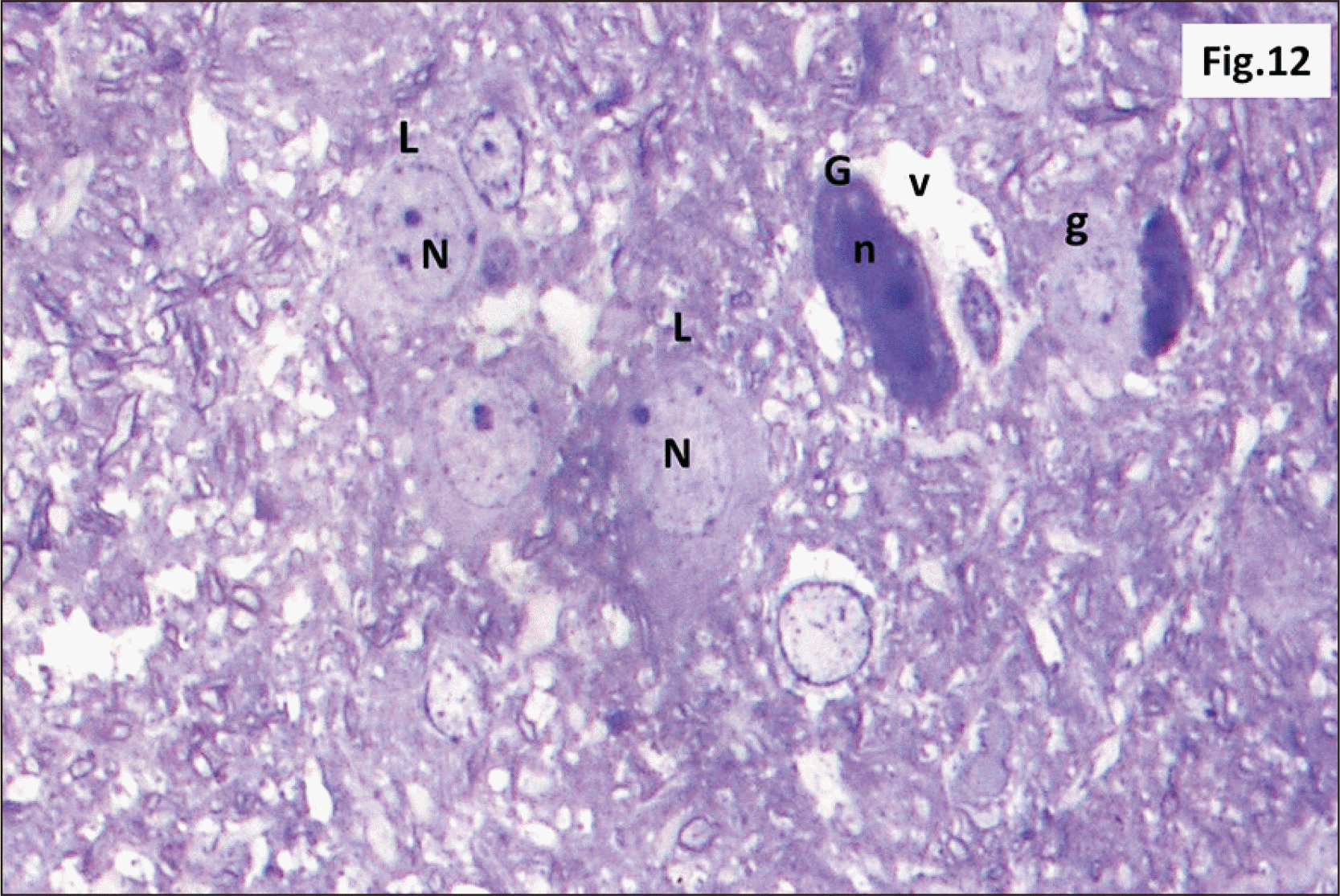 | Fig. 12Semithin sections of hippocampus from group II showing diffuse v within the DG. L with N and other G with n are seen. Some shrunken g are also observed (Toluidine blue, ×1,000). DG, dentate gyrus; g, ghost cells; G, dark cells; L, lightly stained cells; n, dark irregular nuclei; N, vesicular nuclei; v, vacuolations. |
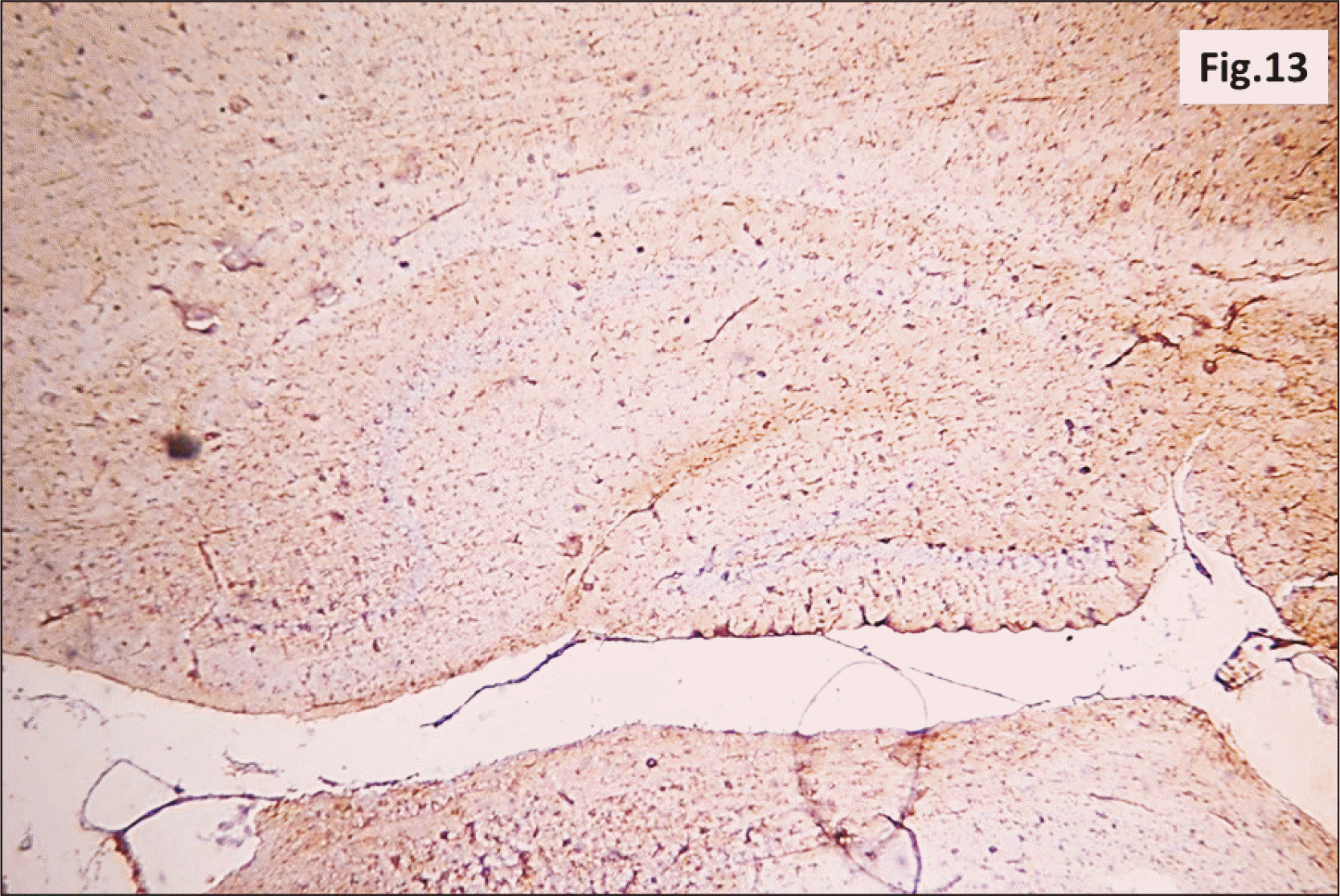 | Fig. 13A photomicrograph of a GFAP immunostaining of hippocampus from group II showing an apparent increase in the brownish positive immuno-reaction in all layers (GFAP, ×200). GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |
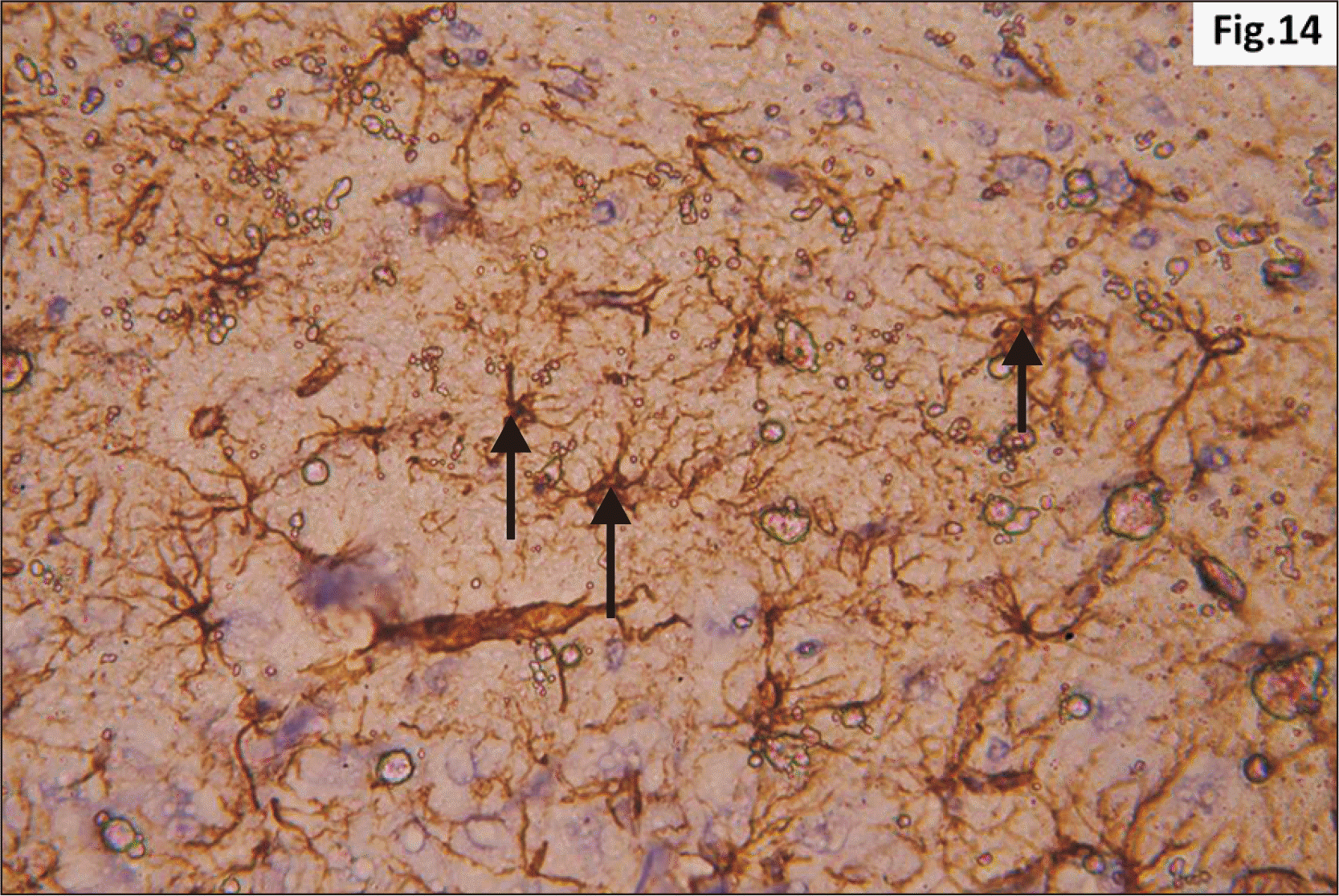 | Fig. 14Higher magnification of a GFAP immunostaining of hippocampus from group II showing increased distribution of brownish star shaped astrocytes (arrow) in the junctional zone between molecular layers of CA1 and DG (GFAP, ×400). CA1, cornu ammonis 1; DG, dentate gyrus; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |
Group III (Long term Red Bull group)
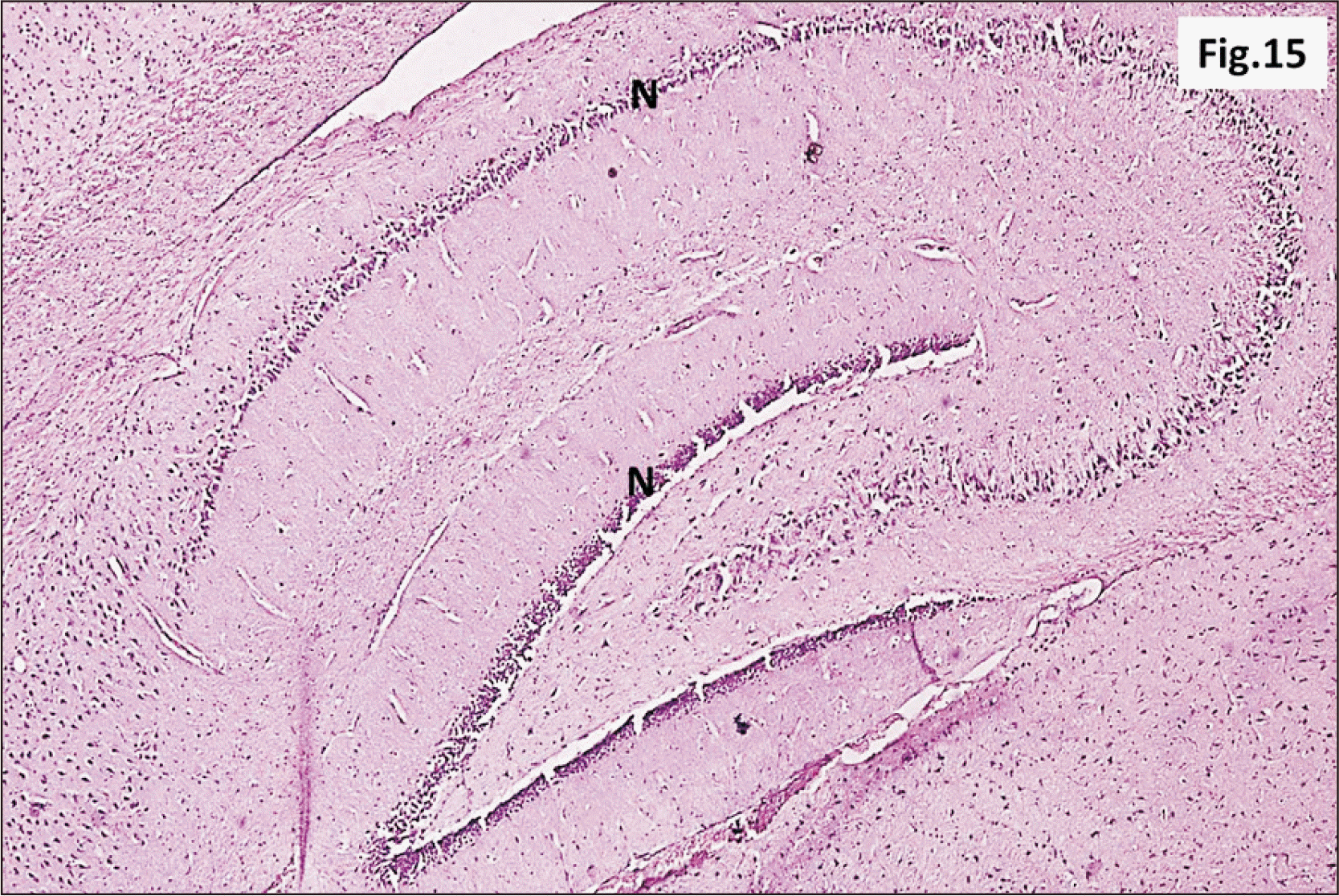 | Fig. 15A photomicrograph of a parasagittal section of hippocampus from group III showing preservation of the general architecture of the hippocampus. However, an apparent marked decrease in thickness of N was observed in all regions (H&E, ×100). N, principal neuronal cell layers. |
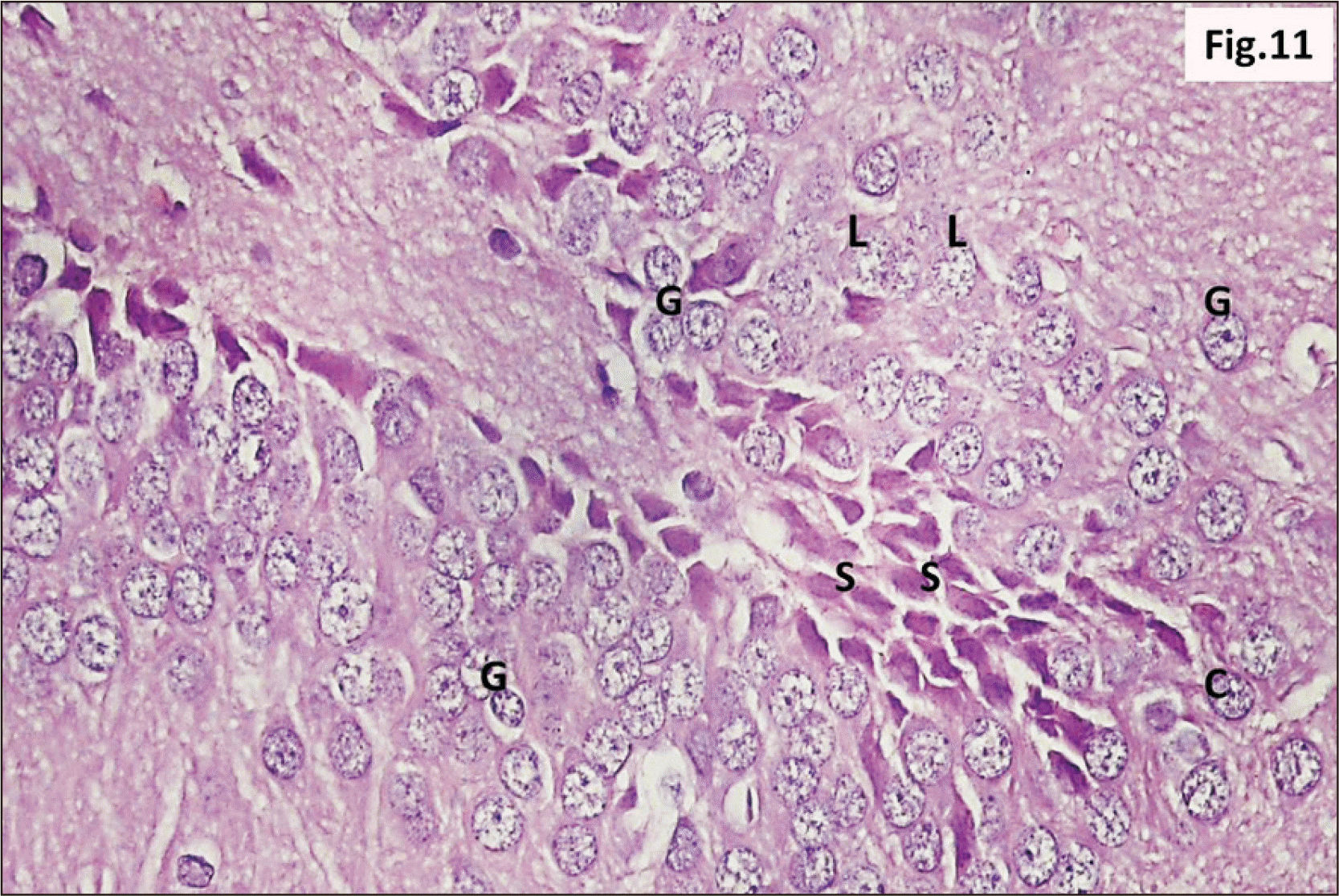
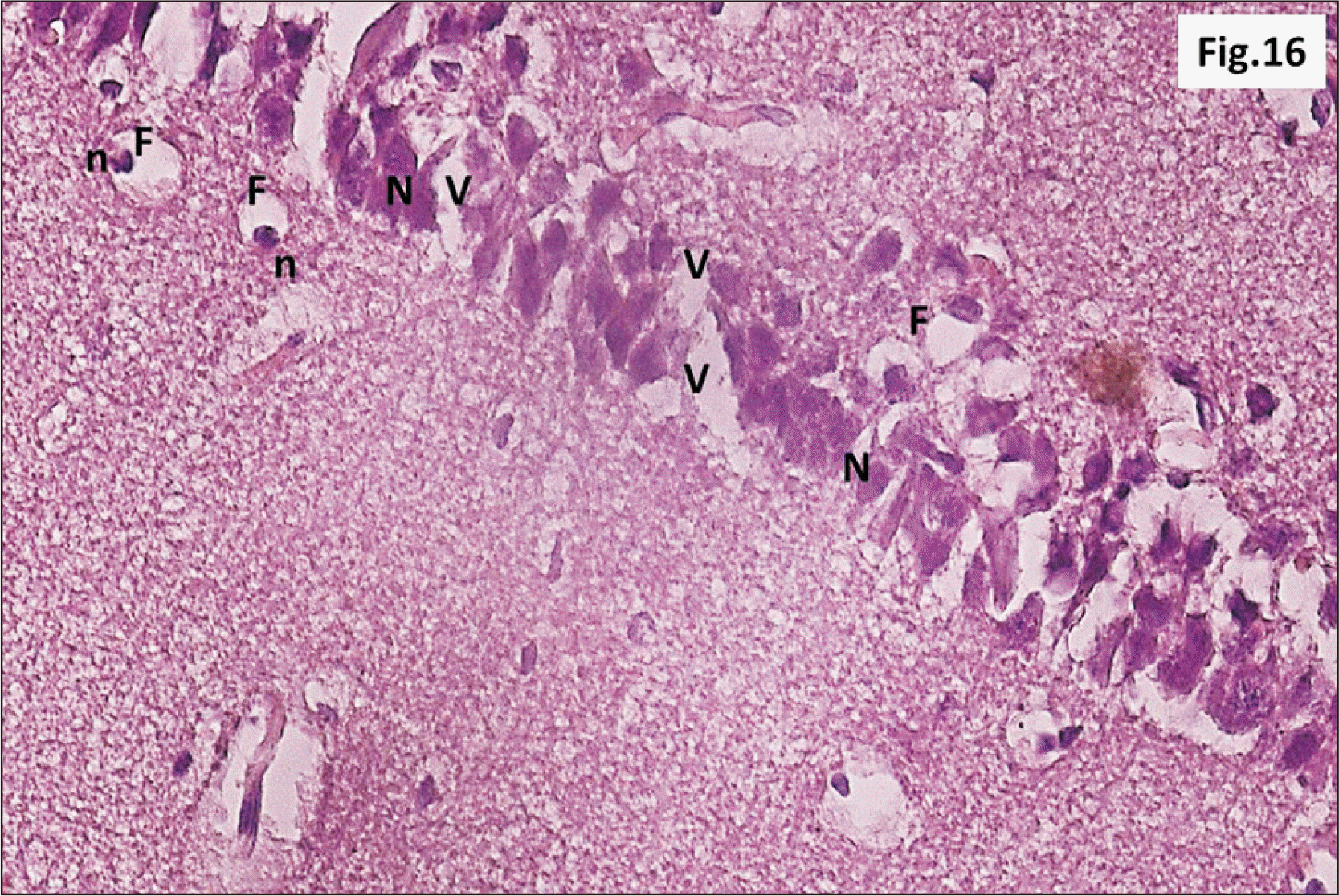 | Fig. 16Higher magnification of a parasagittal section of hippocampus from group III showing that most of CA1 neurons have N (H&E, ×400). F are observed with n. Diffuse V within the R cell layer is also seen. CA1, cornu ammonis 1; F, signet ring cells; n, pyknotic peripheral nuclei; N, dark irregular nuclei; R, pyramidal, V, vacuolation. |
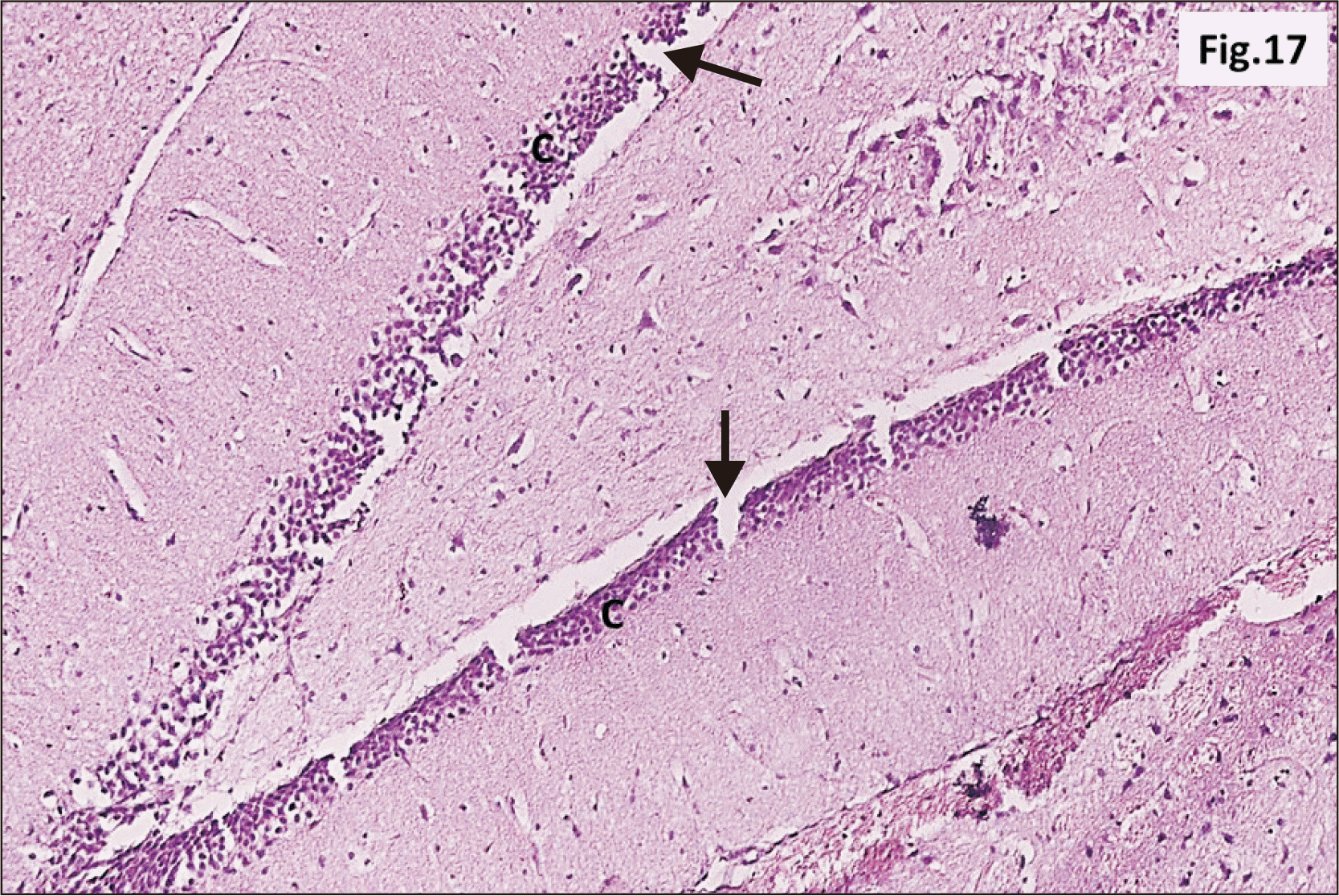 | Fig. 17A photomicrograph of a parasagittal section of hippocampus from group III showing an apparent thinning of C of DG with widespread cracks (arrow) within the layer (H&E, ×200). C, granular cell layer ; DG, dentate gyrus. |
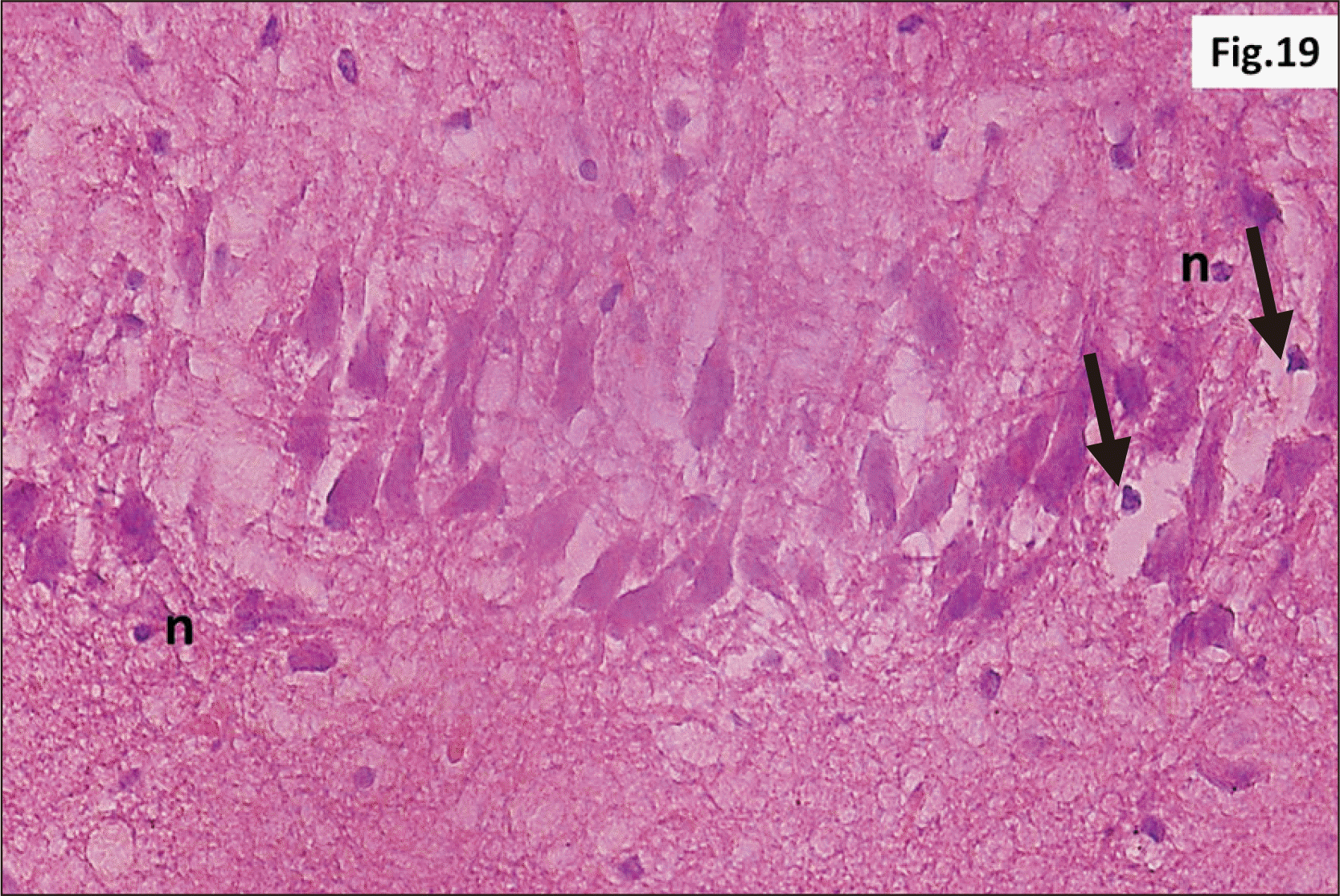
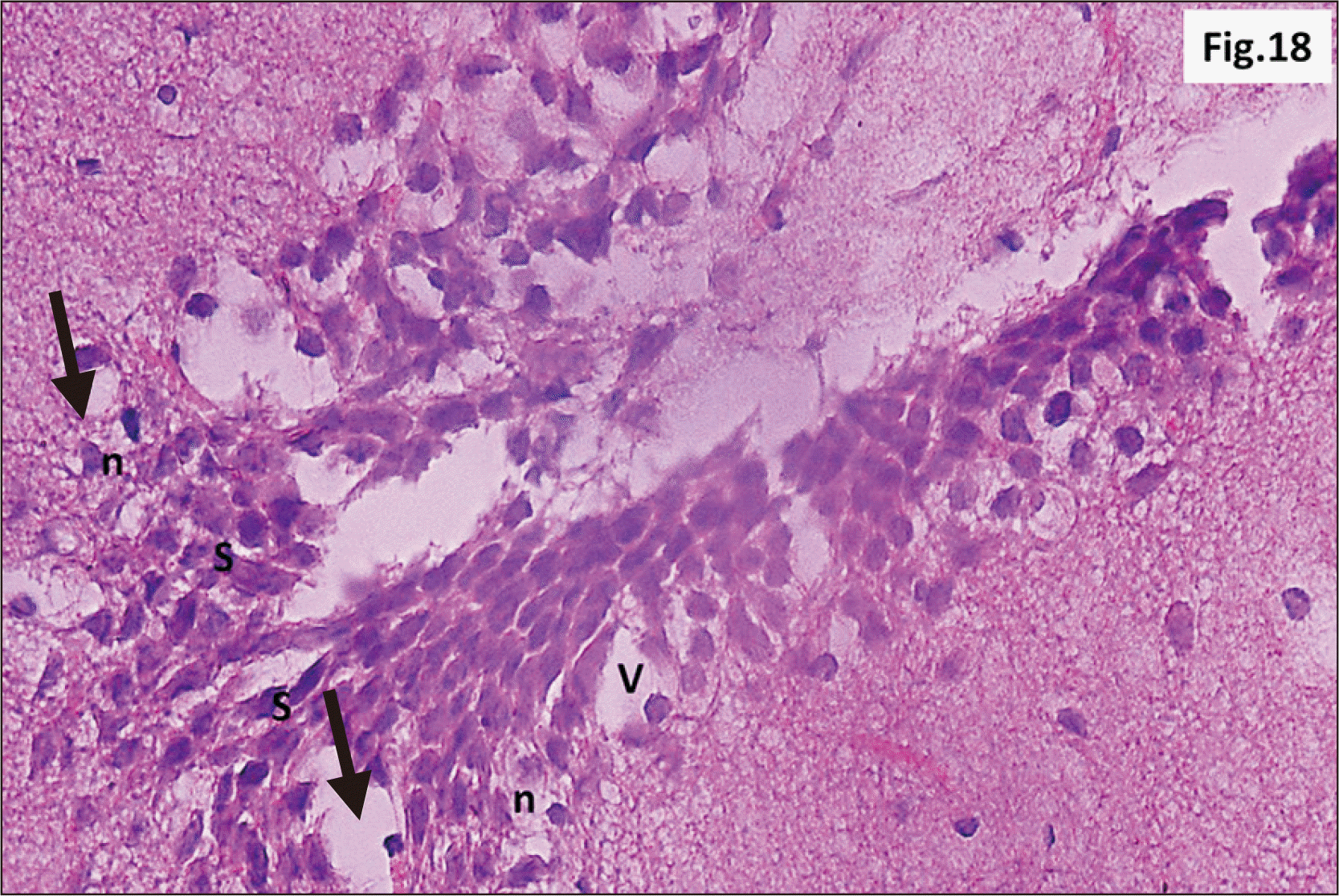 | Fig. 18A photomicrograph of a parasagittal section of hippocampus from group III showing granular neurons of the DG with n, and signet ring neurons (arrow) (H&E, ×400). Intense V and C in between the granular cells are observed. Marked increase in the number of S cells in the crest of DG are also seen. C, cracks; DG, dentate gyrus; n, dark pyknotic nuclei; S, stem; V, vacuolation. |
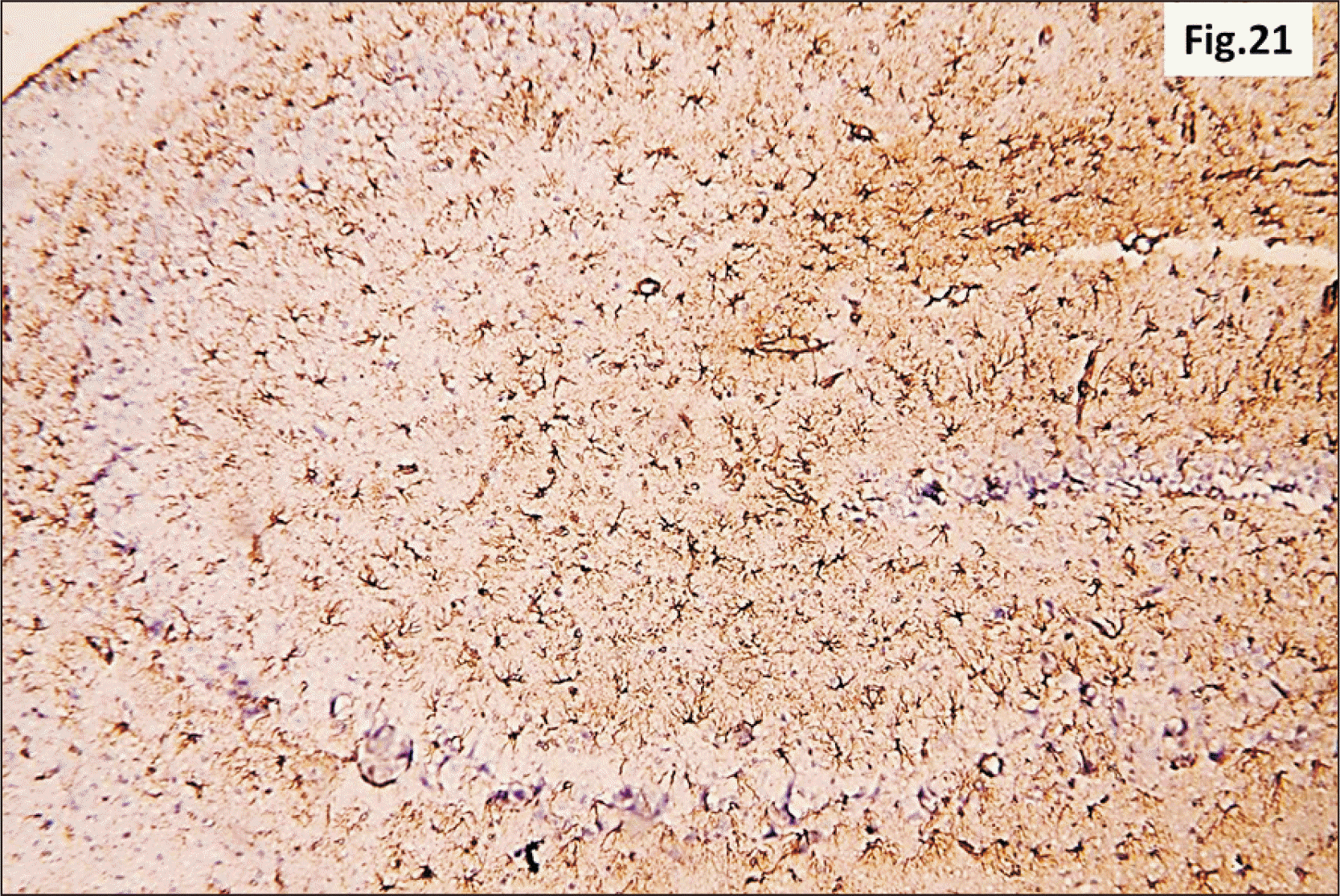 | Fig. 21A photomicrograph of a GFAP immunostaining of hippocampus from group III showing an apparent intense increase in the brownish positive immuno-reaction in all regions (GFAP, ×200). GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |
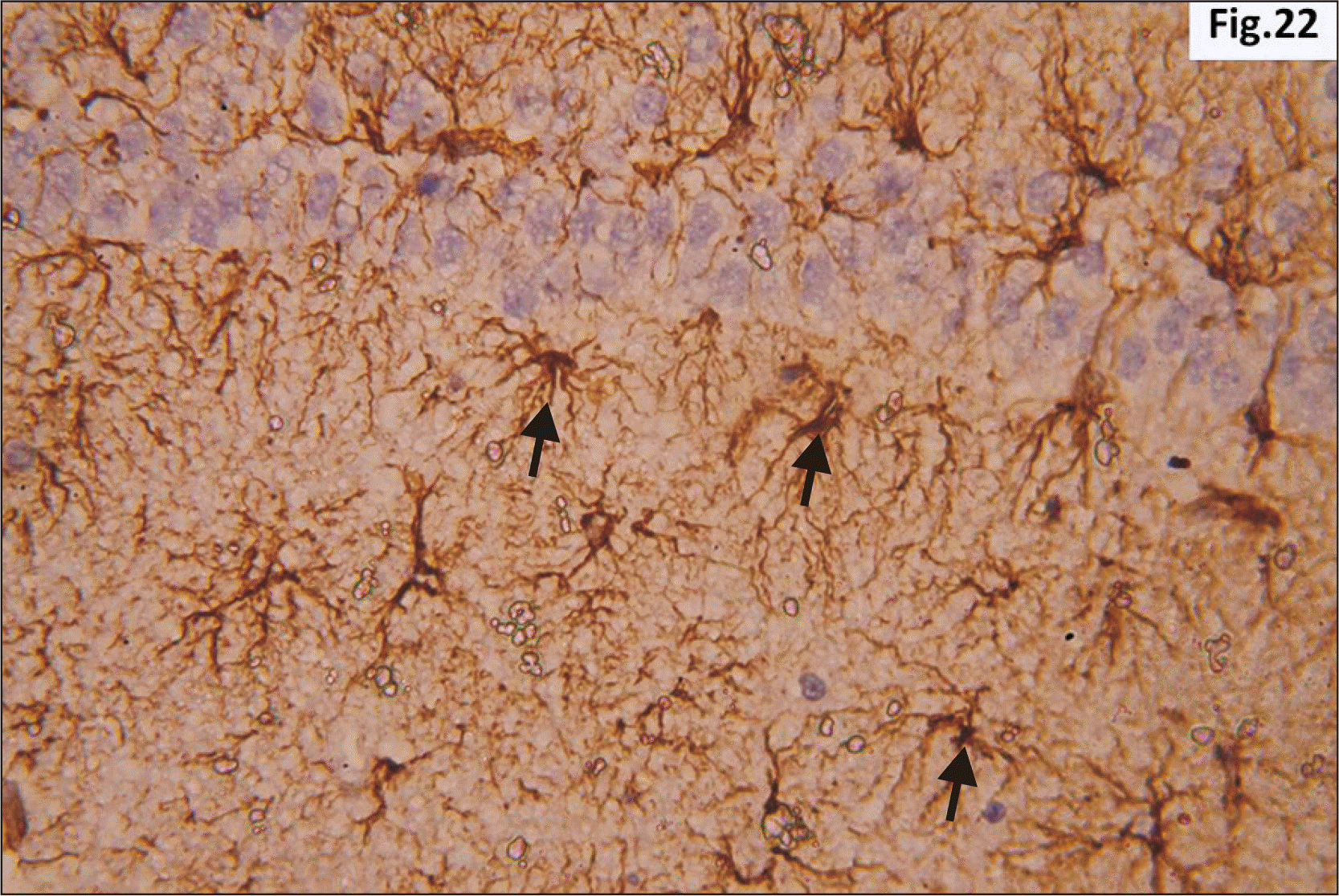 | Fig. 22Higher magnification of a GFAP immunostaining of hippocampus from group III showing wide distribution of large dark brown star shaped astrocytes with multiple thick processes (arrow) in the junctional zone between molecular layers of CA1 and DG (GFAP, ×400). CA1, cornu ammonis 1; DG, dentate gyrus; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |
Statistical results
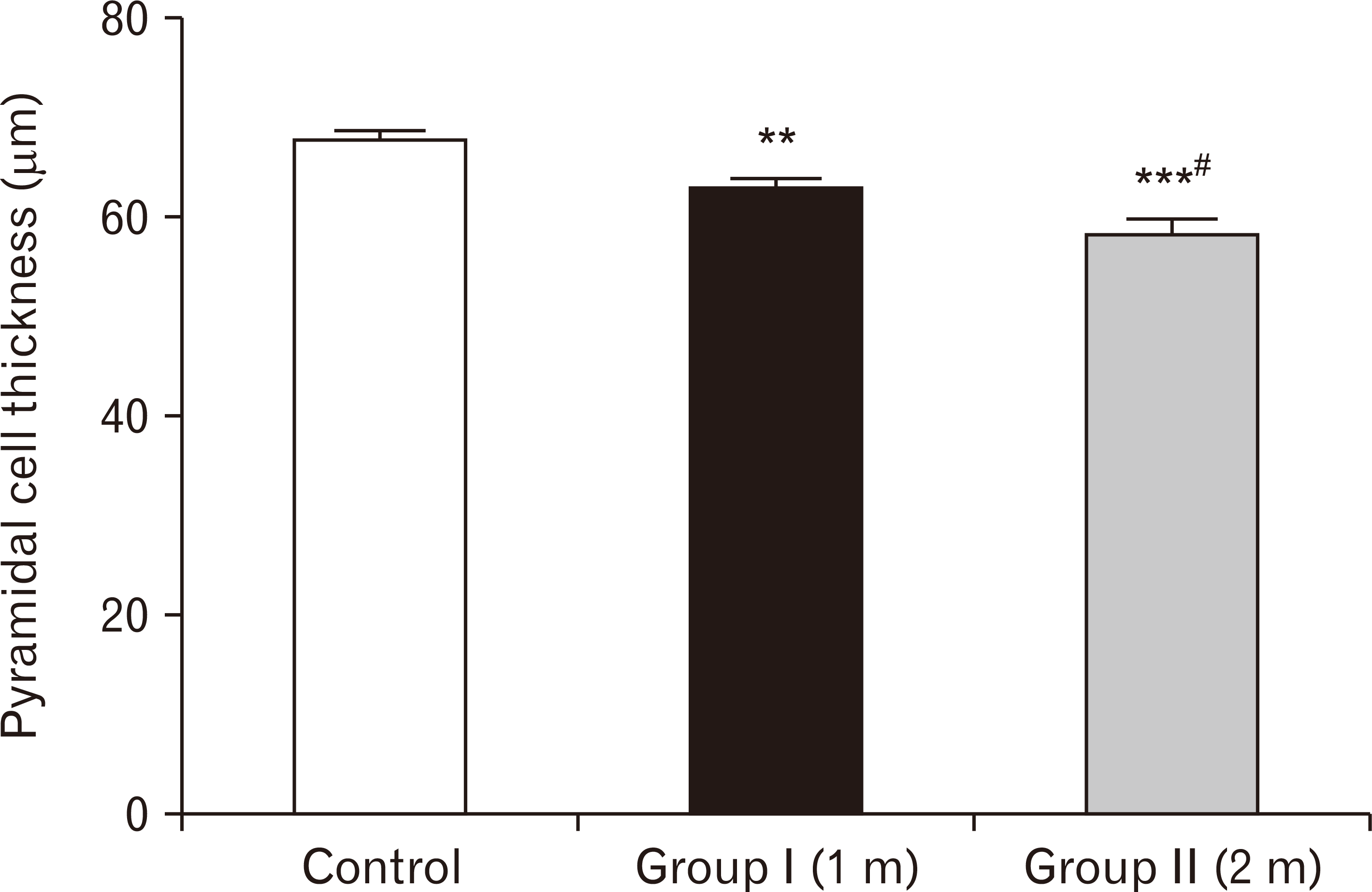 | Fig. 23A bar chart showing pyramidal cell thickness (in µm) among the three groups. Pyramidal cells’ thickness is highly significantly reduced in one-month group and two-months group respectively compared to the control group (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001), and significant reduction was observed in two-months group compared to one-month group (#P<0.05). |
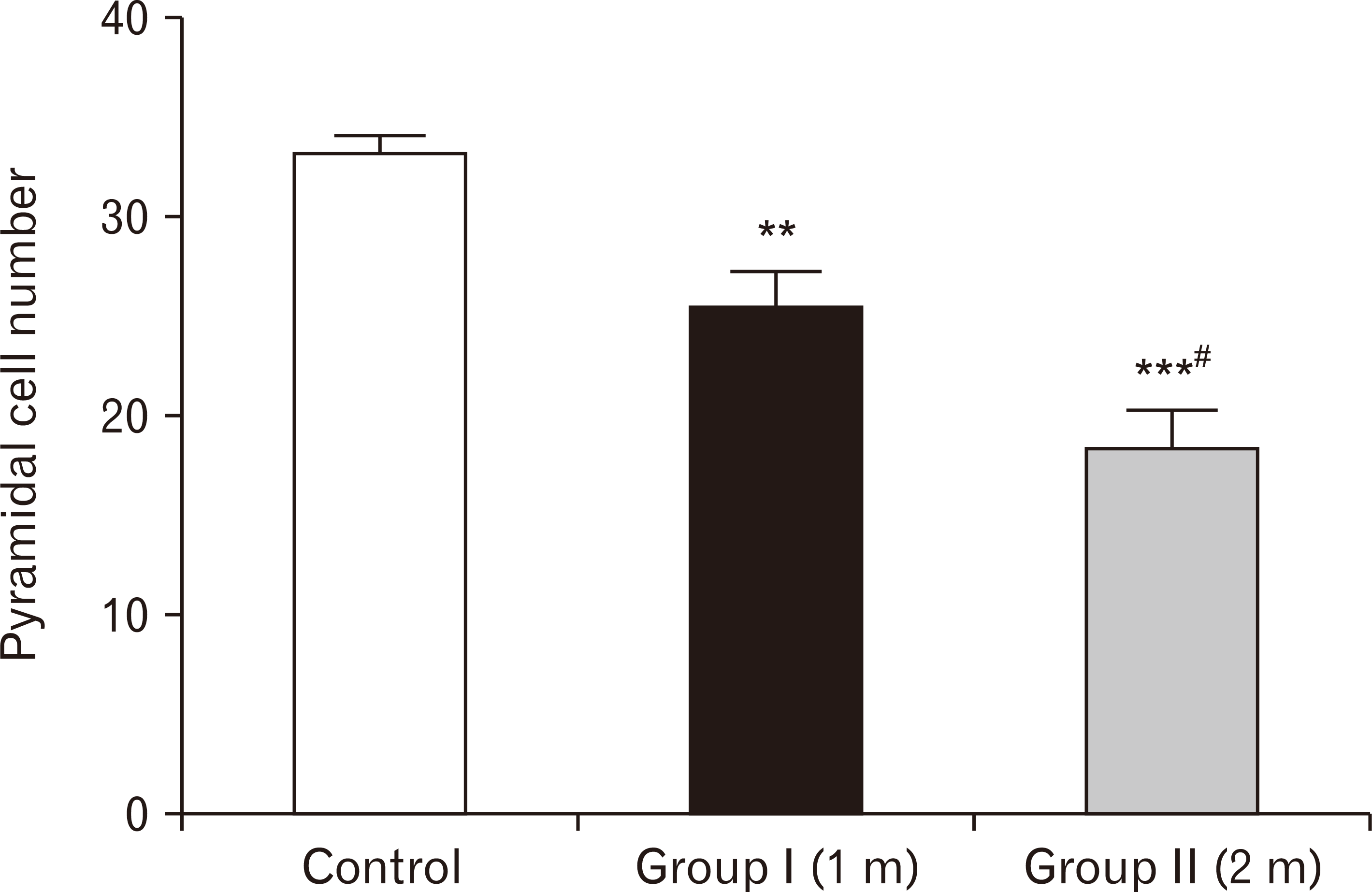 | Fig. 24A bar chart showing pyramidal cell number among the three groups. Pyramidal cells’ number are highly significantly reduced in one-month group and two-months group respectively compared to the control group (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001), with more significant decreased number in the two-months group than one-month group (#P<0.05). |
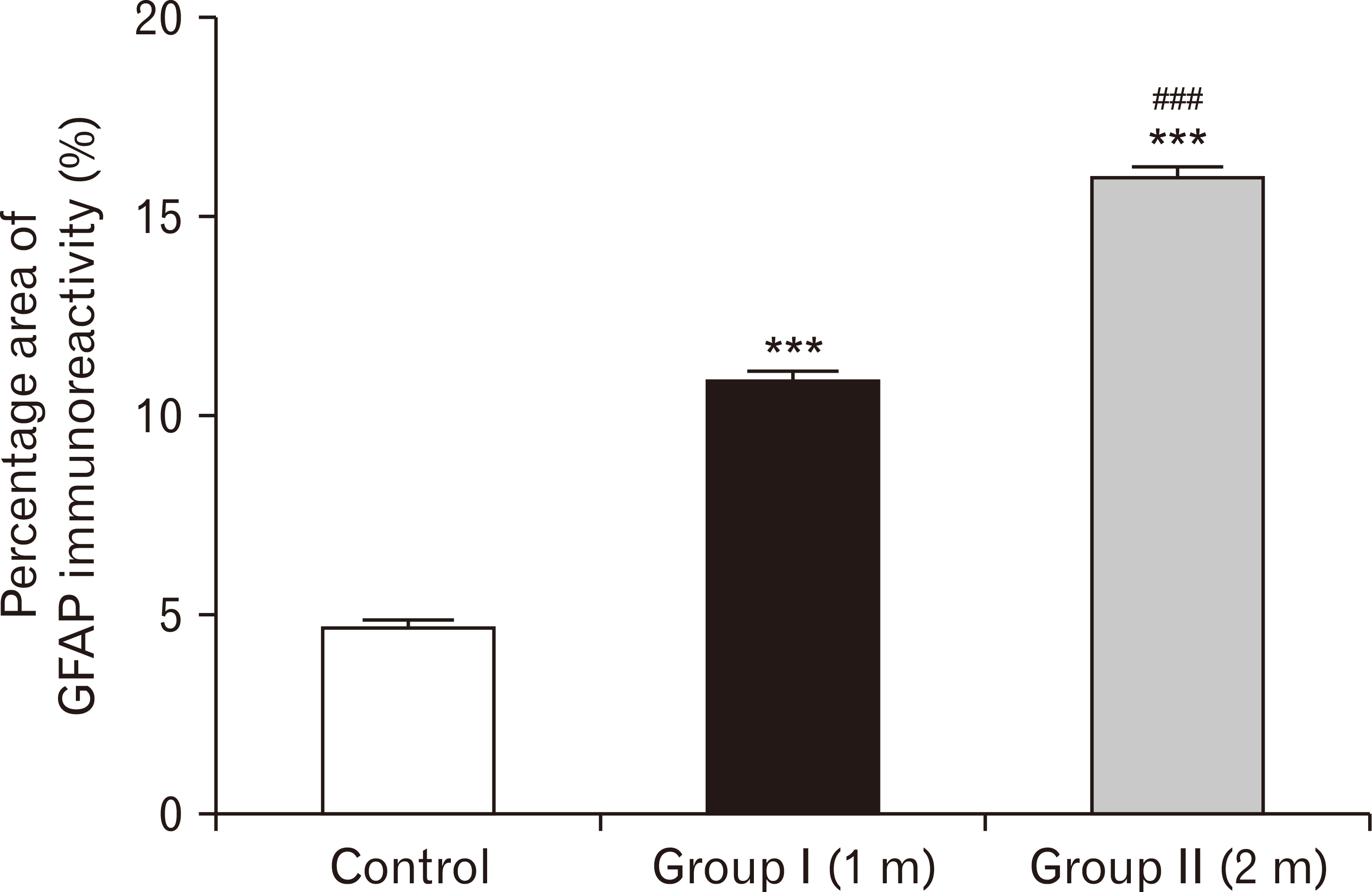 | Fig. 25A bar chart showing the percentage area of GFAP immuno-reactivity in the three groups. The area is highly significantly increased in one-month group and two-months group respectively compared to the control group (***P<0.001), with more significant increase in the two-months group than in one-month (###P<0.001). GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download