Introduction
Methods
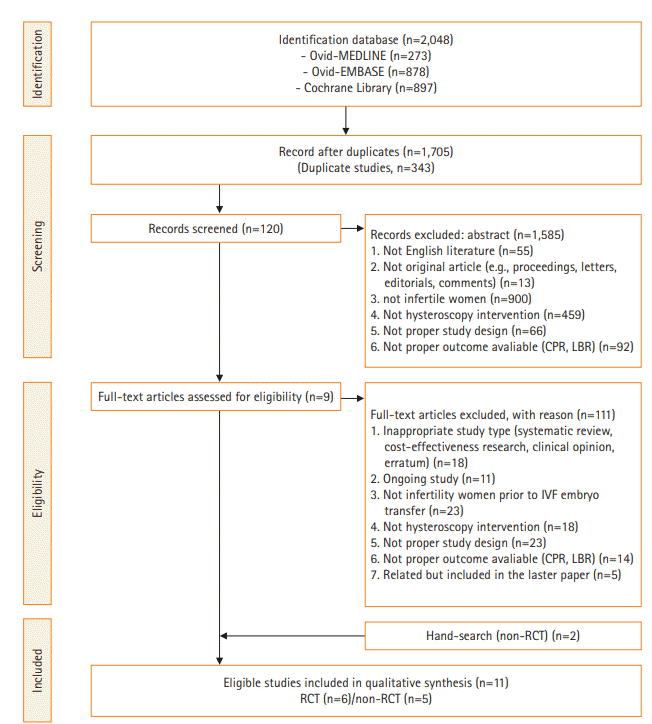
Search strategy
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Risk of bias assessment
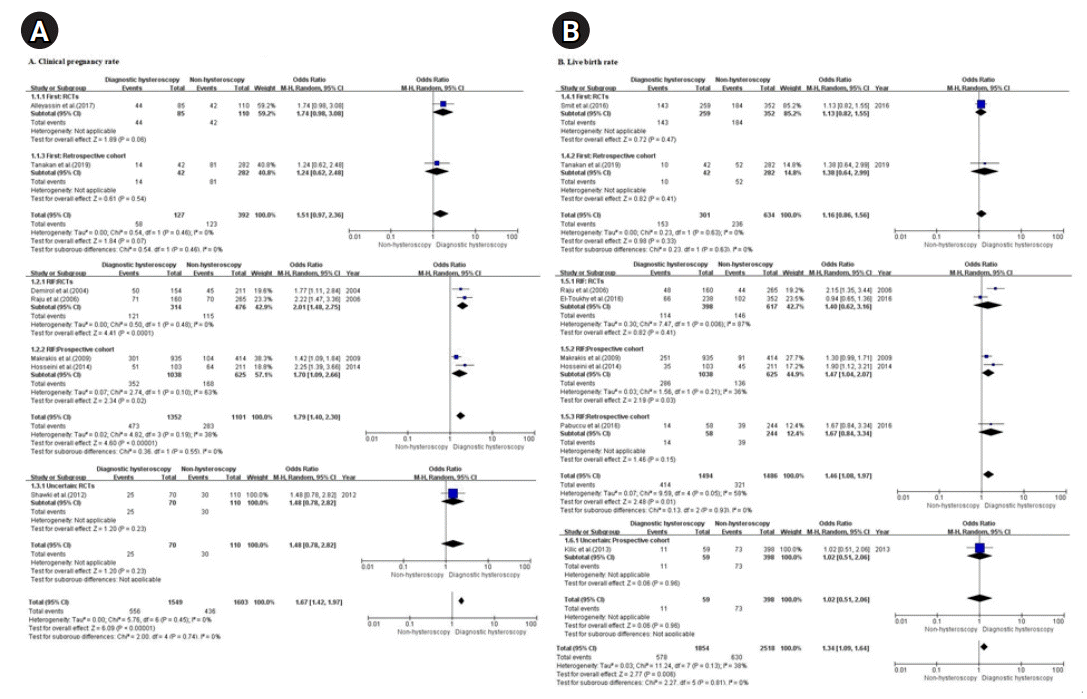
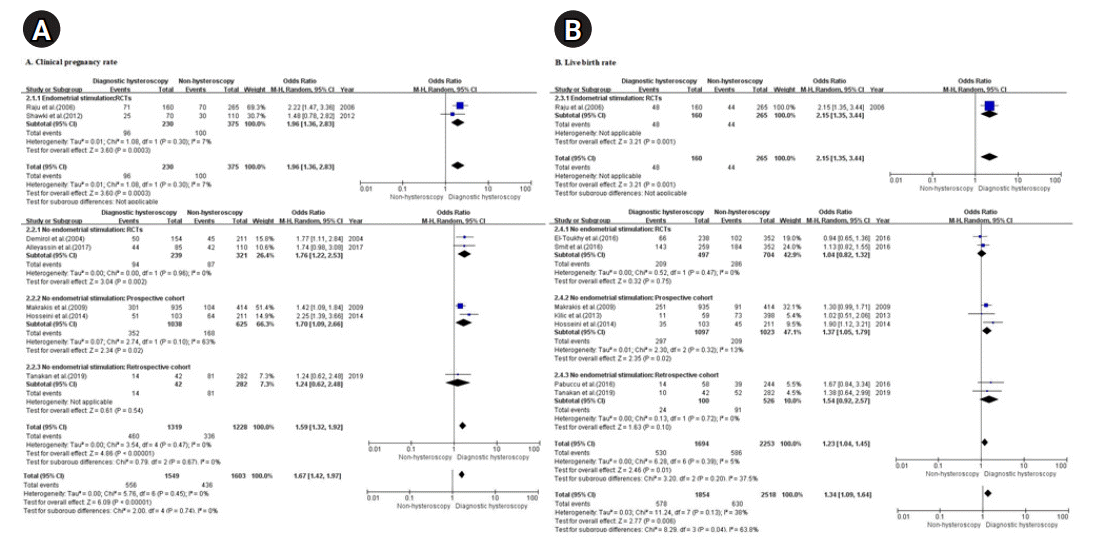
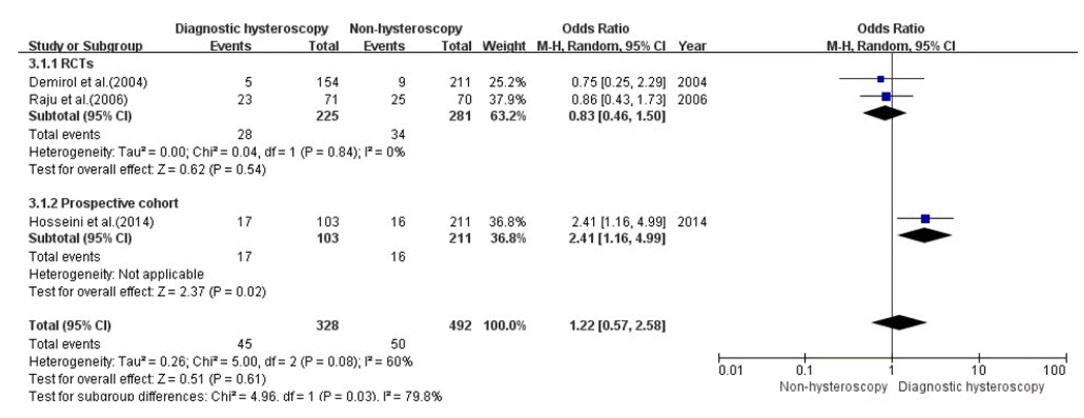
Data extraction and statistical analysis
Results
Study characteristics
Characteristics of the intervention
Table 1.
| First author (year) |
Intervention |
Comparator | Endometrial irritation (I only) | Method of pregnancy attempt (both I and C) | Embryo / day of ET | Authors’ conclusion | Main outcome measures | Intergroup differences | Adverse events of hysteroscopy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timing | Hysteroscope | |||||||||
| Tanacan (2019) [36] | In the early to midfollicular phase of the menstrual cycle (1–3 months before the start of IVF) | Not specified | Without diagnostic hysteroscopy prior to the first IVF cycle | No scratching | IVF | Fresh embryo / day 3 or day 5 | OH before the first IVF treatment cycle did not improve fertility outcomes in patients without previously detected pathology of the uterine cavity. | (1) Implantation rate | (1) .840 | Not specified |
| Distension medium: not specified | Routine usage of hysteroscopy should not be offered to patients in their first IVF cycles. | (2) CPR | (2) .541 | |||||||
| (3) LBR | (3) .420 | |||||||||
| Alleyassin (2017) [35] | Between the 18th and 22nd day of their menstrual cycles (mid-luteal phase) before ICSI cycles | 4-mm diameter diagnostic sheath, continuous flow, rigid, 30° view (Karl Storz, Tuttlingen, Germany) | Did not undergo OH before ICSI cycles | No scratching | ICSI | Fresh embryo / day 3 | Routine OH before ICSI cycles provided direct evaluation of uterine cavity. | (1) CPR | (1) .004 | Not specified |
| Distension medium: Saline | CPR improved after correction of endometrial cavity abnormalities. | (2) Miscarriage rate | (2) NS | |||||||
| El-Toukhy (2016) [32] | Before controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF | 2.9-mm diameter, rigid 30° view, with an atraumatic tip (TROPHY scope; Karl Storz) | Immediate controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF/ICSI | No scratching | IVF (with or without ICSI) | Fresh embryo / | Routine OH did not improve IVF outcomes in women with RIF who had a normal uterine ultrasound scan. | (1) Pregnancy rate | (1) .86 | No hysteroscopy-related adverse events |
| Within 14 days of menstruation | Distension medium: saline | When it is considered top quality (day 2 or days 3–4 or days 5–6) | (2) CPR | (2) .65 | ||||||
| (3) LBR (after 1 cycle of IVF) | (3) .96 | |||||||||
| Smit (2016) [34] | In the early-mid follicular phase of a menstrual cycle (days 3–12) | 5-mm outer diameter continuous flow hysteroscope with a 5-Fr working channel and a 30° direction of view | Immediate start of IVF | No scratching | IVF | Fresh embryo / not specified | Routine OH before the first IVF or ICSI treatment cycle did not improve fertility prospects in infertile women with a normal TVS of the uterine cavity who had not had a previous hysteroscopy. | (1) Implantation rate | (1) .23 | One (<1%) woman: endometritis after hysteroscopy |
| 1–3 months before the start of IVF treatment | Distension medium: saline | (2) CPR | (2) .71 | |||||||
| (3) OPR | (3) .69 | |||||||||
| (4) LBR | (4) .75 | |||||||||
| Pabuçcu (2016) [33] | In early follicular phase (1–6 months before the beginning of a new cycle) | 4-mm outer diameter, rigid, continuous flow; 30° forward and oblique view | Immediately started a new ART cycle | No scratching | IVF/ICSI | Fresh embryo / day 3 or day 5 | Unrecognized intrauterine pathologies can be easily detected and concurrently treated during the OH procedure with high success rates. | (1) Implantation rate | (1) .38 | Not specified |
| Distension medium: saline | The overall beneficial impact in terms of reproductive outcomes seems to depend on the extent of the pathology. | (2) Chemical pregnancy rate | (2) .08 | |||||||
| (3) LBR | (3) .06 | |||||||||
| (4) Miscarriage rate | (4) .26 | |||||||||
| Hosseini (2014) [31] | In the menstrual cycle just before ovarian stimulation or endometrial preparation | 4-mm rigid, continuous flow, 30° forward, and oblique view | Hysteroscopy was not performed | No scratching | ART IVF/ET | Fresh or frozen embryo / day 3 | OH before fresh cycles and frozen-thawed cycles in women experiencing RIF with apparently normal uterine cavity significantly increased the pregnancy rates. | (1) Chemical pregnancy rate | (1) <.001 | Not specified |
| Distension medium: saline | (2) CPR | (2) .001 | ||||||||
| (3) Delivery rate | (3) .026 | |||||||||
| Kilic (2013) [30] | Assessed prior to IVF | 4-mm (Karl Storz) | Underwent IVF without OH evaluation | No scratching | IVF | Not specified | OH before IVF can detect and treat intrauterine pathologies, with positives effect on pregnancy outcomes. | (1) LBR | (1) <.05 | Not specified |
| Follicular phase (days 5–7 of menstrual cycle) | Distension medium: saline | |||||||||
| Shawki (2012) [29] | The early postmenstrual period before controlled ovarian stimulation for ICSI | 3.5 mm with a 0° grade (Versascope; Gynecare, Ethicon, Sommerville, NJ, USA) | Immediate controlled ovarian stimulation for ICSI | Endometrial biopsy | ICSI | Fresh embryo / not specified | Improvement in implantation and CPR were observed after OH prior to ICSI. | (1) CPR | (1) <.05 | Not specified |
| Optic Illumination (250-W Xenon light source) | Routine OH should be an essential step of the infertility workup before ART even in patients with normal HSG and/or TVS. | (2) Implantation rate | (2) <.05 | |||||||
| Distension medium: saline | ||||||||||
| Makrakis (2009) [28] | Less than 12 months before the first IVF attempts | 2.9-mm, 30° angle, external sheath of 5.5-mm diameter providing inflow and outflow (Karl Storz) | Matched control (no hysteroscopy before IVF cycles) | No scratching | IVF | Fresh or frozen embryo / day 3–5 | Hysteroscopy could be seen as a positive prognostic factor for achieving a subsequent IVF pregnancy in women with a history of two consecutive implantation failures. | (1) CPR | (1) .04 | Not specified |
| Shortly after cessation of menses | Distension medium: saline | (2) OPR | (2) .06 | |||||||
| Rama Raju (2006) [27] | The early proliferative phase before controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF treatment | 5-mm diameter, 1.9-mm miniature, 30° view, 3 mm Bettocchi continuous flow sheath with an incorporated 5-Fr working channel (Karl Storz) | Immediate controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF treatment | Endometrial biopsy | IVF | Fresh embryo / day 3 | Patients with recurrent IVF-ET failures after normal HSG should also be reevaluated using hysteroscopy prior to commencing IVF-ET cycles in order to enhance the CPR. | (1) CPR | (1) <.05 | No further complications |
| Distension medium: glycine | (2) Miscarriage rate | (2) NS | ||||||||
| (3) LBR | (3) <.05 | |||||||||
| Demirol and Gurgan (2004) [26] | The early proliferative phase before controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF treatment | 5-mm continuous flow, lens diameter 2.9-mm, 30° view, 5-mm diameter sheath, Bettocchi, size 5 (Karl Storz) | Immediate controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF treatment | No scratching | IVF | Fresh embryo / day 3 | Patients with normal HSG but recurrent IVF-ET failure should be evaluated prior to commencing IVF-ET cycles to improve the clinical PR. | (1) Number of clinical pregnancies | (1) <.05 | Mild pain resembling menstrual cramps |
| (2–6 months after the last failed IVF cycles) | Distension medium: saline | (2) Number of first trimester abortions | (2) NS | |||||||
ART: Artificial reproductive technology; C: control; CPR: clinical pregnancy rate; ET: embryo transfer; Fr: French guage; HSG: hysterosalpingography; I: intervention; ICSI: intracytoplasmic sperm injection; IVF: in vitro fertilization; LBR: live birth rate; NS: not significant; OH: office hysteroscopy; OPR: ongoing pregnancy rate; PR: pregnancy rate; RIF: recurrent implantation failure; TVS: transvaginal sonography.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download