INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), which mainly infects the lungs but can also infect other organs. Although TB can be cured in most cases, it requires antibiotics treatment for six months, or a longer period (1). Moreover, the emergence of drug-resistant M. tuberculosis makes it hard to cure TB with first-line drugs (2). When infection was caused by M. tuberculosis resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin, it is defined as multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), which requires at least 9 - 20 months of treatment. The long treatment period and the severe drug side effects lower the probability of cure (1). For MDR-TB treatment, the use of second-line drugs such as fluoroquinolone (FQ) is enforced. However, when the infection was caused by MDR-TB bacterium resistant to FQ and at least one of the injectable drugs such as capreomycin, kanamycin, and amikacin, it is defined as extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) (1, 2). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2018, about 10 million people suffered from TB, and 1.45 million people died from TB. Moreover, 500,000 new rifampicin-resistant TB cases were reported in 2018, and 78% were MDR-TB. (1) In South Korea, 23,821 new cases were reported in 2019. Among those cases, 580 were MDR-TB, and 33 were XDR-TB. (3) This indicates that, for effective TB treatment, along with the conventional anti-TB drugs, new therapeutics are required.
One such promising therapeutic for TB is Photodynamic therapy (PDT). PDT needs the following three components: light, photosensitizer, and molecular oxygen. (4) In PDT, luminescent light excites the specific photosensitizer and forms singlet oxygen; then, the singlet oxygen induces apoptosis or necrosis of cells (5, 6, 7). PDT has been officially recognized as a cancer treatment by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the US in 1995, and has been used in various cancer treatments worldwide (8, 9, 10). Although currently, PDT is primarily used to treat cancer, antimicrobial PDT (APDT) is also receiving considerable attention in treating microbial infections (11, 12, 13, 14). The major attraction of APDT over conventional antibiotics is that multidrug-resistant strains are as easily killed as sensitive strains. Moreover, due to the production of multiple forms of ROS during PDT, it is less likely that APDT suffers from the resistance problem (14).
PDT has been used to kill mycobacteria or to treat mycobacterial infections. Wiegell, S. G. et al. reported the treatment of granuloma caused by M. marinum with PDT (15) O’Riordan K. et al. also showed that PDW with benzoporphyrin derivative as a photosensitizer could kill M. bovis BCG in vitro and a murine granuloma model (16). More recently, using clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis strains, Sung N. et al. demonstrated that PDT with radachlorin as a photosensitizer could kill not only wild type but also MDR and XDR strains (17).
The TB incidence is high in resource-scarce countries. For the PDT-mediated TB treatment in such countries, therefore, an inexpensive photosensitizer is preferred. One of such photosensitizers is methylene blue (MB). As a phenothiazinium salt, MB was officially approved as PDT photosensitizer for the treatment of oral infectious diseases (18, 19, 20). Compared with other photosensitizers used in previous mycobacterial studies, MB is inexpensive and poses a low barrier to clinical application in resource-scarce settings. It also efficiently absorbs red light (e.g., 660 nm), which can penetrate tissue more efficiently than shorter wavelength lights.
In the previous study, we showed that methylene blue (MB) is an effective photosensitizer for PDT in killing M. smegmatis, a model organism with high genetic similarity to M. tuberculosis (21). Also, we found that ciprofloxacin-resistant M. smegmatis was more sensitive to PDT, as compared with WT M. smegmatis. However, it remained to be determined whether the higher susceptibility of ciprofloxacin mutant can be generalized to MDR strains of M. smegmatis.
To answer the question, in this study, we take advanced of the fast growth of M. smegmatis and generated various isogenic MDR strains from the same parent M. smegmatis strain and examined the effect of the mutations on the sensitivity to PDT. Also, we examined whether the addition radiation step or repeat of the whole PDT process could increase the bactericidal potency of PDT. We found that, in general, MDR strains showed higher sensitivity to PDT. We also found that repeat of radiation significantly increases the bactericidal potency of PDT.
Go to : 
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and antibiotics
In this study, M. smegmatis NCTC8159 was used. M. smegmatis has 2000 homologous genes with M. tuberculosis, the causative agent of TB. M. smegmatis is considered a typical surrogate model for M. tuberculosis because of its rapidly-growing and non-pathogenic character. (22, 23) The bacterium was grown in Middlebrook 7H9 (Difco, USA) broth and 7H10 (Sigma, USA) plate containing OADC (oleic acid, albumin, dextrose, catalase; Sigma-Aldrich) and 0.05% Tween 80 (Sigma, USA). When necessary, the following antibiotics were used: Ciprofloxacin (Ildong pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Korea), levofloxacin (Jeil pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Korea), moxifloxacin (Bayer Korea, Korea), rifampicin, ethambutol, streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich Co., USA), isoniazid (Fluka, USA), kanamycin (Yuhan Co Ltd, Korea).
Generation of multi-drug resistant M. smegmatis
We first generated multi-drug resistant M. smegmatis (MDR-M. smegmatis) resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin. Fluoroquinolone (FQ) resistant MDR-M. smegmatis was generated through the stepwise-selection method. (24) The initiated minimal inhibitory concentrations of ciprofloxacin and moxifloxacin were 0.125 μg/ml. Then M. smegmatis was grown in the presence of 0.25 μg/ml of ciprofloxacin or moxifloxacin. When resistant mutants arose, they were grown in the presence of a two-fold higher concentration of the antibiotics. The highly resistant mutants were isolated through repeated trials and amplification. The mutants were washed with PBS, aliquoted in 1 ml of 20% (vol/vol) glycerol (Sigma, USA), and stored at -80℃. Three aliquots were randomly picked and spread on 7H10 plates to count the CFU.
Drug susceptibility test
The selected resistant mutants were subjected to susceptibility tests in 96-well plates. Ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, isoniazid, ethambutol, rifampicin, streptomycin, and kanamycin were used from 128 μg/ml to 0.125 μg/ml of concentration by two-fold dilution. The 96-well plates containing the mutants and anti-biotics were incubated at 37℃ for two days. The concentrations of antibiotics that the mutants were no longer amplified were noted as MICs.
PCR (Polymerase chain reaction) test and DNA sequencing
The wild-type strain and drug-resistant mutants were grown in 5 ml 7H9 broth. The resulting cultures were centrifuged and washed with PBS twice. The pellet was suspended in 50 ml of distilled water and incubated at 95℃ for 5 min. This suspension was centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatants were used for PCR reaction. The genes gyrA and gyrB, which are associated with fluoroquinolone resistance, were detected with primer gyrAF, gyrAR, gyrBF, and gyrBR (Table 1). The katG gene, which is associated with isoniazid resistance, was detected with primer katGF, katGR. The rpoB gene, which is associated with rifampicin resistance, was detected with primers rpoBF, and rpoBR. PCR was carried out with Takara thermal cycler and G-Taq premix (COSMOgenetech, Korea). The amplification condition was as follows: 95℃ for 20 sec (denaturation), 55℃ for 20 (annealing), 72℃ for 1 min (elongation), and 30 cycles. The PCR-amplified products were sequenced by COSMOgenetech using ABI PRISM 3730XL Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, USA).
Table 1.
Primers used in this study
Effect of MB on M. smegmatis
1 mg of methylene blue (MB; Seoul Hwasung chemical Co Ltd) was suspended in 1 ml of PBS (pH 6.8) and stored at 4℃ in the dark for less than 24 h. The effect of MB as a photosensitizer on the inactivation of M. smegmatis was examined at various concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10, 30, 50, 80, 150 μg/ml). MB was suspended in 1 ml of bacterial solutions (106 CFU/ml) and incubated in a dark room with shaking at 37℃ for 2 h. The solutions were serially diluted to 105 CFU/ml, 104 CFU/ml, and 103 CFU/ml; then, 100 μl of each diluted solution was spread on 7H10 agar plates in triplicate and incubated at 37℃ for 2 days. The CFUs were counted on the agar plates. Each experiment was performed at least three times.
Intermittent PDT (I-PDT)
The bacterium was incubated with MB (5 μg/ml) for 2 h, and then irradiated with a laser (660 nm) at a dose of 18 J/cm2. Then the solution was incubated without additional photosensitizer for 2 h and irradiated with a laser at the same dose. The total irradiation dose was 36 J/cm2. For the control, the bacterial sample was not irradiated after the second incubation (Fig. 1a).
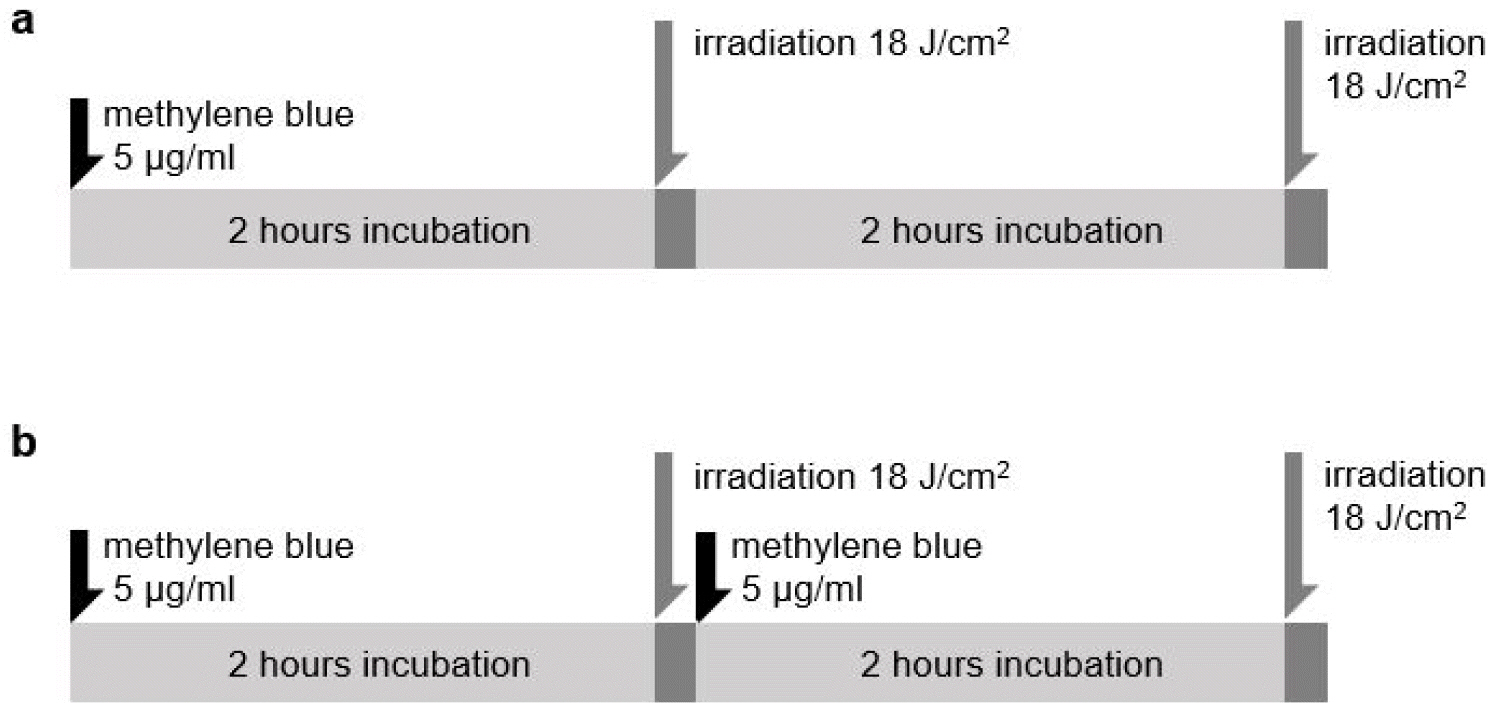 | Fig. 1Method of intermittent PDT and repeated PDT. (a) represents intermittent PDT. M. smegmatis strains were irradiated with 18 J/cm2 light dose after incubation with 5 μg /ml of methylene blue (MB), incubated again for 2 hours without MB exposure, and then irradiated at the same light dose (18 J/cm2). (b) represents repeated PDT. M. smegmatis strains were irradiated with 18 J/cm2 light dose after incubation with 5 μg /ml of MB and re-incubated with MB for 2 h and re-irradiated at 18 J/cm2 dose of laser light. |
Repeated PDT (R-PDT)
The bacterial solution was incubated with MB (5 μg/ml) for 2 h and irradiated with a laser (660 nm) at a dose of 18 J/cm2. Then it was incubated with MB (5 μg/ml) again for 2 h and irradiated with a laser at a dose of 18 J/cm2. As with I-PDT, the total irradiated dose was 36 J/cm2. For control, the bacterial sample was not irradiated after the second MB incubation (Fig. 1b).
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis has been carried out with Student’s t-test by using GraphPad Prism version 7. Data were presented as Mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
Go to : 
RESULTS
Generation of multi-drug resistant mutants of M. smegmatis
Multiple spontaneous drug-resistant mutants were generated by the stepwise-selection method. MIC of ciprofloxacin for the isolated ciprofloxacin-resistant M. smegmatis (CFXR-M. smegmatis) was 128 μg/ml. MIC of moxifloxacin for the moxifloxacin-resistant M. smegmatis (MFXR-M. smegmatis) was 128 μg/ml. Both CFXR and, MFXF-M. smegmatis strains were resistant to levofloxacin (Table 2). The final isolate of MDR-M. smegmatis had resistance for isoniazid (MIC 256 μg/ml) and rifampicin (1,024 μg/ml). The fluoroquinolone-resistant MDR-M. smegmatis (FQR-MDR-M. smegmatis) had MIC of 256 μg/ml to the three of fluoroquinolone drugs (i.e., ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and levofloxacin). Finally, FQR-MDR-M. smegmatis had the isoniazid MIC of 256 μg/ml and rifampicin MIC of 1,024 μg/ml.
Table 2.
Sequencing analysis of drug-resistant Mycobacterium smegmatis and minimal inhibitory concentration of multi-drugs
Analysis of the genes associated with antibiotic resistance
In three FQ resistant mutants, mutations were found in quinolone resistance-determining regions (QRDR) (25): Ala-90 Val substitution in CFXR-M. smegmatis, Asp 94 Asn substitution in MFXR-M. smegmatis and FQR-MDR-M. smegmatis (Table 2). Mutations in rpoB are associated with resistance to rifampicin, the primary drug for TB (26, 27, 28). In MDR-M. smegmatis, His526 of RpoB was replaced by Asp, whereas, in FQR-MDR-M. smegmatis, Ser531 was replaced by Leu. On the other hand, no mutation was found in gyrB or katG.
Inactivation of M. smegmatis by methylene blue (MB)
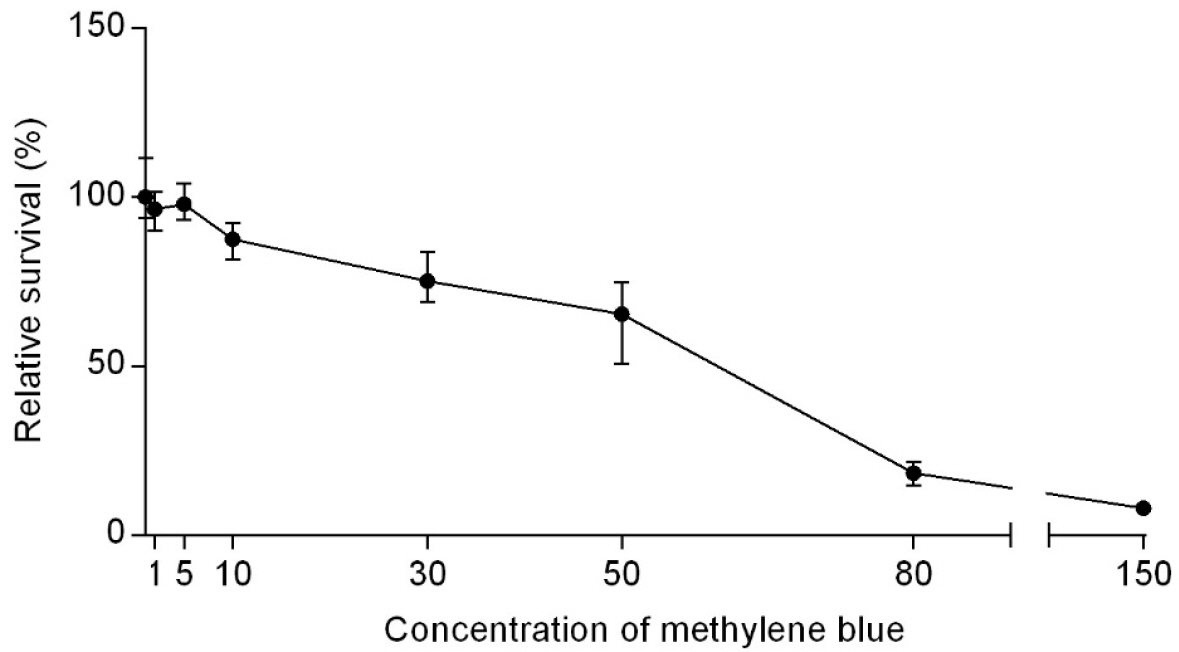
In our previous study, MB showed a weak antimicrobial activity to M. smegmatis (MIC < 150 µg/mL) when incubated with bacteria for 40 min (21). To examine whether longer incubation can increase the bactericidal activity of MB, we incubated M. smegmatis with various concentrations of MB for 2 h; then, bacterial CFU was counted. As with 40 min incubation, 2 h-incubation with MB killed M. smegmatis in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 2). Although it killed only 2.1% of bacteria at 5 μg/ml, it killed 12.4% at 10 μg/ml, 24.8% at 30 μg/ml, 34.6% at 50 μg/ml, and over 80% at 80 μg/ml. However, even at the highest concentration (i.e., 150 μg/ml), MB failed to kill all M. smegmatis cells. These results suggest that MB has a weak antimicrobial activity toward M. smegmatis, and increase of incubation time to 2 h does not significantly increase the antimicrobial activity of MB.
Inactivation of M. smegmatis by PDT
To assess the efficacy of PDT in killing M. smegmatis, first, we incubated the bacterium with MB (0, 5, and 30 mg/ml); then, the bacterium was irradiated by a laser at 18 J/cm2. We used the low concentrations of MB to minimize the cytotoxicity of PDT (21). As shown, the irradiation alone did not significantly kill M. smegmatis (MB 0 mg/ml in Fig. 3). In the presence of MB (either 5 or 30 mg/ml), however, more M. smegmatis were killed by a higher dose of irradiation (Fig. 3). In the presence of 30 mg/ml MB, irradiation at 54 J/cm2 killed 98.2% of bacteria. These results demonstrate that PDT kills M. smegmatis in the MB and irradiation-dependent manner.
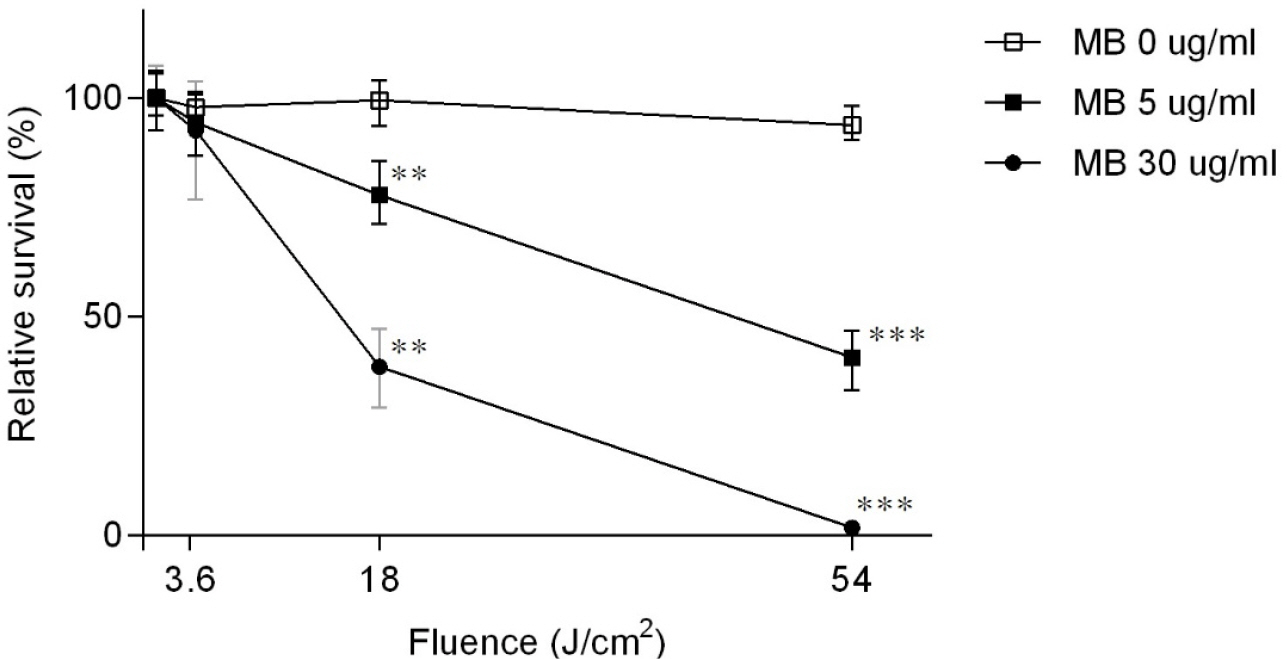 | Fig. 3The bactericidal effect of photodynamic therapy with methylene blue on Mycobacterium smegmatis. M. smegmatis was incubated in various concentrations of methylene blue (0, 5, 30 μg/ml) and irradiated with different light doses (0, 3.6, 18, 54 J/cm2). Data were presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences with respect to the corresponding controls (student’s t-test: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). |
The effect of drug-resistance mutations on the sensitivity to PDT
Next, we examined the effect of drug-resistance of M. smegmatis on the sensitivity to PDT (see Material and Methods). The isolated spontaneous drug-resistant mutants were first incubated in various concentrations of MB (0, 5, and 30 μg/ml), and then irradiated with 3.6, 18, 54 J/cm2 doses of the laser. Interestingly, the drug-resistant M. smegmatis strains appeared more sensitive to PDT than the WT strain. Unlike the WT strain, regardless of the type of resistance, a significant number of drug-resistant strains were killed even by the low irradiation at 3.6 J/cm2 and almost eradicated at 54 J/cm2 (Fig. 4). These results indicate that the mycobacterial mutations commonly found in MDR and XDR-M. tuberculosis render the bacterium more susceptible to PDT.
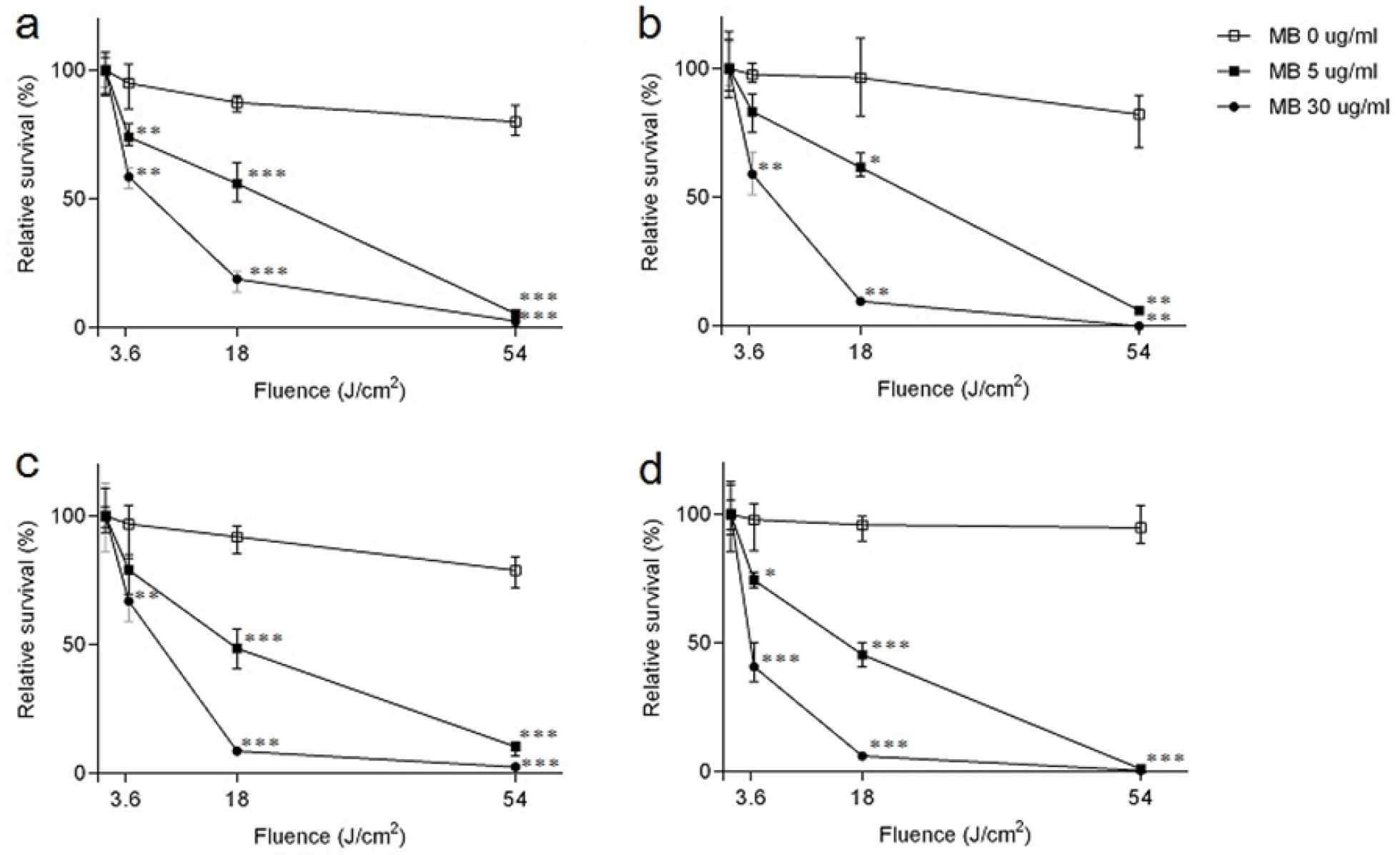 | Fig. 4Effects of photodynamic therapy with methylene blue on drug-resistant Mycobacterium smegmatis. Drug-resistant M. smegmatis strains were incubated in various concentrations of methylene blue (0, 5, 30 μg/ml) and irradiated at different light doses (0, 3.6, 18, 54 J/cm2). (a-d) represents ciprofloxacin resistant-, moxifloxacin resistant-, multi drug-resistant (MDR)-, fluoroquinolone-resistant MDR-M. smegmatis strain, respectively. Data were presented as Mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences with respect to the corresponding controls (student’s t-test: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p <0.001). |
Effect of intermittent PDT (I-PDT) and Repeated PDT (R-PDT)
Next, compared the bactericidal effect of additional radiation (i.e., I-PDT) or additional photosensitizer and radiation (i.e., R-PDT) (see Materials and Methods). PDT was carried out at 5 mg/ml of MB and either 18 or 36 J/cm2 of irradiation (Fig. 5). In I-PDT, 2 h after the completion of PDT at 18 J/cm2, the bacteria were subjected to additional irradiation at 18 J/cm2, resulting in 36 J/ cm2 total irradiation. On the other hand, in R-PDT, the entire PDT procedure at 18 J/cm2 was repeated. As can be seen, both I-PDT and R-PDT showed much higher bactericidal activity to M. smegmatis than PDT did (Fig. 5). Although PDT at 36 J/cm2 killed only 56.7% of WT bacteria, both I-PDT and R-PDT killed more than 93% (Fig. 5a). The higher bactericidal activity of I-PDT and R-PDT was also evident for drug-resistant bacteria (Fig. 5b-e). As expected, control groups for I-PDT and R-PDT did not show significant inactivation of M. smegmatis. These results demonstrate that I-PDT and R-PDT with a low concentration of methylene blue as a photosensitizer can be an effective treatment option for mycobacterial infections, regardless of the drug-resistance of the bacterium.
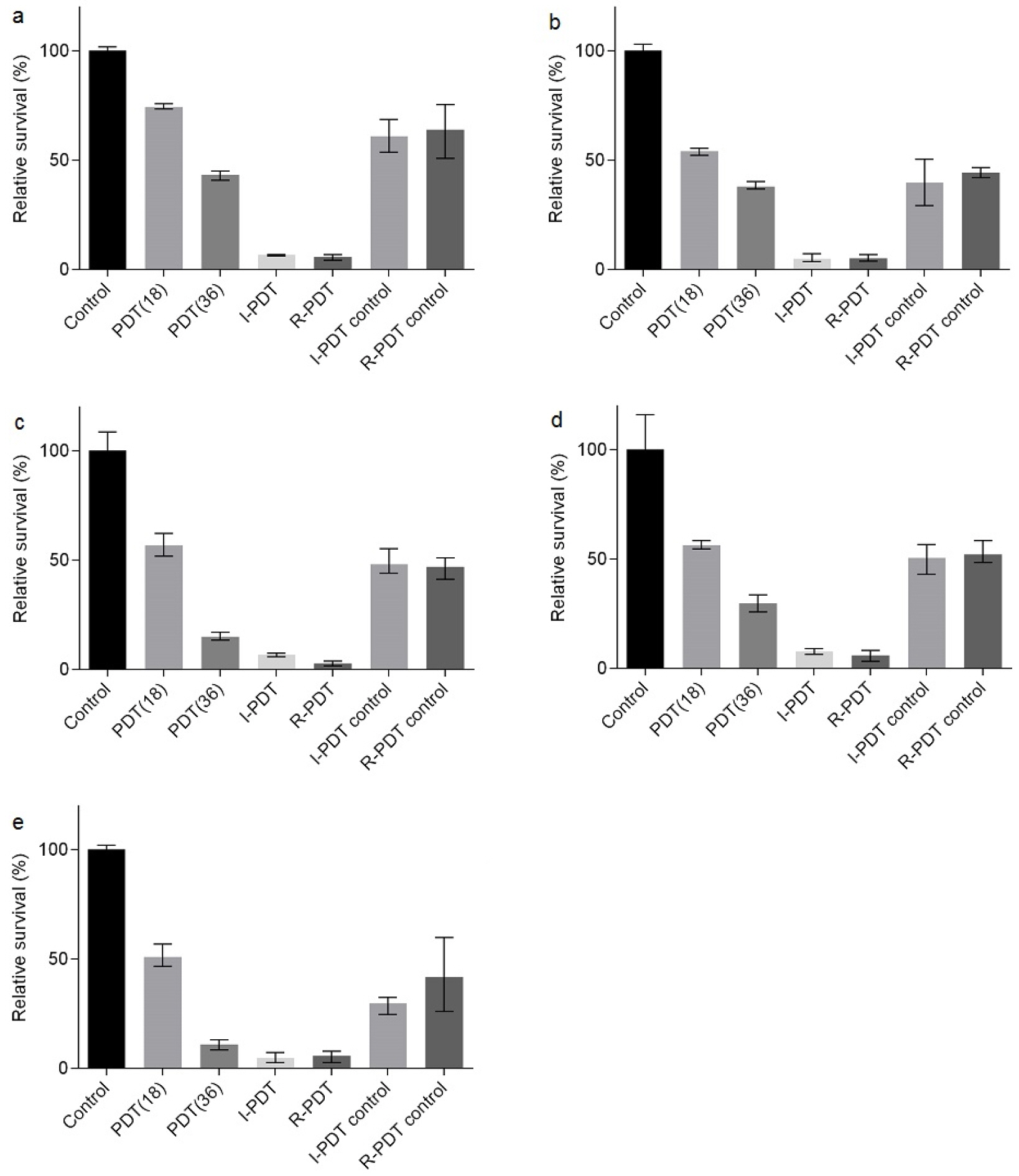 | Fig. 5The survival rate of Mycobacterium smegmatis by intermittent PDT and repeated PDT. (a-e) represents a wild type-, ciprofloxacin resistant-, moxifloxacin resistant, multi drug-resistant (MDR)-, fluoroquinolone-resistant MDR-M. smegmatis strain, respectively. For comparison of intermittent PDT and repeated PDT, M. smegmatis strains were irradiated for a continuous double time period of those PDT, resulting in 36 J/cm2 of irradiation dose. Control: no photosensitizer and laser light, PDT 18 J/cm2: continuous PDT at the dose of 18 J/cm2, PDT 36 J/cm2: continuous PDT at the dose of 36 J/cm2, I-PDT: intermittent PDT, R-PDT: repeated PDT, I-PDT control: M. smegmatis strains were treated by PDT at the dose of 18 J/cm2 and incubated for 2 hours without methylene blue (MB) exposure and irradiation. R-PDT control: M. smegmatis strains were treated by PDT at the dose of 18 J/cm2 and incubated with MB for 2 hours, but not irradiation. Data were presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. |
Go to : 
DISCUSSION
TB is an old disease that has affected humans for thousands of years. The WHO estimates that approximately 2 billion peoples are currently living with the causative agent M. tuberculosis (1). Although antibiotic therapy has been effective in TB treatment, its lengthy treatment time, multiple antibiotics requirements, and the drug side-effects hampered the effectiveness of the therapy. Also, the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains made TB treatment more difficult and calls for new therapeutics. Here, we showed that PDT with MB as a photosensitizer could efficiently kill the model organism M. smegmatis. More importantly, PDT killed drug-resistant strains more efficiently, making PDT with MB an attractive treatment method for TB caused by multi-drug resistant mycobacteria, notably, in the resource-scarce setting.
Along with rifampicin, isoniazid is a primary TB drug. As a pro-drug, isoniazid is activated by KatG (catalase peroxidase) of mycobacterium. Once activated, isoniazid forms a covalent complex with InhA (enoyl-ACP reductase) and blocks the synthesis of mycolic acid (28, 29). Mutations in KatG can confer the bacterium resistance to isoniazid, and the replacement at 275 threonine or 300 tryptophan is most frequent (30, 31). In this study, however, we did not find any mutation in the katG gene of MDR-M. smegmatis strain (Table 2), indicating that the isoniazid resistance of the strain is probably due to mutations in other genes known to be involved in isoniazid resistance (e.g., inhA, acpM, and kasA).
To M. smegmatis, the photosensitizer MB showed weak antimicrobial activity (MIC > 150 mg/ml, Fig. 2), whereas the laser irradiation itself has almost no antimicrobial activity (Fig. 3). However, when both were combined, they showed dramatic synergy and efficiently killed M. smegmatis (Fig. 3), implying that the major mode of bactericidal activity of PDT is through the production of reactive oxygen species (11, 12). It is known that DNA is sensitive to reactive oxygen species (32). Interestingly, the drug-resistant strains contain mutations in proteins that bind to DNA for their functions (i.e., GyrA and/or RpoB). The increased sensitivity of drug-resistant strains to PDT (Fig. 4) might indicate that those mutated proteins might function less efficiently with the damaged DNA. However, further research is needed to delineate the relationship between the sensitivity to PDT and the type of antibiotic resistance.
In PDT, the repetition of the irradiation step alone (i.e., I-PDT) significantly increased the bactericidal activity. For example, when PDT was carried out at 36 J/cm2, it only killed 57% of WT M. smegmatis (Fig. 5a). However, with I-PDT, where irradiation of 18 J/cm2 was repeated, and the total irradiation was 36 J/cm2, 93% were killed. Since there was no significant difference between I-PDT and R-PDT, the extra addition of MB is not necessary for the enhanced bactericidal activity in this in vitro setting, where the MB concentration remains constant. However, in the in vivo treatment setting, where the MB concentration will become lower by diffusion, R-PDT is expected to be more efficient in killing bacteria.
The bactericidal activity of PDT could be further improved. Daniela et al. reported the combination of photosensitizer MB with potassium iodide enhanced the killing of S. aureus and E. coli with PDT (33). Shih et al. also reported that the mix of CFX, MFX, or amikacin to MB enhanced the bactericidal activity of PDT (34). Therefore, the efficient mycobacterial killing of I-PDT/R-PDT used in this study might be further enhanced by such additions. If this is the case, it will further improve the potential of PDT as an alternative therapeutic method for TB treatment and contribute to lessening the burden of antimicrobial resistance of mycobacterium.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download