INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals and reagents
Preparation of Centella asiatica extract
HPLC analysis
Cell culture
Cell viability assay
Protective effects of C. asiatica extracts and compounds against CoCl2
Protective effect of CA-HE50 against oxidized-A2E
2-NBDG uptake assay
Animal care and experiments
Determination of liver tissue damage
H&E staining
Western blot analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Cytoprotective effects of Centella asiatica extract against CoCl2
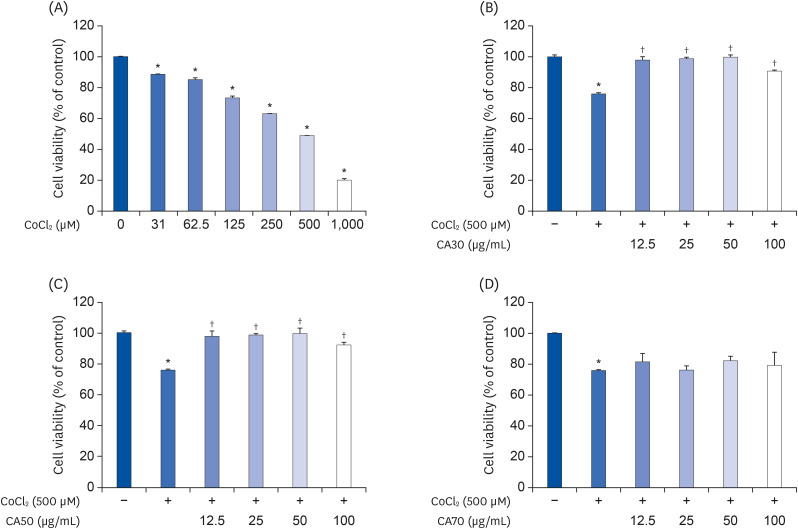 | Fig. 1Cytoprotective effects of CA-HE50 against CoCl2 in ARPE-19 cells. (A) Cytotoxicity by CoCl2 in ARPE-19 cells. Cytoprotective effects of (B) CA30, (C) CA50, and (D) CA70 against 500 µM CoCl2. Representative data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean of three different experiments (n = 3) for each group.
*P < 0.05 compared with the normal control group. †P < 0.05 compared with the CoCl2 control (vehicle) group.
|
HPLC analysis of CA-HE50
Cytoprotective effects of compounds present in CA-HE50
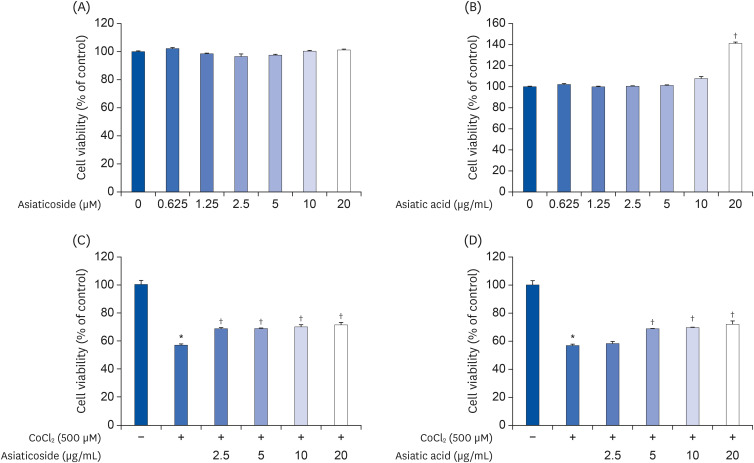 | Fig. 3Cytoprotective effects of asiaticoside and asiatic acid on CoCl2 in ARPE-19 cells. Cytotoxicity of (A) AS and (B) AA in ARPE-19 cells. Cytoprotective effects of (C) AS and (D) AA on CoCl2. Representative data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean of 3 different experiments (n = 3) for each group.
*P < 0.05 compared with the normal control group. †P < 0.05 compared with the CoCl2 control (vehicle) group.
|
Inhibitory effect of CA-HE50 on oxidized-A2E production
 | Fig. 4Cytoprotective effects of CA-HE50 on oxidized-A2E in ARPE-19 cells. (A) Production of oxidized-A2E depends on UV-irradiation time. (B) Inhibitory effect of CA-HE50 on oxidized-A2E production. (C) Cytoprotective effect of CA-HE50 on oxidized-A2E in ARPE-19 cells. Representative data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean of three different experiments (n = 3) for each group.A2E, a lipofuscin fluorophore; UV, ultraviolet.
*P < 0.05 compared with the normal control group. †P < 0.05 compared with the oxidized-A2E control (vehicle) group.
|
CA-HE50 helps transport glucose into retinal pigment cells
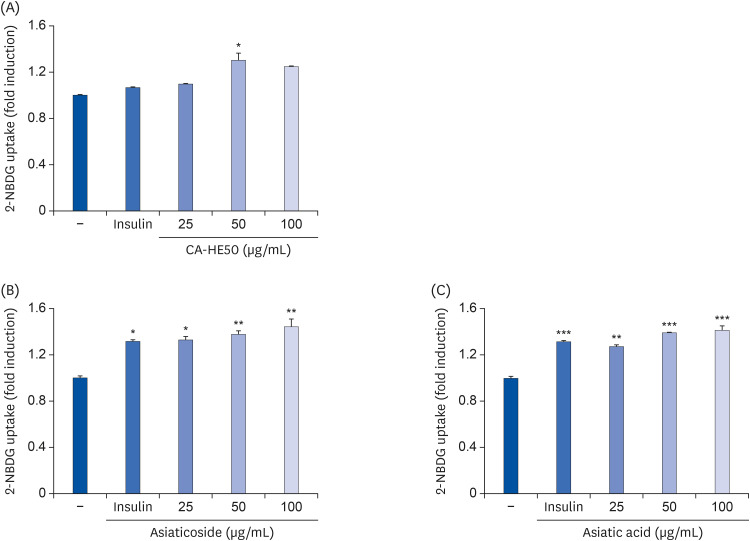 | Fig. 5Effects of CA-HE50, asiaticoside, and asiatic acid on glucose uptake in ARPE-19 cells. Effects of (A) CA-HE50, (B) AS, and (C) AA on glucose uptake in ARPE-19 cells. Representative data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean of 3 different experiments (n = 3) for each group.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P< 0.001 compared with the control group.
|
Protective effect of CA-HE50 in a model of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced retina degeneration
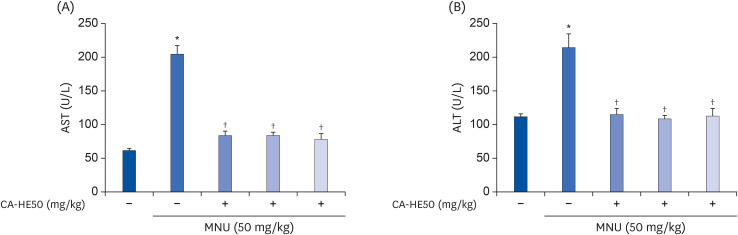 | Fig. 6Hepatoprotective effect of CA-HE50 against MNU-induced hepatotoxicity. (A) AST and (B) ALT release the inhibitory effect of CA-HE50. Representative data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 6) for each group.MNU, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase.
*P < 0.001 compared with the normal control group. †P < 0.001 compared with the MNU (vehicle) control group.
|
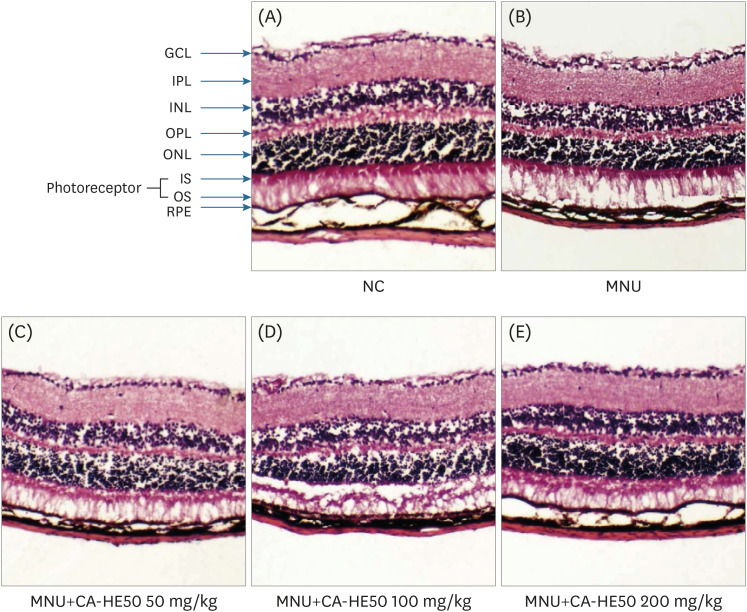 | Fig. 7Histopathology of retinas according to H&E staining from 5 groups of mice at 24 h post-injection. (A) Representative retinal images of H&E-stained retinal sections from normal (MNU-uninjected) eyes. (B) Representative retinal image from the MNU-injection group (vehicle group). (C) Representative retinal image for mice administered 50 mg/kg CA-HE50 for 7 days and then injected with MNU. (D) Representative retinal image for mice administered 100 mg/kg CA-HE50 for 7 days and then injected with MNU. (E) Representative retinal image for mice administered 200 mg/kg CA-HE50 for 7 days and then injected with MNU. Data are representative of 6 independent experiments.MNU, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS, inner segments; OS, outer segments; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.
|
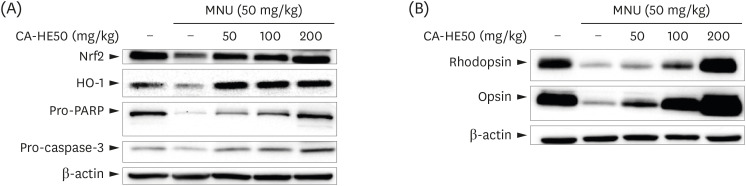 | Fig. 8Western blot analysis for expressions of proteins associated with retinal damage expressed in the eyes of C57BL/6 mice that induced retinal damage with MNU after 7 days of CA-HE50. (A) Effects of CA-HE50 on NRF2, HO-1, pro-PARP, and pro-caspase-3 at the protein level. (B) Effects of CA-HE50 on rhodopsin and opsin at the protein level. β-actin was detected as an internal standard. Data are representative of 6 independent experiments.MNU, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea; NRF2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; PARP, Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download