A 23-year-old male patient was referred to our clinic with a preliminary diagnosis of pericardial effusion. The patient had undergone two surgical operations due to pectus excavatum. His blood pressure was 130/70 mmHg and his heart rate was 78 bpm. Auscultation of heart sounds revealed loud S1 and S2, and a systolic-diastolic murmur at the apex.
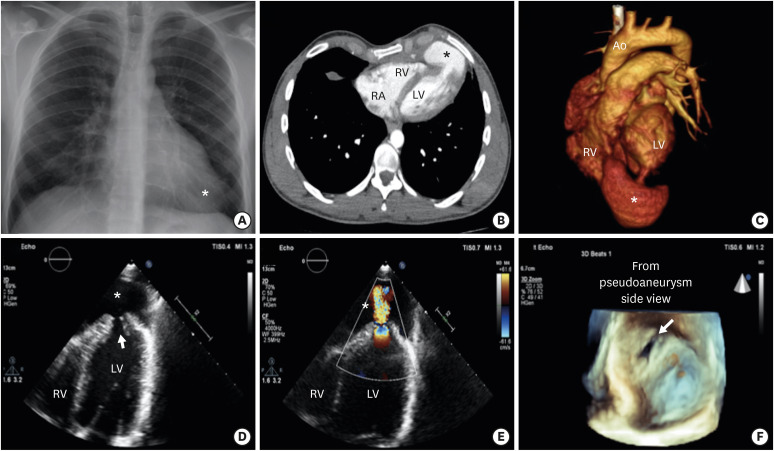
The patient's chest X-ray showed enlargement of the apical cardiac silhouette (Figure 1A). Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) revealed a regional wall motion abnormalities at the left ventricular (LV) apex with a large apical pseudoaneurysm 60×36 mm in size. The pseudoaneurysm was filled with the systolic and diastolic blood flow and its lumen was connected to the LV cavity through a neck (Figure 1D and E, Supplementary Videos 1, 2, 3). Three-dimensional echocardiography well demonstrated 14×10-mm orifice of the pseudoaneurysm in detail (Figure 1F, Supplementary Video 4). A computed tomography (CT) angiography performed for further evaluation confirmed the presence of the pseudoaneurysm and its connection to the LV cavity through a neck (Figure 1B and C, Supplementary Video 5). We offered the treatment options but the patient refused to undergo interventions.
Pseudoaneurysm of the LV is a rare but lethal complication of myocardial infarction,cardiothoracic surgery, and trauma. Because the development of a tamponade after LV rupture is usually fatal. Surgical or percutaneous interventions are primarily preferred for the management of LV pseudoaneurysms. The advances in imaging methods and consequent improvements in the detection of LV pseudoaneurysms have allowed to follow-up asymptomatic patients with medical therapy.
In this case presentation,we presented the development of a non-cardiac surgery-related pseudoaneurysm of LV; which was well-visualized with echocardiography and CT.
Notes
Author Contributions:
Conceptualization: Çiçek MB, Karaduman A.
Data curation: Çiçek MB, Karaduman A.
Formal analysis: Çiçek MB.
Funding acquisition: Balaban İ.
Project administration: Balaban İ.
Software: Balaban İ.
Supervision: Kırma C.
Validation: Kılıçgedik A.
Visualization: Karaduman A.
Writing - original draft: Karaduman A, Kılıçgedik A, Kırma C.
Writing - review & editing: Karaduman A, Kılıçgedik A, Kırma C.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Video 1
Transtorasic echocardiography apical four chamber view showing left ventricle apical pseudoaneurysm (asterisk) and entrance of pseudoaneurysm (arrow).
Supplementary Video 2
Transtorasic echocardiography apical four chamber colour doppler view showing pseudoaneurysm (asterisk) was connected to the left ventricular cavity.
Supplementary Video 3
Transtorasic echocardiography subcostal view showing left ventricle apical pseudoaneurysm (asterisk) and orifice of pseudoaneurysm (arrow).
Figure 1
(A) Chest X-ray showed enlarged apical cardiac silhouette (asterisk). (B) CT angiography transvers view showing large apical pseudoaneurysm (asterisk). (C) Three-dimensional CT angiography showing pseudoaneurysm(asterisk) and connection to the LV cavity through a neck. (D) Transtorasic echocardiography apical 4 chamber view showing left ventricle apical pseudoaneurysm(asterisk) and entrance of pseudoaneurysm (arrow). (E) Transtorasic echocardiography apical 4 chamber colour doppler view showing pseudoaneurysm (asterisk) was connected to the LV cavity. (F) Three-dimensional echocardiography view from pseudoaneurysm side showing pseudoaneurysm entrance orifice of 2.5×1.5 cm.
Ao = aortic; CT = computed tomography; LV = left ventricular; RV = right ventricular.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download