CASE 1
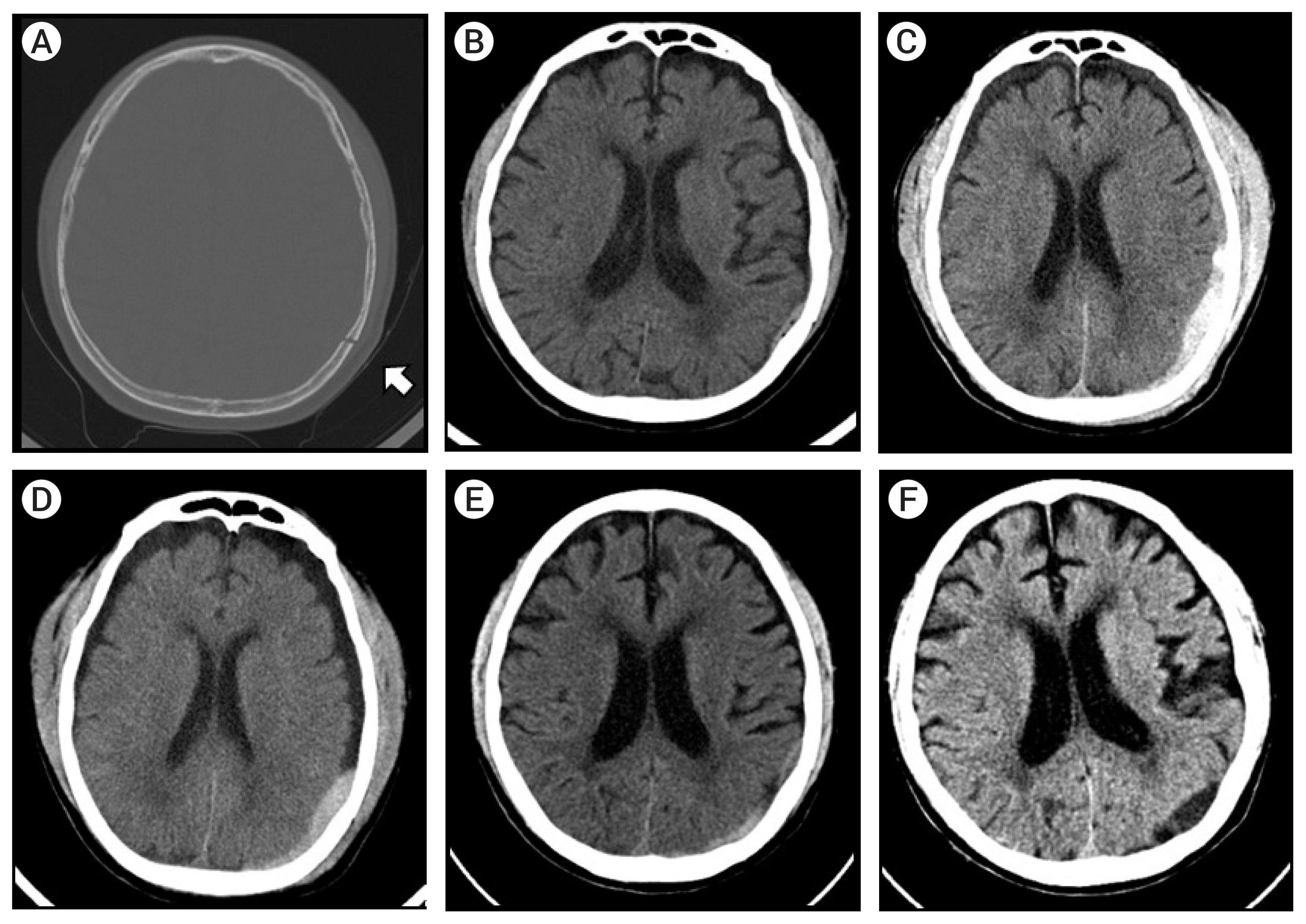 | Fig. 1(A) Initial brain computed tomography (CT) showing a left parietal linear skull fracture (white arrow). (B) Initial brain CT with minimal epidural hematoma (EDH) in a fractured site. (C) Pre-procedure brain CT showing increased EDH over time. (D) Three days post-procedure. (E) Brain CT performed two weeks post-procedure showing decreasing amount of EDH (F) Brain CT taken at a one month follow-up; the EDH is almost completely resolved. |
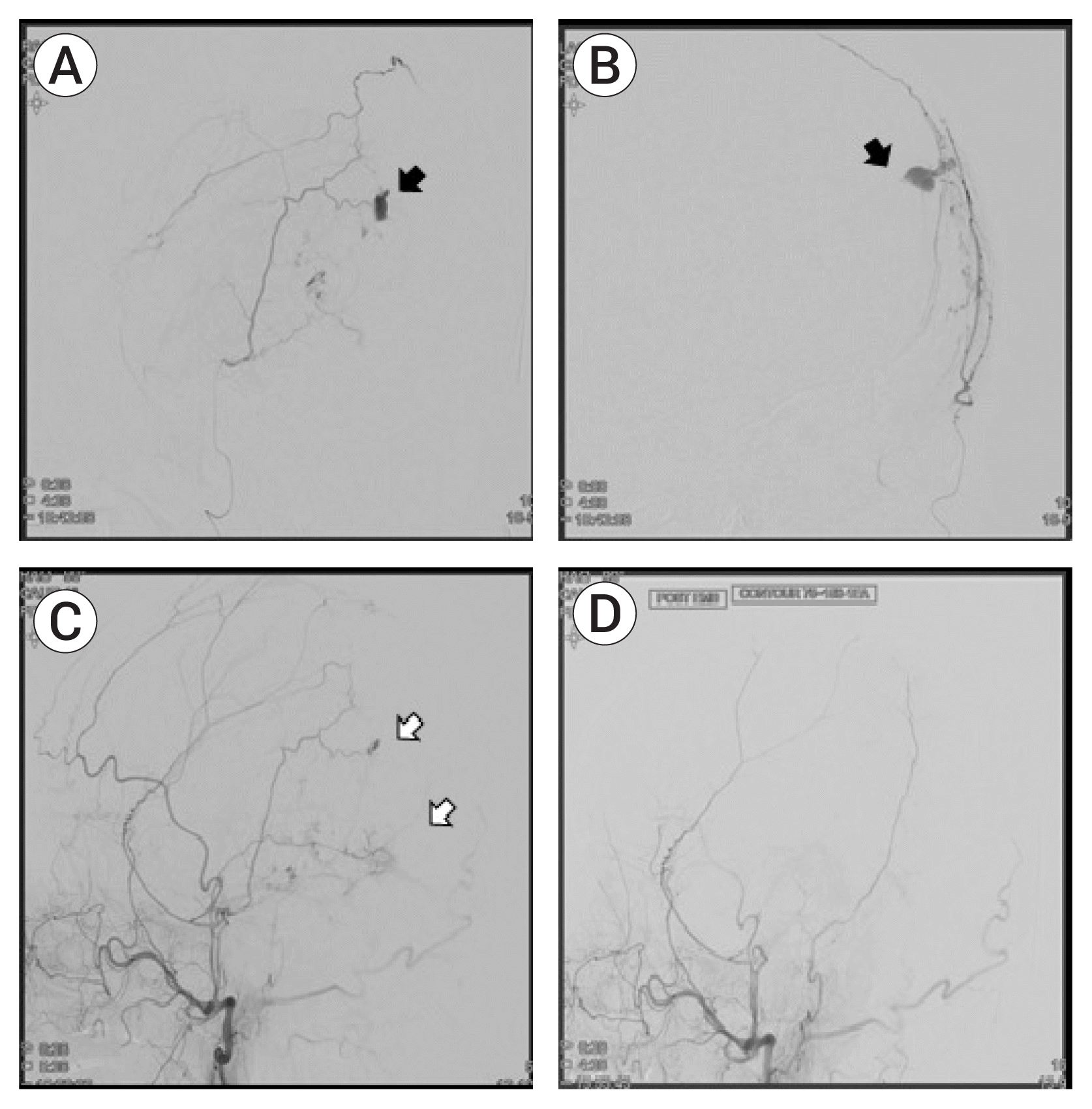 | Fig. 2(A, B) Preoperative selective angiography of parietal branch of middle meningeal artery (MMA) with contrast leakage (black arrow). (C) Preoperative angiography of the external cerebral artery (ECA) showing contrast leakage (white arrow). (D) Postoperative ECA angiography showing resolved contrast leakage in the parietal branch of the MMA. |
Postoperative follow-up
CASE 2
Presenting illness
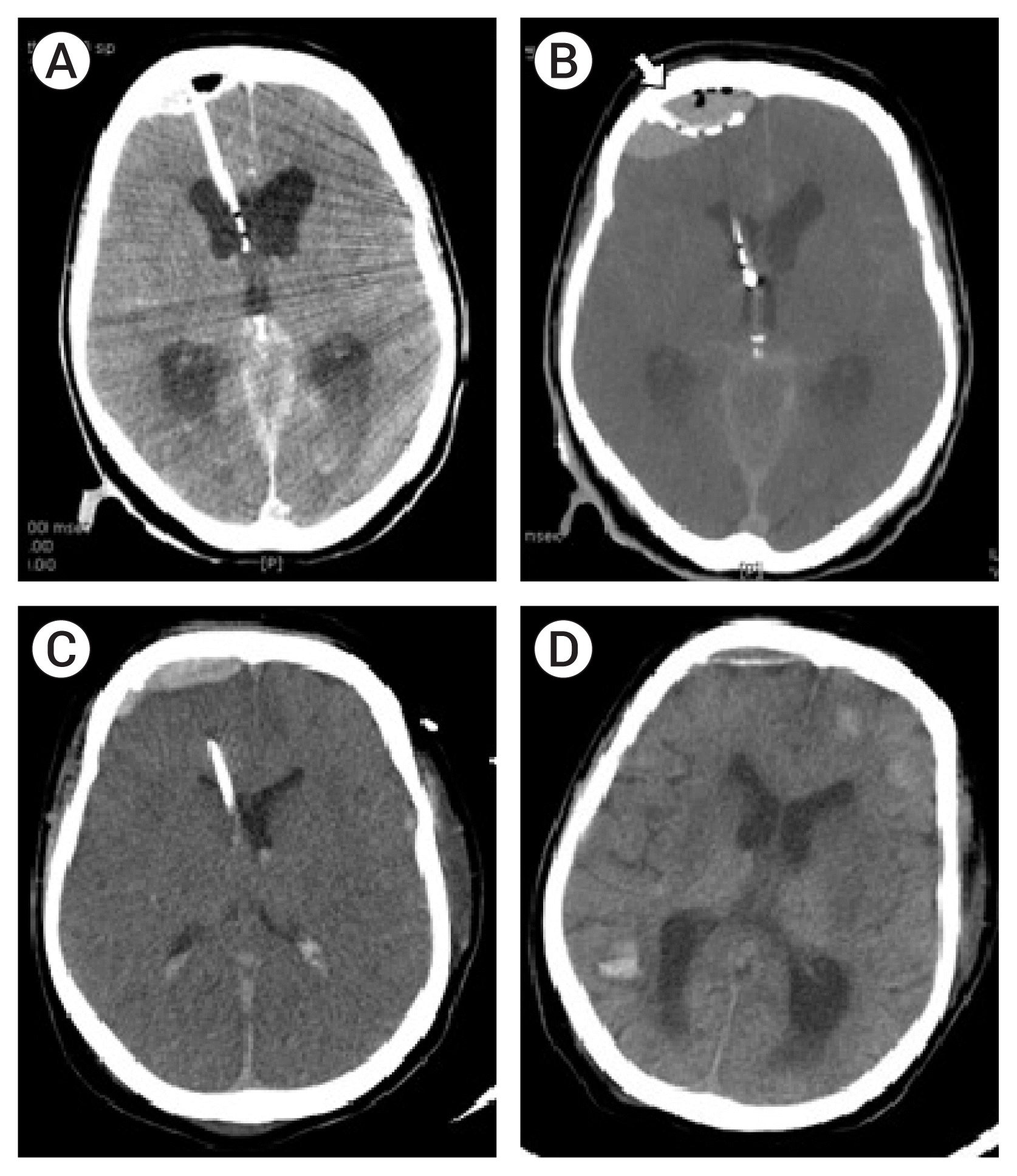 | Fig. 3(A) Post-external ventricular drainage (EVD) CT scan showing small epidural hematoma (EDH) at the EVD site. (B) Additional burr hole made lateral to the first burr hole (white arrow). The brain CT shows increasing size of the EDH with pneumocephalus. (C) Two days after EVD, the catheter to treat the EDH is removed. (D) Follow-up brain CT in one month after the procedure. The EDH is almost completely resolved, but brain CT shows multiple intracerebral hemorrhages due to thrombocytopenia. |
Endovascular procedure and clinical findings
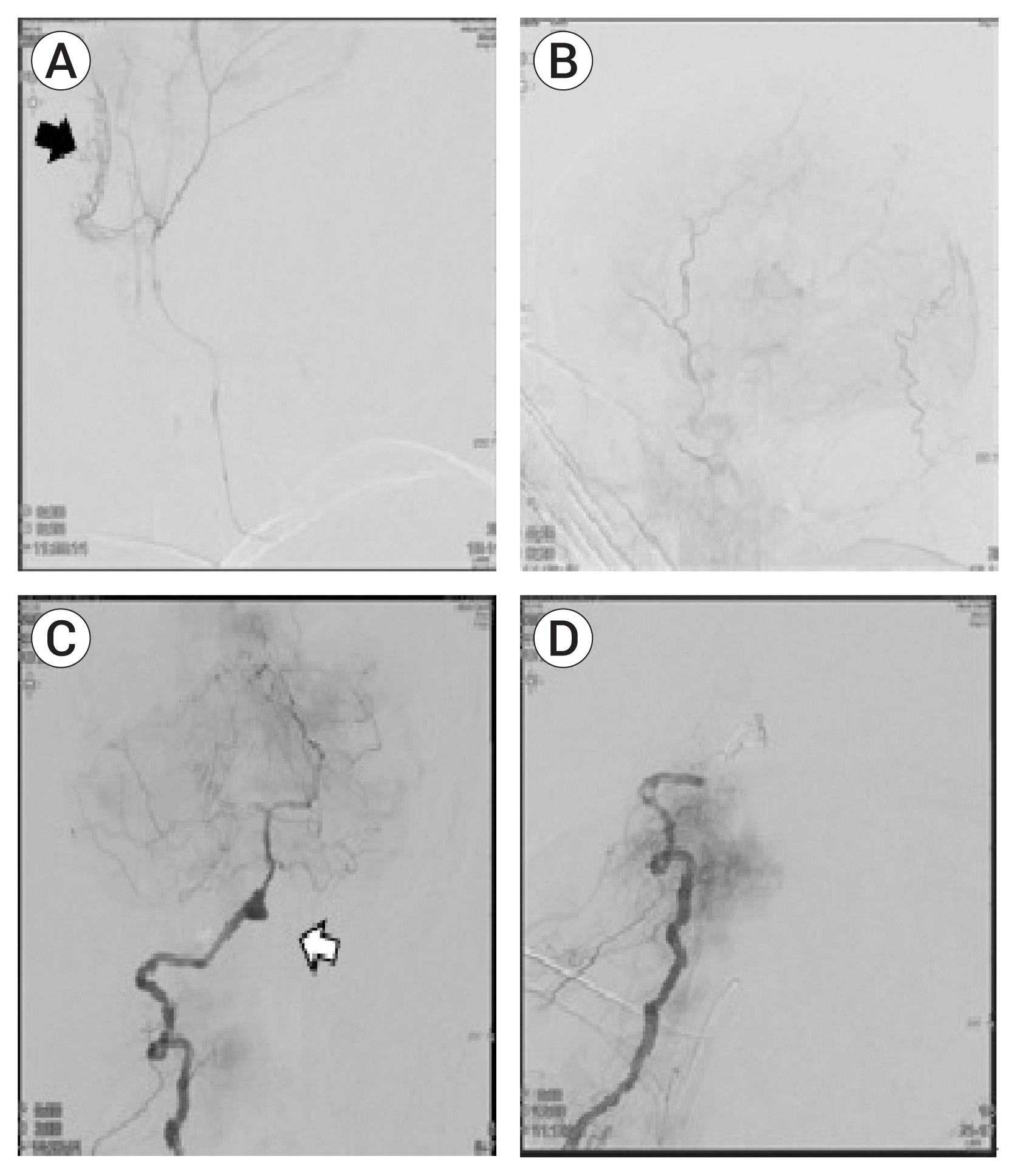 | Fig. 4(A) Selective angiography of the MMA showing a contrast leakage site (black arrow). (B) Postoperative angiography of the ECA showing resolution of the contrast-leakage site. (C) Preoperative right vertebra artery (VA) angiography showing an aneurysm in the V4 segment (white arrow). (D) Angiography after trapping of the right VA with coil. MMA, middle meningeal artery; ECA, external carotid artery. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download