Introduction
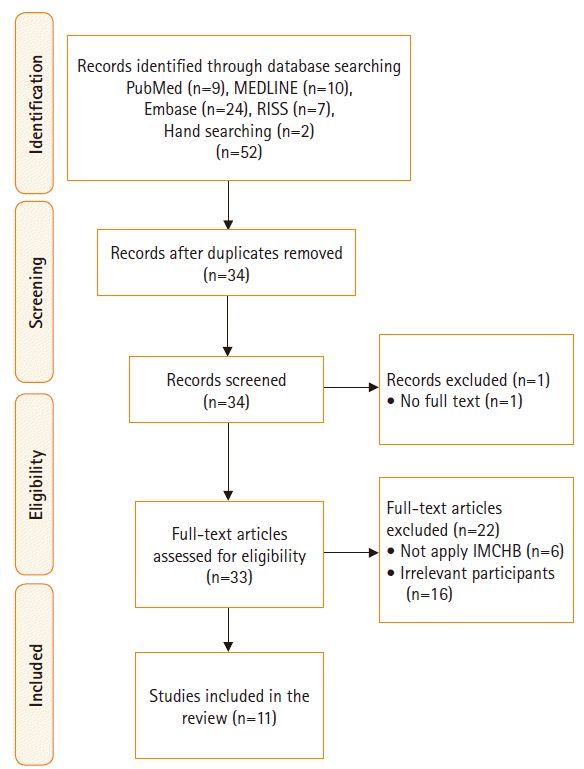
Methods
Design and samples
Data sources
Study selection
Criteria for the evaluation and analysis of theory and literature
Results
General characteristics of the reviewed literature
Table 1.
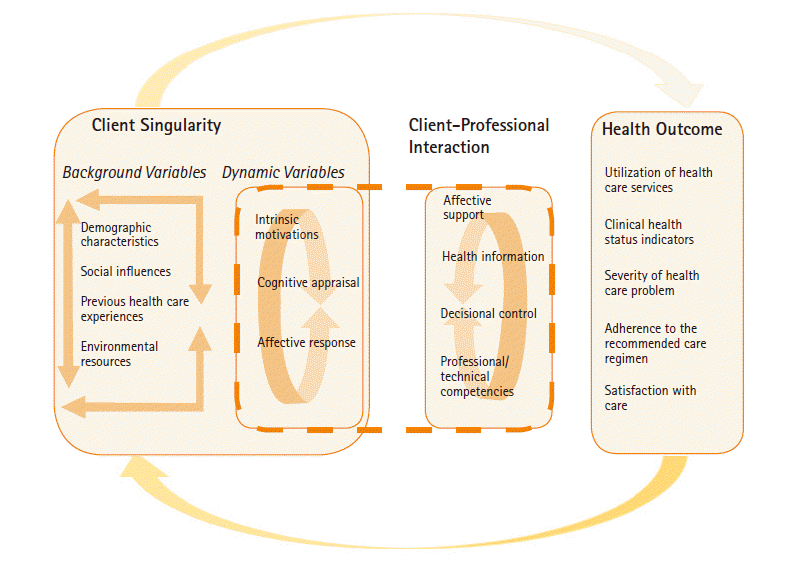
Analysis of the theory
Scope: Level of abstraction
Table 2.
Context: Metaparadigm concepts and propositions
Content: Concepts and propositions
Evaluation of the theory
Significance
Internal consistency
Parsimony
Generality
Testability
Empirical adequacy
Table 3.
| Author, year/ Country | Purpose | Participants | Concept measure | Analytic technique | Main results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ackerson., 2011 [17]/USA | To explore African- American women’s use of Pap smear | 11 women with routine examination (Pap smear) and 13 women with non-routine examination | -Client singularity: age, level of education, income, insurance | Content analysis | The routine and non-routine examination group fit the IMCHB model. Non-routine examination women have negative personal influence. |
| -Outcome: personal influencing factors (social influence, previous health care experience, cognitive appraisal) that contribute to Pap smear testing | |||||
| An et al.,2015 [18]/South Korea | To examine the effect of lifestyle intervention on the development of fatigue, nutritional status and quality of life of patients with gynecological cancer patients | 49 patients with gynecologic cancer patients (E:24; C:25) | -Client singularity: Age, marriage, education, diagnosis, stage, disease period, BMI, body weight, income, fatigue, nutritional states, quality of life | χ2-test, t-test, ANCOVA | Lifestyle intervention was effective in lessening fatigue, and improving nutritional status and social/family well-being |
| -Outcome: FACIT-F, PG-SGA, FACT-G | |||||
| Choi et al., 2011 [19]/USA | To investigate the patterns of physical activity and demographic characteristics with those patterns in Korean immigrants in the USA | 197 women Korean immigrants in the USA | -Client singularity: Age, education, employment, income, marital status, having children | χ2-test, Mann-Whitney tests, ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test, | There was a difference in pattern and amount of activity according to demographic variables (job type, marital status, age, transportation). |
| -Outcome: Physical activity (International physical activity questionnaire) | |||||
| Chun et al., 2017 [20] /South Korea | To examine the effectiveness of a sleep improvement program combined with an aroma-necklace for elderly women | 70 elderly women (E:35; C:35) | -Client singularity: age, religion | χ2-test, t-test, Mann-Whitney test | Group differences were found in sleep quality, sleep duration, sleep satisfaction, depression, and anxiety. |
| - Outcome: CES-D, state trait anxiety inventory- sleep quality, sleep duration, VAS to measure the sleep satisfaction, blood pressure | No differences were found in the systolic or diastolic blood pressure | ||||
| Hanrungcharotorn et al. 2017 [21]/Thailand | To examine the factors influencing physical activity among women with osteoarthritis of the knee | 242 females with osteoarthritis of the knee attending the outpatient | -Client singularity: age, occupational/marital status, education, income, living status, BMI, medical records, onset of diagnosis, comorbidity | Binary logistic regression, multivariate logistic regression, Pearson correlation | BMI and pain-related fear influenced physical activity. Age, knee pain, functional limitation, pain catastrophizing, and social support did not significantly influence physical activity |
| - Outcome: Revised Thai-WOMAC, rMSPSS, CSCSQ, FABQ- PA | |||||
| Kim & Kim., 2013 [22]/South Korea | To examine the effect of an integrated self-management program on self- management, glycemic control, and maternal identity in women with GDM | 55 women with GDM | -Client singularity: Knowledge of GDM, Self-efficacy of GDM management. | χ2-test, Mann-Whitney U test | Integrated self-management program for women with GDM improves self-management, maternal identity, and decreased glycose level. |
| -Outcome: Self-management, maternal identify, 2-hour postprandial glucose levels | There was no statistically significant effect in Hb A1c. | ||||
| Lee et al, 2017 [23]/South Korea | To examine the long-term effectiveness of stretching exercises on the health outcomes of Korean- | 80 Korean-Chinese female migrant workers | -Client-professional interaction: Exercise adherence | χ2-test, t-test, linear mixed model | Community-based stretching program was effective in increasing their flexibility and decreasing work-related musculoskeletal disorder symptoms |
| Chinese female migrant workers | -Outcome: Musculoskeletal fitness, musculoskeletal symptoms, acculturative stress | ||||
| Park & Choi, 2014 [24]/South Korea | To examine reproductive health programs for the improvement of reproductive health of female immigrants and to verify their effectiveness. | 58 female immigrants in South Korea (E:29; C:29) | -Client singularity: Reproductive health knowledge, reproductive health attitude | χ2-test, t-test | Reproductive health program had improved aspects of reproductive health knowledge, reproductive health attitude, and reproductive health behaviors. There were no significant differences in clinical indicators (CBC, urine analysis, vaginal smear) between the experiment group and the control group |
| -Outcome: Reproductive health behavior, clinical indicators (CBC, urine analysis, vaginal smear) | |||||
| Park & Lee., 2018 [25] /South Korea | To compare the effectiveness of the oral health program and walking exercise program for pregnant women | 65 pregnant women (oral health program :23; walking exercise program: 21; C: 21) | - Outcome: Oral health behaviors, nutrition management, international physical activity questionnaire, periodontal disease, CES-D, perceived stress, maternal stress, quality of life related to health (SF-12) | χ2 -test, Fisher’s exact test, ANOVA, repeated measures ANOVA | Oral health program and walking exercise program was effective improvements in oral health behaviors, periodontal disease, and psychological indicators as compared to the control group. |
| Tenfelde et al., 2012 [26]/USA | To examine the factors that affect breastfeeding cessation in low-income mothers | 309 low income breast- feeding participants with special supplemental nutrient program for women | -Client singularity: Age, education, marital status, ethnicity, knowledge of breast-feeding, breast- feeding support, cognitive, motivational, and affective intrapersonal variables | Survival analysis | Risks factors of breastfeeding cessation were younger, not from Mexican descent, and had no breast-feeding support system. |
| -Outcome: Breastfeeding cessation, | |||||
| Wagner et al., 2011 [27]/USA | To investigate the impact of nurses' discharge method on postpartum care | 70 postpartum women in the USA | -Outcome: Self-administered modified client satisfaction tool | χ2-test, Mann-Whitney U test | There is no difference in satisfaction with treatment between demonstration/return demonstration and traditional methods. |
ANOVA: analysis of variance; ANCOVA: analysis of covariance; BMI: body mass index; C: control group; CBC: complete blood count; CES-D: Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale; CSCSQ: the Thai version of the Catastrophizing Subscale of the Coping Strategies Questionnaire; E: experimental group; FABQ-PA: the Thai version of the Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire about Physical Activity; FACIT-F: Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue Scale; FACT-G: Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General; GDM : gestational diabetes mellitus; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; IMCHB: interaction model of client health behavior; Pap: Papanicolaou; PG-SGA: patient-generated subjective global assessment; rMSPSS: the revised Thai Multi-Dimensional scale of Perceived Social Support; SF-12: Short Form 12-item; Thai-WOMAC: Thai version of the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index; VAS: visual analog scale.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download