Abstract
Objectives
We investigated the characteristics of Streptococcus mutans in the national culture collection from Korea. Twenty-nine (dental plaque, n=27; endodontic infections, n=1; blood, n=1) isolates were included in this study.
Methods
Antimicrobial susceptibilities were tested using the disk diffusion test. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST), serotyping, and collagen-binding genes were used for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and direct sequencing. A collagen-binding (to assess the adhesion properties) assay was performed. S. mutans demonstrated high susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. Differences in collagen-binding abilities of the cnm-positive and -negative groups were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test (P<0.05).
Results
MLST analyses revealed 25 sequence types (STs), 17 of which (ST213-ST229) contained new alleles. The strains were classified into four serotypes with the c type encompassing 79.3% of all strains, while the e, f, and k types representing 6.9% each. Analysis of the cnm and cbm genes, which encode the two surface adhesin components of S. mutans, revealed three cnm-positive strains, each displaying greater adhesion ability than those of the cnm-negative strains.
Go to : 
References
1. Ajdić D, McShan WM, McLaughlin RE, Savić G, Chang J, Carson MB, et al. Genome sequence of Streptococcus mutans UA159, a cariogenic dental pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002; 99:14434–14439.
2. Switalski LM, Butcher WG, Caufield PC, Lantz MS. Collagen mediates adhesion of Streptococcus mutans to human dentin. Infect Im-mun. 1993; 61:4119–4125.

3. Miller JH, Avilés-Reyes A, Scott-Anne K, Gregoire S, Watson GE, Sampson E, et al. The collagen binding protein Cnm contributes to oral colonization and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans OMZ175. Infect Immun. 2015; 83:2001–2010.

5. Nakano K, Ooshima T. Serotype classification of Streptococcus mutans and its detection outside the oral cavity. Future Microbiol. 2009; 4:891–902.

6. Nakano K, Nomura R, Nemoto H, Mukai T, Yoshioka H, Shudo Y, et al. Detection of novel serotype k Streptococcus mutans in infective endocarditis patients. J Med Microbiol. 2007; 56:1413–1415.

7. Hirasawa M, Takada K. A new selective medium for Streptococcus mutans and the distribution of S. mutans and S. sobrinus and their serotypes in dental plaque. Caries Res. 2003; 37:212–217.
8. Nakano K, Nomura R, Nakagawa I, Hamada S, Ooshima T. Demonstration of Streptococcus mutans with a cell wall polysaccharide specific to a new serotype, k, in the human oral cavity. J Clin Micro-biol. 2004; 42:198–202.
9. Nakano K, Nomura R, Taniguchi N, Lapirattanakul J, Kojima A, Naka S, et al. Molecular characterization of Streptococcus mutans strains containing the cnm gene encoding a collagen-binding adhesin. Arch Oral Biol. 2010; 55:34–39.

10. Nomura R, Nakano K, Naka S, Nemoto H, Masuda K, Lapirat-tanakul J, et al. Identification and characterization of a collagen-binding protein, Cbm, in Streptococcus mutans. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012; 27:308–323.

11. Sato Y, Okamoto K, Kagami A, Yamamoto Y, Igarashi T, Kizaki H. Streptococcus mutans strains harboring collagen-binding adhesin. J Dent Res. 2004; 83:534–539.

12. Nomura R, Nakano K, Taniguchi N, Lapirattanakul J, Nemoto H, Grönroos L, et al. Molecular and clinical analyses of the gene encoding the collagen-binding adhesin of Streptococcus mutans. J Med Microbiol. 2009; 58:469–475.

13. Nakano K, Hokamura K, Taniguchi N, Wada K, Kudo C, Nomura R, et al. The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke. Nat Commun. 2011; 2:485.

14. Kojima A, Nakano K, Wada K, Takahashi H, Katayama K, Yoneda M, et al. Infection of specific strains of Streptococcus mutans, oral bacteria, confers a risk of ulcerative colitis. Sci Rep. 2012; 2:332.

15. Lapirattanakul J, Nakano K, Nomura R, Hamada S, Nakagawa I, Ooshima T. Demonstration of mother-to-child transmission of Streptococcus mutans using multilocus sequence typing. Caries Res. 2008; 42:466–474.
16. Nomura R, Ogaya Y, Nakano K. Contribution of the collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans to bacterial colonization of inflamed dental pulp. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0159613.

17. Pérez-Losada M, Cabezas P, Castro-Nallar E, Crandall KA. Pathogen typing in the genomics era: MLST and the future of molecular epidemiology. Infect Genet Evol. 2013; 16:38–53.

18. Cai JN, Jung JE, Lee MH, Choi HM, Jeon JG. Sucrose challenges to Streptococcus mutans biofilms and the curve fitting for the biofilm changes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018; 94.

19. Patel J, Cockerill F, Alder J, Bradford P, Eliopoulos G, Hardy D, et al. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-fourth informational supplement. PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2014. 34:p. 1–266.
20. Lapirattanakul J, Nakano K, Nomura R, Leelataweewud P, Chalerm-sarp N, Klaophimai A, et al. Multilocus sequence typing analysis of Streptococcus mutans strains with the cnm gene encoding collagen-binding adhesin. J Med Microbiol. 2011; 60:1677–1684.

21. Momeni SS, Whiddon J, Cheon K, Moser SA, Childers NK. Assessment of two multilocus sequence typing (MLST) schemes available for Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 2015; 60:1769–1776.

22. Nakano K, Nemoto H, Nomura R, Homma H, Yoshioka H, Shudo Y, et al. Serotype distribution of Streptococcus mutans a pathogen of dental caries in cardiovascular specimens from Japanese patients. J Med Microbiol. 2007; 56:551–556.

23. Do T, Gilbert SC, Clark D, Ali F, Fatturi Parolo CC, Maltz M, et al. Generation of diversity in Streptococcus mutans genes demonstrated by MLST. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e9073.

24. Nakano K, Lapirattanakul J, Nomura R, Nemoto H, Alaluusua S, Grönroos L, et al. Streptococcus mutans clonal variation revealed by multilocus sequence typing. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:2616–2625.
25. Lapirattanakul J, Nomura R, Nemoto H, Naka S, Ooshima T, Nakano K. Multilocus sequence typing of Streptococcus mutans strains with the cbm gene encoding a novel collagen-binding protein. Arch Oral Biol. 2013; 58:989–996.

26. Abranches J, Miller JH, Martinez AR, Simpson-Haidaris PJ, Burne RA, Lemos JA. The collagen-binding protein Cnm is required for Streptococcus mutans adherence to and intracellular invasion of human coronary artery endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 2011; 79:2277–2284.

27. Nomura R, Naka S, Nemoto H, Inagaki S, Taniguchi K, Ooshima T, et al. Potential involvement of collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans in infective endocarditis. Oral Dis. 2013; 19:387–393.
28. García-Godoy F, Hicks MJ. Maintaining the integrity of the enamel surface: the role of dental biofilm, saliva and preventive agents in enamel demineralization and remineralization. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008; 139(Suppl):S25–34.
29. Goyal D, Sharma S, Mahmood A. Inhibition of dextransucrase activity in Streptococcus mutans by plant phenolics. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2013; 50:48–53.
30. Shibata Y, Ozaki K, Seki M, Kawato T, Tanaka H, Nakano Y, et al. Analysis of loci required for determination of serotype antigenicity in Streptococcus mutans and its clinical utilization. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:4107–4112.
Go to : 
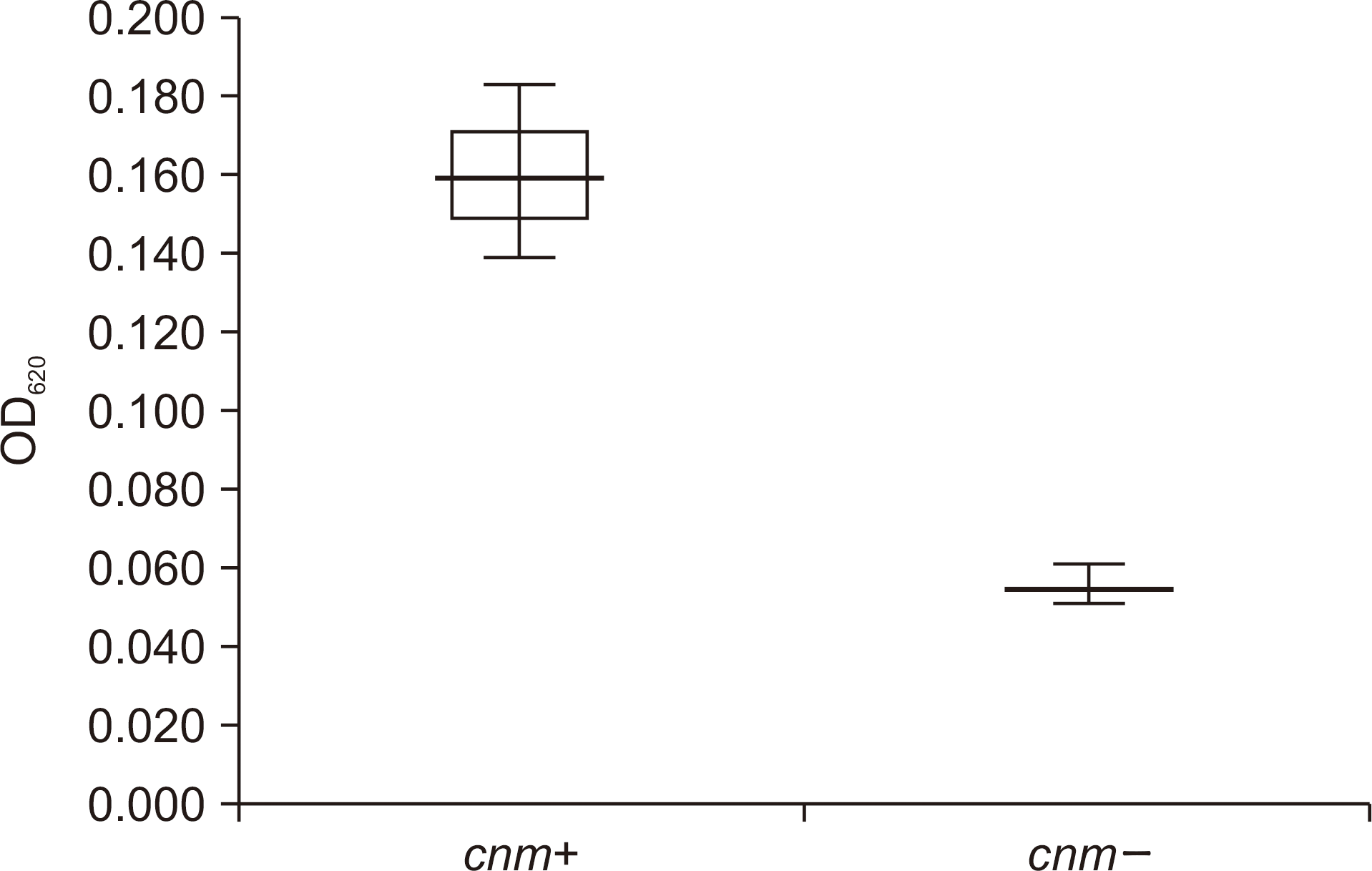 | Fig. 1.Comparison of collagen-binding activities between cnm-positive (cnm+)and cnm-negative (cnm-) strains. |
Table 1.
PCR primers for S. mutans used in this study
Table 2.
Characteristics of S. mutans strains analyzed by PCR and sequencing
Bold letters indicate new alleles and sequence type (ST) registered with PubMLST for S. mutans MLST scheme in this study. tkt (#25), GenBank accession no. AB281747; gltA (#36), GenBank accession no. AB281970; gltA (#37), Genbank accession no. AB281943; gltA (#38), GenBank accession no. AB282001; aroE (#32), GenBank accession no. AB282285; lepC (#35), GenBank accession no. AB282484.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download