Abstract
The consequences of graft failure after liver transplantation (LT) range far beyond the liver. The kidneys are often affected, where persistent and progressive cholestasis can result in acute kidney injury (AKI) leading to the development of bile cast nephropathy (BCN). BCN is an often unrecognized condition that is characterized by proximal tubulopathy and the formation of bile casts in the distal tubules, which is almost diagnosed exclusively on a kidney biopsy or autopsy. This condition is potentially reversible, provided the bilirubin levels can be reduced early. LT may represent a treatment option in the case of irreversible liver (or liver graft) failure, which is beneficial for both the liver and the kidney. This paper reports a case of BCN in a patient with idiopathic graft failure after LT. Despite his chronic kidney disease, liver re-transplantation led to the successful improvement of his AKI.
Go to : 
References
1. Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, et al. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:931–940.

2. Hussaini T, Yoshida EM, Partovi N, et al. Early persistent progressive acute kidney injury and graft failure post liver transplantation. Transplant Direct. 2019; 5:e429.

3. Krones E, Pollheimer MJ, Rosenkranz AR, Fickert P. Cholemic nephropathy - historical notes and novel perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018; 1864(4 Pt B):1356–1366.

4. Aniort J, Poyet A, Kemeny JL, Philipponnet C, Heng AE. Bile cast nephropathy caused by obstructive cholestasis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017; 69:143–146.

5. Chan S, Spraggon ES, Francis L, Wolley MJ. Bile cast nephropathy in a patient with obstructive jaundice. Kidney Int Rep. 2018; 4:338–340.

6. Flores A, Nustas R, Nguyen HL, Rahimi RS. Severe cholestasis and bile acid nephropathy from anabolic steroids successfully treated with plasmapheresis. ACG Case Rep J. 2016; 3:133–135.

7. Torrealba J, Sweed NT, Burguete D, Hendricks AR. Bile cast nephropathy: a pathologic finding with manifold causes dis-played in an adult with alcoholic steatohepatitis and in a child with Wilson's disease. Case Rep Nephrol Dial. 2018; 8:207–215.

8. Betjes MG, Bajema I. The pathology of jaundice-related renal in-sufficiency: cholemic nephrosis revisited. J Nephrol. 2006; 19:229–233.
9. Fickert P, Krones E, Pollheimer MJ, et al. Bile acids trigger cholemic nephropathy in common bile-duct-ligated mice. Hepatology. 2013; 58:2056–2069.

10. Krones E, Wagner M, Eller K, Rosenkranz AR, Trauner M, Fickert P. Bile acid-induced cholemic nephropathy. Dig Dis. 2015; 33:367–375.

11. van Slambrouck CM, Salem F, Meehan SM, Chang A. Bile cast nephropathy is a common pathologic finding for kidney injury associated with severe liver dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2013; 84:192–197.

12. Rector WG Jr, Kanel GC, Rakela J, Reynolds TB. Tubular dysfunction in the deeply jaundiced patient with hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatology. 1985; 5:321–326.

13. Bairaktari E, Liamis G, Tsolas O, Elisaf M. Partially reversible renal tubular damage in patients with obstructive jaundice. Hepatology. 2001; 33:1365–1369.

14. Bomzon A, Holt S, Moore K. Bile acids, oxidative stress, and renal function in biliary obstruction. Semin Nephrol. 1997; 17:549–562.
15. Chawla LS, Eggers PW, Star RA, Kimmel PL. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:58–66.

16. Pitlick M, Rastogi P. All that glitters yellow is not gold: presentation and pathophysiology of bile cast nephropathy. Int J Surg Pathol. 2017; 25:652–658.

17. Sens F, Bacchetta J, Rabeyrin M, Juillard L. Efficacy of extracorporeal albumin dialysis for acute kidney injury due to cholestatic jaundice nephrotoxicity. BMJ Case Rep. 2016; 2016:bcr2015213257.

18. Patel J, Walayat S, Kalva N, Palmer-Hill S, Dhillon S. Bile cast nephropathy: a case report and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:6328–6334.

Go to : 
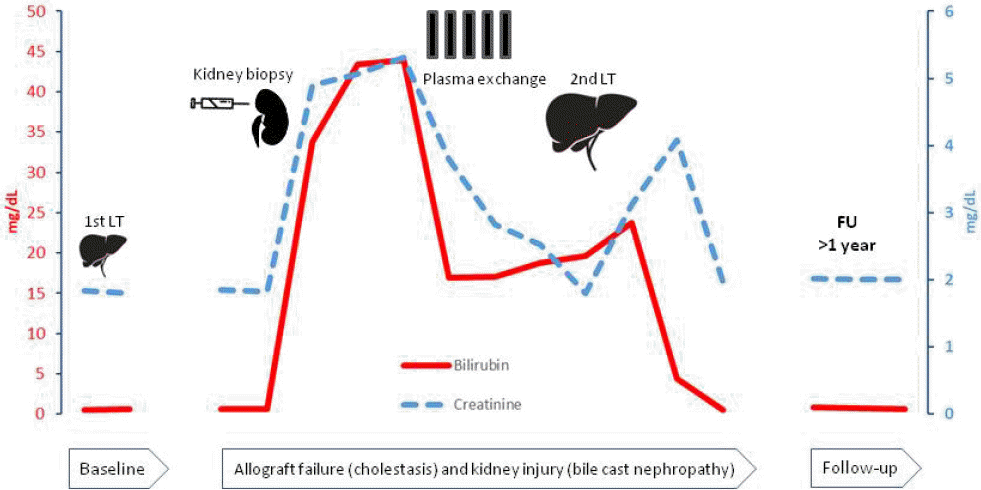 | Fig. 1.Clinical course of liver allograft failure with the development of bile cast nephropathy. The graph shows the bilirubin (red) and creatinine (blue) values in three different periods; 1) baseline period (after the first liver transplant), 2) period of allograft failure with major events; kidney biopsy, plasma exchange (five sessions) and liver re-transplantation with early post-transplant period and 3) long-term follow-up (>1 year after liver re-transplantation). LT, liver transplantation; FU, follow-up. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



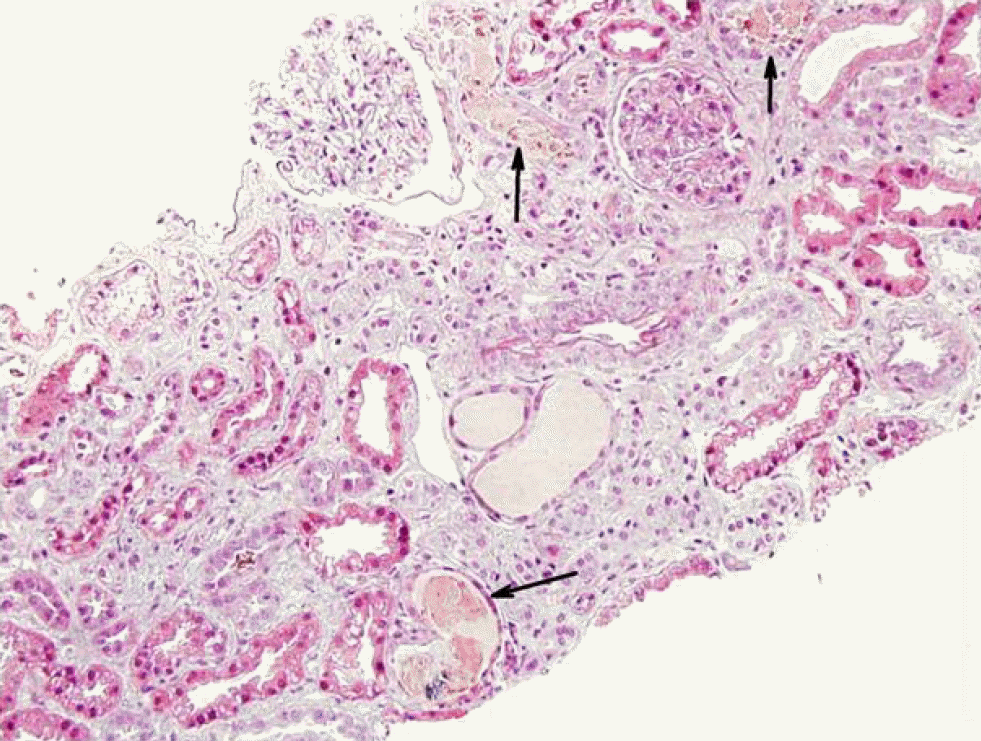
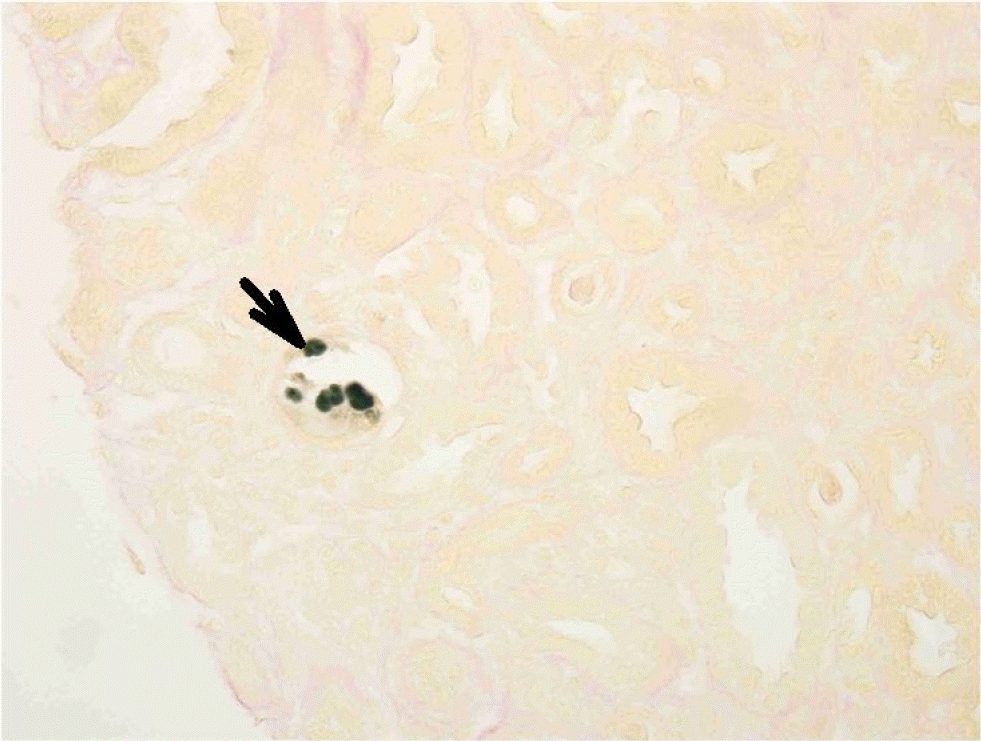
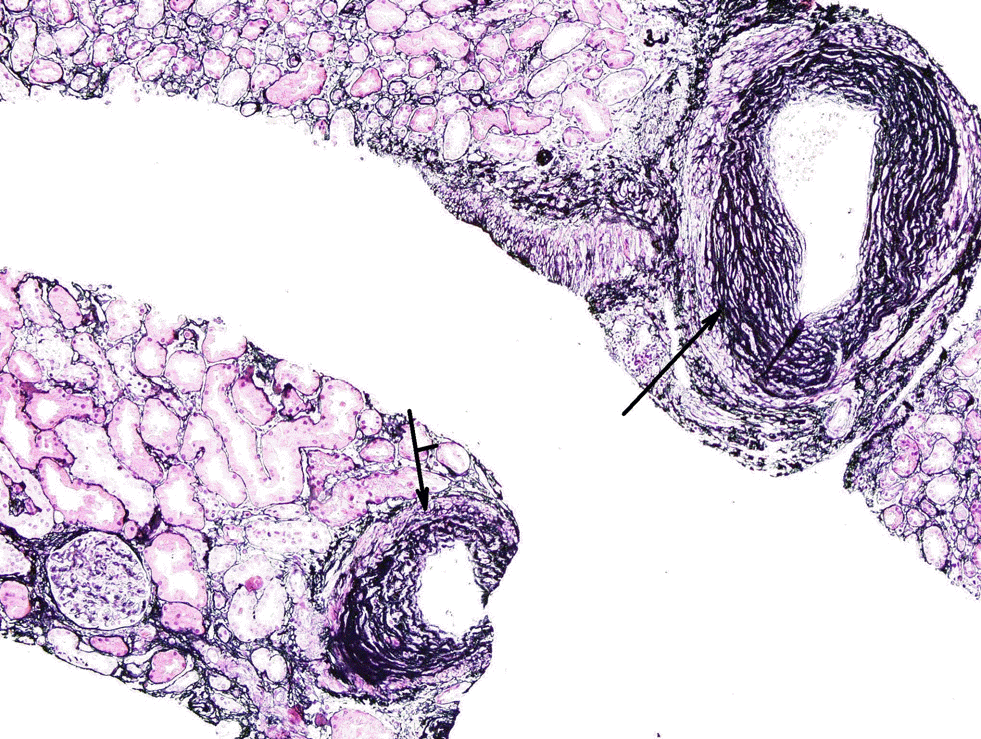
 XML Download
XML Download