1. Sotiropoulos GC, Lang H, Frilling A, et al. Resectability of hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of 333 consecutive cases at a single hepatobiliary specialty center and systematic review of the literature. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006; 53:322–329.
2. Park JW, Chen M, Colombo M, et al. Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management from diagnosis to death: the BRIDGE Study. Liver Int. 2015; 35:2155–2166.
3. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 2003; 37:429–442.

4. Bruix J, Sala M, Llovet JM. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127(5 Suppl 1):S179–S188.

5. Ogasawara S, Chiba T, Ooka Y, et al. Efficacy of sorafenib in inter-mediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients refractory to transarterial chemoembolization. Oncology. 2014; 87:330–341.

6. Korean Liver Cancer Association, National Cancer Center. 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut Liver. 2019; 13:227–299.
7. Yamanaka K, Hatano E, Kitamura K, et al. Early evaluation of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization-refractory hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47:343–346.

8. Kim HY, Park JW, Joo J, et al. Severity and timing of progression predict refractoriness to transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:1051–1056.

9. Kudo M, Izumi N, Kokudo N, et al. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: consensus-based clinical practice guidelines proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated version. Dig Dis. 2011; 29:339–364.

10. European Association For The Study Of The Liver, European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943.
11. Sieghart W, Hucke F, Pinter M, et al. The ART of decision making: retreatment with transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013; 57:2261–2273.

12. Bruix J, Raoul JL, Sherman M, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: sub-analyses of a phase III trial. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:821–829.

13. Hollebecque A, Cattan S, Romano O, et al. Safety and efficacy of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: the impact of the Child-Pugh score. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:1193–1201.

14. Kim JE, Ryoo BY, Ryu MH, et al. Sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma according to Child-Pugh class of liver function. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011; 68:1285–1290.

15. Marrero JA, Kudo M, Venook AP, et al. Observational registry of sorafenib use in clinical practice across Child-Pugh subgroups: the GIDEON study. J Hepatol. 2016; 65:1140–1147.

16. Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010; 30:52–60.

17. Kadalayil L, Benini R, Pallan L, et al. A simple prognostic scoring system for patients receiving transarterial embolisation for hepatocellular cancer. Ann Oncol. 2013; 24:2565–2570.

18. Pinato DJ, Arizumi T, Allara E, et al. Validation of the hepatoma arterial embolization prognostic score in European and Asian populations and proposed modification. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:1204–1208.e2.
19. Chan AO, Yuen MF, Hui CK, Tso WK, Lai CL. A prospective study regarding the complications of transcatheter intraarterial lip-iodol chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2002; 94:1747–1752.

20. Hwang JI, Chow WK, Hung SW, et al. Development of a safety index of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma to prevent acute liver damage. Anticancer Res. 2005; 25(3c):2551–2554.
21. Kudo M. A new era of systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with regorafenib and lenvatinib. Liver Cancer. 2017; 6:177–184.

22. Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018; 391:1301–1314.

23. Kim DY. New systemic therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019; 73:10–15.

24. Dika IE, Abou-Alfa GK. Treatment options after sorafenib failure in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2017; 23:273–239.

25. Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018; 391:1163–1173.

26. Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017; 389:56–66.

27. Villanueva A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:1450–1462.

28. Chung JW. Recent advance in international management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; 56:972–982.

29. Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Ikuno M, Okumura K, Yoshida M. Ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinoma guided by automated tumor-feeders detection software: technical success and short-term tumor response. Abdom Imaging. 2014; 39:645–656.

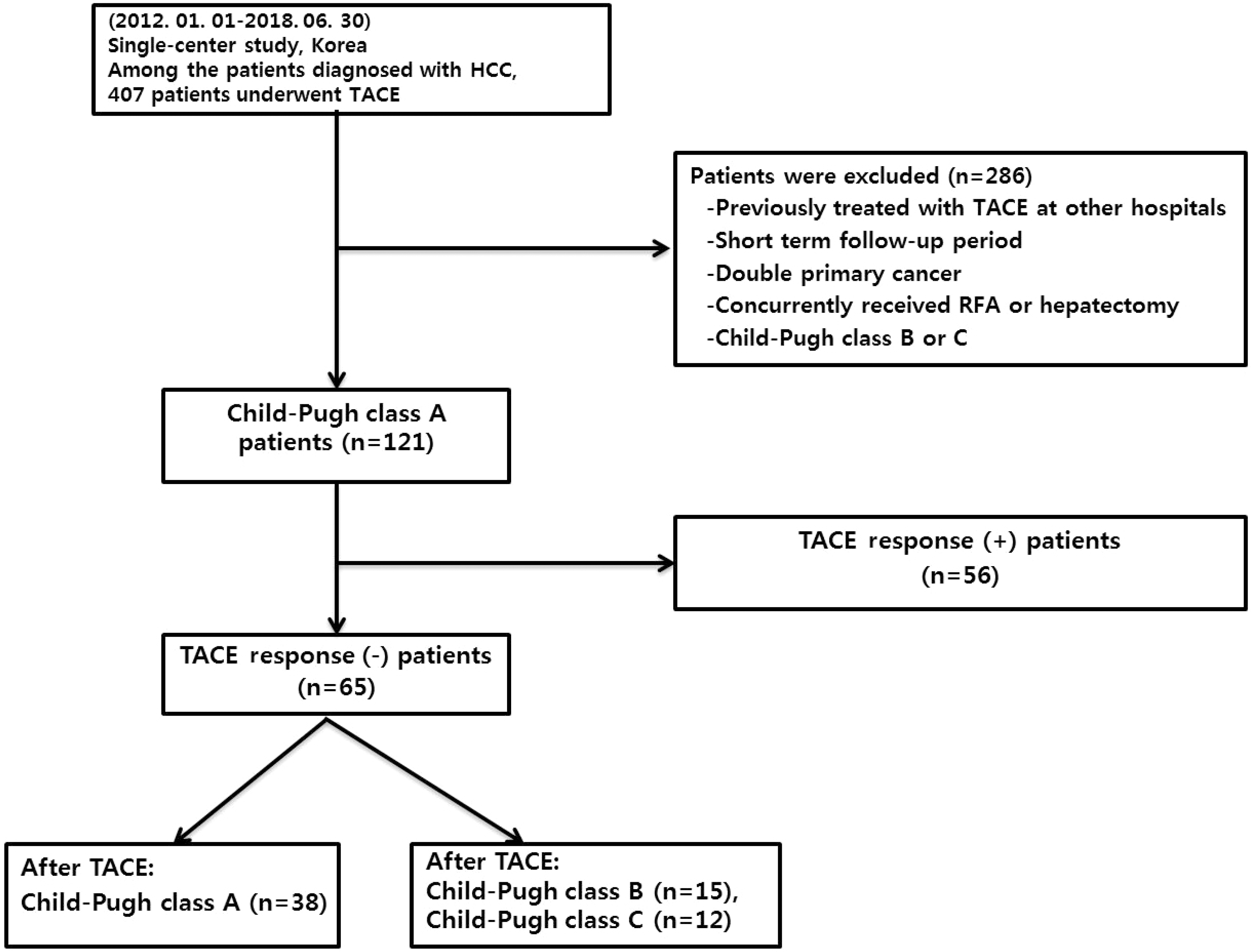
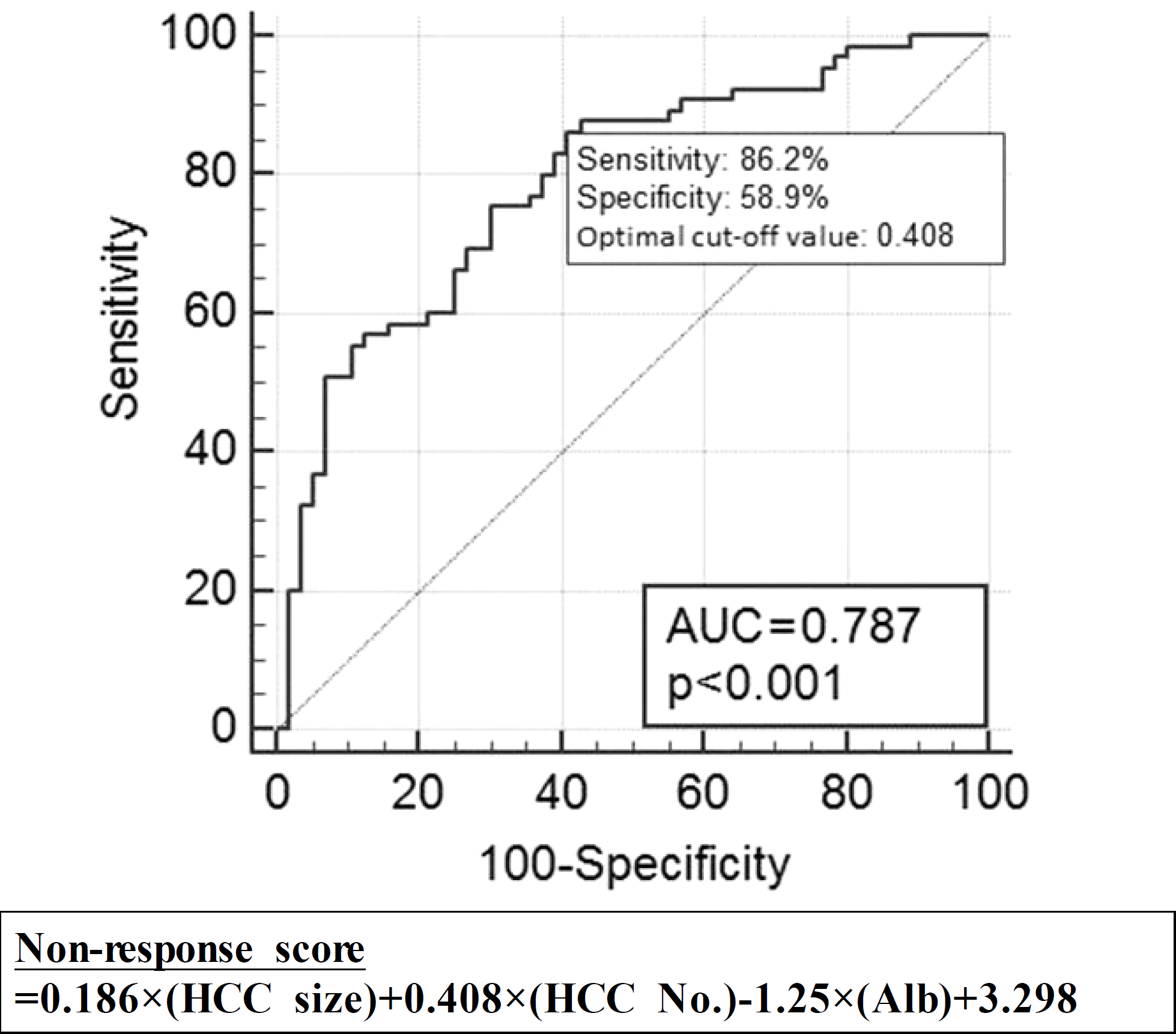
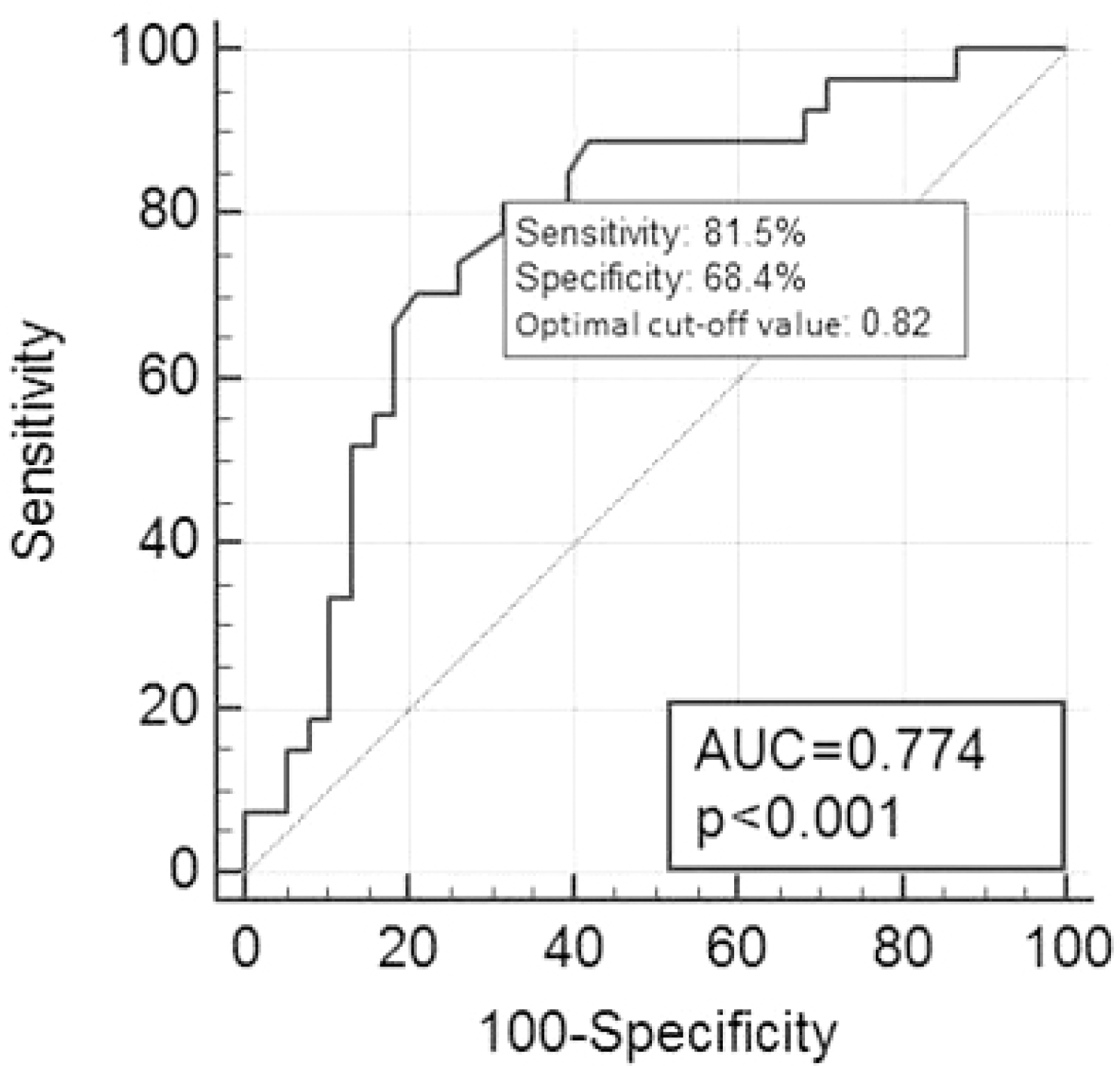
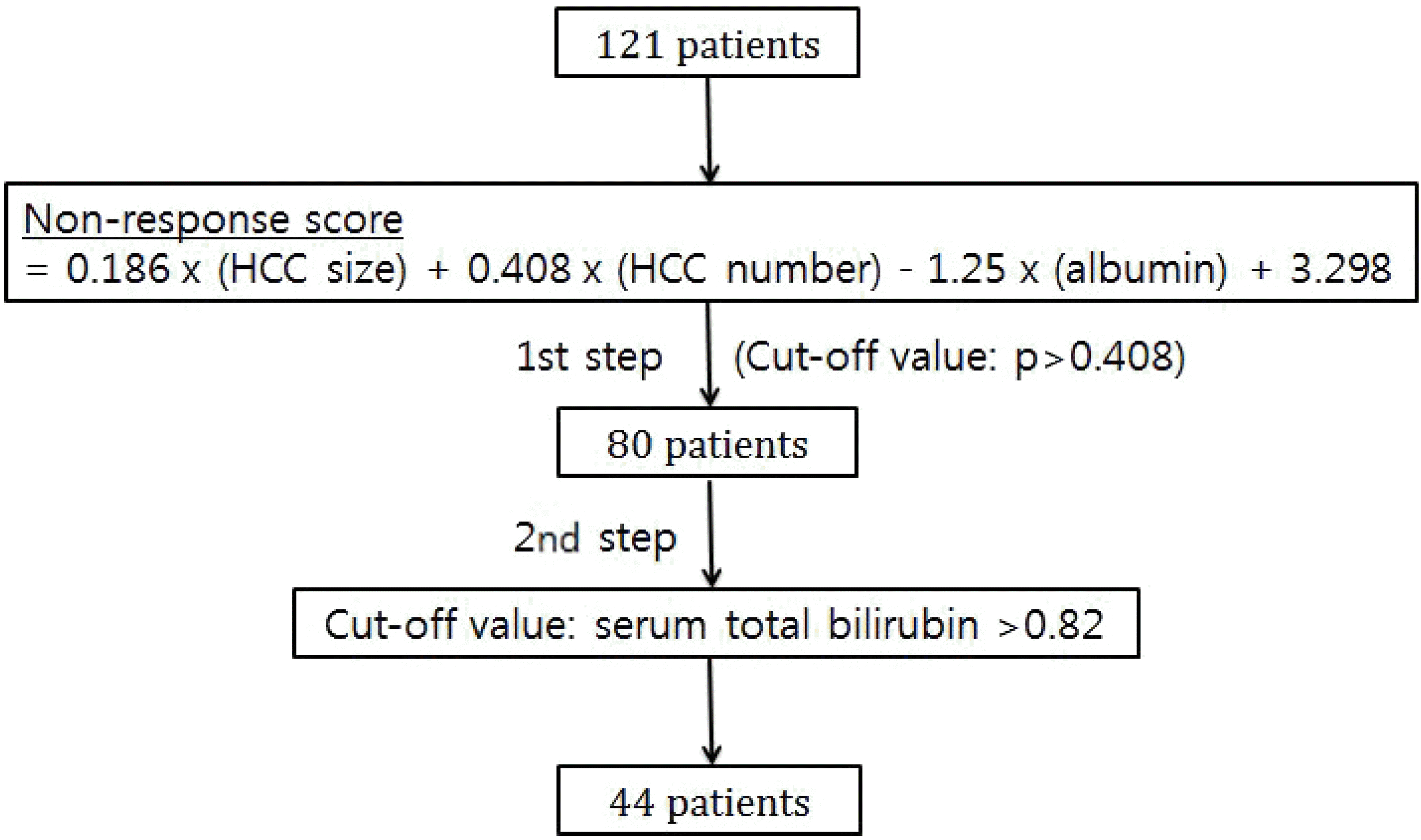




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download