Abstract
Background/Aims
Dysbiosis is an important factor in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Several studies have reported promising results using probiotics for the treatment of IBS. This study evaluated the efficacy of novel probiotics isolated from Kimchi, a Korean fermented food, and the feces of healthy Vietnamese people in a murine model of IBS.
Methods
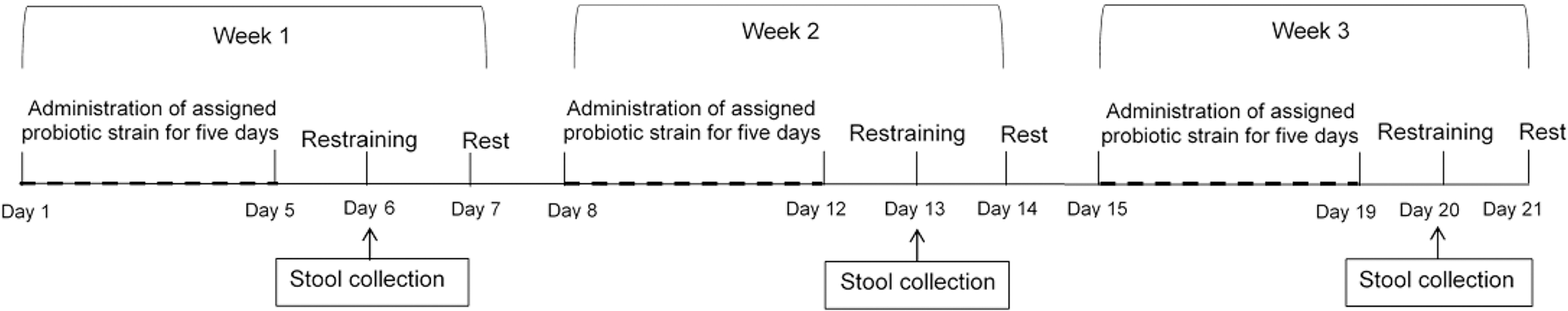
Lactobacillus paracasei DK121 was isolated from Kimchi, and L. salivarius V4 and L. plantarum V7 were isolated from the feces of healthy Vietnamese people residing in Korea. Forty rats were allocated to receive one of the study strains, a mixture of the strains, or the vehicle. After 5 days of administration, the rats were restrained in a cage to induce IBS. The effects of the probiotics on IBS were analyzed by evaluating the stool weights and stool consistency scores.
Results
The primary outcome was analyzed upon the completion of a three-week experiment. The rats in the V7 group showed lower stool weights than those in the control group at week 2 (median: 1.10 [V7] vs. 2.35 [control], p=0.04, Mann-Whitney U-test) and week 3 (median: 1.10 [V7] vs. 2.80 [control], p=0.017). The rats in the DK121 (median: 2.00, p=0.007), V7 (median: 2.00, p=0.004), and mixture (median: 1.50, p=0.001) groups showed better stool consistency scores at week 2 than the control group (median: 3.00).
Go to : 
References
2. Chey WD, Kurlander J, Eswaran S. Irritable bowel syndrome: a clinical review. JAMA. 2015; 313:949–958.
3. Makharia GK, Verma AK, Amarchand R, et al. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome: a community based study from northern India. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011; 17:82–87.

4. Quigley EMM. The gut-brain axis and the microbiome: clues to pathophysiology and opportunities for novel management strategies in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J Clin Med. 2018; 7:E6.

5. Pimentel M. Evidence-based management of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Am J Manag Care. 2018; 24(3 Suppl):S35–S46.
6. Principi N, Cozzali R, Farinelli E, Brusaferro A, Esposito S. Gut dysbiosis and irritable bowel syndrome: the potential role of probiotics. J Infect. 2018; 76:111–120.

7. Zhang Y, Li L, Guo C, et al. Effects of probiotic type, dose and treatment duration on irritable bowel syndrome diagnosed by Rome III criteria: a meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016; 16:62.

8. Whelan K, Quigley EM. Probiotics in the management of irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2013; 29:184–189.

9. Eutamene H, Lamine F, Chabo C, et al. Synergy between Lactobacillus paracasei and its bacterial products to counteract stress-induced gut permeability and sensitivity increase in rats. J Nutr. 2007; 137:1901–1907.

10. Moayyedi P, Ford AC, Talley NJ, et al. The efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review. Gut. 2010; 59:325–332.

11. Hungin AP, Mulligan C, Pot B, et al. Systematic review: probiotics in the management of lower gastrointestinal symptoms in clinical practice – an evidence-based international guide. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 38:864–886.

12. Williams CL, Villar RG, Peterson JM, Burks TF. Stress-induced changes in intestinal transit in the rat: a model for irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1988; 94:611–621.

13. Gué M, Del Rio-Lacheze C, Eutamene H, Théodorou V, Fioramonti J, Buéno L. Stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity to rectal distension in rats: role of CRF and mast cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1997; 9:271–279.

14. Distrutti E, Monaldi L, Ricci P, Fiorucci S. Gut microbiota role in irritable bowel syndrome: new therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:2219–2241.

15. Ford AC, Moayyedi P, Lacy BE, et al. American College of Gastroenterology monograph on the management of irritable bowel syndrome and chronic idiopathic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109(Suppl 1):S2–S26.

16. Stern EK, Brenner DM. Gut microbiota-based therapies for irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018; 9:e134.

17. Zhuang X, Xiong L, Li L, Li M, Chen M. Alterations of gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32:28–38.

18. Cho YH, Hong SM, Kim CH. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from Kimchi, Korean traditional fermented food to apply into fermented dairy products. Korean J Food Sci An. 2013; 33:75–82.

19. Shin HS, Yoo SH, Jang JA, Won JY, Kim CH. Probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from feces and Kimchi. J Milk Sci Biotechnol. 2017; 35:255–261.
20. Trentacosti AM, He R, Burke LB, Griebel D, Kennedy DL. Evolution of clinical trials for irritable bowel syndrome: issues in end points and study design. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:731–735.

21. Kobayashi S, Ikeda K, Suzuki M, Yamada T, Miyata K. Effects of YM905, a novel muscarinic M3-receptor antagonist, on ex-perimental models of bowel dysfunction in vivo. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2001; 86:281–288.

22. Dai C, Guandalini S, Zhao DH, Jiang M. Antinociceptive effect of VSL#3 on visceral hypersensitivity in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome: a possible action through nitric oxide pathway and enhance barrier function. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012; 362:43–53.

23. Miyata K, Ito H, Fukudo S. Involvement of the 5-HT3 receptor in CRH-induce defecation in rats. Am J Physiol. 1998; 274:G827–G831.
24. Traini C, Evangelista S, Girod V, Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Vannucchi MG. Changes of excitatory and inhibitory neuro-transmitters in the colon of rats underwent to the wrap partial re-straint stress. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016; 28:1172–1185.

25. Bashashati M, Moossavi S, Cremon C, et al. Colonic immune cells in irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018; 30:e13192.

26. Bradesi S, Schwetz I, Ennes HS, et al. Repeated exposure to water avoidance stress in rats: a new model for sustained visceral hyperalgesia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005; 289:G42–G53.

27. Barreau F, Salvador-Cartier C, Houdeau E, Bueno L, Fioramonti J. Long-term alterations of colonic nerve-mast cell interactions induced by neonatal maternal deprivation in rats. Gut. 2008; 57:582–590.

28. Lee JY, Kim N, Nam RH, et al. Probiotics reduce repeated water avoidance stress-induced colonic microinflammation in Wistar rats in a sex-specific manner. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0188992.

29. Chen CC, Chow B, Sun Y, et al. Probiotic-mediated protection against chronic water-avoidance stress enteritis in mice is associated with lamina propria plasmacytoid dendritic cell infiltration. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152:S622.

30. Min YW, Rhee PL. The clinical potential of ramosetron in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D). Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2015; 8:136–142.

31. Hungin APS, Mitchell CR, Whorwell P, et al. Systematic review: probiotics in the management of lower gastrointestinal symptoms - an updated evidence-based international consensus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 47:1054–1070.

32. Pace F, Pace M, Quartarone G. Probiotics in digestive diseases: focus on Lactobacillus GG. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2015; 61:273–292.
33. Clarke G, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Quigley EM. Review article: probiotics for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome–focus on lactic acid bacteria. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:403–413.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 2.Cylindrical cage used to confine the rats during the experiment (diameter, 70 mm; height, 220 mm). Each rat was restrained in this cage for 1 hour on days 6, 13, and 20, provoking stress-induced defecation. |
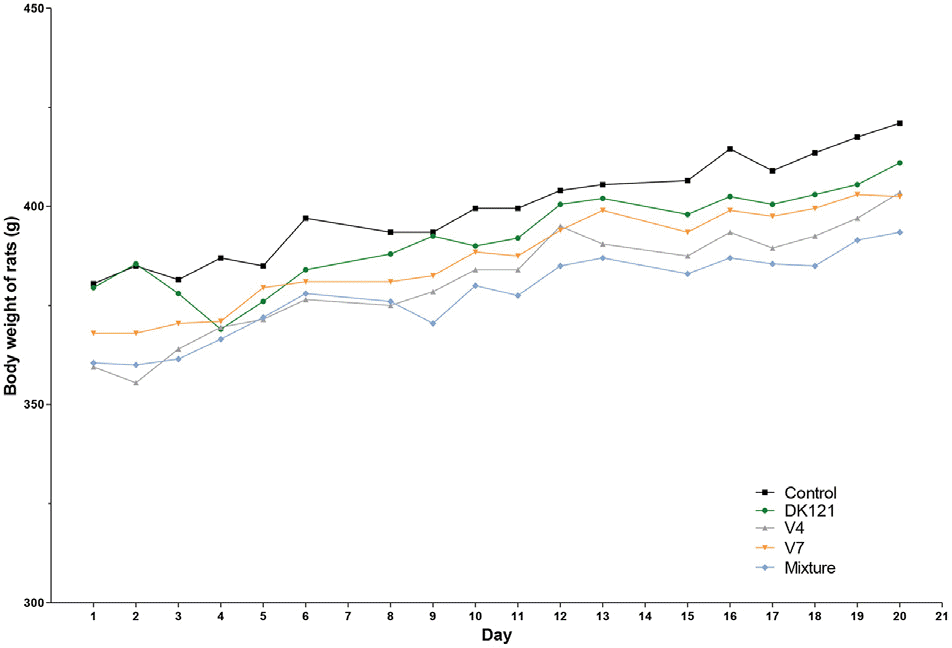 | Fig. 3.Body weights of rats during the 3-week study period. Each dot represents the median body weight (g) of the rats in the assigned group. |
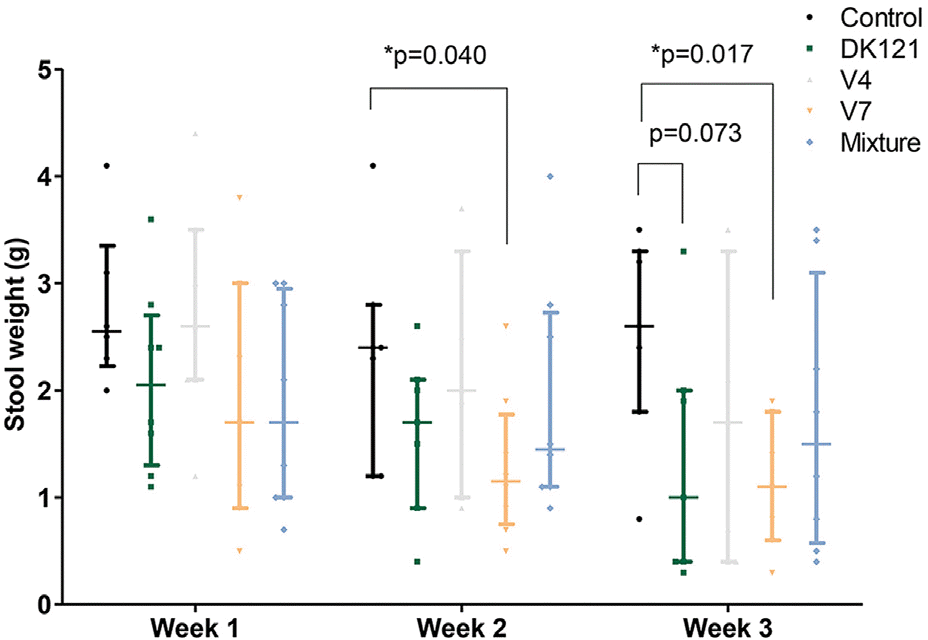 | Fig. 4.Stool weights of the rats in each study group during the 3 weeks of probiotics administration. The rats in the V7 group had lower stool weights than those in the control group at weeks 2 (p=0.040) and 3 (p=0.017). The rats in the DK121 group had lower stool weights than the control group at week 3 with marginal statistical significance (p=0.073). ∗ The lines are the median and interquartile range of the eight animals in each group. Each value is shown as a scatter dot. Lines and scatter dots are shown for the control, DK121, V4, V7, and the mixture groups. |
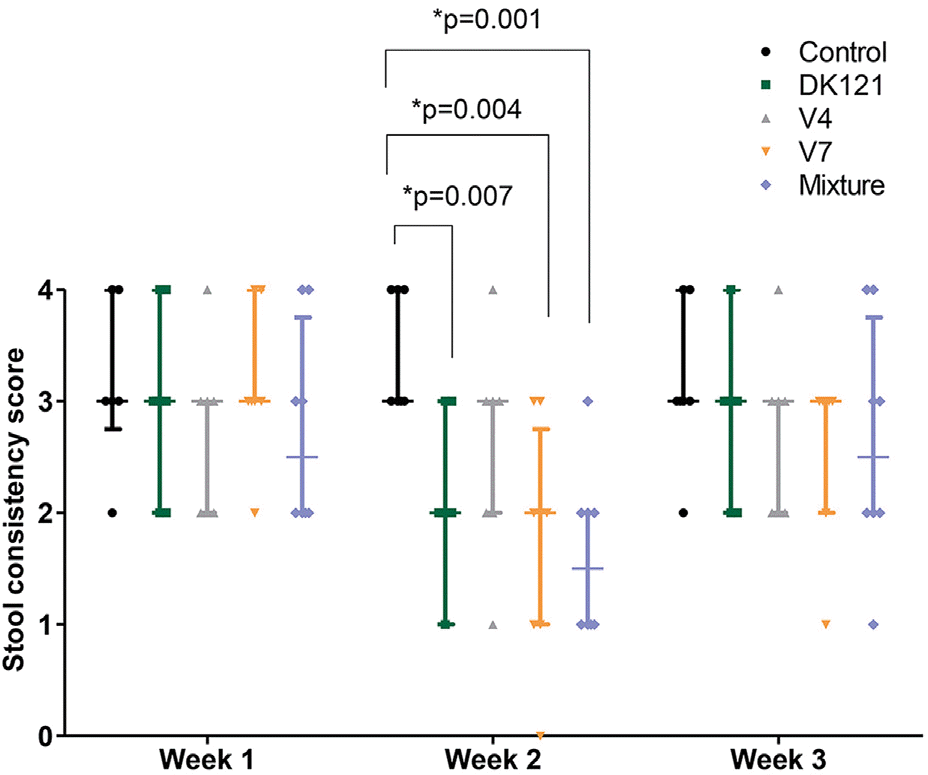 | Fig. 5.Stool consistency scores of the rats in each study group during the 3-week probiotics treatment experiment. The rats in the DK121(p=0.007), V7 (p=0.004), and the mixture (p=0.001) groups showed better (lower) stool consistency scores than the control group at week 2. No significant difference was observed among the study groups at week 3. ∗ The lines represent the median and interquartile range of the eight animals in each group. Each value is shown as a scatter dot. The lines and scatter dots are shown for the control, DK121, V4, V7, and the mixture groups. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download