Abstract
The treatment of adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) aims to control systemic inflammation and prevent organ damage. Systemic inflammation can be controlled with corticosteroid (CS) monotherapy in most cases. However, symptoms often flare as CS is tapered, often requiring long-term CS treatment, with its associated risks of infection, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are often used as CS-sparing agents; however, the choice of DMARD has been largely empirical. Methotrexate (MTX) is recommended as the first-line steroid-sparing drug due to its well-known efficacy and safety in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). When MTX treatment is unsuccessful in AOSD, the choice of a second-line drug has not been established. In RA, leflunomide (LEF) has been used as an alternative to or in combination with MTX. To date, there has been no adequate assessment of the combination of LEF and MTX in AOSD. Here, we report a case of refractory chronic AOSD successfully treated with the MTX-LEF combination.
REFERENCES
1. Govoni M, Bortoluzzi A, Rossi D, Modena V. How I treat patients with adult onset Still's disease in clinical practice. Autoimmun Rev. 2017; 16:1016–23.

2. van der Goes MC, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW. The value of glucocorticoid co-therapy in different rheumatic diseases–positive and adverse effects. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014; 16(Suppl 2):S2.
3. Mimura T, Kondo Y, Ohta A, Iwamoto M, Ota A, Okamoto N, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline for adult Still's disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2018; 28:736–57.

4. Fautrel B, Borget C, Rozenberg S, Meyer O, Le Loët X, Masson C, et al. Corticosteroid sparing effect of low dose methotrexate treatment in adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1999; 26:373–8.
5. Cefle A. Leflunomide and azathioprine combination in refractory adult-onset Still's disease. Ann Pharmacother. 2005; 39:764–7.

6. Pirildar T. Treatment of adult-onset Still's disease with leflunomide and chloroquine combination in two patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2003; 22:157.
7. Sayarlioglu M, Ucmak H, Ozkaya M, Ucar MA, Sayarlioglu H. Leflunomide and methotrexate combination in refractory adult-onset Still's disease. Ann Pharmacother. 2007; 41:1319–20.

8. Sayarlioglu M, Sahin M, Cetin GY, Avan R, Cerit M. Maternal exposure to leflunomide and methotrexate in a patient with adult-onset Still's disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:1787–9.

9. Kong XD, Xu D, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Zeng X, Zhang F. Clinical features and prognosis in adult-onset Still's disease: a study of 104 cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 29:1015–9.

10. Teschner S, Burst V. Leflunomide: a drug with a potential beyond rheumatology. Immunotherapy. 2010; 2:637–50.

11. Cherwinski HM, McCarley D, Schatzman R, Devens B, Ransom JT. The immunosuppressant leflunomide inhibits lymphocyte progression through cell cycle by a novel mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995; 272:460–8.
12. Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH. Rheumatology. 5th ed.Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier;2011.
13. Yao Y, Ding CZ, Fang Y. Combination of MTX and LEF attenuates inflammatory bone erosion by downregulation of receptor activator of NF-kB ligand and interleukin-17 in type II collagen-induced arthritis rats. Rheumatol Int. 2013; 33:1845–53.

14. Kremer JM, Genovese MC, Cannon GW, Caldwell JR, Cush JJ, Furst DE, et al. Concomitant leflunomide therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite stable doses of methotrexate. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 137:726–33.
Figure 1.
Changes in laboratory test results of the patient after a diagnosis of AOSD. Asterisk represents flare. AOSD: adult-onset Still's disease, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hs-CRP: high sensitivity C-reactive protein, WBC: white blood cell, LEF: leflunomide, MTX: methotrexate.
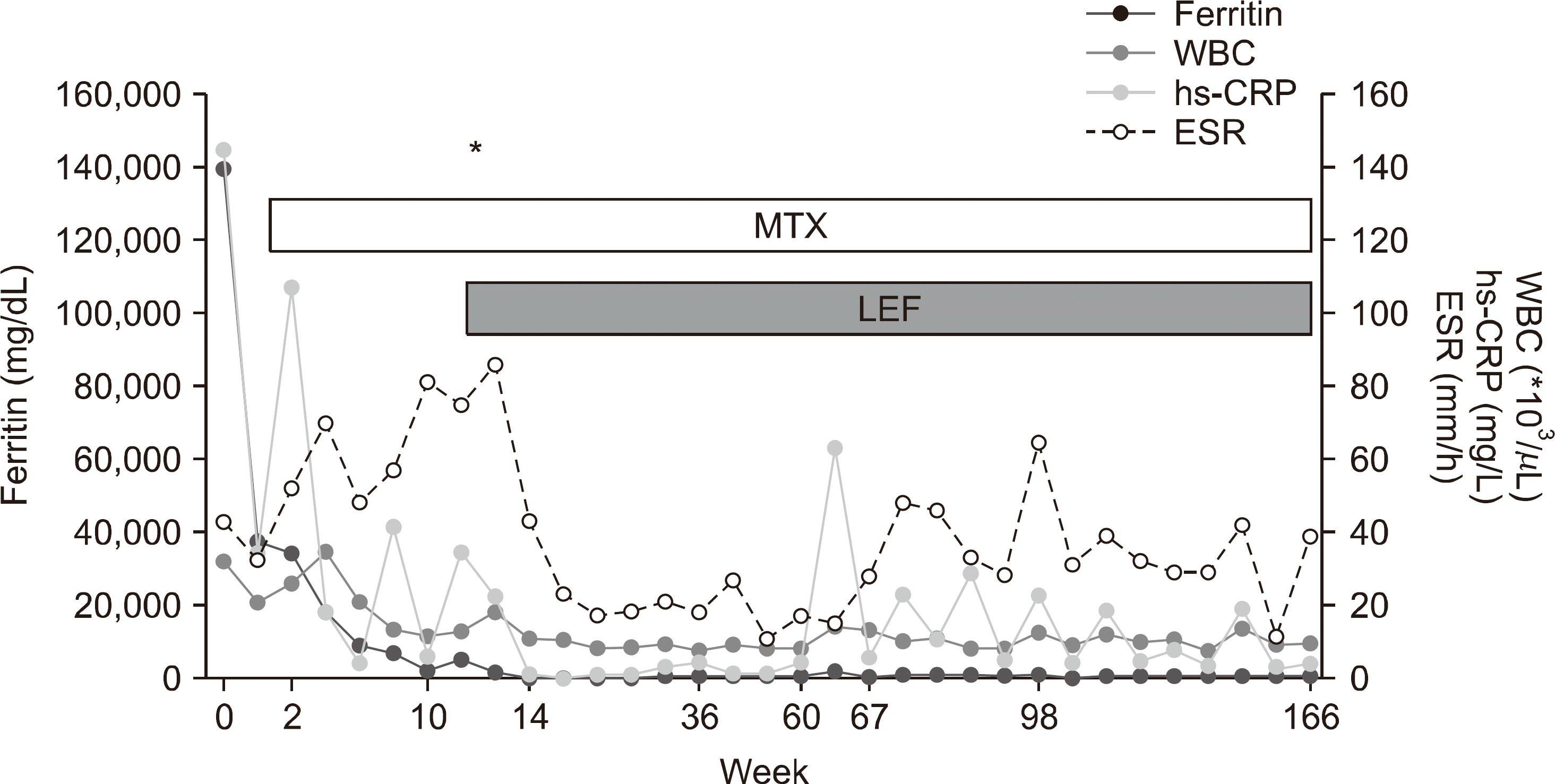
Table 1.
Summary of the literature




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download