Abstract
Canine adenovirus type 1 (CAV-1) causes infectious hepatitis in members of the family Canidae, including dogs. An indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (I-ELISA) that detects CAV-1 antibodies is required for large-throughput tests of dog sera. We collected 165 serum samples from dogs of Chungbuk and Gyeongbuk provinces between February 2016 and October 2018. The Korean CAV-1 vaccine strain CAV1V was propagated in Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells and purified via Nuvia cPrime anion-exchange chromatography; the virus served as an I-ELISA antigen. Virus-neutralizing anti-CAV-1 titers in dog sera were measured using the virus neutralization (VN) method. The I-ELISA was optimized using purified CAV-1 antigen and serum samples. This kit was used to evaluate dog sera. The VN and I-ELISA data were compared. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the I-ELISA were 97.0%, 74.2%, and 92.7% compared to the VN assay, respectively. The I-ELISA data significantly correlated with those of VN (r = 0.88). These results suggest that the I-ELISA is useful for serosurveillance of CAV-1 in dog sera.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Hu RL, Huang G, Qiu W, Zhong ZH, Xia XZ, Yin Z. Detection and differentiation of CAV-1 and CAV-2 by polymerase chain reaction. Vet Res Commun. 2001; 25:77–84.
2). Timurkan MO, Aydin H, Alkan F. Detection and molecular characterization of canine adenovirus type 2 (CAV-2) in dogs with respiratory tract symptoms in shelters in Turkey. Veterinarski arhiv. 2018; 88:467–79.
3). Liu YC, Abouhaidar MG, Sira S, Campbell JB. Characterization of the genome of a vaccine strain of canine adenovirus type 1. Virus Genes. 1988; 2:69–81.

5). Walker D, Abbondati E, Cox AL, Mitchell GB, Pizzi R, Sharp CP, et al. Infectious canine hepatitis in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in wildlife rescue centres in the UK. Vet Rec. 2016; 178:421.
7). Choi JW, Lee HK, Kim SH, Kim YH, Lee KK, Lee MH, et al. Canine adenovirus type 1 in a fennec fox (Vulpes zerda). J Zoo Wildl Med. 2014; 45:947–50.

8). Cabasso VJ. Infectious canine hepatitis virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962; 101:498–514.
9). Wong M, Woolford L, Hasan NH, Hemmatzadeh F. A Novel Recombinant Canine Adenovirus Type 1 Detected from Acute Lethal Cases of Infectious Canine Hepatitis. Viral Immunol. 2017; 30:258–63.

10). Yang DK, Kim HH, Yoon SS, Ji M, Cho IS. Incidence and Sero-survey of Canine Adenovirus Type 2 in Various Animal Species. J Bacteriol Virol. 2018; 48:102–8.

11). Marusyk RG, Yamamoto T. Characterization of a canine adenovirus hemagglutinin. Can J Microbiol. 1971; 17:151–5.

12). Noon KF, Rogul M, Binn LN, Keefe TJ, Marchwicki RH, Thomas R, et al. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of canine antibodies to canine adenoviruses. Lab Anim Sci. 1979; 29:603–9.
13). Segura MM, Puig M, Monfar M, Chilló n M. Chromatography purification of canine adenoviral vectors. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2012; 23:182–97.

14). Coronel J, Behrendt I, Bü rgin T, Anderlei T, Sandig V, Reichl U, et al. Influenza A virus production in a single-use orbital shaken bioreactor with ATF or TFF perfusion systems. Vaccine. 2019; 37:7011–8.

15). Muhamuda K, Madhusudana SN, Ravi V. Development and evaluation of a competitive ELISA for estimation of rabies neutralizing antibodies after post-exposure rabies vaccination in humans. Int J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:441–5.

16). Gschwender HH, Brummund M, Lehmann-Grube F. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus. I. Concentration and purification of the infectious virus. J Virol. 1975; 15:1317–22.

17). Schagen FH, Rademaker HJ, Rabelink MJ, van Ormondt H, Fallaux FJ, van der Eb AJ, et al. Ammonium sulphate precipitation of recombinant adenovirus from culture medium: an easy method to increase the total virus yield. Gene Ther. 2000; 7:1570–4.

18). Kanegae Y, Makimura M, Saito I. A simple and efficient method for purification of infectious recombinant adenovirus. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1994; 47:157–66.

19). Yang DK, Kim HH, Lee SH, Ji M, Cho IS. Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Rabies Virus Antibodies in Dog Sera. J Bacteriol Virol. 2017; 47:148–55.

20). Burova E, Ioffe E. Chromatographic purification of recombinant adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vectors: methods and implications. Gene Ther. 2005; 12(Suppl 1):S5–17.

21). Konz JO, Livingood RC, Bett AJ, Goerke AR, Laska ME, Sagar SL. Serotype specificity of adenovirus purification using anion-exchange chromatography. Hum Gene Ther. 2005; 16:1346–53.

Go to : 
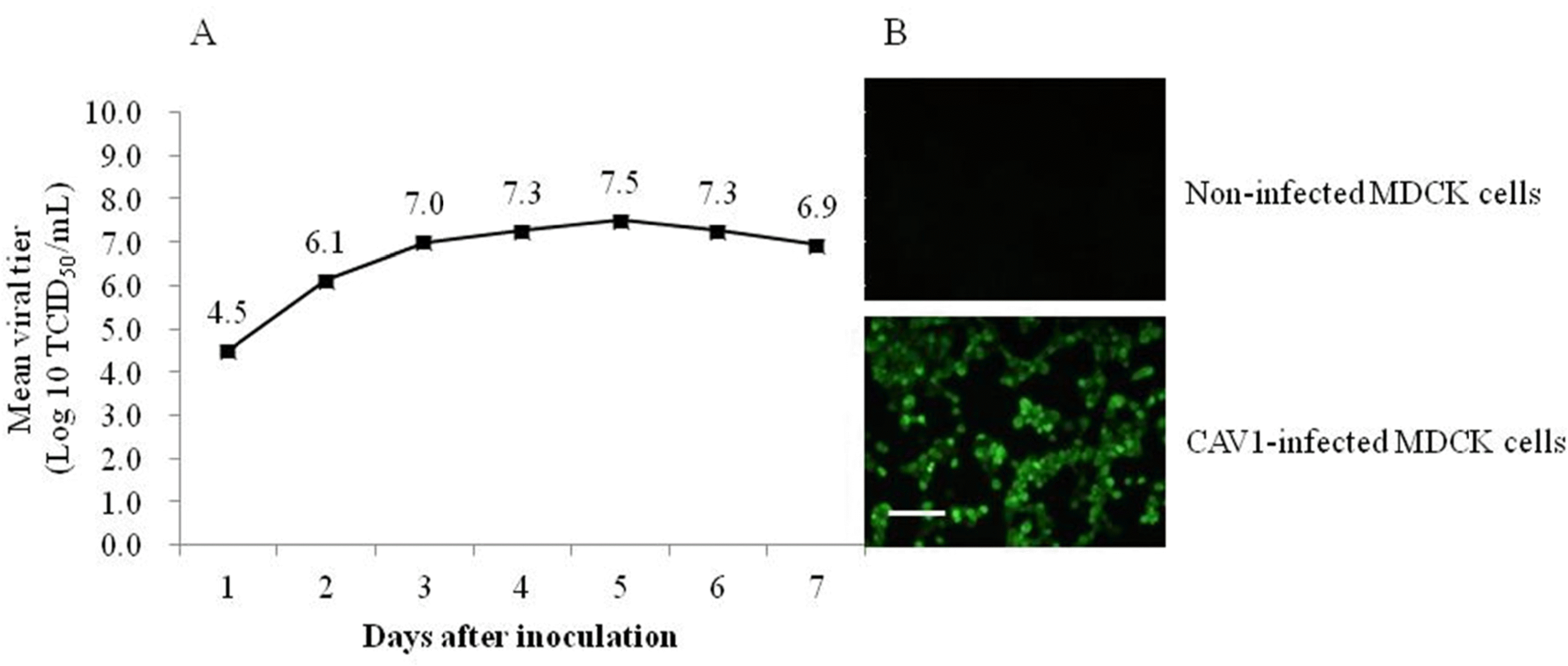 | Fig. 1.Optimal harvesting time determined via analyses of the CAV1V growth kinetics (A). The titer of CAV1V propagated in MDCK cells was measured two times and expressed as mean viral titer. Infected MDCK cells (staining with monoclonal antibody against CAV-1 and the anti-mouse IgG FITC conjugate) show specific nuclear fluorescence (B), Scale bars, 100 μm. |
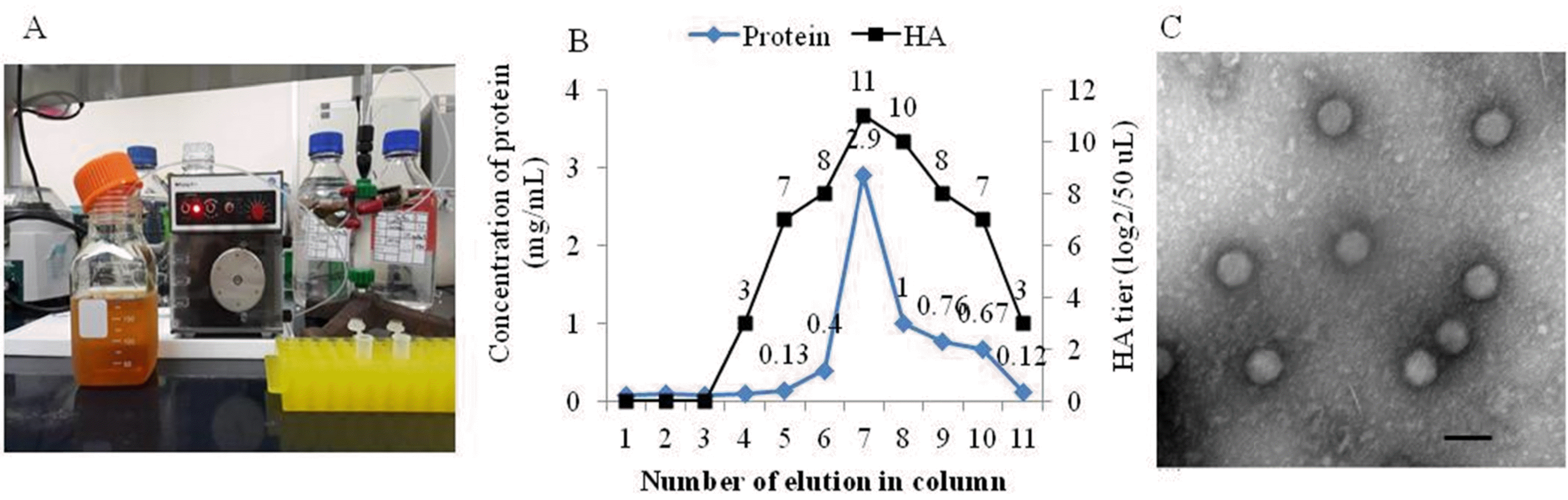 | Fig. 2.CAV-1 antigen loaded onto a Nuvia cPrime column connected to a peristaltic pump (P-1) (A). The concentrations of proteins eluted from the Nuvia cPrime column and their hemagglutinating activities as measured using NanoDrop 1000 UV/Vis spectrophotometry and admixture with 0.6% (v/v) guinea pig erythrocytes, respectively (B). Canine adenovirus type 1 particles were evident via electron microscopy of the seventh eluate, scale bar, 100 nm (C). |
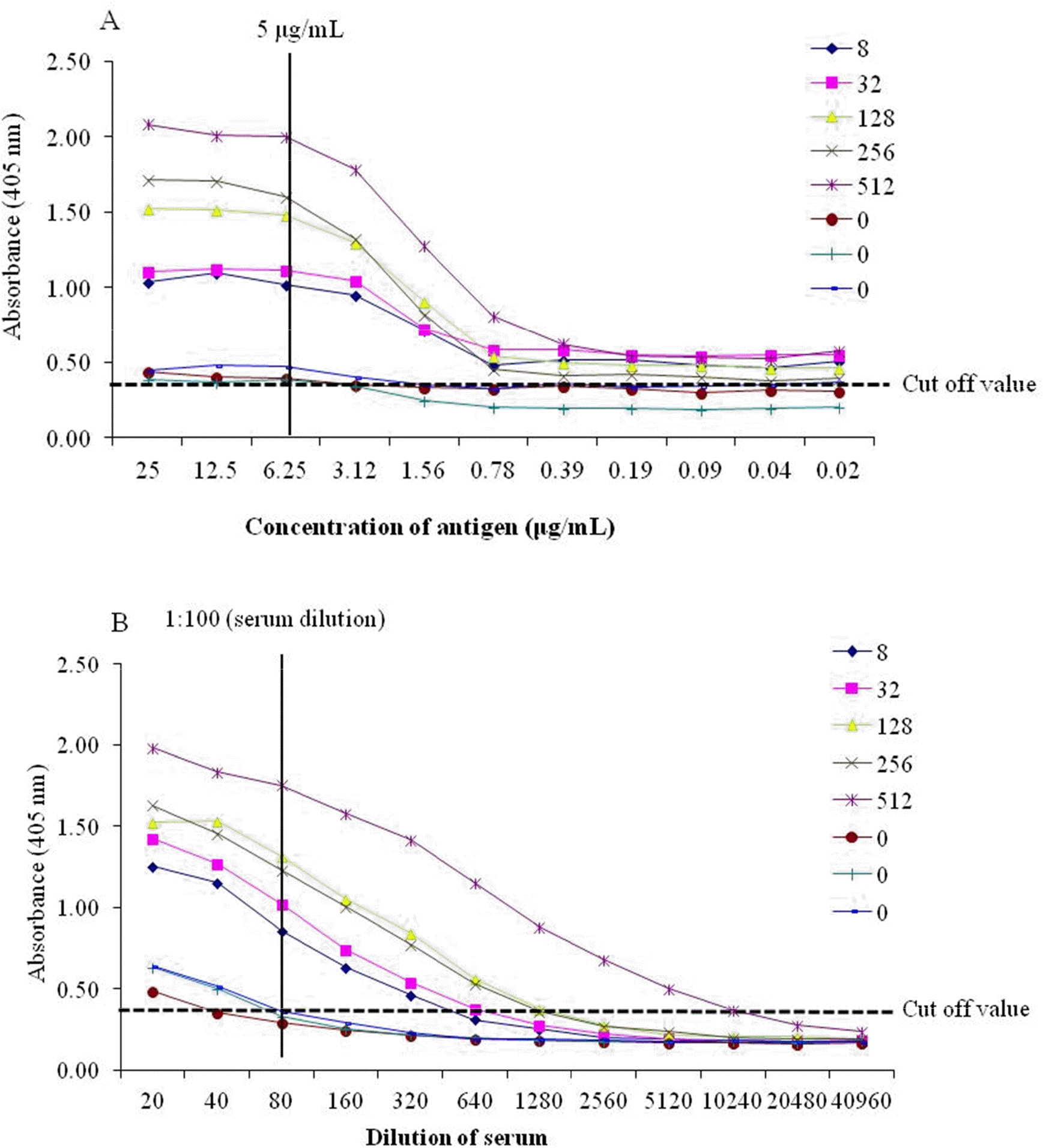 | Fig. 3.Determination of the concentration of the purified CAV-1 antigen (A) and serum dilution (B) by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (I-ELISA). The concentrations of antigen and dilutions of serum were analyzed according to cut-off values (> 0.4). The numbers in the legend are the virus-neutralizing antibody (VNA) titers (0-512) of CAV-1 in dog serum. |
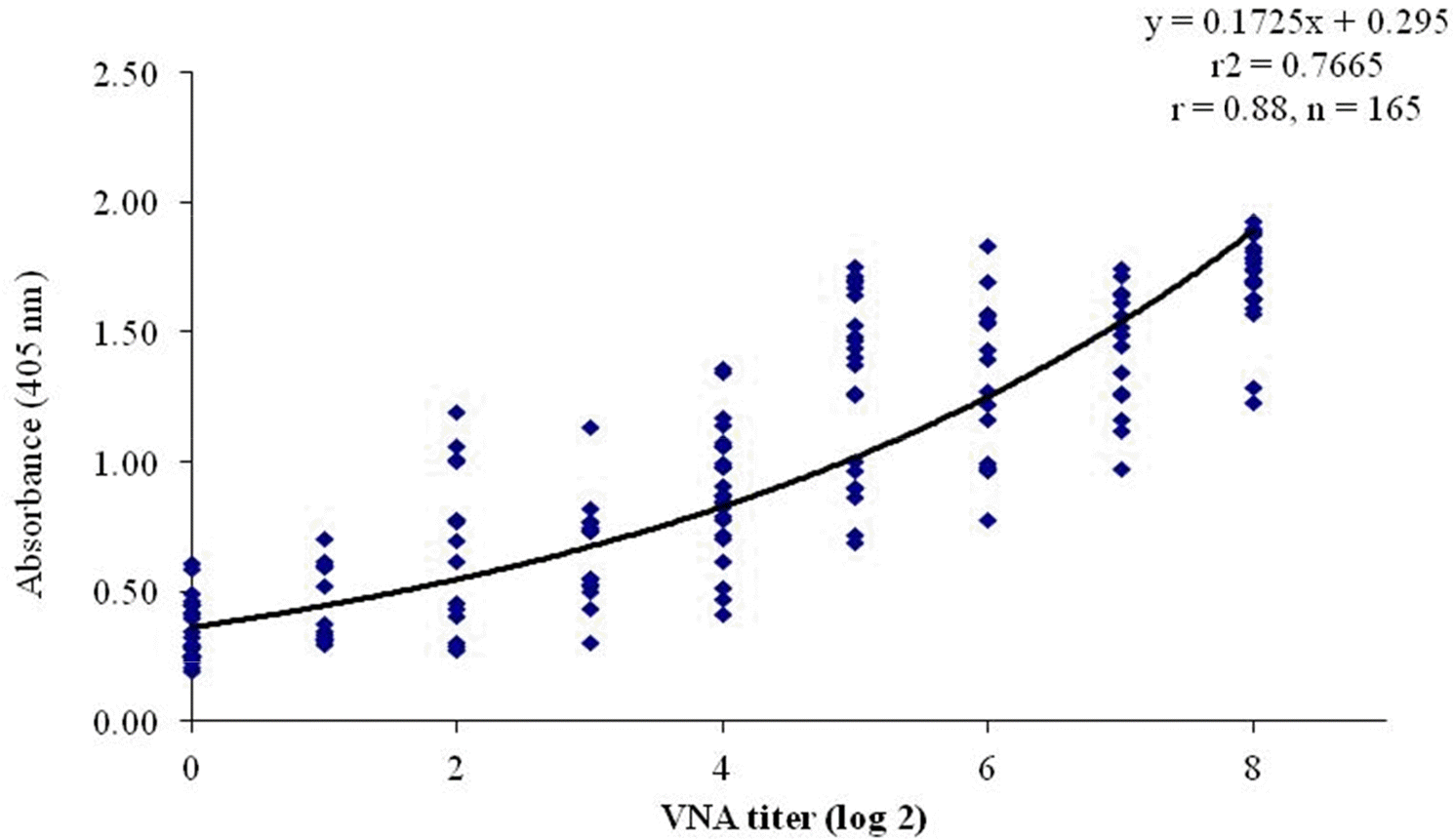 | Fig. 4.Correlation between the VNA titer and absorbance of l-ELISA for detecting CAV-1 antibodies in 165 dog serum samples. The correlation is indicated by the linear regression line and r-value (0.88). |
Table 1.
The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of I-ELISA for the detection of CAV-1 antibodies compared to the VN test
| VN test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Sum | |||
| Positive | 130 | 8 | 138 | ||
| I-ELISA | Negative | 4 | 23 | 27 | |
| Sum | 134 | 31 | 165 | ||
| Sensitivity∗ | 97.0% | ||||
| Specificity† | 74.2% | ||||
| Accuracy# | 92.7% | ||||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download