INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Population and Mass Characteristics
Image Acquisition
Image Analysis
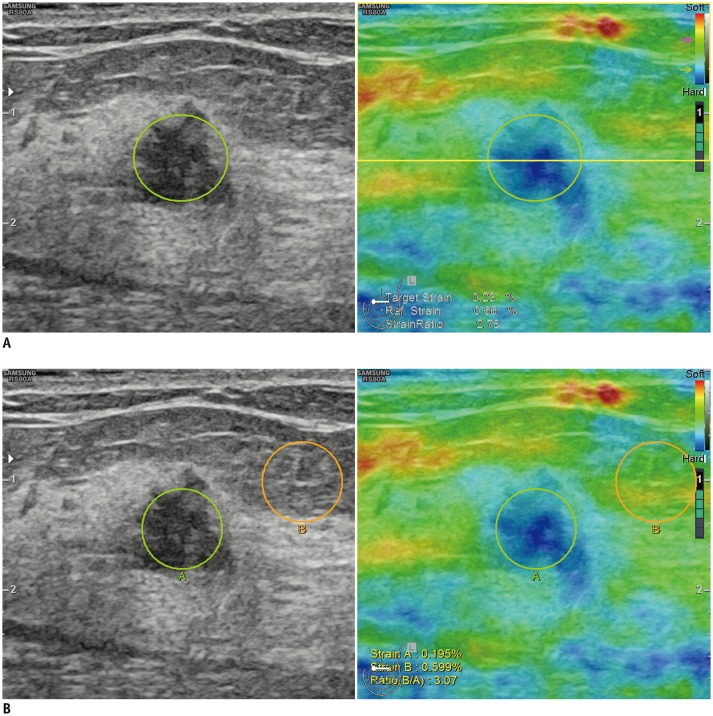 | Fig. 1Representative images showing ROI used to obtain strain ratio using 1-ROI (A) and 2-ROI methods (B).
A. For 1-ROI method, oval ROI was set to include mass (green circle) in which US unit automatically calculated and visualized strain ratio as mean strain within ROI drawn along border of mass divided by mean strain of fat located at and above level of ROI set for mass strain measurement, excluding strain measured within ROI set for mass measurement (yellow box). B. For 2-ROI method, one ROI was drawn along border of targeted breast mass (green circle) and another was drawn in lateral subcutaneous fat tissue located near target lesion (orange circle). Reference strain for 2-ROI method (B) was measured as average strain within orange circle. ROI = region of interest, US = ultrasonography
|
Pathological Examination and Follow-Up
Statistical Analysis
RESULTS
Demographics of the Study Population
Table 1
Patient Demographics and Lesion Characteristics
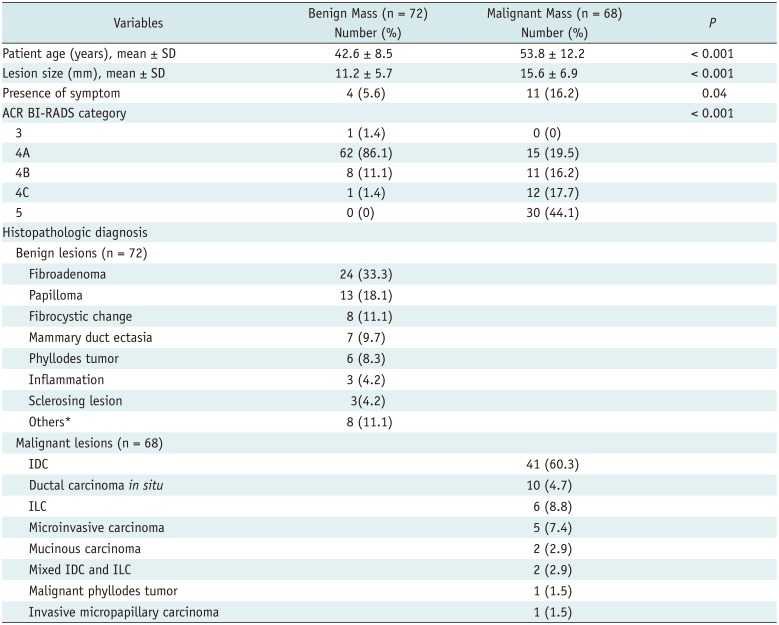
*Diabetic mastopathy, lactating adenoma, pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia, tubular adenoma, mucocele like tumor, atypical ductal hyperplasia, and flat epithelial atypia. ACR BI-RADS = American College of Radiology breast imaging reporting and data system, IDC = invasive ductal carcinoma, ILC = invasive lobular carcinoma, SD = standard deviation
Diagnostic Performances
Table 2
Mean Strain Ratio of Benign and Malignant Masses Measured by 1- and 2-ROI Methods
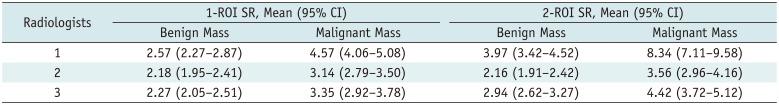
Table 3
Cut-Off Strain Ratios Obtained by Two ROI Methods by Three Radiologists and Proportion of Benign and Malignant Breast Masses
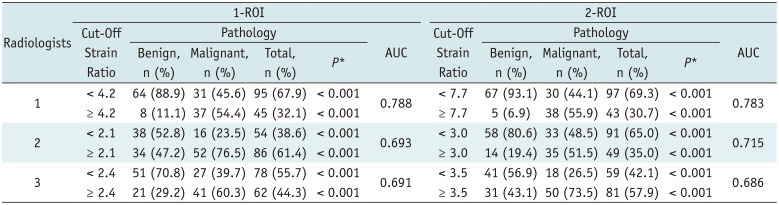
Table 4
Diagnostic Performance of Conventional US and US Combined with 1-ROI or 2-ROI Strain Ratio
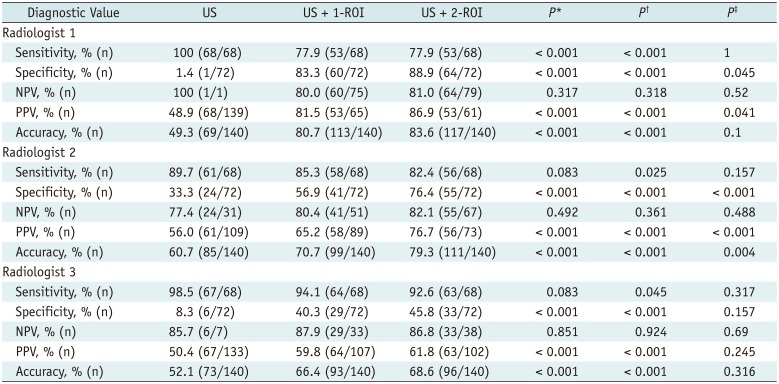
*Comparison of US and US + 1-ROI, †Comparison of US and US + 2-ROI, ‡Comparison of US + 1-ROI and US + 2-ROI. NPV = negative predictive value, PPV = positive predictive value, US = ultrasonography, US + 1-ROI = gray-scale US combined with 1-ROI strain ratio, US + 2-ROI = gray-scale US combined with 2-ROI strain ratio
Interobserver Agreement of Strain Ratios Measured by the 1-ROI and 2-ROI Methods
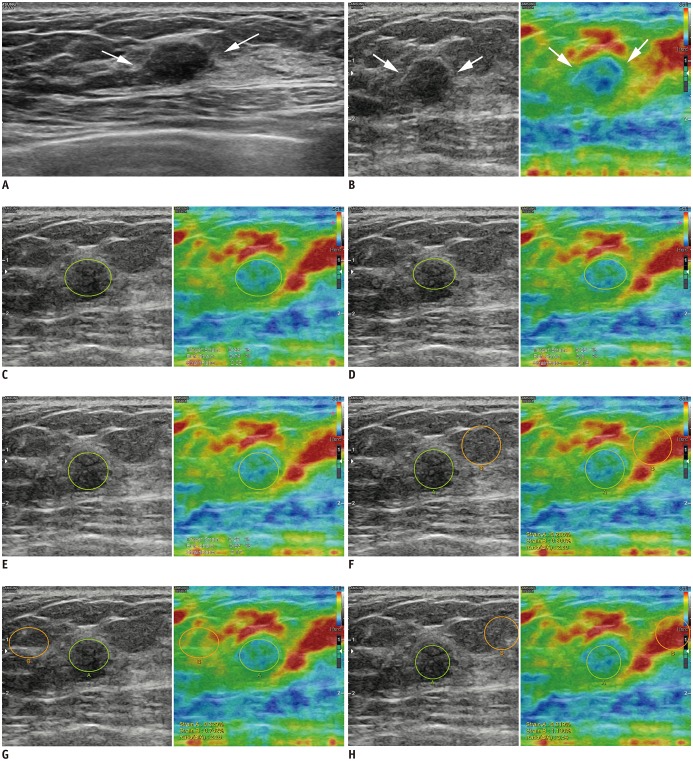 | Fig. 227-year-old woman diagnosed with fibroadenoma on US-guided biopsy was stable during > 2 years of follow-up.
A. Transverse B-mode US image shows 9-mm indistinct oval hypoechoic mass (arrows) in left breast that was categorized as Category 4a by each radiologist. B. Strain elastography showed that mass had some hard areas (arrows). Strain ratios using 1-ROI method were 2.25 (C), 2.16 (D), and 2.17 (E) according to three radiologists (green circle indicated ROI for target lesion). Strain ratios using 2-ROI method were 2.80 (F), 2.26 (G), and 3.54 (H) according to three radiologists (green circle indicated ROI for target lesion, orange circle indicated ROI for reference fat).
|
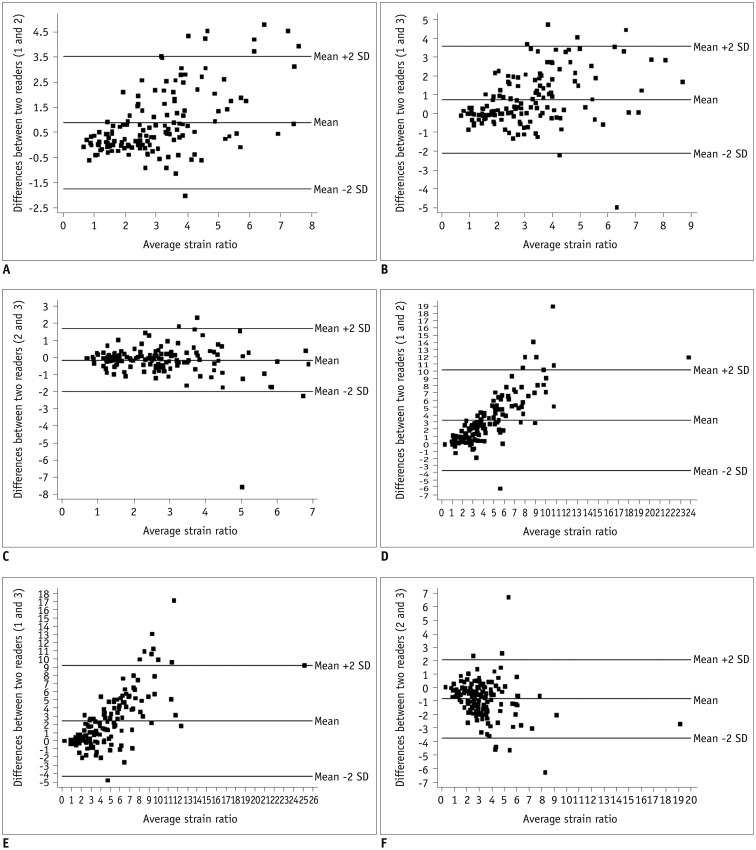 | Fig. 3Series of Bland-Altman plots show interobserver agreement of strain ratios for both 1-ROI (A–C) and 2-ROI methods (D–F).Each dot represents difference in strain ratios between two radiologists measured using same ROI method for each of 140 breast masses. Middle horizontal line represents mean difference in strain ratio, and each line above and below horizontal line represents mean difference between upper and lower limits of 95% agreement limit. For 1-ROI method, mean differences in strain ratios were as follows: (A) 0.891, with upper and lower limits of 3.533 and −1.751 between radiologists 1 and 2; (B) 0.746 with upper and lower limits of 3.599 and −2.108 between radiologists 1 and 3; and (C) −0.145 with upper and lower limits of 1.712 and −2.003 between radiologists 2 and 3. For 2-ROI method, mean differences in strain ratios were as follows: (D) 3.251, with upper and lower limits of 10.228 and −3.726 between radiologists 1 and 2; (E) 2.431 with upper and lower limits of 9.213 and −4.350, between radiologists 1 and 3; and (F) −0.820, with upper and lower limits of 2.106 and −3.746 between radiologists 2 and 3. SD = standard deviation
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download