1. Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology. 2016; 278:563–577. PMID:
26579733.

2. Lee G, Lee HY, Park H, Schiebler ML, van Beek EJR, Ohno Y, et al. Radiomics and its emerging role in lung cancer research, imaging biomarkers and clinical management: state of the art. Eur J Radiol. 2017; 86:297–307. PMID:
27638103.

3. Legland D, Kiêu K, Devaux MF. Computation of Minkowski measures on 2D and 3D binary images. Image Anal Stereol. 2007; 26:83–92.

4. Zwanenburg A, Leger S, Vallières M, Löck S. Image biomarker standardisation initiative [updated May 2019]. arXiv:1612.07003 [cs.CV]. 2016. Accessed August 31, 2019. Available at:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.07003v9.
5. Parekh V, Jacobs MA. Radiomics: a new application from established techniques. Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev. 2016; 1:207–226. PMID:
28042608.

6. Park HJ, Lee SS, Park B, Yun J, Sung YS, Shim WH, et al. Radiomics analysis of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for staging liver fibrosis. Radiology. 2019; 290:380–387. PMID:
30615554.

7. Scalco E, Rizzo G. Texture analysis of medical images for radiotherapy applications. Br J Radiol. 2017; 90:20160642. PMID:
27885836.

8. Wang K, Lu X, Zhou H, Gao Y, Zheng J, Tong M, et al. Deep learning radiomics of shear wave elastography significantly improved diagnostic performance for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: a prospective multicentre study. Gut. 2019; 68:729–741. PMID:
29730602.

9. Chen S, Feng S, Wei J, Liu F, Li B, Li X, et al. Pretreatment prediction of immunoscore in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics-based clinical model based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI imaging. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:4177–4187. PMID:
30666445.

10. Feng ST, Jia Y, Liao B, Huang B, Zhou Q, Li X, et al. Preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics model using Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:4648–4659. PMID:
30689032.

11. Ji GW, Zhu FP, Zhang YD, Liu XS, Wu FY, Wang K, et al. A radiomics approach to predict lymph node metastasis and clinical outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:3725–3735. PMID:
30915561.

12. Liu F, Ning Z, Liu Y, Liu D, Tian J, Luo H, et al. Development and validation of a radiomics signature for clinically significant portal hypertension in cirrhosis (CHESS1701): a prospective multicenter study. EBioMedicine. 2018; 36:151–158. PMID:
30268833.

13. Zheng BH, Liu LZ, Zhang ZZ, Shi JY, Dong LQ, Tian LY, et al. Radiomics score: a potential prognostic imaging feature for postoperative survival of solitary HCC patients. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18:1148. PMID:
30463529.

14. Szczypiński PM, Strzelecki M, Materka A, Klepaczko A. MaZda--a software package for image texture analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2009; 94:66–76. PMID:
18922598.

15. van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V, et al. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017; 77:e104–e107. PMID:
29092951.

16. Berenguer R, Pastor-Juan MDR, Canales-Vázquez J, Castro-García M, Villas MV, Mansilla Legorburo F, et al. Radiomics of CT features may be nonreproducible and redundant: influence of CT acquisition parameters. Radiology. 2018; 288:407–415. PMID:
29688159.
17. Ji GW, Zhang YD, Zhang H, Zhu FP, Wang K, Xia YX, et al. Biliary tract cancer at CT: a radiomics-based model to predict lymph node metastasis and survival outcomes. Radiology. 2019; 290:90–98. PMID:
30325283.

18. Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB, et al. Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 30:1234–1248. PMID:
22898692.

19. Cozzi L, Dinapoli N, Fogliata A, Hsu WC, Reggiori G, Lobefalo F, et al. Radiomics based analysis to predict local control and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy. BMC Cancer. 2017; 17:829. PMID:
29207975.

20. Guo D, Gu D, Wang H, Wei J, Wang Z, Hao X, et al. Radiomics analysis enables recurrence prediction for hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Eur J Radiol. 2019; 117:33–40. PMID:
31307650.

21. Li W, Huang Y, Zhuang BW, Liu GJ, Hu HT, Li X, et al. Multiparametric ultrasomics of significant liver fibrosis: a machine learning-based analysis. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:1496–1506. PMID:
30178143.

22. Kim S, Shin J, Kim DY, Choi GH, Kim MJ, Choi JY. Radiomics on gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for prediction of postoperative early and late recurrence of single hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019; 25:3847–3855. PMID:
30808773.

23. Parmar C, Grossmann P, Rietveld D, Rietbergen MM, Lambin P, Aerts HJ. Radiomic machine-learning classifiers for prognostic biomarkers of head and neck cancer. Front Oncol. 2015; 5:272. PMID:
26697407.

24. Xu X, Zhang HL, Liu QP, Sun SW, Zhang J, Zhu FP, et al. Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2019; 70:1133–1144. PMID:
30876945.

25. Zhou Y, He L, Huang Y, Chen S, Wu P, Ye W, et al. CT-based radiomics signature: a potential biomarker for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017; 42:1695–1704. PMID:
28180924.

26. Hu HT, Wang Z, Huang XW, Chen SL, Zheng X, Ruan SM, et al. Ultrasound-based radiomics score: a potential biomarker for the prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:2890–2901. PMID:
30421015.

27. Ogutu JO, Schulz-Streeck T, Piepho HP. Genomic selection using regularized linear regression models: ridge regression, lasso, elastic net and their extensions. BMC Proc. 2012; 6 Suppl 2:S10. PMID:
22640436.

28. Wang S, Summers RM. Machine learning and radiology. Med Image Anal. 2012; 16:933–951. PMID:
22465077.

29. Lubner MG, Malecki K, Kloke J, Ganeshan B, Pickhardt PJ. Texture analysis of the liver at MDCT for assessing hepatic fibrosis. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017; 42:2069–2078. PMID:
28314916.

30. Naganawa S, Enooku K, Tateishi R, Akai H, Yasaka K, Shibahara J, et al. Imaging prediction of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using computed tomography texture analysis. Eur Radiol. 2018; 28:3050–3058. PMID:
29404772.

31. Shan QY, Hu HT, Feng ST, Peng ZP, Chen SL, Zhou Q, et al. CT-based peritumoral radiomics signatures to predict early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative tumor resection or ablation. Cancer Imaging. 2019; 19:11. PMID:
30813956.

32. Yuan C, Wang Z, Gu D, Tian J, Zhao P, Wei J, et al. Prediction early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for curative ablation using a radiomics nomogram. Cancer Imaging. 2019; 19:21. PMID:
31027510.

33. Akai H, Yasaka K, Kunimatsu A, Nojima M, Kokudo T, Kokudo N, et al. Predicting prognosis of resected hepatocellular carcinoma by radiomics analysis with random survival forest. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018; 99:643–651. PMID:
29910166.

34. Iwatsuki S, Dvorchik I, Marsh JW, Madariaga JR, Carr B, Fung JJ, et al. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a proposal of a prognostic scoring system. J Am Coll Surg. 2000; 191:389–394. PMID:
11030244.
35. Lim KC, Chow PK, Allen JC, Chia GS, Lim M, Cheow PC, et al. Microvascular invasion is a better predictor of tumor recurrence and overall survival following surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma compared to the Milan criteria. Ann Surg. 2011; 254:108–113. PMID:
21527845.

36. Iguchi T, Shirabe K, Aishima S, Wang H, Fujita N, Ninomiya M, et al. New pathologic stratification of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: predicting prognosis after living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2015; 99:1236–1242. PMID:
25427164.
37. Peng J, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Xu Y, Zhou J, Liu L. A radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion risk in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018; 24:121–127. PMID:
29770763.

38. Zhao B, Tan Y, Tsai WY, Qi J, Xie C, Lu L, et al. Reproducibility of radiomics for deciphering tumor phenotype with imaging. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:23428. PMID:
27009765.

39. Park JE, Park SY, Kim HJ, Kim HS. Reproducibility and generalizability in radiomics modeling: possible strategies in radiologic and statistical perspectives. Korean J Radiol. 2019; 20:1124–1137. PMID:
31270976.

40. Orlhac F, Frouin F, Nioche C, Ayache N, Buvat I. Validation of a method to compensate multicenter effects affecting CT radiomics. Radiology. 2019; 291:53–59. PMID:
30694160.

41. Chartrand G, Cheng PM, Vorontsov E, Drozdzal M, Turcotte S, Pal CJ, et al. Deep learning: a primer for radiologists. Radiographics. 2017; 37:2113–2131. PMID:
29131760.

42. Lee JG, Jun S, Cho YW, Lee H, Kim GB, Seo JB, et al. Deep learning in medical imaging: general overview. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:570–584. PMID:
28670152.

43. Zhou LQ, Wang JY, Yu SY, Wu GG, Wei Q, Deng YB, et al. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging of the liver. World J Gastroenterol. 2019; 25:672–682. PMID:
30783371.

44. Choy G, Khalilzadeh O, Michalski M, Do S, Samir AE, Pianykh OS, et al. Current applications and future impact of machine learning in radiology. Radiology. 2018; 288:318–328. PMID:
29944078.

45. Choi KJ, Jang JK, Lee SS, Sung YS, Shim WH, Kim HS, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning system for staging liver fibrosis by using contrast agent-enhanced CT images in the liver. Radiology. 2018; 289:688–697. PMID:
30179104.
46. Iranmanesh P, Vazquez O, Terraz S, Majno P, Spahr L, Poncet A, et al. Accurate computed tomography-based portal pressure assessment in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2014; 60:969–974. PMID:
24362073.

47. Nakayama Y, Li Q, Katsuragawa S, Ikeda R, Hiai Y, Awai K, et al. Automated hepatic volumetry for living related liver transplantation at multisection CT. Radiology. 2006; 240:743–748. PMID:
16857979.

48. Wang K, Mamidipalli A, Retson T, Bahrami N, Hasenstab K, Blansit K, et al. Automated CT and MRI liver segmentation and biometry using a generalized convolutional neural network. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 2019; 3. 27. [Epub]. DOI:
10.1148/ryai.2019180022.
49. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv:1505.04597 [cs.CV]. 2015. Accessed August 31, 2019. Available at:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597.
50. Hu P, Wu F, Peng J, Liang P, Kong D. Automatic 3D liver segmentation based on deep learning and globally optimized surface evolution. Phys Med Biol. 2016; 61:8676–8698. PMID:
27880735.

51. Huo Y, Terry JG, Wang J, Nair S, Lasko TA, Freedman BI, et al. Fully automatic liver attenuation estimation combing CNN segmentation and morphological operations. Med Phys. 2019; 46:3508–3519. PMID:
31228267.

52. Lu F, Wu F, Hu P, Peng Z, Kong D. Automatic 3D liver location and segmentation via convolutional neural network and graph cut. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017; 12:171–182. PMID:
27604760.

53. van Gastel MDA, Edwards ME, Torres VE, Erickson BJ, Gansevoort RT, Kline TL. Automatic measurement of kidney and liver volumes from MR images of patients affected by autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019; 30:1514–1522. PMID:
31270136.

54. Wang CJ, Hamm CA, Savic LJ, Ferrante M, Schobert I, Schlachter T, et al. Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part II: convolutional neural network interpretation using radiologic imaging features. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:3348–3357. PMID:
31093705.

55. Liu X, Song JL, Wang SH, Zhao JW, Chen YQ. Learning to diagnose cirrhosis with liver capsule guided ultrasound image classification. Sensors (Basel). 2017; 17:E149. PMID:
28098774.

56. Yasaka K, Akai H, Kunimatsu A, Abe O, Kiryu S. Deep learning for staging liver fibrosis on CT: a pilot study. Eur Radiol. 2018; 28:4578–4585. PMID:
29761358.

57. Yasaka K, Akai H, Kunimatsu A, Abe O, Kiryu S. Liver fibrosis: deep convolutional neural network for staging by using gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MR images. Radiology. 2018; 287:146–155. PMID:
29239710.

58. Biswas M, Kuppili V, Edla DR, Suri HS, Saba L, Marinhoe RT, et al. Symtosis: a liver ultrasound tissue characterization and risk stratification in optimized deep learning paradigm. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018; 155:165–177. PMID:
29512496.

59. Byra M, Styczynski G, Szmigielski C, Kalinowski P, Michałowski Ł, Paluszkiewicz R, et al. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for liver steatosis assessment in ultrasound images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2018; 13:1895–1903. PMID:
30094778.

60. Cao W, An X, Cong L, Lyu C, Zhou Q, Guo R. Application of deep learning in quantitative analysis of 2-dimensional ultrasound imaging of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2020; 39:51–59. PMID:
31222786.

61. Vorontsov E, Cerny M, Régnier P, Di Jorio L, Pal CJ, Lapointe R, et al. Deep learning for automated segmentation of liver lesions at CT in patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 2019; 3. 13. [Epub]. DOI:
10.1148/ryai.2019180014.
62. Schmauch B, Herent P, Jehanno P, Dehaene O, Saillard C, Aubé C, et al. Diagnosis of focal liver lesions from ultrasound using deep learning. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019; 100:227–233. PMID:
30926443.

63. Yasaka K, Akai H, Abe O, Kiryu S. Deep learning with convolutional neural network for differentiation of liver masses at dynamic contrast-enhanced CT: a preliminary study. Radiology. 2018; 286:887–896. PMID:
29059036.
64. Hamm CA, Wang CJ, Savic LJ, Ferrante M, Schobert I, Schlachter T, et al. Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part I: development of a convolutional neural network classifier for multi-phasic MRI. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:3338–3347. PMID:
31016442.

65. Ma J, Dercle L, Lichtenstein P, Wang D, Chen A, Zhu J, et al. Automated identification of optimal portal venous phase timing with convolutional neural networks. Acad Radiol. 2020; 27:e10–e18. PMID:
31151901.

66. Esses SJ, Lu X, Zhao T, Shanbhogue K, Dane B, Bruno M, et al. Automated image quality evaluation of T2-weighted liver MRI utilizing deep learning architecture. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018; 47:723–728. PMID:
28577329.

67. Liu F, Samsonov A, Chen L, Kijowski R, Feng L. SANTIS: Sampling-Augmented Neural neTwork with Incoherent Structure for MR image reconstruction. Magn Reson Med. 2019; 82:1890–1904. PMID:
31166049.

68. Tamada D, Kromrey ML, Ichikawa S, Onishi H, Motosugi U. Motion artifact reduction using a convolutional neural network for dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging of the liver. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2020; 19:64–76. PMID:
31061259.

69. Chaudhary K, Poirion OB, Lu L, Garmire LX. Deep learning-based multi-omics integration robustly predicts survival in liver cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018; 24:1248–1259. PMID:
28982688.

70. Park SH, Han K. Methodologic guide for evaluating clinical performance and effect of artificial intelligence technology for medical diagnosis and prediction. Radiology. 2018; 286:800–809. PMID:
29309734.
71. Moons KG, Altman DG, Reitsma JB, Ioannidis JP, Macaskill P, Steyerberg EW, et al. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2015; 162:W1–W73. PMID:
25560730.

72. England JR, Cheng PM. Artificial intelligence for medical image analysis: a guide for authors and reviewers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019; 212:513–519. PMID:
30557049.

73. Collins GS, Reitsma JB, Altman DG, Moons KGM. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD). Ann Intern Med. 2015; 162:735–736.

74. Han K, Song K, Choi BW. How to develop, validate, and compare clinical prediction models involving radiological parameters: study design and statistical methods. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:339–350. PMID:
27134523.

75. Kim DW, Jang HY, Kim KW, Shin Y, Park SH. Design characteristics of studies reporting the performance of artificial intelligence algorithms for diagnostic analysis of medical images: results from recently published papers. Korean J Radiol. 2019; 20:405–410. PMID:
30799571.

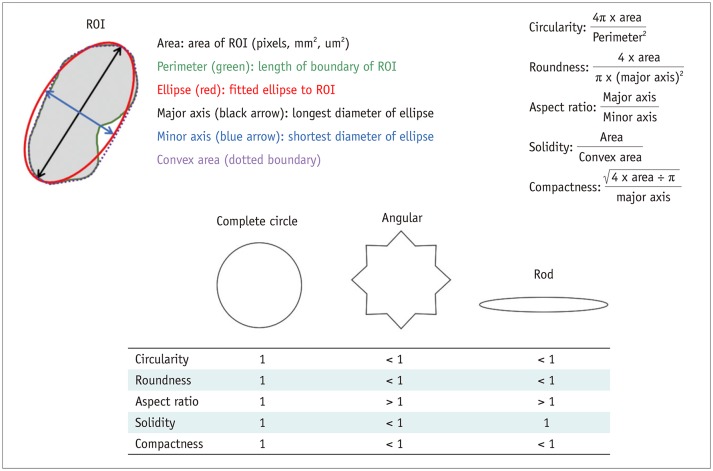
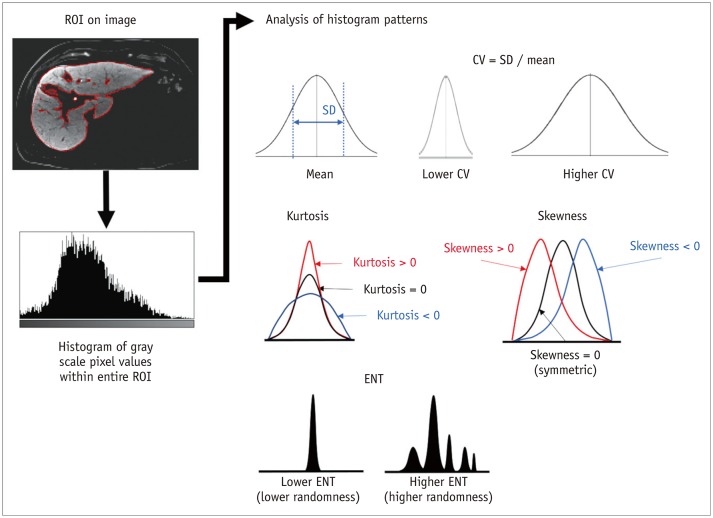
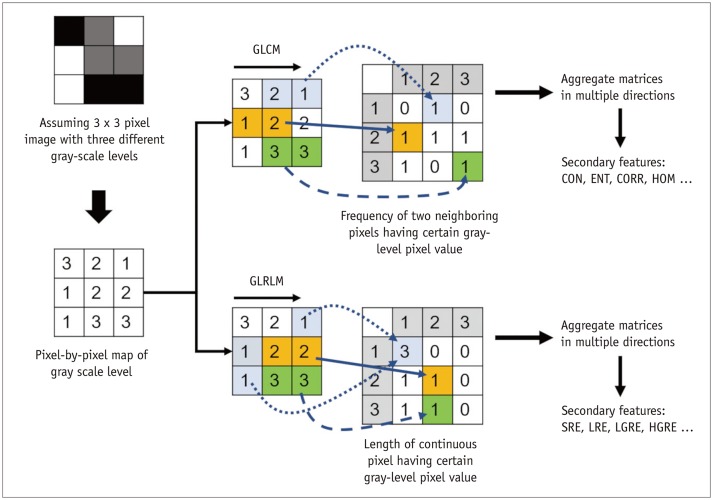
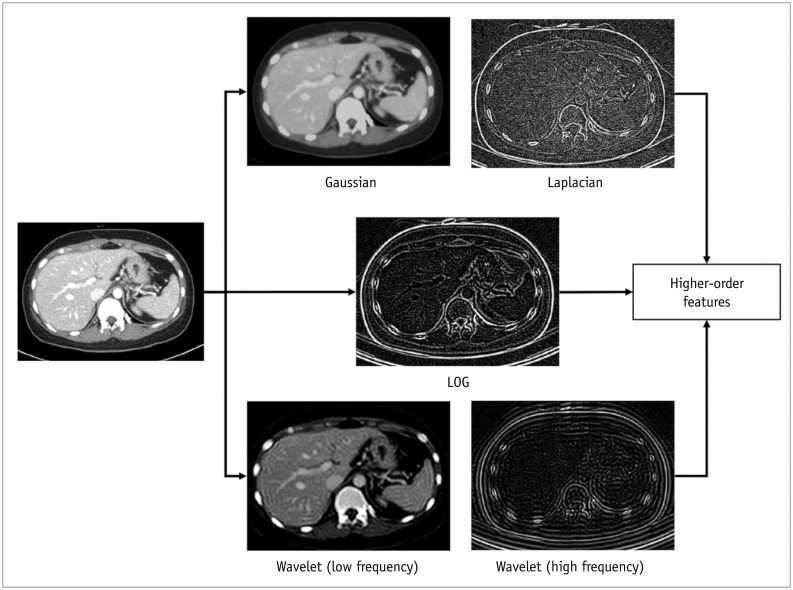
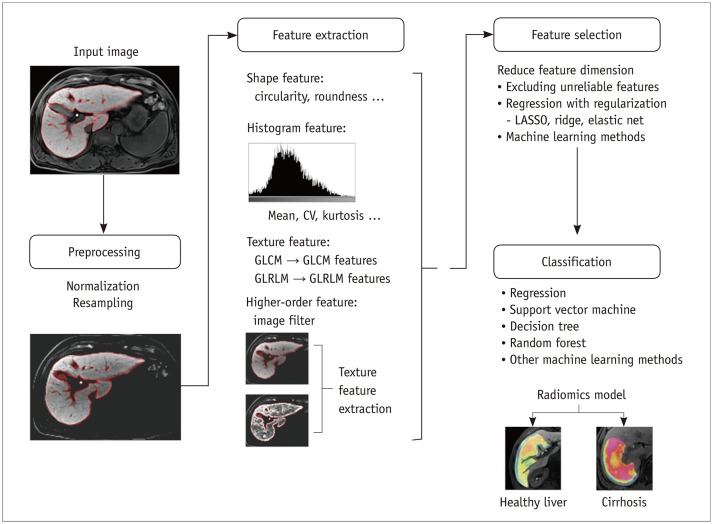
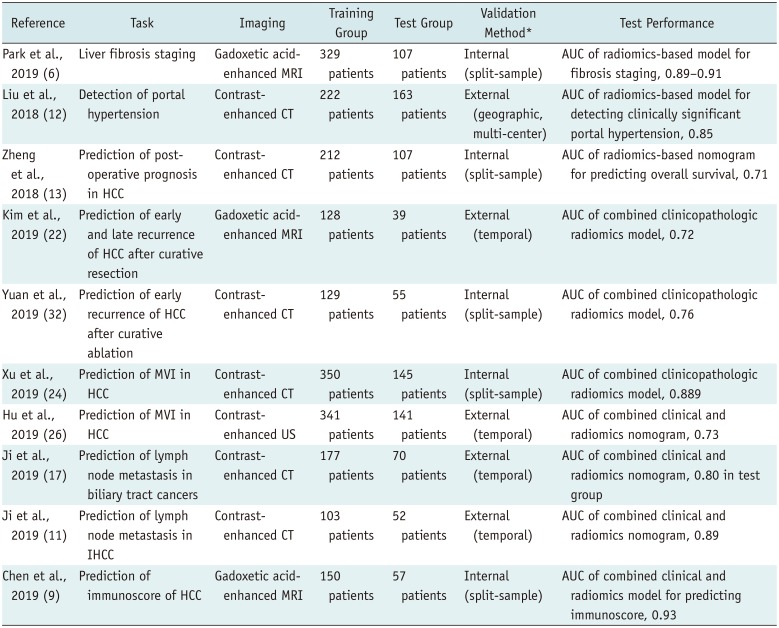
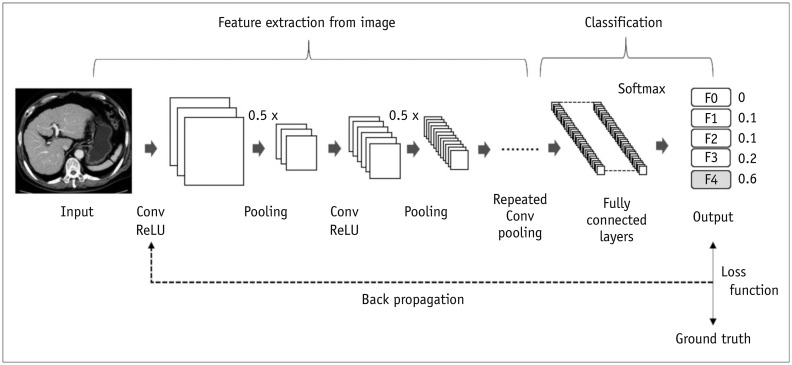
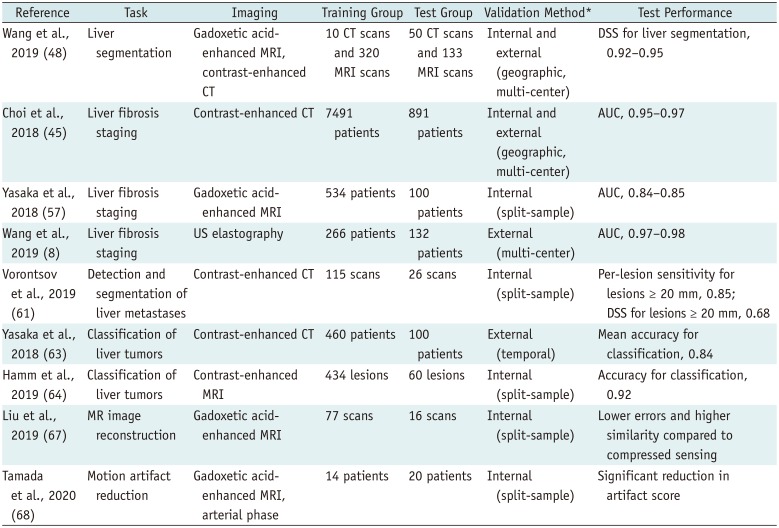




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download