Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
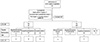 | Fig. 1Number of subjects in this study. Thyroid function was classified as normal (TSH <5 mIU/L and fT4 <0.9 ng/dL), hypothyroxinemia of prematurity (TSH <5 mIU/L and fT4 <0.9 ng/dL), hyperthyrotropinemia (TSH ≥5 mIU/L and fT4 ≥0.9 ng/dL), and hypothyroidism (TSH ≥5 mIU/L and fT4 <0.9 ng/dL), respectively. Thyroid function was defined with the last values of serum TSH and fT4 during hospital stays or prior to LT4 administration. LT4 was initiated when serum TSH was >20 mIU/L, TSH was 5 to 20 mIU/L or rising, and/or fT4 was <0.9 ng/dL on 2 or more consecutive tests with 1 or 2-week interval. LT4, levothyroxine sodium; LCC, late circulatory collapse; TFT, thyroid function test; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone; fT4, free T4. |
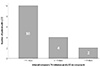 | Fig. 2Time interval (days) from initiation of LT4 and development of LCC, and number of patients with LCC in premature infants with ≤32 weeks of gestation. LCC, late circulatory collapse; LT4, levothyroxine sodium. |
Table 1
Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Premature Infants with and without Late Circulatory Collapse
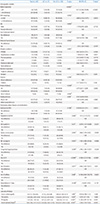
Values are presented as number (%) or median (IQR), or median (n, IQR).
Abbreviations: LCC, late circulatory collapse; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; PPROM, prolonged premature rupture of membrane with more than 18 hours; hypertensive condition included essential hypertension, pregnancy induced hypertension, or preeclampsia; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; VD, vaginal delivery; CS, cesarean section; AS, Apgar score; RDS, respiratory distress syndrome; hsPDA, hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; LT4, levothyroxine sodium; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone; fT4, free T4; IQR, interquartile range.
*P-value was derived from logistic regression model with Firth's peneralized likelihood.
†P-value was derived from Fisher's exact test, respectively.
‡P-value was derived from Chi-square test, respectively.
§P-value was derived from Wilcoxon rank-sum test, respectively.
∥The lowest serum sodium during hospital stays in each premature infant was analyzed.
Table 2
OR of Risk Factors for Late Circulatory Collapse in Premature Infants
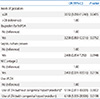
P-value was derived from logistic regression model with Firth's peneralized likelihood.
Abbreviations: OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; hsPDA, hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus; NEC (≥stage 2), necrotizing enterocolitis with modified Bell's class stage 2 and more; LT4, levothyroxine sodium.
*Use of LT4 (without congenital hypothyroidism) means LT4 supplementation in cases with thyroid dysfunction except congenital hypothyroidism, such as persistent hypothyroxinemia or hyperthyrotropinemia.
Table 3
Short-term Outcomes and Influences of Late Onset Circulatory Collapse in Premature Infants

Values are presented as number (%).
Abbreviations: LCC, late circulatory collapse; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; BPD, bronchopulmonary dysplasia; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity.
*P-value was derived from logistic regression model adjusted to gestational age with Firth's peneralized likelihood (event=“LCC”).
†P-value was derived from Fisher's exact test, respectively.
‡P-value was derived from and Chi-square test, respectively.
§Gross motor delay was investigated as premature infants undergoing rehabilitation therapy in 1 year with adjusted gestational age.
∥Moratlity was investigated as premature infants who were died in 1 year after birth.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download