Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of simultaneous bilateral acute angle closure attack combined with bilateral choroidal detachment in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Case summary
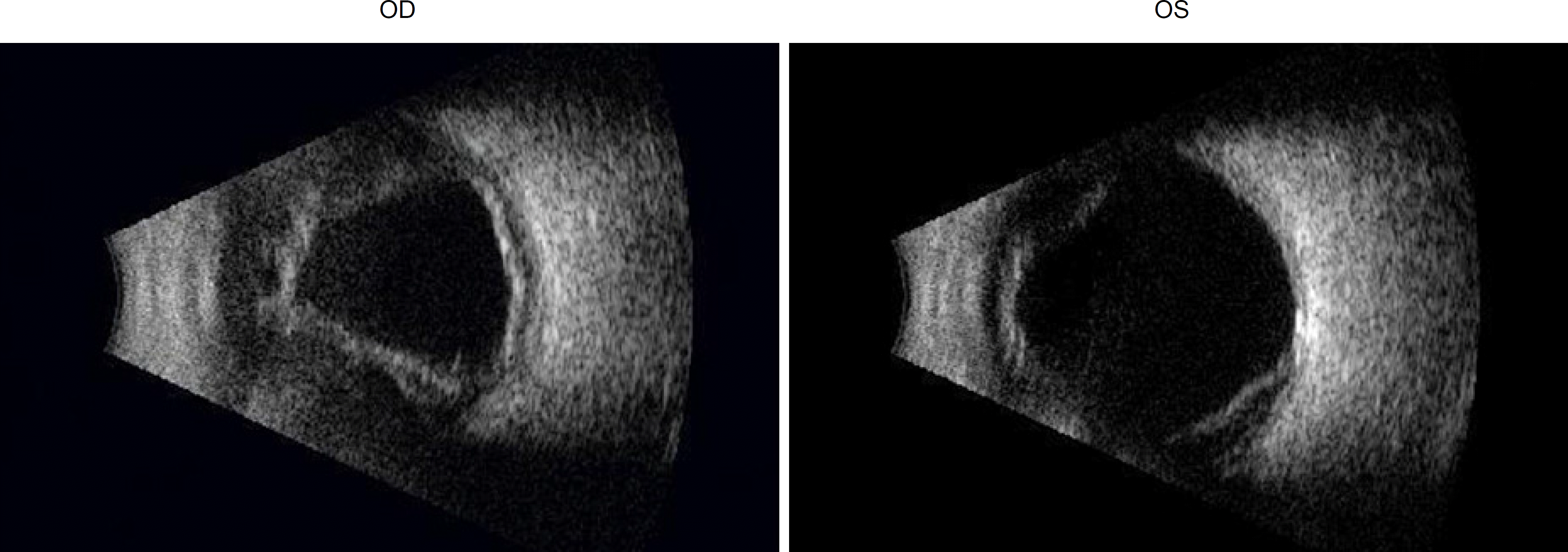
A 63-year-old male who had a history of several months of diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss visited the emergency room with sudden bilateral blurred vision accompanied with headache, periocular pain, nausea, and vomiting. His visual acuity was finger counting in both eyes and the intraocular pressure (IOP) was 49/44 mmHg (right/left). The anterior chamber depth was three times the corneal thickness in the center and less than 1/4 of the corneal thickness in the periphery in both eyes. Maximum medical therapy had no effect and emergency cataract surgery combined with vitrectomy was performed on the right eye. During surgery, severe choroidal detachment was noted. One day after surgery, choroidal detachment was also found in the left eye and emergency cataract surgery with suprachoroidal fluid drainage was performed. Approximately 1 month after surgery, choroidal detachment of both eyes regressed without systemic therapy. The IOP was 14/7 mmHg (right/left) with a visual acuity of 0.32/0.4 (right/left). The blood test performed in the emergency room showed a positive result for AIDS and the patient started medical therapy.
Go to : 
References
1. Song GW, Jin KH, Kim JM. Clinical data on glaucomatous patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1179–83.
2. Lee TY, Yu S, Kim JH, et al. Seasonal variations of acute abdominal glaucoma in patients visiting the hospital. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1637–41.
3. Foster PJ. The epidemiology of primary angle closure and abdominal glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Semin Ophthalmol. 2002; 17:50–8.
4. Jeong KD, Kim B, Oh WH. Angle closure and the acute rise of abdominal pressure after administration of methazolamide. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017; 58:1420–4.
5. Hong EH, Lee MJ, Song IS. A case of bilateral acute angle closure attack induced by common cold medication. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:334–40.

6. Kim JH, Lim JS, Lee JW, et al. Bilateral acute myopia and abdominal due to ciliochoroidal effusion in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1194–9.
7. Nash RW, Lindquist TD. Bilateral abdominal glaucoma abdominal with uveal effusion: presenting sign of HIV infection. Surv Ophthalmol. 1992; 36:255–8.
8. Ullman S, Wilson RP, Schwartz L. Bilateral abdominal abdominal in association with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986; 101:419–24.
9. Dawson DG, Johnson MW. Ciliochoroidal effusion and pulmonary hypertension in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Retina. 2001; 21:672–4.

10. Cristol SM, Baumblatt JG, Icasiano E, et al. Bilateral acute abdominal-closure associated with systemic lymphoma: a report of 2 cases. J Glaucoma. 2011; 20:115–7.
11. Aronow ME, Portell CA, Sweetenham JW, Singh A. Uveal abdominal: clinical features, diagnostic studies, treatment selection, and outcomes. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:334–41.
12. Higginbotham E, Parrish RK. Uveal effusion syndrome. J Glaucoma. 1996; 5:63–7.
13. Fineman MS, Emerick G, Dudley D, et al. Bilateral choroidal abdominals and abdominal glaucoma associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Retina. 1997; 17:455–7.
Go to : 
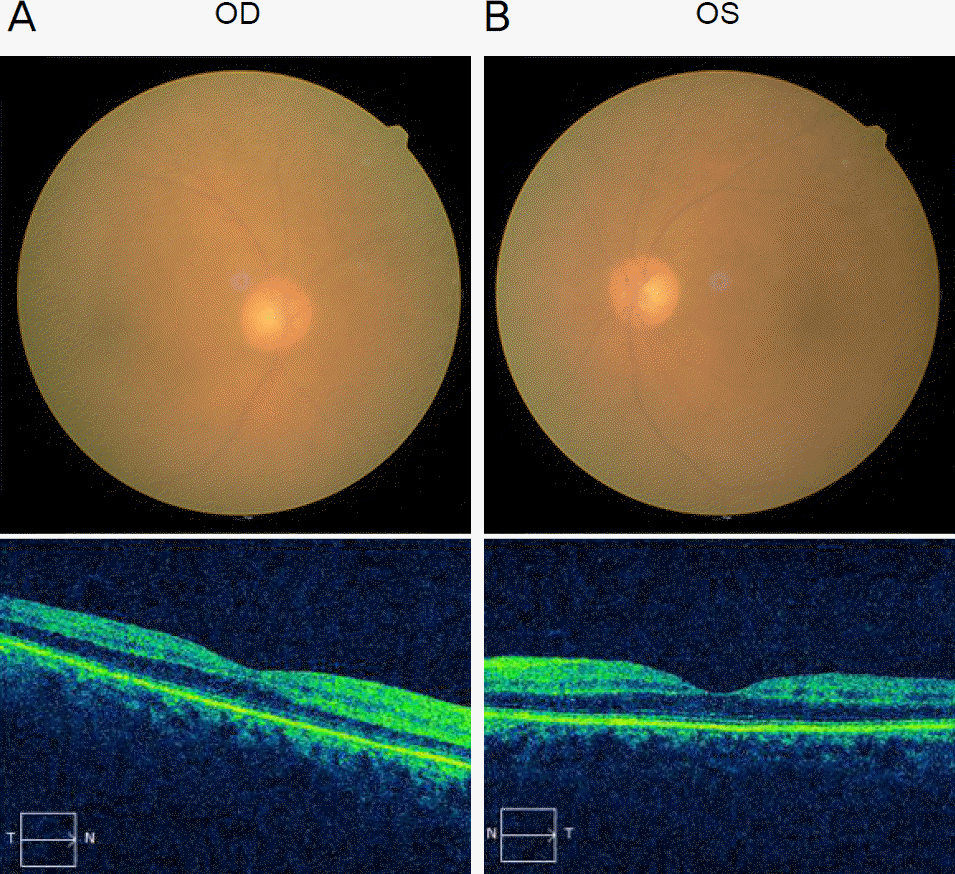 | Figure 1.Color fundus photo (upper) and optical coherence tomography (lower) of both eye at the day of angle closure attack. The images demonstrate no remarkable macular lesion in both eyes (A, B). Fundus photos are blurry visible because of the corneal edema. OD = oculus dexter; OS = oculus sinister; N = nasal; T = temporal. |
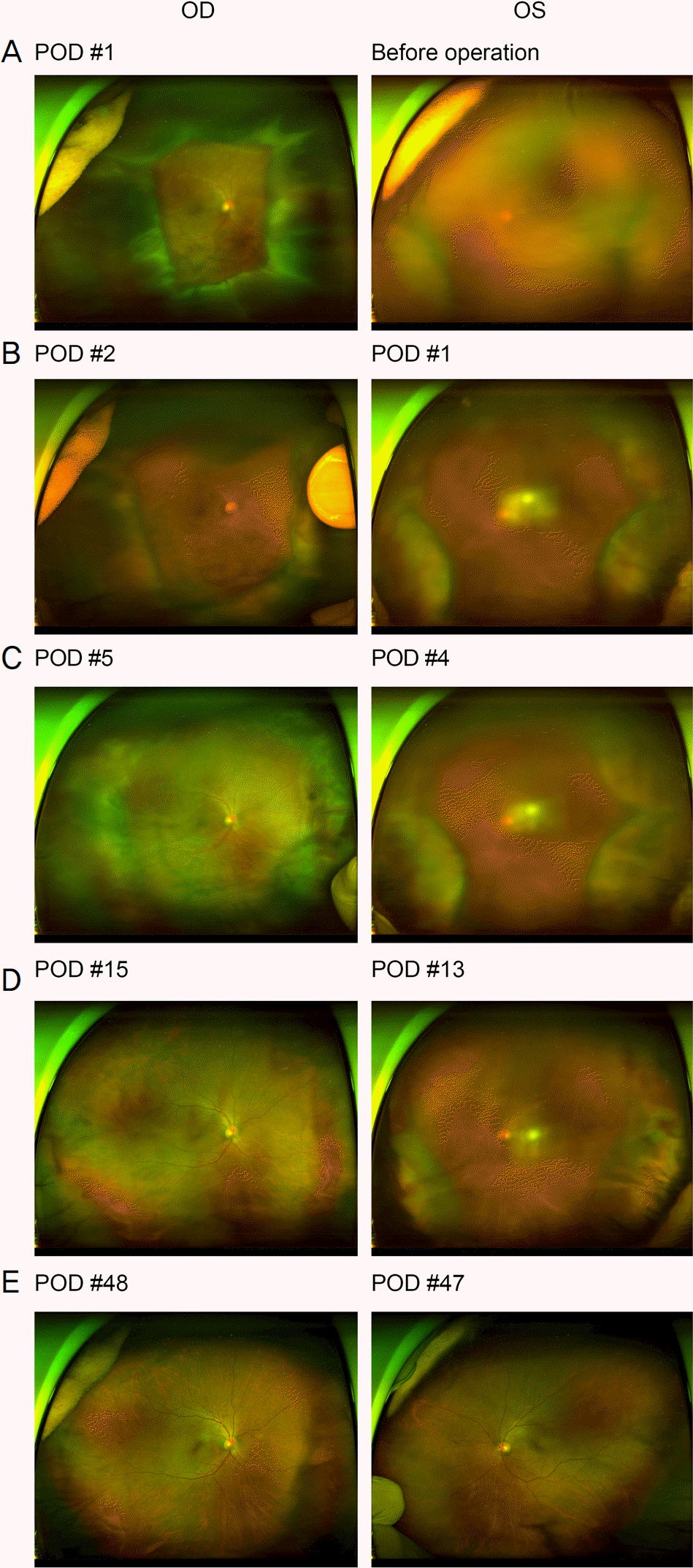 | Figure 2.Wide fundus photographs of the both eyes. After right eye cataract surgery combined with total vitrectomy, 360˚ choroidal detachment was found in both eyes (A). Spontaneous regression of the detachment was noted gradually without therapy as shown in the fundus photographs (B-D). Choroidal detachment was almost completely regressed after 1.5 months (E). OD = oculus dexter; OS = oculus sinister; POD = post-oper-ative day. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download