Abstract
Purpose
We report a case of nodular fasciitis of the conjunctiva that has not been previously reported in the Republic of Korea.
Case summary
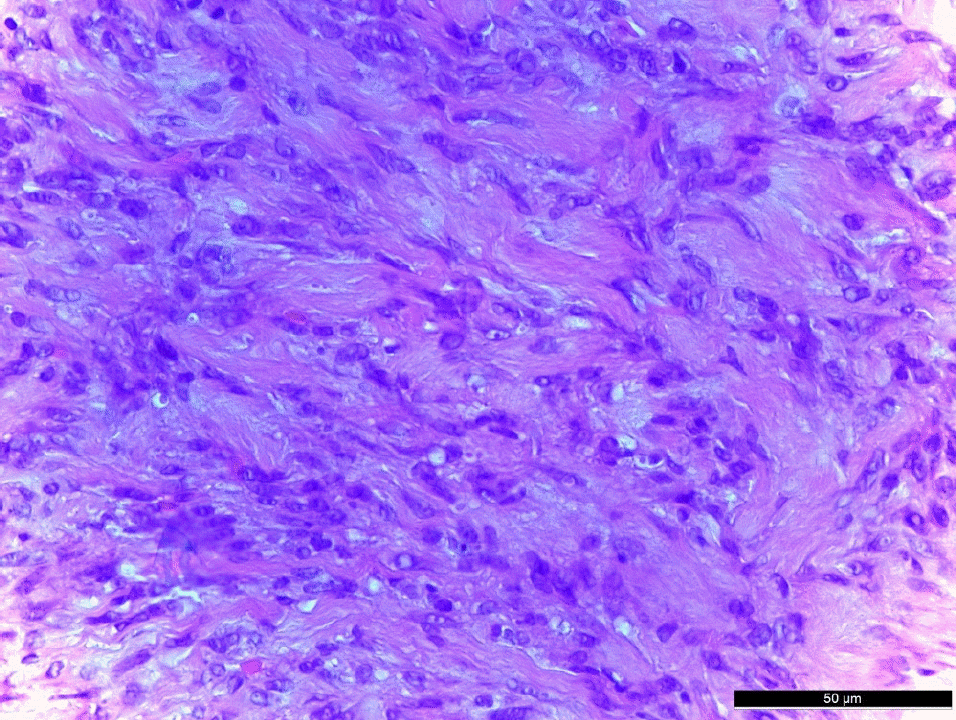
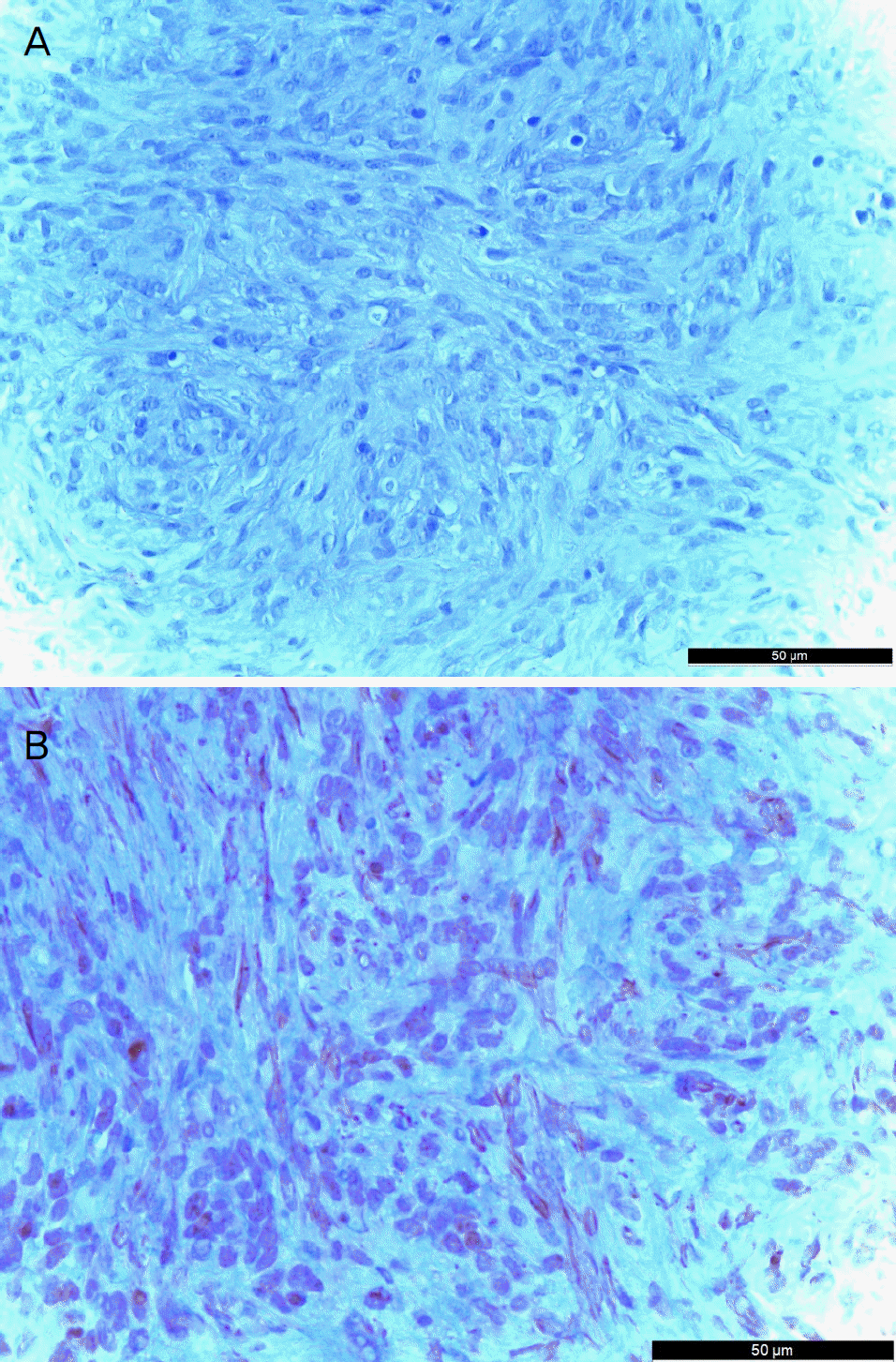
A 18-year-old female patient presented with a left conjunctival mass, which had been enlarging for 1 month. The tumor was located at the corner of the conjunctiva of the left eye. The size of the tumor was 1 mm in width and 1.5 mm in height, and tenderness and redness were not observed. There was no history of trauma, but bilateral upper lid blepharoplasty was performed 2 months prior to her visit. Excision of a conjunctival mass was performed and there was no evidence of involvement of the sclera or peripheral conjunctiva around the mass. We performed immunohistochemistry and PCR for human herpes virus 8 (HHV8). Immunohistochemistry was positive for S-100 and negative for smooth muscle actin and HHV8. The mass was myofi-broblastic in nature and the histopathological features and clinical findings of this case were diagnosed as nodular fasciitis with the features as described above. There was no recurrence for 4 months after removal of the mass.
Go to : 
References
1. Riffle JE, Prosser AH, Lee JR, Lynn JJ. Nodular fasciitis of the abdominal: a case report and brief review of the literature. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2011; 2011:235956.
2. Konwaler BE, Keasbey L, Kaplan L. Subcutaneous pseudosarcom-atous fibromatosis (fasciitis). Am J Clin Pathol. 1955; 25:241–52.

3. Lee YJ, Kim SM, Lee JH, et al. Nodular fasciitis of the periorbital area. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2014; 15:43–6.

4. Park MS, Kwon MJ, Lee MJ. Three cases of periorbital nodular fasciitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:1946–52.

5. Font RL, Zimmerman LE. Nodular fasciitis of the eye and adnexa. A report of ten cases. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966; 75:475–81.
6. Stone DU, Chodosh J. Epibulbar nodular fasciitis associated with floppy eyelids. Cornea. 2005; 24:361–2.

7. Massop DJ, Frederick PA, Li HE, Lin A. Epibulbar nodular fasciitis. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2016; 7:262–7.

8. Jung SW, Kang NY. A case of nodular fasciitis in the upper eyelid. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:357–61.

9. Price EB Jr, Silliphant WM, Shuman R. Nodular fasciitis: a clinicopathological analysis of 65 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961; 35:122–36.
10. Shimizu S, Hashimoto H, Enjoji M. Nodular fasciitis: an analysis of 250 patients. Pathology. 1983; 16:161–6.

11. Hseu A, Watters K, Perez-Atayde A, et al. Pediatric nodular abdominal in the head and neck evaluation and management. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 141:54–9.
12. Pandian TK, Zeidan MM, Ibrahim KA, et al. Nodular fasciitis in the pediatric population: a single center experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2013; 48:1486–9.

13. Velagaleti GVN, Tapper JK, Panova NE, et al. Cytogenetic abdominal in a case of nodular fasciitis of subclavicular region. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2003; 141:160–3.
Go to : 
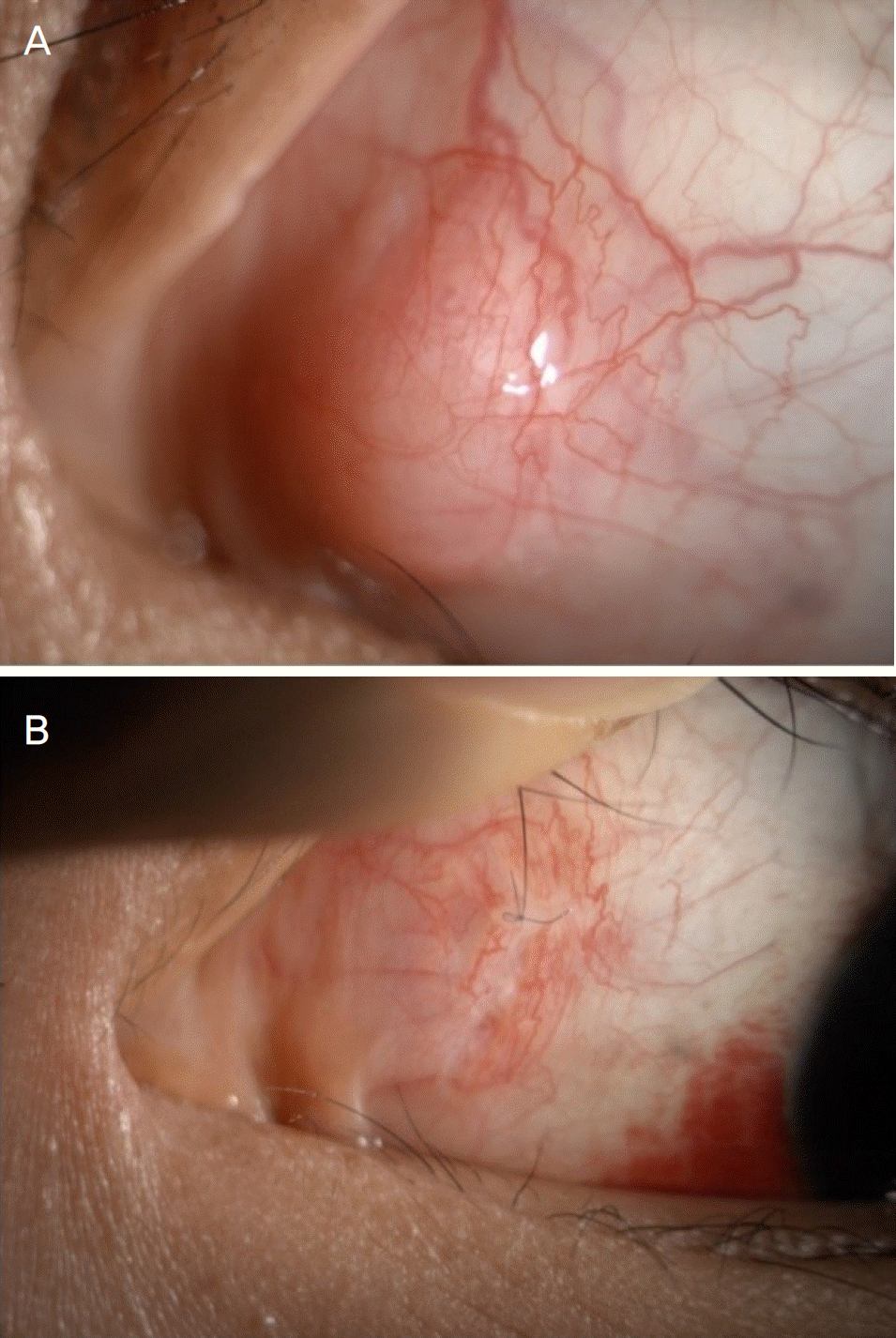 | Figure 1.Preoperative and postoperative appearance of conjunctival mass. (A) Preoperative appearance showing 1 × 1.5 mm sized, movable, nontender, well circumscribed mass at nasal side of conjunctiva on slit-lamp examination. (B) Postoperative appearance of the next day after excision of the conjunctival mass on slit-lamp examination. Well approximated excision suture site was shown. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download