Abstract
The Nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) plays a key role in the cellular defense against oxidative stress. Low K+ increased the reactive oxygen species and it stimulate Nrf2 activation. Previous our study demonstrated that low potassium promoted expression of H/K-ATPase and kNBC1 by Nrf2 transcription factor in cultured models. In addition, phosphorylation of ERK, JNK, p38 and PI3K was involved in the activation of Nrf2 expression. This study aims to elucidate the mechanism which low potassium regulates Nrf2 expression through various in vitro and in vivo models. Using various kinase inhibitors, promotion of Nrf2 expression in low potassium condition was inhibited by LY294002 and SP600125 while PD98059 and SB203580 did not affect Nrf2, suggesting that phosphorylation of Akt and JNK is specifically involved in Nrf2 expression in low potassium condition. Kidney tissues from low potassium diet rats showed increased phospho-ERK1/2 and phospho-Akt in diet time dependent manner but no effect to JNK and p38 phosphorylation. Specifically, Phospho-Nrf2 was also increased in nuclear compartment by low potassium diet. In order to demonstrate direct evidence that low potassium regulates ionic transporters by Nrf2, Nrf2 knockout mice were employed. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) were harvested for the study. As expected, low potassium promotes expression of Nrf2 and level of phospho-ERK1/2 and phospho-Akt in MEF-Nrf2 (+/+). Low potassium promoted expression of kNBC1 and H/K-ATPase in MEF-Nrf2 (+/+), but unchanged or even decreased in MEF-Nrf2 (+/−) and MEF-Nrf2 (−/−). Taken together, these results show that Nrf2 was activated by ERK1/2 and AKT in low potassium condition and further regulates expression of kNBC1 and colonic H/K-ATPase.
Figures and Tables
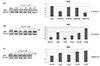 | Fig. 1Akt and JNK specific inhibitors block low-potassium stimulated Nrf2 activation. (a) 293T cells were treated with indicated pharmacological inhibitors in the normal or low potassium media for 12 h (LY294002, 10 µM; PD98059, 20 µM; SB203580, 20 µM; SP600125, 20 µM). Cells were lysed, and Western blotting was performed using anti-Nrf2 antibodies. (b), (c) Cells were treated with indicated concentration of LY294002 or SP600125 for 12 h. Cells were lysed, and Western blotting was performed using anti-Nrf2 antibodies. |
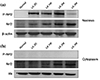 | Fig. 2P-Nrf2 accumulates in the nucleus following low K+ stimulation. (a) Western blot analysis reveal that the accumulation of p-Nrf2 and Nrf2 protein from nuclear extract increased in the rat kidney according to potassium depleted diet. (b) In cytoplasm extract, the abundance of Nrf2 protein increased but p-Nrf2 protein was undetected. |
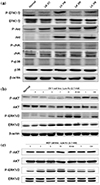 | Fig. 3Effect of low K+ on phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Akt in rat kidney, CV-1 cell and MEF cell. (a) Expression levels of both phosphorylated and total ERK1/2, Akt, JNK and p38 were measured by western blot analysis in the kidney of potassium depleted rats. A transient increase in the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Akt was observed in potassium depleted rat kidney, whereas the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 did not changed. (b) CV-1 cells exposed to normal or low potassium media for indicated time periods and harvested in protein lysis buffer. Western blotting was performed using specific antibodies. In low potassium condition, stimulated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 as early as 5 min, and this increase persisted through 30min. The activation of Akt was observed at 30min, and this activation persisted through 24 h. (c) MEF cells stimulated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 as early as 3 min, and this increase persisted through 30min. The activation of Akt was observed at 10min, and this activation persisted through 3 h. |
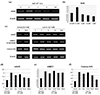 | Fig. 4Low-potassium Enhances Nrf2 gene in MEF cells. (a, b) MEF cells were treated with low potassium media, total RNA was extracted, and Nrf2 mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR. Nrf2 expression was measured with various concentrations of low potassium at 12 h (control 5.4 mM; low potassium 2.7 mM, 2 mM, 1.5 mM, 1 mM). The expression levels of Nrf2 are up-regulated during low potassuim at 2.7 mM. (c) Expression of Nrf2, kNBC1 and colonic H/K at various time periods in 2.7mM low potassium conditions. (d~f) Densitometric analysis of mRNA expression levels of Nrf2, kNBC1 and colonic H/K. |
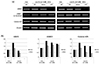 | Fig. 5Effect of low K+ on Nrf2 expression in Nrf2 (−/−) MEF cell. (a) MEF cells of each genotype were incubated in low potassium (2.7 mM) media for 24 and 48 hr. (b) Densitometric analysis of mRNA expression levels of Nrf2, kNBC1 and colonic H/K in MEF cells during pretreatment with low potassium. Low potassium promoted expression of Nrf2, kNBC1 and colonic H/K-ATPasein MEF-Nrf2 (+/+), but unchanged or even decreased in MEF-Nrf2 (+/−) and MEF-Nrf2 (−/−). |
References
1. Giebisch G. Renal potassium transport: mechanisms and regulation. Am J Physiol. 1998; 274:F817–F833.

2. Bae CS, Cho HJ, Ahn KY. Alteration of Akt, p-AKT, ERK, and p-ERK proteins expression in the kidney of hypokalemic rat. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2017; 30:87–98. Korean.

3. Ahn KY, Turner PB, Madsen KM, Kone BC. Effect of chronic hypokalemia on renal expression of the gene encoding the “gastric” H(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit. Am J Physiol. 1996; 270:F557–F566.
4. Ahn KY, Park KW, Kim KK, Kone BC. Chronic hypokalemia enhances expression of the H(+)-K(+)-ATPase α2 alpha 2-subunit gene in renal medulla. Am J Physiol. 1996; 271:F314–F321.
5. Ahn KY, Kim SC, Moon B, Kim KK, Kim BY. Renal adaptive responses of Na+-K+-ATPase subunit isoforms to chronic hypokalemia. Korean J Anat. 1998; 31:405–418. Korean.
6. Kim JH, Cho HJ, Bae MO, Park JJ, Ahn KY. Regulation of biocarbonate ions hypokalemic rat kidney. Korean J Anat. 2004; 37:337–345. Korean.
7. Lim JS, Ahn KY. Expression of Nrf2 transcription factor in rat kidney. Korean J Nephrol. 2011; 30:239–245. Korean.
8. Lee CB, Lee YS, Lee JY, Lee SE, Ahn KY. Nrf2 and Sp synergistically enhance the expression of ion transporters in potassium-depleted conditions. J Nephrol. 2012; 25:225–232.

9. Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, Cao A, Kan YW. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91:9926–9930.

10. Itoh K, Igarashi K, Hayashi N, Nishizawa M, Yamamoto M. Cloning and characterization of a novel erythroid cell-derived CNC family transcription factor heterodimerizing with the small Maf family proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995; 15:4184–4193.

11. Liu M, Grigoryev DN, Crow MT, Haas M, Yamamoto M, Reddy SP, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 is protective during ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2009; 76:277–285.

12. Yu R, Chen C, Mo YY, Hebbar V, Owuor ED, Tan TH, et al. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways induces antioxidant response element-mediated gene expression via a Nrf2-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:39907–39913.

13. Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med. 2004; 10:549–557.

14. Shen G, Jeong WS, Hu R, Kong AN. Regulation of Nrf2, NF-kappaB, and AP-1 signaling pathways by chemopreventive agents. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005; 7:1648–1663.

15. Cho HJ, Ahn KY. Alteration of Nrf2 and p-Nrf2 proteins expression in hypokalemic rat kidney. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2015; 28:55–62. Korean.

16. Zhou X, Yin W, Doi SQ, Robinson SW, Takeyasu K, Fan X. Stimulation of Na, K-ATPase by low potassium requires reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003; 285:C319–C326.
17. Babilonia E, Wei Y, Sterling H, Kaminski P, Wolin M, Wang WH. Superoxide anions are involved in mediating the effect of low K intake on c-Src expression and renal K secretion in the cortical collecting duct. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:10790–10796.

18. Deplancke B, Gaskins HR. Redox control of the transsulfuration and glutathione biosynthesis pathways. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2002; 5:85–92.

19. Kwon T, Kwon DY, Chun J, Kim JH, Kang SS. Akt protein kinase inhibits Rac1-GTP binding through phosphorylation at serine 71 of Rac1. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:423–428.

20. Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:489–501.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download