INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A. 2% solution-1.8 ml of the local anesthetic in cartridges containing 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine (Novocol Pharmaceutical Inc, Cambridge, Canada) was withdrawn into a 3-ml plastic syringe.
B. 4% solution (72 mg lidocaine solution)- 0.02 ml of the local anesthetic in a 2-ml ampule containing 40 mg/ml lidocaine (Jayson Pharmaceuticals Ltd; Dhaka, Bangladesh) was withdrawn using a micropipette. Then, 0.02 ml of 1:1000 epinephrine bitartrate (1 mg/ml) was withdrawn from a 1-ml ampule into the lidocaine ampule.
Type of impaction
Total volume of local anesthetic used during the operation (in ml).
Subjective onset: Vincent sign (in seconds)
Objective onset: Absence of pain to the pinprick test on the canine vestibule and molar lingual vestibule mucosa (in seconds) If the volunteer still responded to a pinprick after 15 min post-injection, the anesthesia was judged to have failed. Then, the operator injected 1.5 ml of the same local anesthetic solution for a second IANB. If local anesthesia was not achieved even after this second injection, the subject was withdrawn from the study.
Pulpal anesthesia: After administration of the local anesthetic, an electric pulp testing (EPT) value of 80 µA indicated profound pulpal anesthetic [1213141516]. Ten minutes post-injection, EPT was performed at the healthy canine and lower first or second molar, on the side of the injection and the obtained EPT values were compared to the base line values.
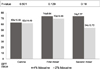
Pain assessment: The 100-mm visual analogue scale (VAS) was used for measuring pain during the procedure. This scale uses 4 levels of pain, which is counted from the extreme left side and is categorized as: no pain (0-4 mm), mild pain (5-44 mm), moderate pain (45-74 mm), and unbearable pain (75-100 mm) [17]. The VAS was measured when the drug was dispensed into the tissue for the first time, during the operation, and 1-h post operation.
Duration of local anesthesia: This was recorded by each patient in the patient report chart and signified the time lapsed from the subjective onset of anesthesia to the time when the numbness at the lower lip wore off (in minutes).
Incidence of postoperative severe adverse effects: This was observed by the surgeon and also reported by the patient during the operation and in the first few hours after the operation (e.g., dizziness, anxiety, any neuron dysfunction, etc.).
-
pH of local anesthetic solutions: This was measured using a millivolt pH meter (Orion 3 Star pH Benchtop; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA)
a. 4% lidocaine without epinephrineb. 4% lidocaine with epinephrine 1:100,000c. 2% lidocaine with epinephrine 1:100,000




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download