References
1. Chirica M, Bonavina L, Kelly MD, Sarfati E, Cattan P. Caustic ingestion. Lancet. 2017; 389:2041–2052.

2. Park KS. Evaluation and management of caustic injuries from ingestion of acid or alkaline substances. Clin Endosc. 2014; 47:301–307.

3. Dhamrait RS. Airway obstruction following potassium permanganate ingestion. Anaesthesia. 2003; 58:606–607.

4. Cevik SE, Yesil O, Ozturk TC, Guneysel O. Potassium permanganate ingestion as a suicide attempt. Clin Pract. 2012; 2:e32.

5. Korkut E, Saritas A, Aydin Y, Korkut S, Kandis H, Baltaci D. Suicidal ingestion of potassium permanganate. World J Emerg Med. 2013; 4:73–74.

6. Ong KL, Tan TH, Cheung WL. Potassium permanganate poisoning–a rare cause of fatal self poisoning. J Accid Emerg Med. 1997; 14:43–45.

7. Cheng HT, Cheng CL, Lin CH, et al. Caustic ingestion in adults: the role of endoscopic classification in predicting outcome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2008; 8:31.

8. Lurie Y, Slotky M, Fischer D, Shreter R, Bentur Y. The role of chest and abdominal computed tomography in assessing the severity of acute corrosive ingestion. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2013; 51:834–837.

9. Kamijo Y, Kondo I, Kokuto M, Kataoka Y, Soma K. Miniprobe ultrasonography for determining prognosis in corrosive esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:851–854.

10. Kochhar R, Das K, Mehta SK. Potassium permanganate induced oesophageal stricture. Hum Toxicol. 1986; 5:393–394.

Fig. 1.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopic findings at the time of potassium permanganate ingestion. (A) Mucosal edema and hyperemia of oropharynx. (B) Blackish brown staining with erosion of esophagus. (C) Deep ulceration with whitish exudates on gastroesophageal junction and cardia. (D) Mucosal hyperemia, edema, and multiple erosions from cardia to the posterior wall of the high body.

Fig. 2.
Chest computed tomographic findings. (A, B) Diffuse and mild esophageal wall thickening of whole esophagus (arrows) with no evidence of perforation or mediastinitis.
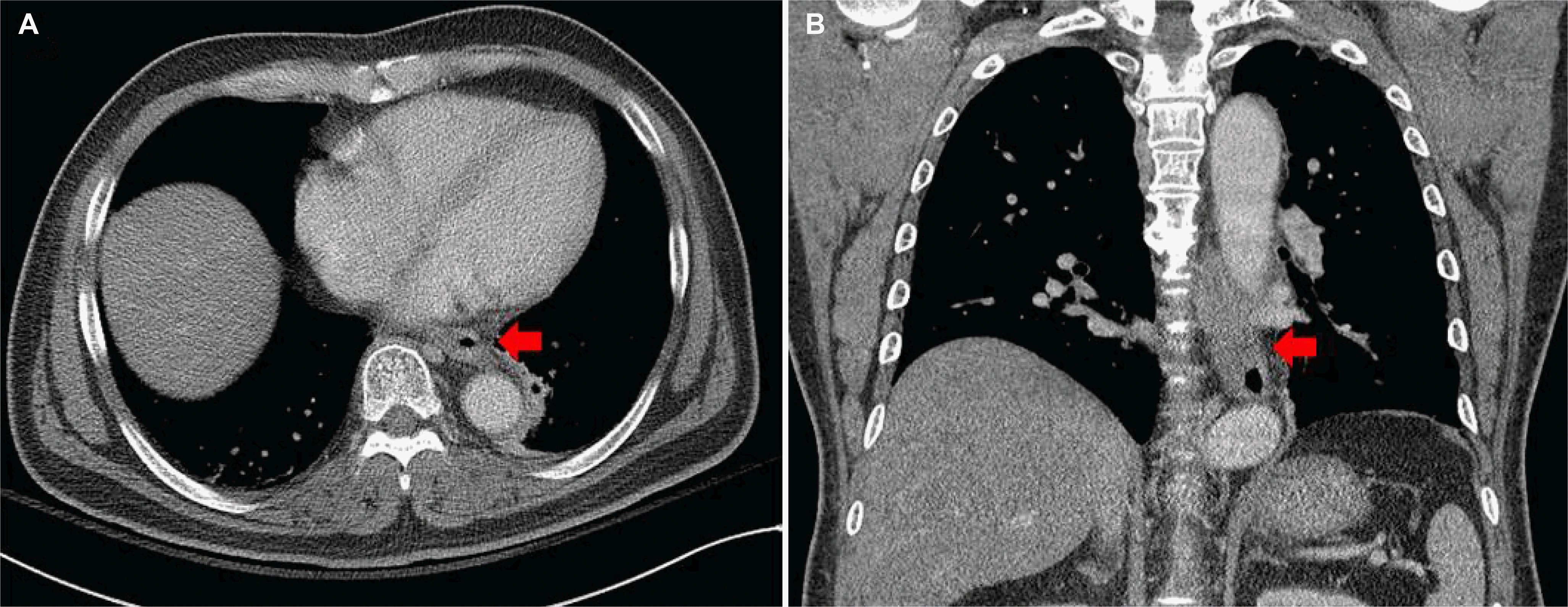
Fig. 3.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopic findings 9 months after corrosive injury. (A) Improved state of corrosive esophagitis. (B) Reflux esophagitis LA grade B. (C) About 5 mm sized subepithelial tumor on posterior wall of cardia, and (D) Linear erosion with mucosal hyperemia on the greater curvature of the mid body. LA, Los Angeles.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download