INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Animals
Study design
 | Figure 1Experimental design in the rabbit calvarium. (A) Four circular defects 8 mm in diameter were prepared using a trephine bur. (B) Each defect was randomly assigned to an experimental group. Clockwise from top left; M, sham control, BG, and BG+M.BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, M: group of defects covered with an a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane without graft material, BG: group of defects filled with BCP particles without membrane coverage, BG+M: group of defects filled with BCP particles and covered with a UV-crosslinked collagen membrane with added BCP in a conventional guided bone regeneration procedure.
|
Surgical procedure
Evaluation method
Clinical observations
Micro-CT analysis
- Total augmented volume (TAV; mm3): Total augmented volume of the ROI, including mineralized tissue, graft material, and fibrovascular connective tissue in the defect.
- New bone volume (NBV; mm3): Sum of volumetric measurements of newly-formed bone in the defect.
- Residual material volume (RMV; mm3): Sum of volumetric measurements of the remaining BCP in the defect.
Histologic and histometric analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Clinical observations
Micro-CT analysis
Table 1
TAV, NBV, and RMV measured by micro-CT grayscale values

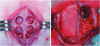
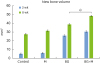 | Figure 2In micro-CT images taken at 8 weeks, the new bone volume of the BG+M group (48.39±5.47 mm3) showed a significant difference compared to the BG group (38.71±2.24 mm3).CT: computed tomography, BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, M: group of defects covered with an a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane without graft material, BG: group of defects filled with BCP particles without membrane coverage, BG+M: group of defects filled with BCP particles and covered with a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane in a conventional guided bone regeneration procedure.
a)P=0.032.
|
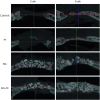 | Figure 3Micro-CT views of the defects after 2 week, and 8 weeks of healing. At 2 weeks in the control and M groups, the defects were rarely filled, and even at 8 weeks, the defects were partially filled with a thin new bone bridge. Compared to natural bone, the newly-formed bone can be observed as a grayish area, and the BCP particles are observed as a more whitish area.CT: computed tomography, BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, M: group of defects covered with an a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane without graft material, BG: group of defects filled with BCP particles without membrane coverage, BG+M: group of defects filled with BCP particles and covered with a UV-crosslinked collagen membrane with added BCP in a conventional guided bone regeneration procedure.
|
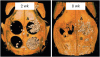 | Figure 4Reconstructed images of micro-CT views at 2 weeks and 8 weeks. At both 2 and 8 weeks, the BG group (upper right; A) showed scattering of BCP particles outside of the defect, while the BG+M group (B) showed enclosed BCP particles in the defect area.CT: computed tomography, BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, M: group of defects covered with an a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane without graft material, BG: group of defects filled with BCP particles without membrane coverage, BG+M: group of defects filled with BCP particles and covered with a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane in a conventional guided bone regeneration procedure.
|
Histomorphologic analysis
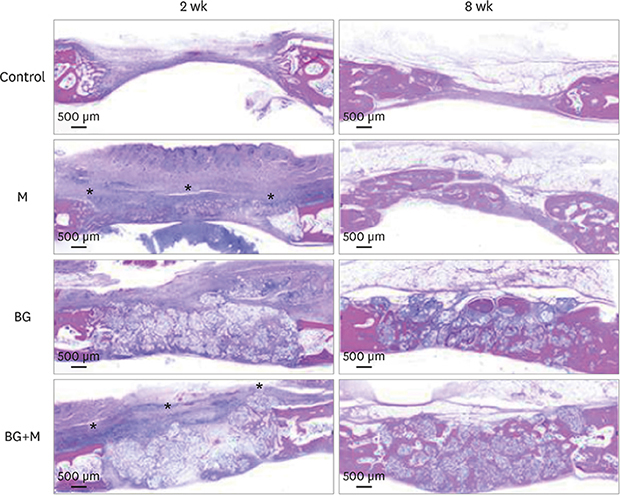
 | Figure 5Histological images obtained at 2 and 8 weeks. Low-magnification views of the sham control, BG, M, and BG+M groups, respectively (hematoxylin and eosin staining). The applied collagen membrane remained intact over the defects at 2 weeks in the M and BG+M groups. The remaining collagen membranes in the 2-week groups are marked with an asterisk (*).BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, M: group of defects covered with an a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane without graft material, BG: group of defects filled with BCP particles without membrane coverage, BG+M: group of defects filled with BCP particles and covered with a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane in a conventional guided bone regeneration procedure.
|
Control
M group
 | Figure 6A few membrane remnants were observed in the M group at 8 weeks. Both in hematoxylin and eosin and Masson trichrome stained slides, the remaining portion of the crosslinked collagen membrane is observed as a thin film shape. The remaining membrane is marked with an asterisk (*).BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, M: group of defects covered with a BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane without graft material.
|
BG group
BG+M group
 | Figure 7At 8 weeks in the BG+M group, matured new bone was found above the graft material area where the membrane was located, while new bone formation in the BCP-augmented area was insufficient. New bone that substituted the crosslinked collagen membrane is marked with an asterisk (*).BCP: biphasic calcium phosphate, UV: ultraviolet, BG+M: group of defects filled with BCP particles and covered with an BCP-supplemented UV-crosslinked collagen membrane in a conventional guided bone regeneration procedure.
|
Histometric analysis
Table 2
TAA, NBA, and RMA measured by histometric analysis





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download