INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Cell culture reagents
Structure-based computational screening
Protein expression and purification
MST assay
Site directed mutagenesis
Western blot analysis
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
Three-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats associated Cas9 nuclease (CRISPR/Cas9) mediated CtBP1 knockout
Scratch assay
Transwell assay
Immunofluorescence
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Computational screening for compounds against CtBP1 and binding validation
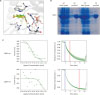 | Figure 1PA directly binds to CtBP1. (A) Docking mode of PA against CtBP1. CtBP1 is shown in cartoon, phenylpyruvate in green sticks, and PA in yellow sticks. Arg97, Arg266, Trp318, and NAD401 are in gray sticks. The distances are shown with yellow dashes. (B) Wild-type and CtBP1 mutant proteins with Arg97Ala and Arg266Ala substitutions were expressed in BL21(DE3) Escherichia coli strain and purified. The sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel shows the proteins before and after purification. (C) Quantification of the binding affinity of PA to CtBP1 using Microscale thermophoresis assay. The binding affinity of PA for wild-type CtBP1 was 245 ± 23.5 nM (shown in the upper panel). The lower panel shows the thermophoresis signal from PA to CtBP1 mutant, which was too chaotic to obtain a typical dose-response curve indicating there is no significant binding between PA and CtBP1 mutant.PA = protocatechuic aldehyde; CtBP1 = C-terminal binding protein 1.
|
PA inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells
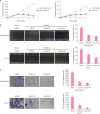 | Figure 2PA inhibits the growth and migration of breast cancer cells. (A) Growth curves of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells treated with 0.1% DMSO or 100 μM PA, respectively. (B) Migratory ability of breast cancer cells was tested using the scratch assay. PA exhibited inhibitory effect at the concentration of 50 μM in both MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. Representative images show the wound with or without PA treatment. (C) Migratory ability of breast cancer cells was tested using the transwell assay. The number of cells that migrated were calculated from 3 randomly chosen microscopic fields. Results shown in the bar diagram are mean ± SD from triplicate experiments.PA = protocatechuic aldehyde; DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide; SD = standard deviation.
*p < 0.05.
|
PA attenuates CtBP1 repression activity on p21 and E-cadherin
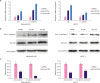 | Figure 3PA upregulates p21 and E-cadherin expression in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. (A) PA upregulated p21 and E-cadherin mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner following treatment for 48 hours. (B) PA upregulated p21 and E-cadherin protein levels following treatment for 48 hours. (C) The CtBP1 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay showed PA treatment decreased CtBP1 binding intensities at the promoter regions of p21 and E-cadherin.PA = protocatechuic aldehyde; CtBP1 = C-terminal binding protein 1; DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; mRNA = messenger RNA.
*p < 0.05.
|
CtBP1 knockout breast cancer cells exhibit resistance to PA-mediated repression of growth and migration
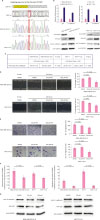 | Figure 4Knockout of CtBP1 increases the resistance to PA. (A) Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats associated Cas9 nuclease-mediated CtBP1 knockout in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. The sgRNA used in this study is highlighted in yellow. The targeting sequence of the sgRNA is in the minus strand of the 2nd exon of CtBP1. Sanger sequencing confirmed that both the knockout cell lines had an adenine insertion between the 57th and the 58th nucleotides in the 2nd CDS exon of human CtBP1. The red rectangles indicate the position of the inserted adenine from Sanger sequencing and alignment results. (B) Knockout of CtBP1 in breast cancer cells increased p21 and E-cadherin mRNA and protein expression. (C) Complete deletion of CtBP1 in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells increased the IC50 values of PA in the breast cancer cells after 48 hours of treatment. (D and E) The CtBP1 knockout MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells showed resistance to PA-mediated inhibition of migration. 50 μM PA did not show any inhibition in the knockout cells while 100 μM PA showed slight inhibition. (F) The inhibition of migration mediated by 100 μM PA was reduced in the CtBP1 knockout cells compared to CtBP1 expressing cells. The relative inhibitory effect is presented by the covered area or migrated cells ratios of the DMSO group/100 μM PA treated group which were calculated using the mean values of the groups. (G) p21 and E-cadherin expression did not respond to PA treatment in the CtBP1 knockout cells.CtBP1 = C-terminal binding protein 1; PA = protocatechuic aldehyde; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide; sgRNA = single-guide RNA; mRNA = messenger RNA.
*p < 0.05.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download