Abstract
Purpose
To determine the through-focus optical bench test performance of monofocal, bifocal, and extended depth-of-focus intraocular lenses (IOLs), and to measure their defocus curves.
Methods
A model eye was placed on an optical bench to test three different IOLs (TECNIS ZXR00, ZMB00, and ZCB00; Abbott Medical Optics, Santa Ana, CA, USA). The focus was changed by inserting trial lenses from +1.00 diopters to −4.00 diopters, in increments of +0.25 diopters. The 1951 United States Air Force Resolution chart was used to determine the quality of the images. The degree of similarity with reference images was given by the cross-correlation coefficient, and defocus curves were drawn and compared.
Results
Bifocal IOLs showed lower image quality with the addition of minus diopter trial lenses, but showed good image quality at near distance. Bifocal IOLs also showed a ‘double peak’ in their defocus curve. Monofocal IOLs showed a lower image quality and cross-correlation coefficient with addition of lower-diopter trial lenses. The extended depth of focus IOLs showed a single peak in their defocus curve, but had a wider range of diopters and better image quality than monofocal IOLs.
Figures and Tables
 | Figure 1Schematic diagram of optical bench system. Optical bench system is composed of resolution target, artificial pupil, trial lens, model eye and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor camera. IOL = intraocular lens; CMOS = complementary metal oxide semiconductor. |
 | Figure 2Photo of optical bench system. Optical bench system is composed of resolution target, artificial pupil, trial lens, model eye and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor camera. |
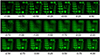 | Figure 3Captured images of 1951 United States Air Force resolution test chart using bifocal intraocular lens (TECNIS® ZKB00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA). Minus diopter represents near distance. |
 | Figure 4Captured images of 1951 United States Air Force resolution test chart using monofocal (TECNIS® ZCB00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA), bifocal (TECNIS® ZKB00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc.) and extended depth of focus intraocular lens (TECNIS® Symfony ZXR00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc.). EDOF = extended depth of focus. |
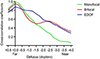 | Figure 5Through-focus correlation coefficients of the three different intraocular lenses. Bifocal intraocular lens (TECNIS® ZKB00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA) showed double peak appearance but monofocal (TECNIS® ZCB00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc.) and extended depth of focus showed single peak appearance. Extended depth of focus intraocular lens (TECNIS® Symfony ZXR00, Abbott Medical Optics, Inc.) had a wider range of diopters with a cross-correlation coefficient of 0.7 or greater than monofocal intraocular lens. EDOF = extended depth of focus. |
Notes
This study was Supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HI17C0659), Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Republic of Korea (No. 2017R1A1A2A10000681), and the Sodam Scholarship Foundation of Busan Sungmo Eye Hospital.
References
1. Maxwell WA, Cionni RJ, Lehmann RP, Modi SS. Functional outcomes after bilateral implantation of apodized diffractive aspheric acrylic intraocular lenses with a +3.0 or +4.0 diopter addition power Randomized multicenter clinical study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:2054–2056.

2. de Vries NE, Webers CA, Touwslager WR, et al. Dissatisfaction after implantation of multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:859–865.


3. Weeber HA, Meijer ST, Piers PA. Extending the range of vision using diffractive intraocular lens technology. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:2746–2754.


4. Kohnen T, Böhm M, Hemkeppler E, et al. Visual performance of an extended depth of focus intraocular lens for treatment selection. Eye (Lond). 2019; 33:1556–1563.



5. Cochener B. Concerto Study Group. Clinical outcomes of a new extended range of vision intraocular lens: International Multicenter Concerto Study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016; 42:1268–1275.


6. Attia MSA, Auffarth GU, Kretz FTA, et al. Clinical evaluation of an extended depth of focus intraocular lens with the salzburg reading desk. J Refract Surg. 2017; 33:664–669.


7. Kim MJ, Zheleznyak L, Macrae S, et al. Objective evaluation of through-focus optical performance of presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses using an optical bench system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1305–1312.



8. Hwang HS, Lee CS. Analysis of autofocusing evaluation functions of intraocular lens. J Inst Contr Robot Syst. 2017; 23:758–763.
9. Carson D, Hill WE, Hong X, Karakelle M. Optical bench performance of AcrySof((R)) IQ ReSTOR((R)), AT LISA((R)) tri, and FineVision((R)) intraocular lenses. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014; 8:2105–2113.


10. Gatinel D, Houbrechts Y. Comparison of bifocal and trifocal diffractive and refractive intraocular lenses using an optical bench. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1093–1099.


11. Montés-Micó R, Madrid-Costa D, Ruiz-Alcocer J, et al. In vitro optical quality differences between multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:928–936.


12. Yoo YS, Whang WJ, Byun YS, et al. Through-focus optical bench performance of extended depth-of-focus and bifocal intraocular lenses compared to a monofocal lens. J Refract Surg. 2018; 34:236–243.


13. Plaza-Puche AB, Alió JL, MacRae S, et al. Correlating optical bench performance with clinical defocus curves in varifocal and trifocal intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2015; 31:300–307.


14. Ruiz-Mesa R, Abengózar-Vela A, Aramburu A, Ruiz-Santos M. Comparison of visual outcomes after bilateral implantation of extended range of vision and trifocal intraocular lenses. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2017; 27:460–465.


15. Kaymak H, Hohn F, Breyer DR, et al. Functional results 3 months after implantation of an “extended range of vision” intraocular lens. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2016; 233:923–927.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download