Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
References
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Distribution of the four types of body composition according to sex and age groups at (A, B) baseline and (C, D) their respective changes after the 5-year follow-up period.
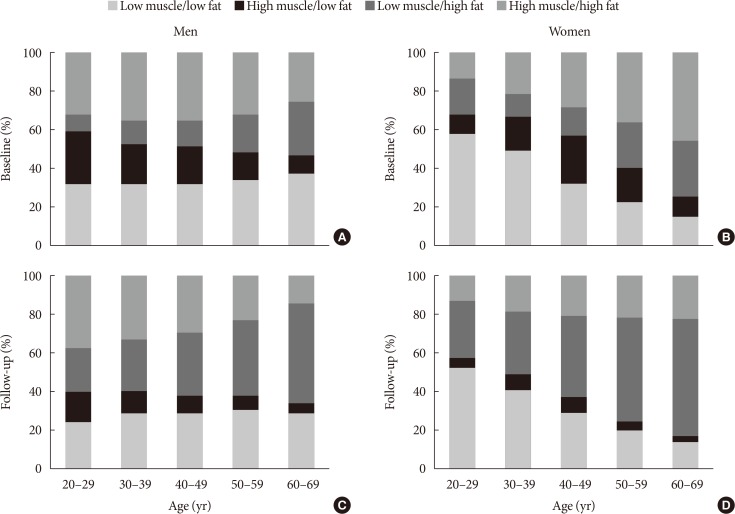
Fig. 2
(A) Transitions of each body composition phenotype from baseline to follow-up after 5 years. (B) Incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the baseline “high muscle/low fat” group according to the transition of body composition during the follow-up period. aP<0.01 between the groups by chi-square test.
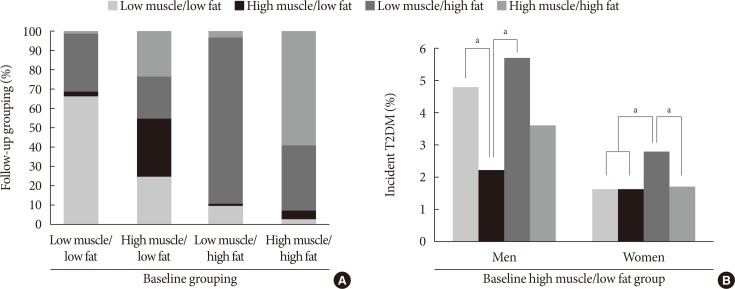
Table 1
Baseline characteristics of the participants
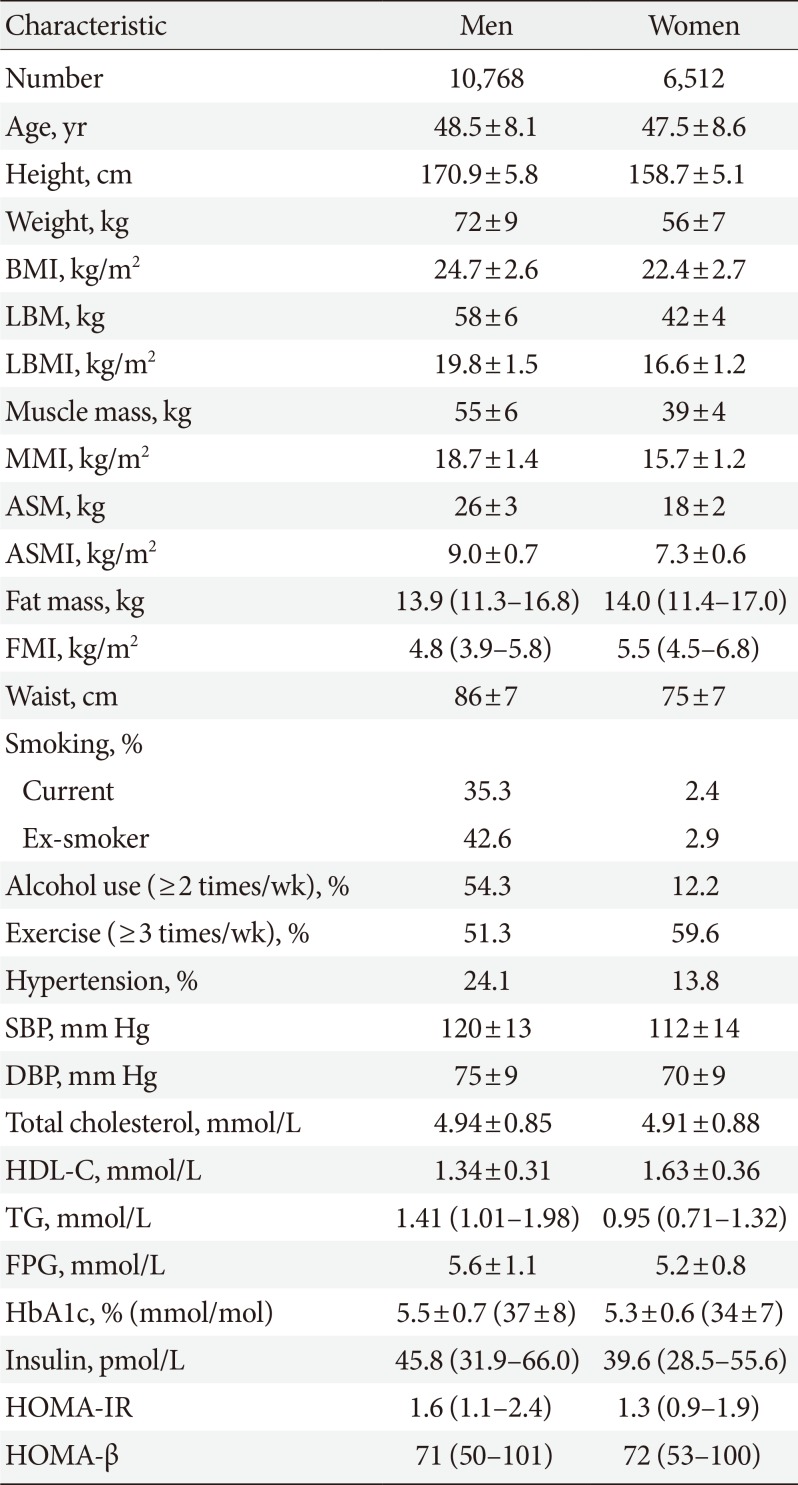
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or median (interquartile range).
BMI, body mass index; LBM, lean body mass; LBMI, lean body mass index; MMI, muscle mass index; ASM, appendicular skeletal muscle mass; ASMI, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; FMI, fat mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function index.
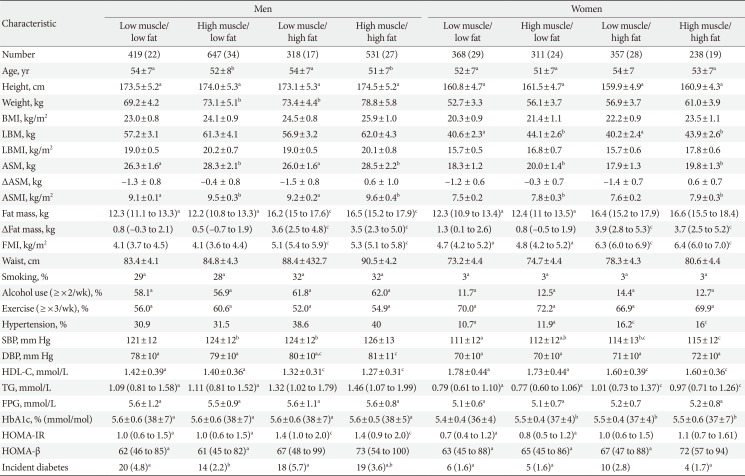
Table 2
Comparison of baseline characteristics and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus according to four body composition phenotypes at baseline
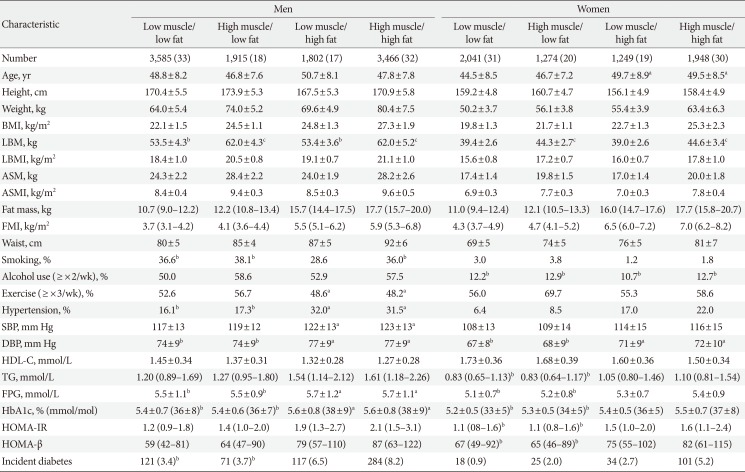
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range). All continuous variables were significantly different among the four groups with analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal-Wallis test except for those designated by the same symbols such as a,b,c. All categorical variables were also significantly different with chi-square tests except for those designated by the same symbols a,b,c.
BMI, body mass index; LBM, lean body mass; LBMI, lean body mass index; ASM, appendicular skeletal muscle mass; ASMI, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; FMI, fat mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function index.
Not significantly different from a“low muscle/high fat” group, b“low muscle/low fat” group, c“high muscle/low fat” group by post hoc analysis with Tukey test or chi-square test.
Table 3
Comparison of changes in characteristics among four transition types of body composition in the baseline high muscle/low fat group
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range). Comparisons among groups were performed with analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and chi-square test for categorical variables. ‘Δ’ means change from baseline to follow-up.
BMI, body mass index; LBM, lean body mass; LBMI, lean body mass index; ASM, appendicular skeletal muscle mass; ASMI, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; FMI, fat mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function index.
No significant difference from a“low muscle/low fat” group, b“high muscle/low fat” group, and c“low muscle/high fat” group by post hoc analysis with Tukey test or chi-square test. The values with different symbols have significant difference between them. All other values without any symbol were significantly different among the four groups.
Table 4
ORs for incident diabetes in men and women according to obesity status
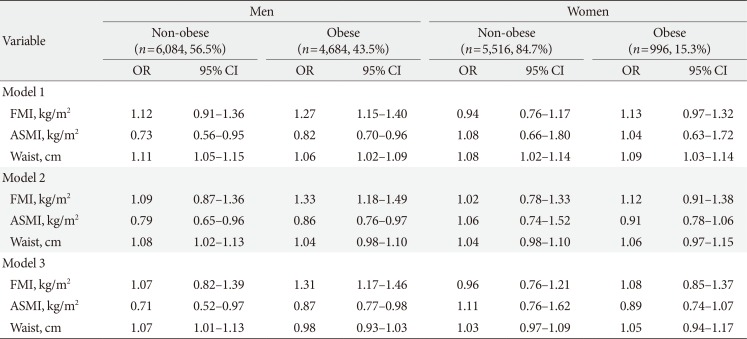
Model 1, adjusted for age; Model 2, adjusted for age, baseline glycosylated hemoglobin, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; Model 3, adjusted for factors in Model 2+physical activity, smoking, alcohol drinking, family history of diabetes, systolic blood pressure, serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol. Obesity was defined as body mass index ≥25 kg/m2.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; FMI, fat mass index; ASMI, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download