1. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Lawman HG, Fryar CD, Kruszon-Moran D, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Trends in obesity prevalence among children and adolescents in the United States, 1988-1994 through 2013-2014. JAMA. 2016; 315:2292–2299. PMID:
27272581.

2. Kumar S, Kelly AS. Review of childhood obesity: from epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical assessment and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017; 92:251–265. PMID:
28065514.
3. Kelsey MM, Zaepfel A, Bjornstad P, Nadeau KJ. Age-related consequences of childhood obesity. Gerontology. 2014; 60:222–228. PMID:
24434909.

4. Legeay S, Faure S. Is bisphenol A an environmental obesogen? Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2017; 31:594–609. PMID:
28622415.

5. Mikołajewska K, Stragierowicz J, Gromadzinska J. Bisphenol A: application, sources of exposure and potential risks in infants, children and pregnant women. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2015; 28:209–241. PMID:
26182919.
6. Gore AC, Chappell VA, Fenton SE, Flaws JA, Nadal A, Prins GS, Toppari J, Zoeller RT. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society's second scientific statement on endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Endocr Rev. 2015; 36:E1–E150. PMID:
26544531.

9. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Draft assessment of bisphenol A for use in food contact applications. Bethesda: U.S. Food and Drug Administration;2008.
10. Rochester JR, Bolden AL. Bisphenol S and F: a systematic review and comparison of the hormonal activity of bisphenol a substitutes. Environ Health Perspect. 2015; 123:643–650. PMID:
25775505.

11. Wu LH, Zhang XM, Wang F, Gao CJ, Chen D, Palumbo JR, Guo Y, Zeng EY. Occurrence of bisphenol S in the environment and implications for human exposure: a short review. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 615:87–98. PMID:
28963899.

12. Zhang J, Zhang T, Guan T, Ruan P, Ren D, Dai W, Yu H, Li T. Spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches to investigate the interaction of bisphenol A, bisphenol F and their diglycidyl ethers with PPARα. Chemosphere. 2017; 180:253–258. PMID:
28411541.

13. Ahmed S, Atlas E. Bisphenol S- and bisphenol A-induced adipogenesis of murine preadipocytes occurs through direct peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016; 40:1566–1573. PMID:
27273607.

15. Barr DB, Wilder LC, Caudill SP, Gonzalez AJ, Needham LL, Pirkle JL. Urinary creatinine concentrations in the U.S. population: implications for urinary biologic monitoring measurements. Environ Health Perspect. 2005; 113:192–200. PMID:
15687057.

16. Ogden CL, Flegal KM. Changes in terminology for childhood overweight and obesity. Natl Health Stat Report. 2010; 25:1–5.
17. Ashwell M, Gibson S. Waist-to-height ratio as an indicator of ‘early health risk’: simpler and more predictive than using a ‘matrix’ based on BMI and waist circumference. BMJ Open. 2016; 6:e010159.

18. Trasande L, Attina TM, Blustein J. Association between urinary bisphenol A concentration and obesity prevalence in children and adolescents. JAMA. 2012; 308:1113–1121. PMID:
22990270.

19. Guenther PM, Kirkpatrick SI, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM, Buckman DW, Dodd KW, Casavale KO, Carroll RJ. The Healthy Eating Index-2010 is a valid and reliable measure of diet quality according to the 2010 dietary guidelines for Americans. J Nutr. 2014; 144:399–407. PMID:
24453128.

20. Liu B, Lehmler HJ, Sun Y, Xu G, Liu Y, Zong G, Sun Q, Hu FB, Wallace RB, Bao W. Bisphenol A substitutes and obesity in US adults: analysis of a population-based, cross-sectional study. Lancet Planet Health. 2017; 1:e114–e122. PMID:
29308453.

21. Bearer CF. How are children different from adults? Environ Health Perspect. 1995; 103(Suppl 6):7–12.

22. Moreman J, Lee O, Trznadel M, David A, Kudoh T, Tyler CR. Acute toxicity, teratogenic, and estrogenic effects of bisphenol a and its alternative replacements bisphenol S, bisphenol F, and bisphenol AF in zebrafish embryo-larvae. Environ Sci Technol. 2017; 51:12796–12805. PMID:
29016128.

23. Le Fol V, Ait-Aissa S, Sonavane M, Porcher JM, Balaguer P, Cravedi JP, Zalko D, Brion F. In vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity of BPA, BPF and BPS in zebrafish-specific assays. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2017; 142:150–156. PMID:
28407500.

24. Verbanck M, Canouil M, Leloire A, Dhennin V, Coumoul X, Yengo L, Froguel P, Poulain-Godefroy O. Low-dose exposure to bisphenols A, F and S of human primary adipocyte impacts coding and non-coding RNA profiles. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0179583. PMID:
28628672.

25. Yang Q, Yang X, Liu J, Ren W, Chen Y, Shen S. Effects of BPF on steroid hormone homeostasis and gene expression in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis of zebrafish. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017; 24:21311–21322. PMID:
28741210.

26. Schneider JE. Energy balance and reproduction. Physiol Behav. 2004; 81:289–317. PMID:
15159173.

27. Zheng S, Shi JC, Hu JY, Hu WX, Zhang J, Shao B. Chlorination of bisphenol F and the estrogenic and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma effects of its disinfection byproducts. Water Res. 2016; 107:1–10. PMID:
27780033.

28. Kidani T, Kamei S, Miyawaki J, Aizawa J, Sakayama K, Masuno H. Bisphenol A downregulates Akt signaling and inhibits adiponectin production and secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010; 17:834–843. PMID:
20467186.

29. Li DK, Miao M, Zhou Z, Wu C, Shi H, Liu X, Wang S, Yuan W. Urine bisphenol-A level in relation to obesity and overweight in school-age children. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e65399. PMID:
23776476.

30. Bhandari R, Xiao J, Shankar A. Urinary bisphenol A and obesity in U.S. children. Am J Epidemiol. 2013; 177:1263–1270. PMID:
23558351.

31. Wells EM, Jackson LW, Koontz MB. Association between bisphenol A and waist-to-height ratio among children: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003-2010. Ann Epidemiol. 2014; 24:165–167. PMID:
23830935.

32. LaKind JS, Naiman DQ. Temporal trends in bisphenol A exposure in the United States from 2003-2012 and factors associated with BPA exposure: spot samples and urine dilution complicate data interpretation. Environ Res. 2015; 142:84–95. PMID:
26121292.

33. Wang HX, Zhou Y, Tang CX, Wu JG, Chen Y, Jiang QW. Association between bisphenol A exposure and body mass index in Chinese school children: a cross-sectional study. Environ Health. 2012; 11:79. PMID:
23083070.

34. Mauvais-Jarvis F. Estrogen and androgen receptors: regulators of fuel homeostasis and emerging targets for diabetes and obesity. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 22:24–33. PMID:
21109497.

35. Vandenberg LN, Colborn T, Hayes TB, Heindel JJ, Jacobs DR Jr, Lee DH, Shioda T, Soto AM, vom Saal FS, Welshons WV, Zoeller RT, Myers JP. Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr Rev. 2012; 33:378–455. PMID:
22419778.

36. Xu X, Tan L, Himi T, Sadamatsu M, Tsutsumi S, Akaike M, Kato N. Changed preference for sweet taste in adulthood induced by perinatal exposure to bisphenol A: a probable link to overweight and obesity. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2011; 33:458–463. PMID:
21704699.
37. Dekant W, Volkel W. Human exposure to bisphenol A by biomonitoring: methods, results and assessment of environmental exposures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008; 228:114–134. PMID:
18207480.

38. Nepomnaschy PA, Baird DD, Weinberg CR, Hoppin JA, Longnecker MP, Wilcox AJ. Within-person variability in urinary bisphenol A concentrations: measurements from specimens after long-term frozen storage. Environ Res. 2009; 109:734–737. PMID:
19463991.

39. Mahalingaiah S, Meeker JD, Pearson KR, Calafat AM, Ye X, Petrozza J, Hauser R. Temporal variability and predictors of urinary bisphenol A concentrations in men and women. Environ Health Perspect. 2008; 116:173–178. PMID:
18288314.

40. Vafeiadi M, Roumeliotaki T, Myridakis A, Chalkiadaki G, Fthenou E, Dermitzaki E, Karachaliou M, Sarri K, Vassilaki M, Stephanou EG, Kogevinas M, Chatzi L. Association of early life exposure to bisphenol A with obesity and cardiometabolic traits in childhood. Environ Res. 2016; 146:379–387. PMID:
26821262.

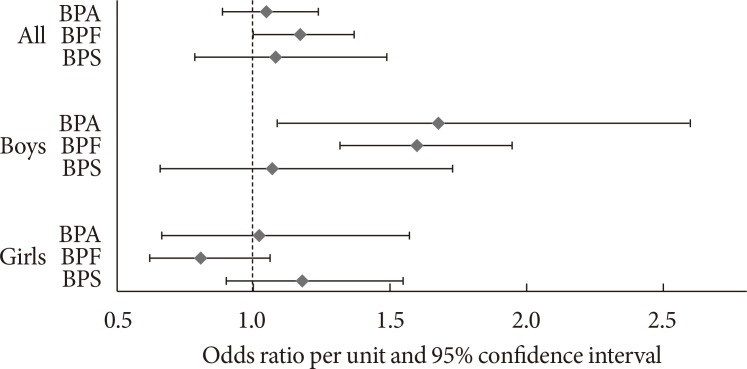
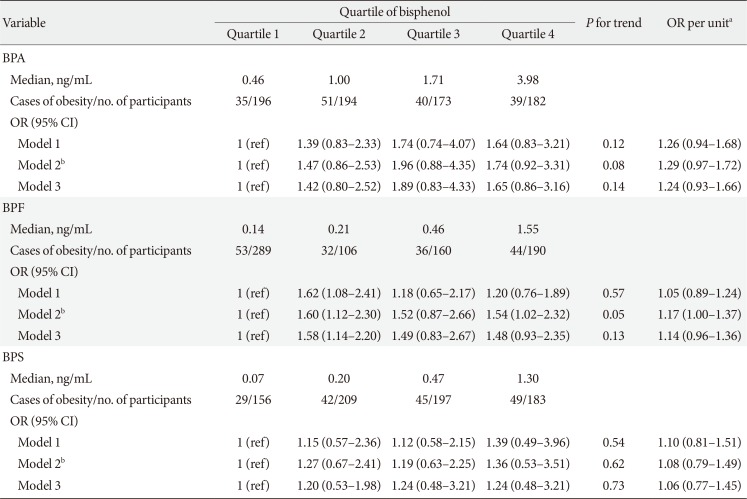
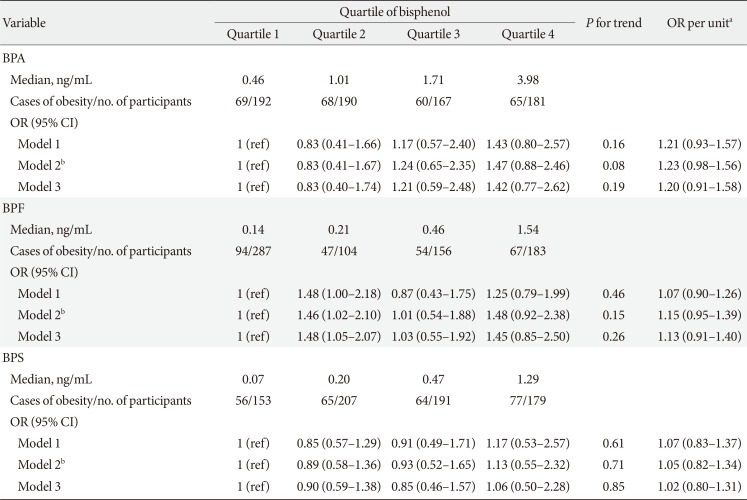
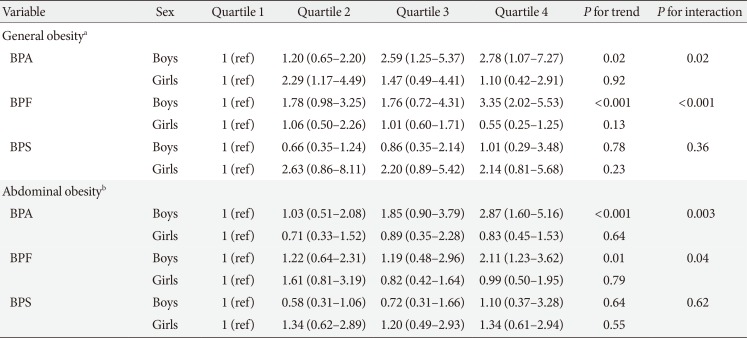




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download