Abstract
Figures and Tables
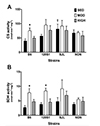 | Fig. 1Effect of moderate-intensity continuous (MOD) and high-intensity interval training (HIT) on oxidative enzyme activity in gastrocnemius muscle from four inbred mouse strains.Eight-week old male mice (B6, 129S1, SJL, and NON) were trained with MOD or HIT for 4 weeks. (A) Responses of citrate synthase (CS) activity (nmol · min−1 · mg−1) to two training intensities. (B) Responses of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity (nmol · min−1 · mg−1) to two exercise training intensities. Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. *p < 0.05 significantly different from sedentary controls (SED) within the same strain. †p < 0.05 significantly different from SED of B6.
|
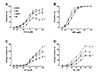 | Fig. 2Differences in intrinsic vascular reactivity among sedentary mice from four inbred strains.Intrinsic vascular reactivity was assessed using cumulative concentration-response curves to four different vasoactive agents in aortas from sedentary mice (13-week old) of four inbred strains. (A) acetylcholine (ACh), (B) sodium nitroprusside (SNP), (C) phenylephrine (PE), and (D) potassium chloride (KCl). Cumulative concentration-response curves are expressed by percent relaxation or change in tension (%). Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per strain. †p < 0.05 significantly different from sedentary controls (SED) of B6.
|
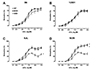 | Fig. 3Effect of moderate-intensity continuous (MOD) and high-intensity interval training (HIT) on acetylcholine-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in aortas from four inbred mouse strains.After exercise training with moderate intensity continuous running training (MOD) or high intensity interval training (HIT) for 4 weeks, cumulative concentration-response curves to acetylcholine (ACh, 10−9 to 10−5 M) were assessed in isolated thoracic aortas from four inbred strains, (A) B6, (B) 129S1, (C) SJL, and (D) NON. Cumulative concentration-response curves are expressed by percent relaxation (%). Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. *p < 0.05 significantly different from sedentary controls (SED) within the same strain.
|
 | Fig. 4Effect of moderate-intensity continuous (MOD) and high-intensity interval training (HIT) on sodium nitroprusside-induced endothelium-independent vasorelaxation in aortas from four inbred mouse strains.After exercise training with moderate intensity continuous running training (MOD) or high intensity interval training (HIT) for 4 weeks, cumulative concentration-response curves to sodium nitroprusside (SNP, 10−9 to 10−5 M) were assessed in isolated thoracic aortas from 4 inbred strains, (A) B6, (B) 129S1, (C) SJL, and (D) NON. Cumulative concentration-response curves are expressed by percent relaxation (%). Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. SNP-induced endothelium-independent vasorelaxation was not different among groups within any of strains.
|
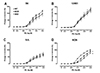 | Fig. 5Effect of moderate-intensity continuous (MOD) and high-intensity interval training (HIT) on phenylephrine-induced contraction in aortas from four inbred mouse strains.After exercise training with moderate intensity continuous running training (MOD) or high intensity interval training (HIT) for 4 weeks, cumulative concentration-response curves to phenylephrine (PE, 10−9 to 10−5 M) were assessed in isolated thoracic aortas from four inbred strains, (A) B6, (B) 129S1, (C) SJL, and (D) NON. Cumulative concentration-response curves are expressed by change in tension (%). Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. *p < 0.05 significantly different from sedentary controls (SED) within the same strain.
|
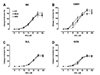 | Fig. 6Effect of moderate-intensity continuous (MOD) and high-intensity interval training (HIT) on potassium chloride-induced contraction in aortas from four inbred mouse strains.After exercise training with moderate intensity continuous running training (MOD) or high intensity interval training (HIT) for 4 weeks, cumulative concentration-response curves to potassium chloride (KCl, 5–100 mM) were assessed in isolated thoracic aortas from four inbred strains, (A) B6, (B) 129S1, (C) SJL, and (D) NON. Cumulative concentration-response curves are expressed by change in tension (%). Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. KCl-induced contraction was not different among groups within any of strains.
|
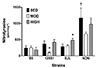 | Fig. 7Effect of moderate-intensity continuous (MOD) and highintensity interval training (HIT) on nitrotyrosine level in gastrocnemius muscle from four inbred mouse strains.8-week old male mice were trained with moderate intensity continuous running training (MOD) or high intensity interval training (HIT) for 4 weeks. Values are expressed as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. *p < 0.05 significantly different from sedentary controls (SED) within the same strain. †p < 0.05 significantly different from SED of B6.
|
Table 1
Body, heart mass and exercise capacity before and after exercise training in four inbred mouse strains

Values are presented as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. Pre-training BM, body mass before training; Change in BM, body mass after training minus before training; Terminal HM:BM, the heart mass to body mass ratio after training; Pre-training exercise capacity, total run to exhaustion time before training; Change in time, run to exhaustion time after training minus before training; SED, sedentary controls; MOD, moderate-intensity continuous exercise training; HIT, high-intensity interval training. *p < 0.05 significantly different from SED within the same strain. †p < 0.05 significantly different from SED of C57BL/6J. ‡p < 0.05 significantly different from C57BL/6J. A portion of data presented here is reproduced from our previous publish (Avila et al . Front Physiol 2017;8:974 [34]).
Table 2
IC50 and EC50 in cumulative concentration-response curves to vasoactive agents after exercise training in four inbred mouse strains

Values are presented as mean ± SE. n = 6 mice per group per strain. ACh, acetylcholine; SNP, sodium nitroprusside; PE, phenylephrine; KCl, potassium chloride; IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration in cumulative centration-response curve to ACh or SNP; EC50, half maximal effective concentration in cumulative concentration-response curve to PE or KCl; SED, sedentary controls; MOD, moderate-intensity continuous exercise training; HIT, high-intensity interval training. *p < 0.05 significantly different from SED within the same strain. †p < 0.05 significantly different from SED of C57BL/6J. A portion of data presented here is reproduced from our previous publish (Kim et al . Front Physiol 2016;7:571 [16]).
Table 5
Top three canonical pathways for genes significantly altered by exercise training

MOD, moderate-intensity continuous exercise training; HIT, high-intensity interval training. Canonical pathways to which genes significantly altered by exercise training belong were identified by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). Selection of top 3 canonical pathways was based on p-value which is a measure of the likelihood that the association between a set of genes and a given pathway is due to random chance. The p-value is calculated by the right-tailed Fisher Exact Test in IPA. Data from the other groups/strains were excluded due to limited changes in both gene expression (Tables 3 and 4) and endothelial function after exercise training (Fig. 3).
Table 6
Top three molecular and cellular functions for genes significantly altered by exercise training

MOD, moderate-intensity continuous exercise training; HIT, high-intensity interval training. Diseases or molecular functions with which genes significantly altered by exercise training are associated were identified by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). Selection of top 3 functions was based on p-value calculated by the right-tailed Fisher Exact Test in IPA. Data from the other groups/strains were excluded due to limited changes in both gene expression (Tables 3 and 4) and endothelial function after exercise training (Fig. 3).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download