Abstract
Recently, as the elderly population increases, the incidence of total knee arthroplasty has increased, with a concomitant increase in the frequency of periprosthetic fractures. To determine the treatment plan for fractures, the treatment method should be determined by the patient's age, osteoporosis, fixation status of the implant, and type of fracture. In recent years, operative treatment with reduction and stable fixation, rather than non-operative treatment, was used to promote early joint movement and gait. On the other hand, it is necessary to select an appropriate operative method to reduce complications of surgery, such as nonunion and infection, and expect a good prognosis. In this review, periprosthetic fractures were divided into femur, tibia, and patella fractures, and their causes, risk factors, classification, and treatment are discussed.
Figures and Tables
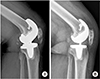
 | Fig. 1Periprosthetic fracture with a comminuted fracture in the medial cortex of the distal femur was fixed with dual locking plates using the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique. (A, B) Preoperative radiographs. (C, D) Postoperative radiographs. (E-G) Radiographs one year after surgery. |
References
1. Dennis DA. Periprosthetic fractures following total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2001; 50:379–389.


2. Cordeiro EN, Costa RC, Carazzato JG, Silva Jdos S. Periprosthetic fractures in patients with total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (252):182–189.

3. Engh GA, Ammeen DJ. Periprosthetic fractures adjacent to total knee implants: treatment and clinical results. Instr Course Lect. 1998; 47:437–448.

4. Chen F, Mont MA, Bachner RS. Management of ipsilateral supracondylar femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1994; 9:521–526.


5. Figgie MP, Goldberg VM, Figgie HE 3rd, Sobel M. The results of treatment of supracondylar fracture above total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1990; 5:267–276.


6. Rorabeck CH, Taylor JW. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999; 30:265–277.


7. Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM. Anterior femoral notching and ipsilateral supracondylar femur fracture in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1988; 3:185–187.


8. Scott RD. Anterior femoral notching and ipsilateral supracondylar femur fracture in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1988; 3:381.

9. Bonutti PM, Dethmers D, Ulrich SD, Seyler TM, Mont MA. Computer navigation-assisted versus minimally invasive TKA: benefits and drawbacks. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:2756–2762.


10. Culp RW, Schmidt RG, Hanks G, Mak A, Esterhai JL Jr, Heppenstall RB. Supracondylar fracture of the femur following prosthetic knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (222):212–222.

11. Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE. Periprosthetic femoral fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:12–20.


12. Kim KI, Egol KA, Hozack WJ, Parvizi J. Periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 446:167–175.


13. Bong MR, Egol KA, Koval KJ, et al. Comparison of the LISS and a retrograde-inserted supracondylar intramedullary nail for fixation of a periprosthetic distal femur fracture proximal to a total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17:876–881.


14. Cain PR, Rubash HE, Wissinger HA, McClain EJ. Periprosthetic femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (208):205–214.

15. Ostrum RF, Geel C. Indirect reduction and internal fixation of supracondylar femur fractures without bone graft. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:278–284.


16. Bolhofner BR, Carmen B, Clifford P. The results of open reduction and Internal fixation of distal femur fractures using a biologic (indirect) reduction technique. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:372–377.


17. Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, Tscherne H. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury. 1997; 28 Suppl 1:A20–A30.

18. Russell GV Jr, Smith DG. Minimally invasive treatment of distal femur fractures: report of a technique. J Trauma. 1999; 47:799–801.


19. Ricci WM, Loftus T, Cox C, Borrelli J. Locked plates combined with minimally invasive insertion technique for the treatment of periprosthetic supracondylar femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:190–196.


20. Farouk O, Krettek C, Miclau T, Schandelmaier P, Guy P, Tscherne H. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis: does percutaneous plating disrupt femoral blood supply less than the traditional technique? J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:401–406.


21. Herrera DA, Kregor PJ, Cole PA, Levy BA, Jönsson A, Zlowodzki M. Treatment of acute distal femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty: systematic review of 415 cases (1981–2006). Acta Orthop. 2008; 79:22–27.

22. DiGioia AM 3rd, Rubash HE. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty A literature review and treatment algorithm. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (271):135–142.
23. Frigg R, Appenzeller A, Christensen R, Frenk A, Gilbert S, Schavan R. The development of the distal femur Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Injury. 2001; 32 Suppl 3:SC24–SC31.

24. Zlowodzki M, Williamson S, Cole PA, Zardiackas LD, Kregor PJ. Biomechanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization system, angled blade plate, and retrograde intramedullary nail for the internal fixation of distal femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:494–502.


25. Murrell GA, Nunley JA. Interlocked supracondylar intramedullary nails for supracondylar fractures after total knee arthroplasty. A new treatment method. J Arthroplasty. 1995; 10:37–42.


26. Lee SS, Lim SJ, Moon YW, Seo JG. Outcomes of long retrograde intramedullary nailing for periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134:47–52.


27. Pelfort X, Torres-Claramunt R, Hinarejos P, Leal J, Gil-González S, Puig L. Extension malunion of the femoral component after retrograde nailing: no sequelae at 6 years. J Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27:158–161.

28. Jabczenski FF, Crawford M. Retrograde intramedullary nailing of supracondylar femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty. A preliminary report of four cases. J Arthroplasty. 1995; 10:95–101.


29. Rolston LR, Christ DJ, Halpern A, O'Connor PL, Ryan TG, Uggen WM. Treatment of supracondylar fractures of the femur proximal to a total knee arthroplasty. A report of four cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:924–931.


30. McLaren AC, Dupont JA, Schroeber DC. Open reduction internal fixation of supracondylar fractures above total knee arthroplasties using the intramedullary supracondylar rod. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (302):194–198.

31. Maniar RN, Umlas ME, Rodriguez JA, Ranawat CS. Supracondylar femoral fracture above a PFC posterior cruciate-substituting total knee arthroplasty treated with supracondylar nailing. A unique technical problem. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:637–639.


32. Freedman EL, Hak DJ, Johnson EE, Eckardt JJ. Total knee replacement including a modular distal femoral component in elderly patients with acute fracture or nonunion. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:231–237.


33. Felix NA, Stuart MJ, Hanssen AD. Periprosthetic fractures of the tibia associated with total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (345):113–124.

34. Rand JA, Coventry MB. Stress fractures after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980; 62:226–233.


35. Stuart MJ, Hanssen AD. Total knee arthroplasty: periprosthetic tibial fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999; 30:279–286.

36. Born CT, Gil JA, Johnson JP. Periprosthetic tibial fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018; 26:e167–e172.

37. Ruchholtz S, Tomás J, Gebhard F, Larsen MS. Periprosthetic fractures around the knee-the best way of treatment. Eur Orthop Traumatol. 2013; 4:93–102.


38. Haller JM, Kubiak EN, Spiguel A, Gardner MJ, Horwitz DS. Intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures distal to total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28:e296–e300.

39. Abbas AM, Morgan-Jones RL. Revision total knee arthroplasty for failure of primary treatment of periprosthetic knee fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:1996–2001.


40. Berger RA, Meneghini RM, Jacobs JJ, et al. Results of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty at a minimum of ten years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:999–1006.


41. Seeger JB, Jaeger S, Röhner E, Dierkes H, Wassilew G, Clarius M. Treatment of periprosthetic tibial plateau fractures in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: plates versus cannulated screws. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:253–257.

42. Preston S, Somerville L, Lanting B, Howard J. Are nucleated cell counts useful in the diagnosis of infection in periprosthetic fracture? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473:2238–2243.



44. Ortiguera CJ, Berry DJ. Patellar fracture after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84:532–540.

45. Meding JB, Fish MD, Berend ME, Ritter MA, Keating EM. Predicting patellar failure after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:2769–2774.



46. Gross AE. Periprosthetic fractures of the knee: puzzle pieces. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19:4 Suppl 1. 47–50.

47. Tharani R, Nakasone C, Vince KG. Periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:4 Suppl 2. 27–32.


48. Parvizi J, Kim KI, Oliashirazi A, Ong A, Sharkey PF. Periprosthetic patellar fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 446:161–166.


49. Ritter MA, Herbst SA, Keating EM, Faris PM, Meding JB. Patellofemoral complications following total knee arthroplasty. Effect of a lateral release and sacrifice of the superior lateral geniculate artery. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:368–372.

50. Tria AJ Jr, Harwood DA, Alicea JA, Cody RP. Patellar fractures in posterior stabilized knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (299):131–138.

51. Lynch AF, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Extensor mechanism complications following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1987; 2:135–140.


52. Grace JN, Sim FH. Fracture of the patella after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (230):168–175.

53. Clayton ML, Thirupathi R. Patellar complications after total condylar arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982; (170):152–155.

54. Willert HG, Ludwig J, Semlitsch M. Reaction of bone to methacrylate after hip arthroplasty: a long-term gross, light microscopic, and scanning electron microscopic study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974; 56:1368–1382.

55. Marmor L. Technique for patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (230):166–167.

56. Reuben JD, McDonald CL, Woodard PL, Hennington LJ. Effect of patella thickness on patella strain following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1991; 6:251–258.

57. Bourne RB. Fractures of the patella after total knee replacement. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999; 30:287–291.


58. Windsor RE, Scuderi GR, Insall JN. Patellar fractures in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1989; 4 Suppl:S63–S67.

59. Healy WL, Wasilewski SA, Takei R, Oberlander M. Patellofemoral complications following total knee arthroplasty. Correlation with implant design and patient risk factors. J Arthroplasty. 1995; 10:197–201.

60. Larson CM, McDowell CM, Lachiewicz PF. One-peg versus three-peg patella component fixation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (392):94–100.

61. Hozack WJ, Goll SR, Lotke PA, Rothman RH, Booth RE Jr. The treatment of patellar fractures after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Rela Res. 1988; (236):123–127.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download