Abstract
Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) has been increasingly used in recent years for the as-sessment of peripheral neuropathies. Fat suppression T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and diffu-sion-weighted imaging (DWI) have typically been used to provide high contrast MRN. Isotropic 3-dimensional (3D) sequences with fast spin echo, post-processing imaging techniques, and fast imaging methods, among others, allow good visualization of peripheral nerves that have a small diameter, complex anatomy, and oblique course within a reasonable scan time. However, there are still several issues when performing high contrast and high resolution MRN includ-ing standard sequence; fat saturation techniques; balance between resolution, field of view, and slice thickness; post-processing techniques; 2D vs. 3D image acquisition; different T2 contrasts between proximal and distal nerves; high T2 signal intensity of adjacent veins or joint flu-id; geometric distortion; and appropriate p-values on DWI. The proper understanding of these issues will help novice radiologists evaluate peripheral neuropathies using MRN.
Go to : 
Index terms
Peripheral Nervous System Diseases, Diagnostic Imaging, Magnetic Resonance ImagingREFERENCES
1. Chhabra A, Lee PP, Bizzell C, Soldatos T. 3 Tesla MR neurography–technique, interpretation, and pitfalls. Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40:1249–1260.

2. Ohana M, Moser T, Moussaouï A, Kremer S, Carlier RY, Liverneaux P, et al. Current and future imaging of the peripheral nervous system.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2014; 95:17–26.
3. Donovan A, Rosenberg ZS, Cavalcanti CF. MR imaging of entrapment neuropathies of the lower extremity. Part 2. The knee, leg, ankle, and foot.Radiographics. 2010; 30:1001–1019.
4. Andreisek G, Crook DW, Burg D, Marincek B, Weishaupt D. Peripheral neuropathies of the median, radial, and ulnar nerves: MR imaging features.Radiographics. 2006; 26:1267–1287.
5. Chhabra A, Madhuranthakam AJ, Andreisek G. Magnetic resonance neurography: current perspectives and literature review.Eur Radiol. 2018; 28:698–707.
6. Madhuranthakam AJ, Lenkinski RE. Technical advancements in MR neurography. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015; 19:86–93.

7. Chhabra A, Andreisek G, Soldatos T, Wang KC, Flammang AJ, Belzberg AJ, et al. MR neurography: past, present, and future. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:583–591.

8. Thawait SK, Chaudhry V, Thawait GK, Wang KC, Belzberg A, Carrino JA, et al. High-resolution MR neurography of diffuse peripheral nerve lesions.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1365–1372.
9. Rangavajla G, Mokarram N, Masoodzadehgan N, Pai SB, Bellamkonda RV. Noninvasive imaging of peripheral nerves. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014; 200:69–77.

10. Mikityansky I, Zager EL, Yousem DM, Loevner LA. MR Imaging of the brachial plexus.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2012; 20:791–826.
11. Vargas MI, Gariani J, Delattre BA, Dietemann JL, Lovblad K, Becker M. Three-dimensional MR imaging of the brachial plexus. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015; 19:137–148.

12. Takahara T, Hendrikse J, Yamashita T, Mali WP, Kwee TC, Imai Y, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR neurography of the brachial plexus: feasibility study. Radiology. 2008; 249:653–660.

13. Bao H, Wang S, Wang G, Yang L, Hasan MU, Yao B, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR neurography of median and ulnar nerves in the wrist and palm.Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:2359–2366.
14. Lacour-Petit MC, Lozeron P, Ducreux D. MRI of peripheral nerve lesions of the lower limbs.Neuroradiology. 2003; 45:166–170.
15. Amrami KK, Felmlee JP, Spinner RJ. MRI of peripheral nerves. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2008; 19:559–572.

16. Cho Sims G, Boothe E, Joodi R, Chhabra A. 3D MR neurography of the lumbosacral plexus: obtaining opti-mal images for selective longitudinal nerve depiction.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37:2158–2162.
17. Naraghi A, White LM. Three-dimensional MRI of the musculoskeletal system.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 199:W283–W293.
18. Lell MM, Anders K, Uder M, Klotz E, Ditt H, Vega-Higuera F, et al. New techniques in CT angiography.Radiographics. 2006; 26(Suppl 1):S45–S62.
19. Fishman EK, Ney DR, Heath DG, Corl FM, Horton KM, Johnson PT. Volume rendering versus maximum intensity projection in CT angiography: what works best, when, and why.Radiographics. 2006; 26:905–922.
20. Mürtz P, Kaschner M, Lakghomi A, Gieseke J, Willinek WA, Schild HH, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR neurography of the brachial and lumbosacral plexus: 3.0 T versus 1.5 T imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2015; 84:696–702.
21. Chhabra A, Zhao L, Carrino JA, Trueblood E, Koceski S, Shteriev F, et al. MR neurography: advances.Radiol Res Pract. 2013; 2013:809568.
22. Glaser C, D'Anastasi M, Theisen D, Notohamiprodjo M, Horger W, Paul D, et al. Understanding 3D TSE sequences: advantages, disadvantages, and application in MSK imaging. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015; 19:321–327.

23. Chhabra A, Soldatos T, Subhawong TK, Machado AJ, Thawait SK, Wang KC, et al. The application of three-dimensional diffusion-weighted PSIF technique in peripheral nerve imaging of the distal extremities. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 34:962–967.

24. Wang X, Harrison C, Mariappan YK, Gopalakrishnan K, Chhabra A, Lenkinski RE, et al. MR neurography of brachial plexus at 3.0 T with robust fat and blood suppression.Radiology. 2017; 283:538–546.
25. Kasper JM, Wadhwa V, Scott KM, Rozen S, Xi Y, Chhabra A. SHINKEI–a novel 3D isotropic MR neurography technique: technical advantages over 3DIRTSE-based imaging.Eur Radiol. 2015; 25:1672–1677.
26. Chhabra A, Subhawong TK, Bizzell C, Flammang A, Soldatos T. 3T MR neurography using three-dimensional diffusion-weighted PSIF: technical issues and advantages.Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40:1355–1360.
27. Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, Ogata H, Yamasaki R, et al. Evaluation of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: 3D nerve-sheath signal increased with inked rest-tissue rapid acquisition of relaxation enhancement imaging (3D SHINKEI).Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:447–453.
28. Bäumer P, Pham M, Ruetters M, Heiland S, Heckel A, Radbruch A, et al. Peripheral neuropathy: detection with diffusion-tensor imaging. Radiology. 2014; 273:185–193.

29. Tsuchiya K, Fujikawa A, Tateishi H, Nitatori T. Visualization of cervical nerve roots and their distal nerve fibers by diffusion-weighted scanning using parallel imaging. Acta Radiol. 2006; 47:599–602.

30. Zaharchuk G, Saritas EU, Andre JB, Chin CT, Rosenberg J, Brosnan TJ, et al. Reduced field-of-view diffusion imaging of the human spinal cord: comparison with conventional single-shot echo-planar imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:813–820.
31. Hu J, Li M, Dai Y, Geng C, Tong B, Zhou Z, et al. Combining SENSE and reduced field-of-view for high-resolu-tion diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Biomed Eng Online. 2018; 17:77.

32. Mekle R, Mortamet B, Granziera C, Krueger G, Chevrey N, Theumann N, et al. Magnetization transfer-based 3D visualization of foot peripheral nerves. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 37:1234–1237.

33. Bendszus M, Stoll G. Caught in the act: in vivo mapping of macrophage infiltration in nerve injury by magnetic resonance imaging.J Neurosci. 2003; 23:10892–10896.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.MR neurography of the normal brachial plexus. A, B. Recent MR neurography is commonly based on fat suppression T2-weighted (A) and diffusion-weight-ed imaging (B) because of their high tissue contrast. Fat suppression T2-weighted MR neurography (A) can show detailed anatomy due to its high spatial resolution. Diffusion-weighted MR neurography (B) can sup-press the adjacent vascular signal but produces low spatial resolution images. |
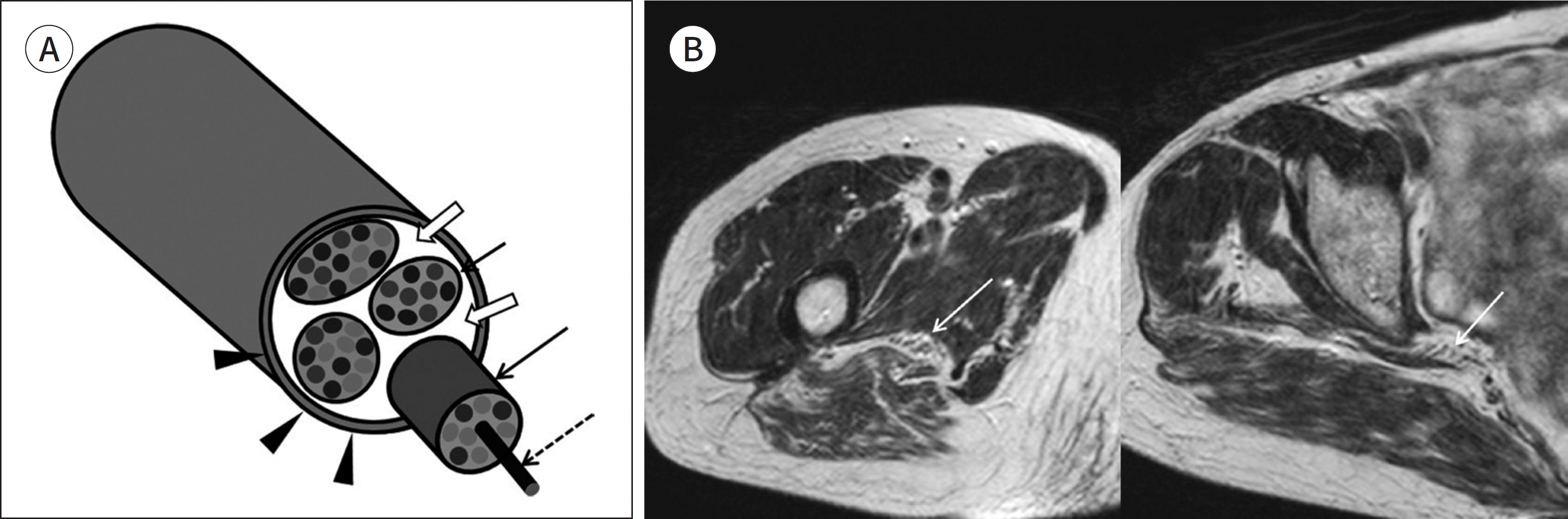 | Fig. 2.Fascicular appearance of peripheral nerve. A, B. A schematic of features of peripheral nerves (A) and axial T1-weighted images of the sciatic nerve (B). The axon (dashed arrow on A) is a basic building block of peripheral nerves. They aggregate to form a fasci-cle (arrows on A). Several fascicles are grouped together and form a peripheral nerve. Several fascicles are interspersed with variable amounts of adipose tissue within a peripheral nerve (empty arrows on A) and surrounded by a dense fibrous connective tissue, the epineurium (arrowheads on A). These features and perineural fat give nerves the characteristic fascicular, honeycomb, or reticular appearance (arrows on B). This pattern is well shown on axial T1-weighted images. |
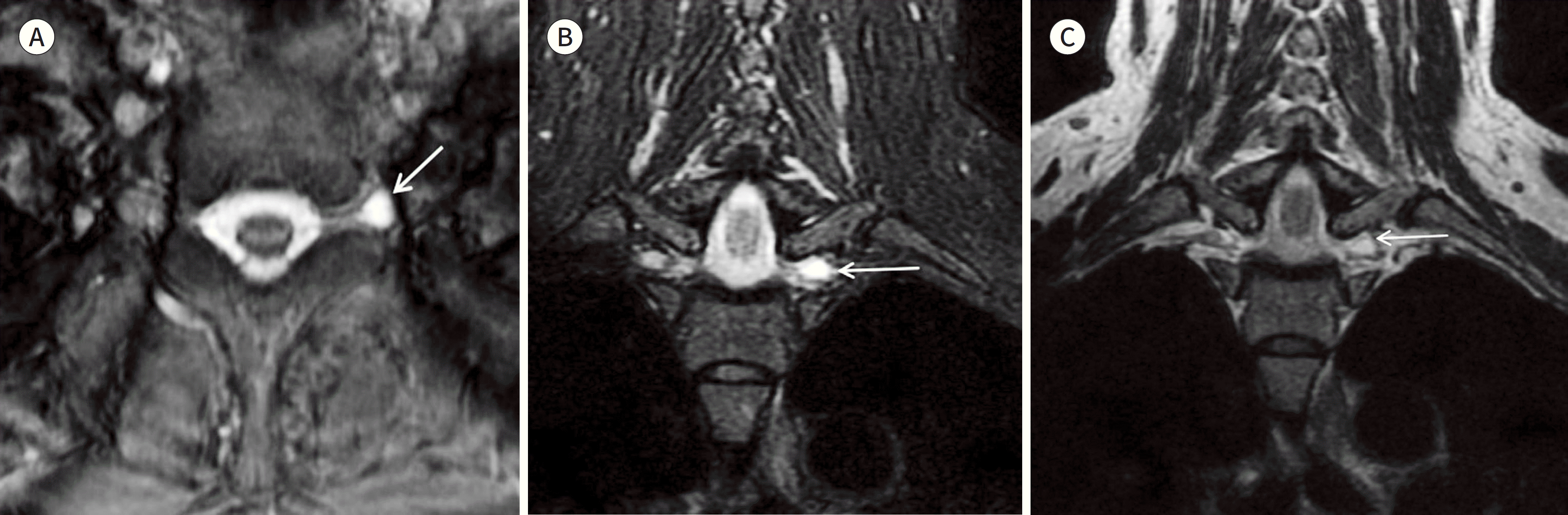 | Fig. 3.A 66-year-old women with a cyst along the root of left brachial plexus. A-C. An axial gradient echo image (A), a coronal FS T2WI with three-point Dixon method (B), and a coronal spine echo T2WI (C). The cyst along the roof is well visualized on the gradient echo image (arrow on A). The cyst is also well demarcated on the FS T2WI with three-point Dixon method (arrow on B). However, the spin echo T2WI does not clearly show the cyst (arrow on C) due to the surrounding high signal intensity of fat. |
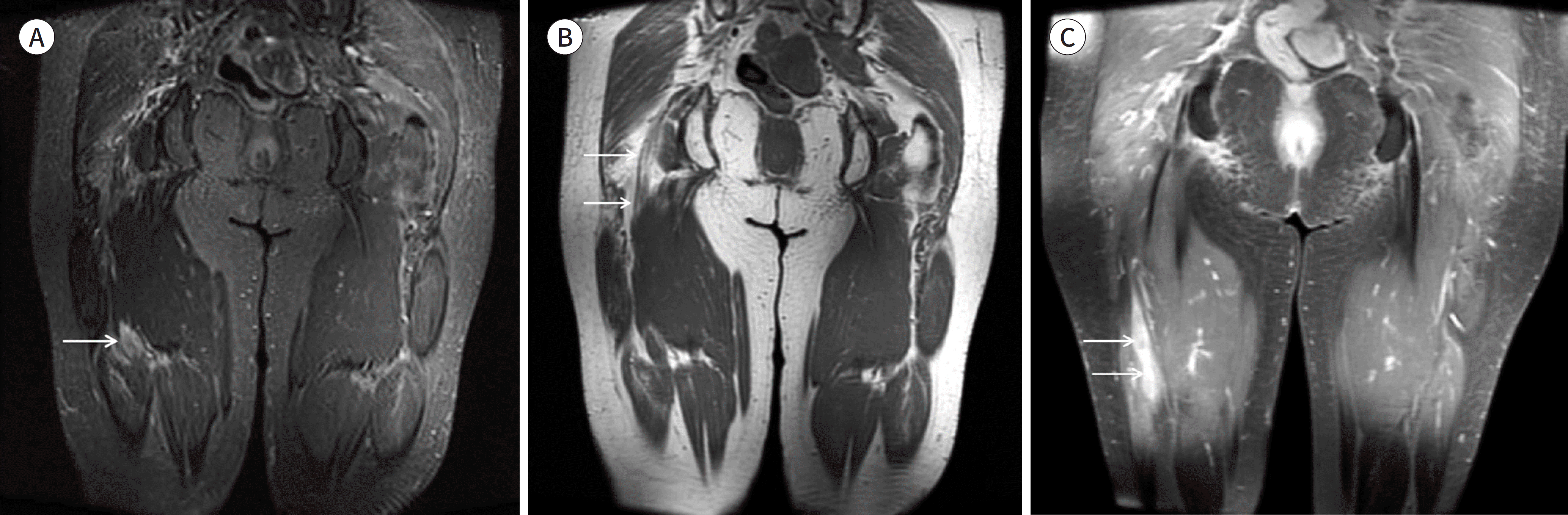 | Fig. 4.A 64-year-old women with lymphoma involving right sciatic nerve. A-C. A coronal FS T2WI (A), a coronal T1WI (B), and a coronal FS T1WI with contrast enhancement (C). The FS T2WI is not sufficient to visualize the normal sciatic nerve. A mass is suspected (arrow on A) because of the heterogeneous high signal intensity of the lesion. The T1WI clearly demonstrates the fascicular appearance of the normal sciatic nerve (arrows on B). The normal sciatic nerve is not enhanced but the mass is clearly seen on the contrast-enhanced FS T1WI (arrows on C). FS = fat suppression, WI = weighted image |
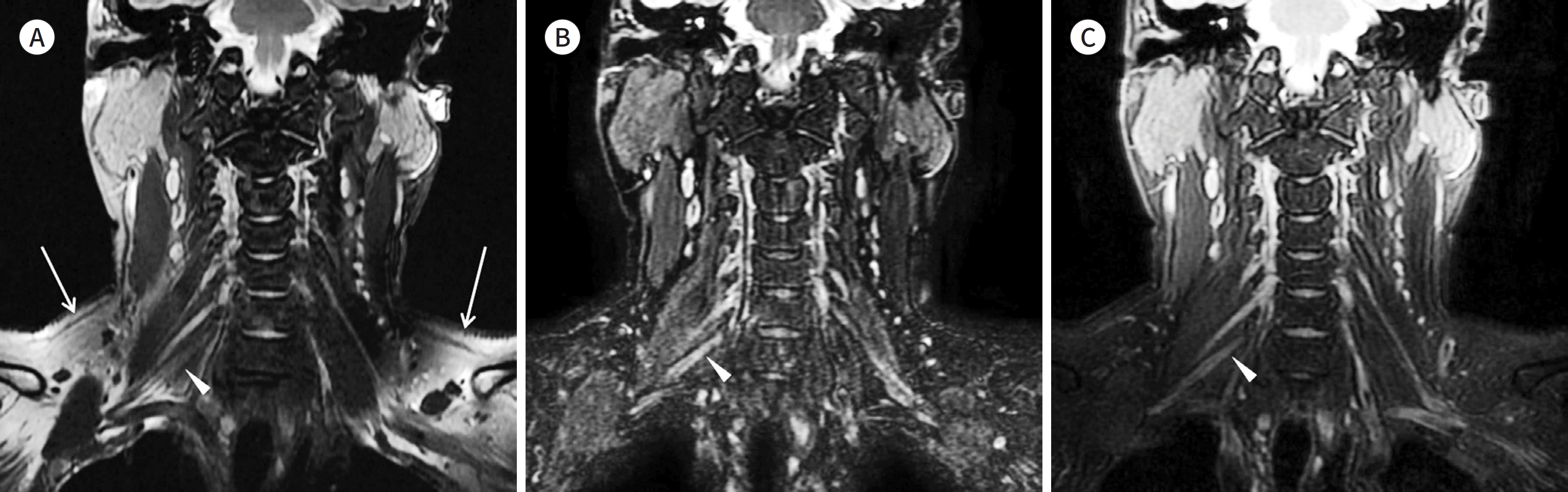 | Fig. 5.Various fat suppression techniques. A-C. Fat saturation images using the (A) chemical shift-selective fat suppression method, (B) short T1 inversion recovery method, and (C) Dixon (water-selective fat saturation) method. On MR neurography with a large field of view, peripheral far off-center areas frequently produce in-complete fat saturation (arrows on A) and high signal intensity artifacts. This can obscure the normal anatomy (arrowhead on A) or pathology of the peripheral nerve on fat suppression image with chemical shift-selective fat suppression method. Fat suppression images with short T1 |
 | Fig. 6.Comparing the images between with thin slice thickness and with thick slice thickness. A, B. A coronal T2WI of 2-mm thickness (A) and a coronal T2WI of 5-mm thickness (B). The image using a thinner slice thickness (A) shows the sciatic nerve (arrows on A and B) more clearly than the image using the thicker slice thickness (B). WI = weighted image |
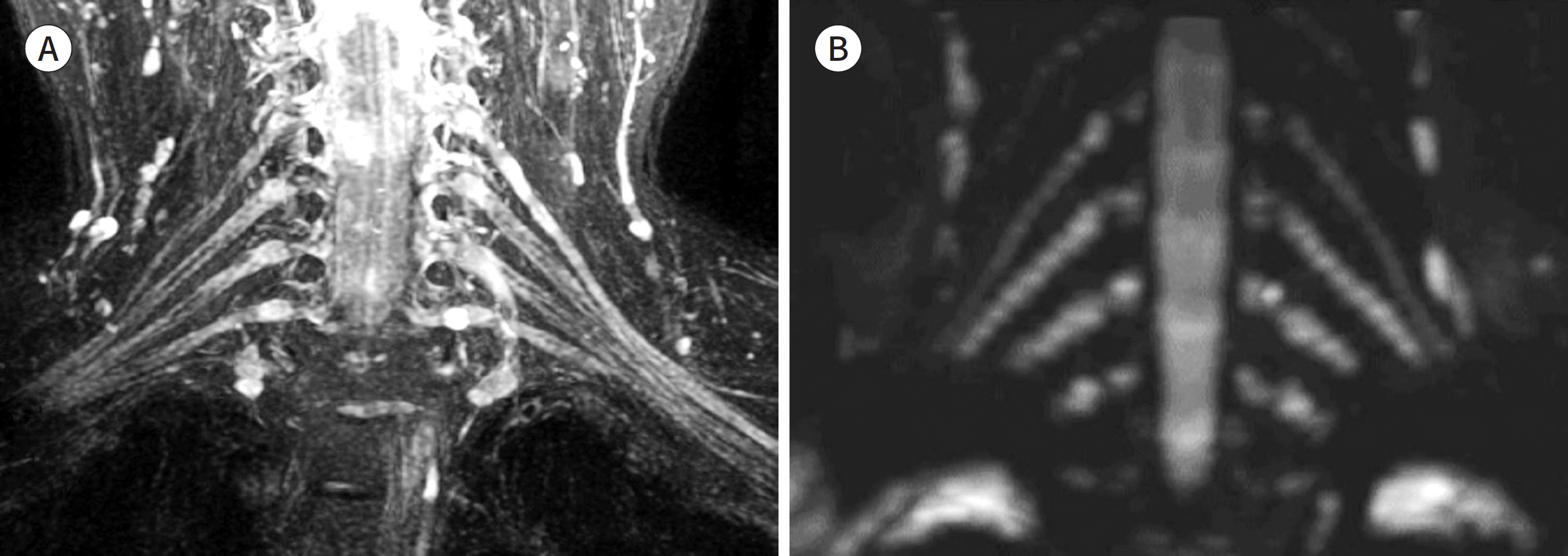
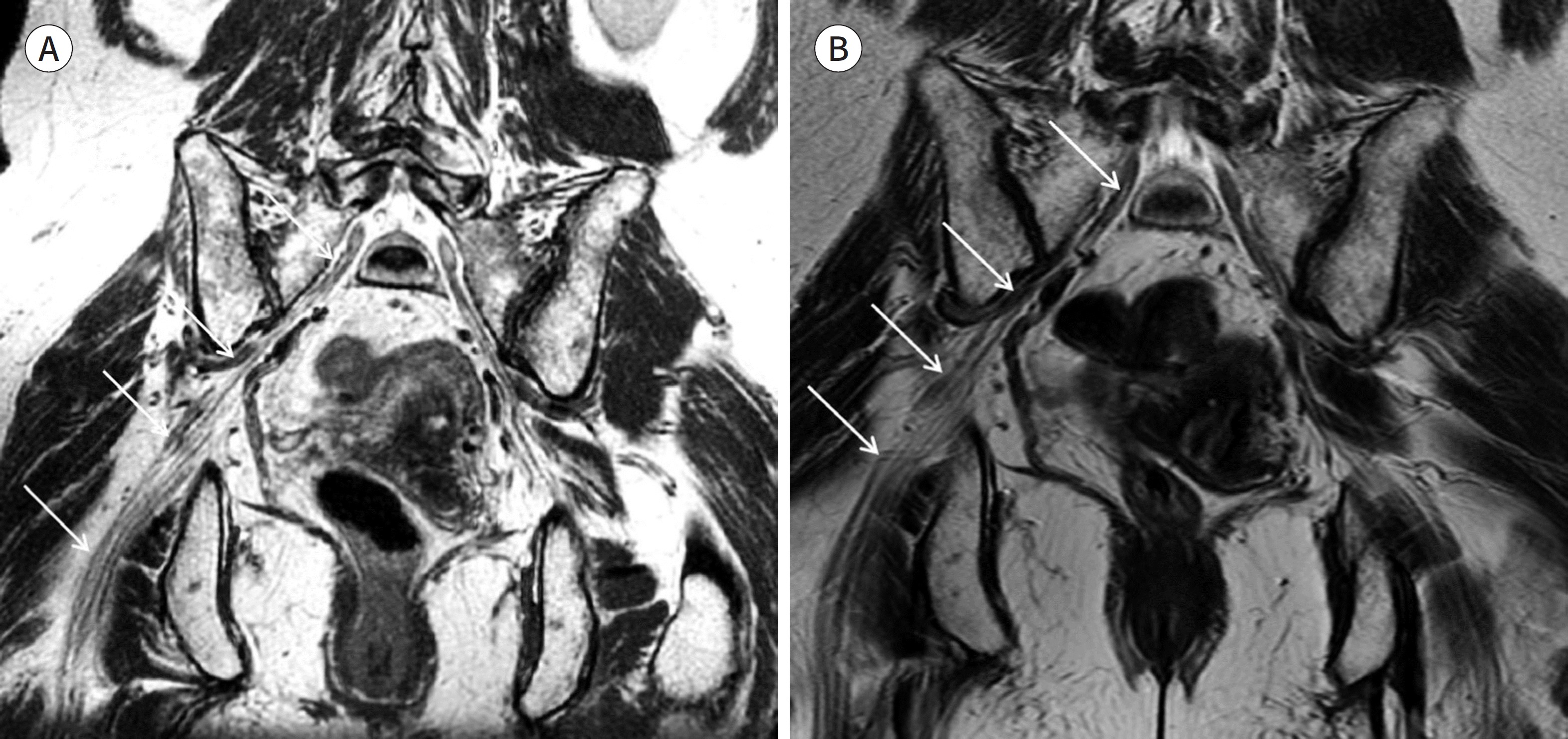
 | Fig. 7.A 62-year-old woman with right arm pain and a tingling sensation, clinically suspected of having brachial plexus radiculopathy. A, B. Serial axial T2WIs of the cervical spine (A) and a coronal MIP image of the brachial plexus (B). On serial axial T2WIs, right intervertebral foramina are suspected of having intermediate signal intensity due to a mass and obliteration of the intervertebral foramen (arrows on A). However, clinicians could not fully un-derstand the brachial plexus involvement. The MIP image clearly shows obliteration of the roots of the right lower brachial plexus (arrowheads on B). MIP = maximum intensity projection, WI = weighted image |
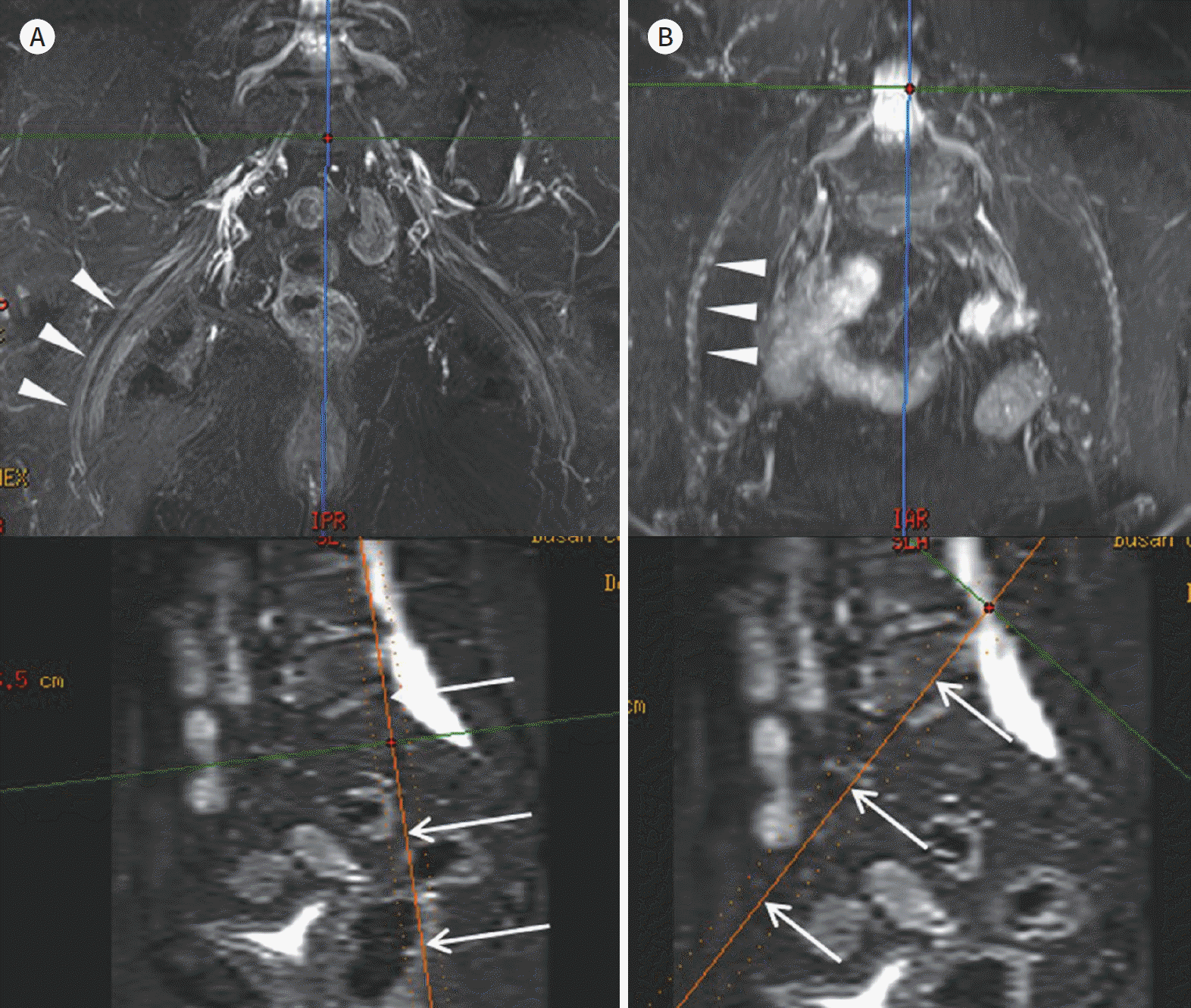 | Fig. 8.Reconstructed images using anisotropic coronal 2-dimensional images. A, B. A coronal MIP image along the sciatic nerve (arrowheads on upper image of A) and a coronal MIP image along the femoral nerve (arrowheads on upper image of A). Both lower row images are sagittal multiplanar reconstruction images for identifying the reconstructive angle. The sagittal angle of the sciatic nerve (arrows on lower image of A) is less than 10° (A), but the sagittal angle of the femoral nerve (arrows on lower image of B) is approximately 45° (B). The sciatic nerve travels in a coronal orientation, but the femoral nerve travels with a more axial orientation. The MIP image of the sciatic nerve (upper image of A) has a high resolution with smooth continuity. However, the MIP image of the more axially oriented femoral nerve (upper image of B) shows rela-tively low spatial resolution with prominent stair-step artifacts (arrowheads on upper image of B). |
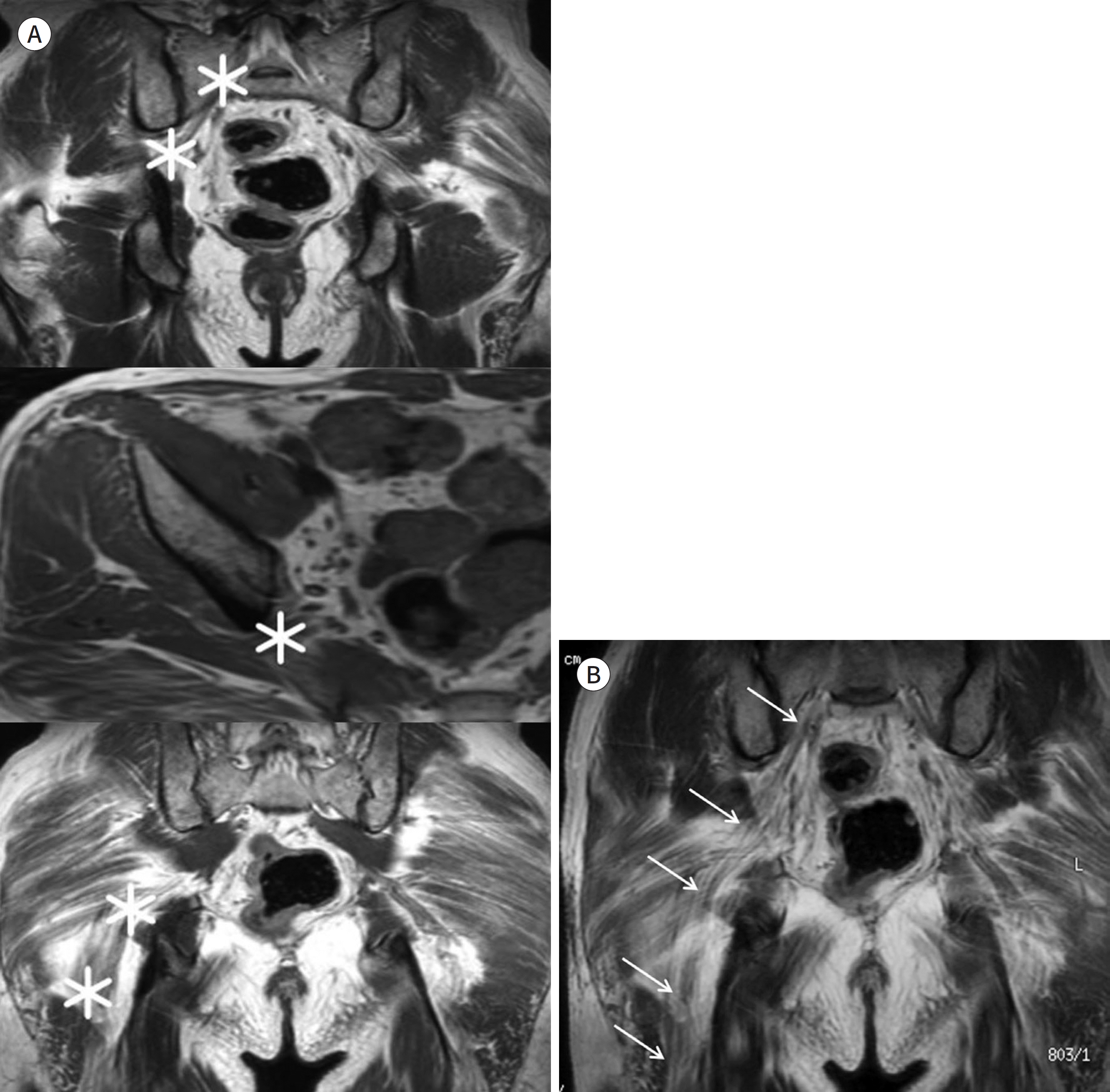 | Fig. 9.Curved MPR technique method. A, B. Serial T1-weighted images (A) and a curved MPR image of the sciatic nerve (arrows on B). The pre-defined curved planes (asterisks on A) are determined manually along the sciatic nerve The curved MPR image (B) can show the whole length of the sciatic nerve (arrows on B) on a single image. MPR = multiplanar reconstruction |
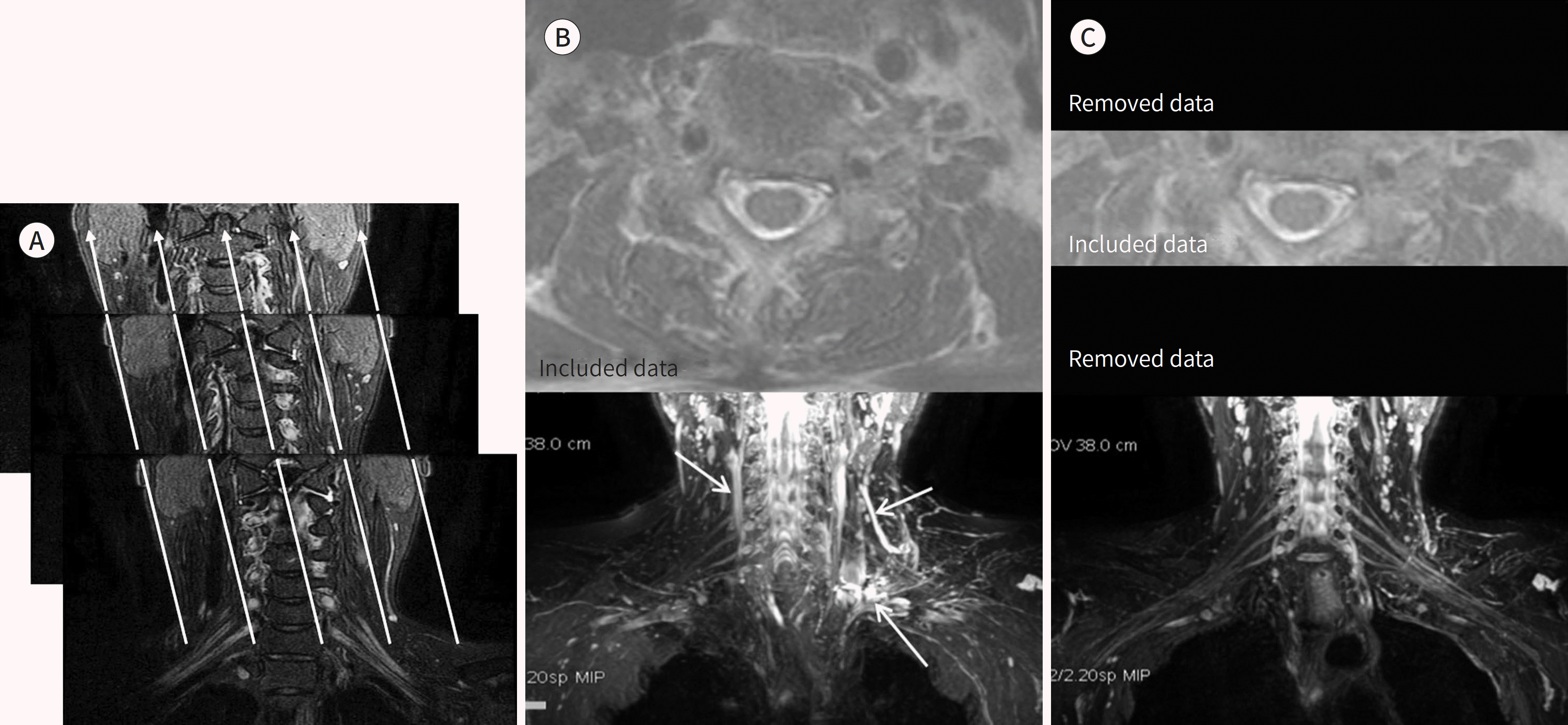 | Fig. 10.MIP technique with whole slab and thin slab. A-C. Serial coronal FS T2WI (A), a MIP image with whole slab (B), and an MIP image with a thin slab (C). The high signal intensity data within serial coronal images (A) are projected along parallel projections (arrows on A) and displayed with maximum intensity in a single 2-dimen-sional image. An MIP image with a whole slab (B) shows an overlapping appearance of high signal intensity vessels (arrows on B), anterior or posterior to the brachial plexus. An MIP image with a thin slab (C) can exclude overlapping high signal intensity lesions and shows the brachial plexus more clearly. FS = fat suppression, MIP = maximum intensity projection, WI = weighted image |
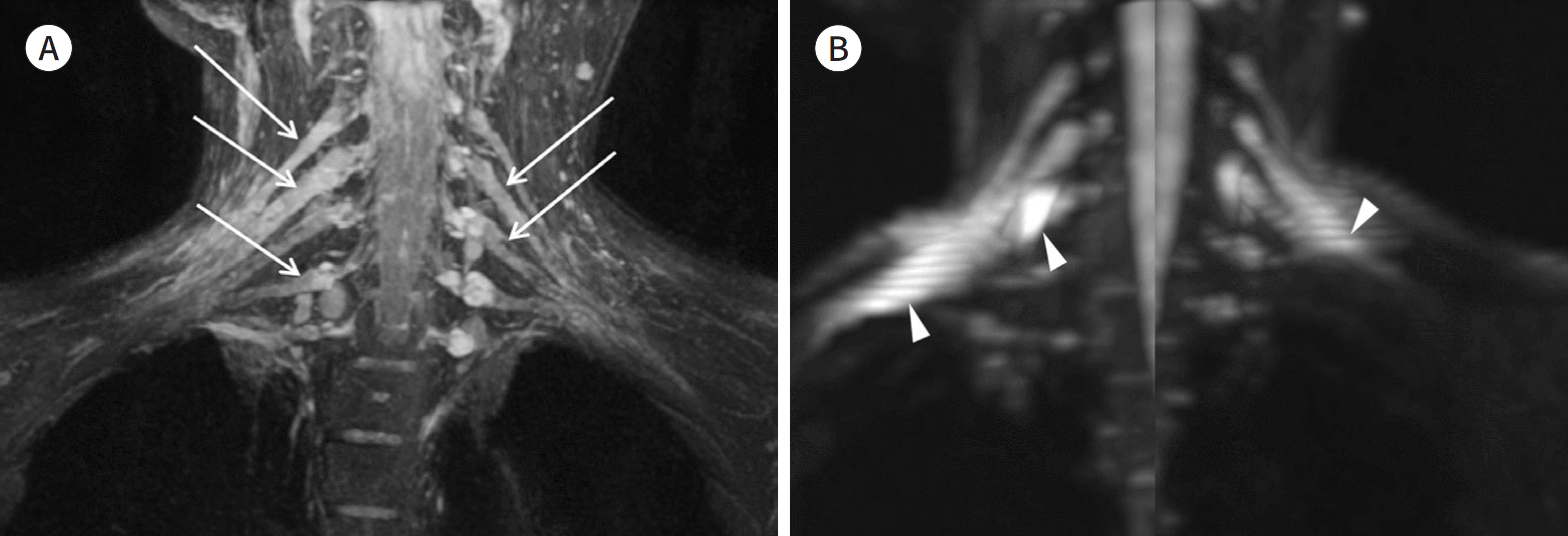 | Fig. 11.A 63-year-old female patient with brachial plexus neuritis. A, B. A MIP image based on a fat suppression T2-weighted image (A) and two oblique MIP images based on a diffusion-weighted image (B). The MIP images show bilateral diffuse enlargement (arrows on A) of the brachial plexus with increased signal intensity, relative to MIP images of the normal brachial plexus (Fig. 1). MIP images preserve the signal intensity change of pathology. Diffusion-weighted images can have marked artifacts in distant peripheral areas (arrowheads on B). |
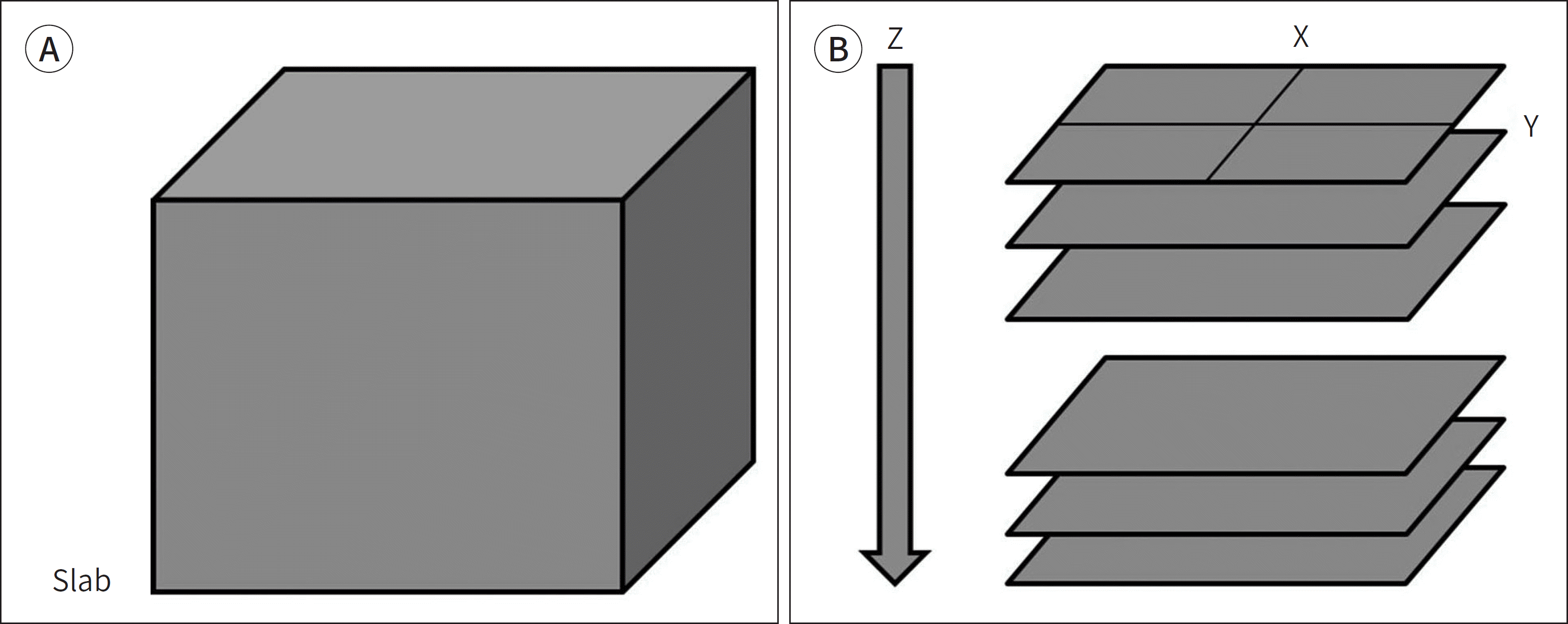 | Fig. 12.3D k-space sampling. A, B. A slab for excitation of a 3D volume (A) and 3D k-space sampling needs an additional phase encoding along the slice direction (z-axis) and leads to long scan times (B). To obtain 3D volume data within a reasonable scan time, long echo train length, high spin echo factors, and parallel imaging techniques need to be implemented. These techniques might result in signal decay and image blurring. D = dimensional |
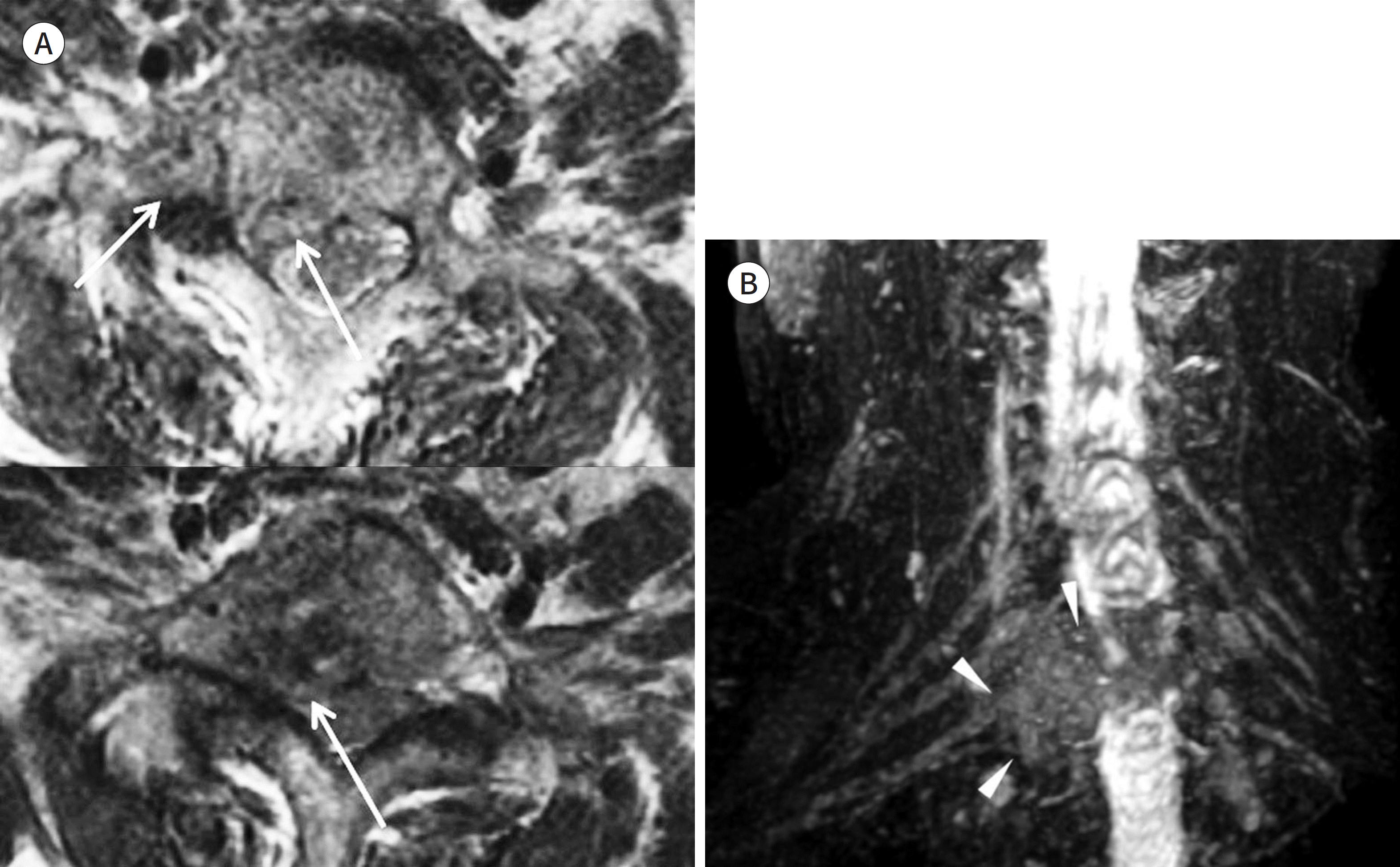
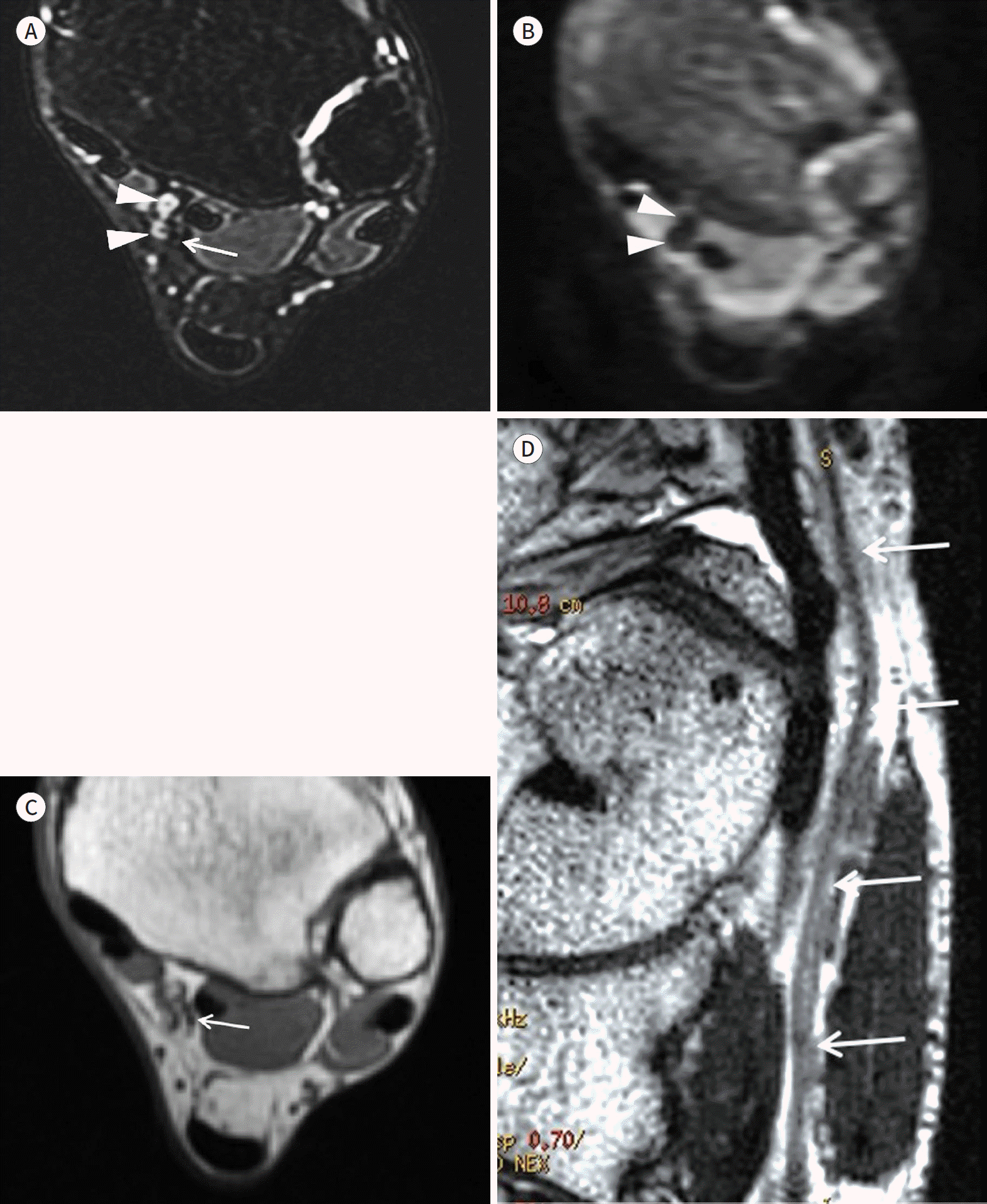 | Fig. 13.MR images of the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel. A-D. An axial FS T2WI (A), an axial diffusion-weighted image (B), an axial T1WI (C), and a curved MPR image based on a T2WI of the tibial nerve (D). The FS T2WI cannot clearly define the tibial nerve (arrow on A) because of its intermediate signal intensity. In addition, adjacent veins with slow flow (arrowheads on A) show high signal intensity on FS T2WI. The signal intensities of adjacent veins can be suppressed on diffusion-weighted images (arrowheads on B). The T1WI and T2WI can define the tibial nerve by visualization of its fascicular appearance (arrow on C). The curved MPR image based on a T1WI or T2WI (D) is more suitable for visualization of distal peripheral nerves (arrows on D) on a single image than maximum intensity projection images based on FS T2WI. |
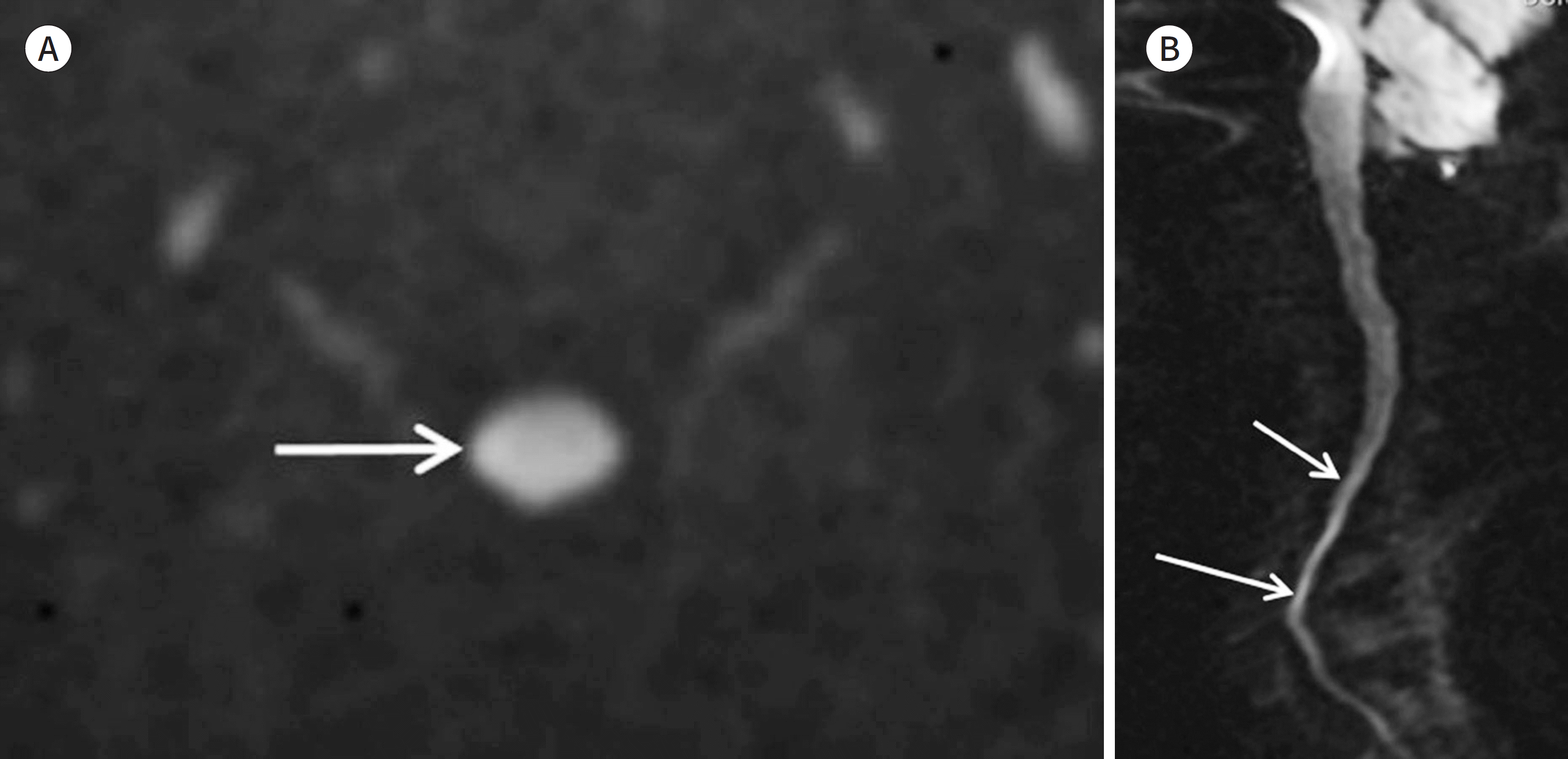 | Fig. 14.Geometric image distortion of diffusion-weighed images depends on acquisition plans. A, B. An axial acquisition image of the cervical spine (A). A sagittal acquisition image of the cervical spine (B). The image distortion may be absent or minimal (arrow on A) on axial diffusion-weighted images (A). Sagit-tal or coronal diffusion-weighted images might show geometric image distortion (arrows on B) due to inho- |
Table 1.
Imaging Criteria for the Interpretation of MR Neurography




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download