Abstract
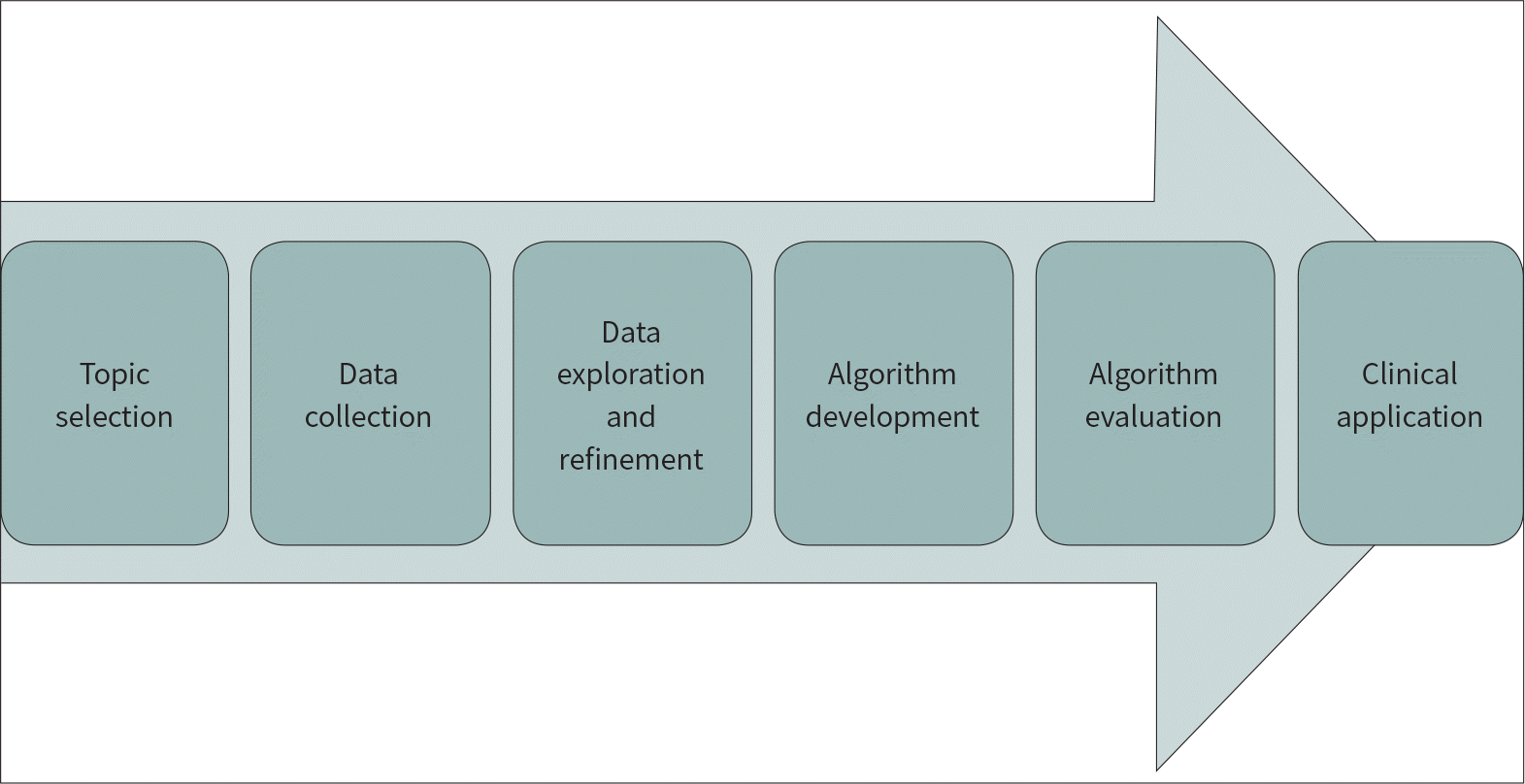
Recently, considerable progress has been made in interpreting perceptual information through artificial intelligence, allowing better interpretation of highly complex data by machines. Furthermore, the applications of artificial intelligence, represented by deep learning technology, to the fields of medical and biomedical research are increasing exponentially. In this article, we will explain the stages of deep learning algorithm development in the field of medical imaging, namely topic selection, data collection, data exploration and refinement, algorithm development, algorithm evaluation, and clinical application; we will also discuss the latest trends for each stage.
References
1. Lee H, Yune S, Mansouri M, Kim M, Tajmir SH, Guerrier CE, et al. An explainable deep-learning algorithm for the detection of acute intracranial haemorrhage from small datasets. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018; 3:173–182.

2. Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal. 2017; 42:60–88.

3. Topol E. There's been a recent burst of peer-reviewed deep neural network #AI publications in medicine. Available at.https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1051174567882907648. Published Oct 13, 2018. Accessed Jan 1,. 2019.
4. Shin SY, Lyu Y, Shin Y, Choi HJ, Park J, Kim WS, et al. Lessons learned from development of de-identification system for biomedical research in a Korean Tertiary Hospital.Healthc Inform Res. 2013; 19:102–109.
5. Batten L, Kim DS, Zhang X, Li G.Applications and Techniques in Information Security: 8th International Confer ence, ATIS 2017. Auckland: Springer;2017.
6. Chang K, Balachandar N, Lam C, Yi D, Brown J, Beers A, et al. Distributed deep learning networks among institutions for medical imaging.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018; 25:945–954.
7. Rolnick D, Veit A, Belongie S, Shavit N. Deep learning is robust to massive label noise. .arXiv preprint 2017;arX-iv: 1705.10694.
8. Shin HC, Roth HR, Gao M, Lu L, Xu Z, Nogues I, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016; 35:1285–1298.
9. Roth HR, Lu L, Farag A, Shin HC, Liu J, Turkbey EB, et al. Deeporgan: multi-level deep convolutional networks for automated pancreas segmentation.arXiv preprint. 2015; arXiv:1506. .06448.
10. Lee H, Kim M, Do S. Practical window setting optimization for medical image deep learning.arXiv preprint. 2018; arXiv:1812. .00572.
11. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition.arXiv preprint. 2015; arXiv:1512. .03385.
12. Huang G, Liu Z, Van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. ensely connected convolutional networks.arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv:1608. .06993.
13. Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. arXiv preprint 2015: arXiv: 1512.00567.
14. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation.arXiv preprint. 2015; arXiv:1812. .00572.
15. Canziani A, Paszke A, Culurciello E. An analysis of deep neural network models for practical applications. arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv:1605. .07678.
Fig. 1.
Annual trend in the number of papers related to deep learning in the medical field. Results from PubMed in December 2018 using ‘deep learning' and ‘convolutional' search terms.
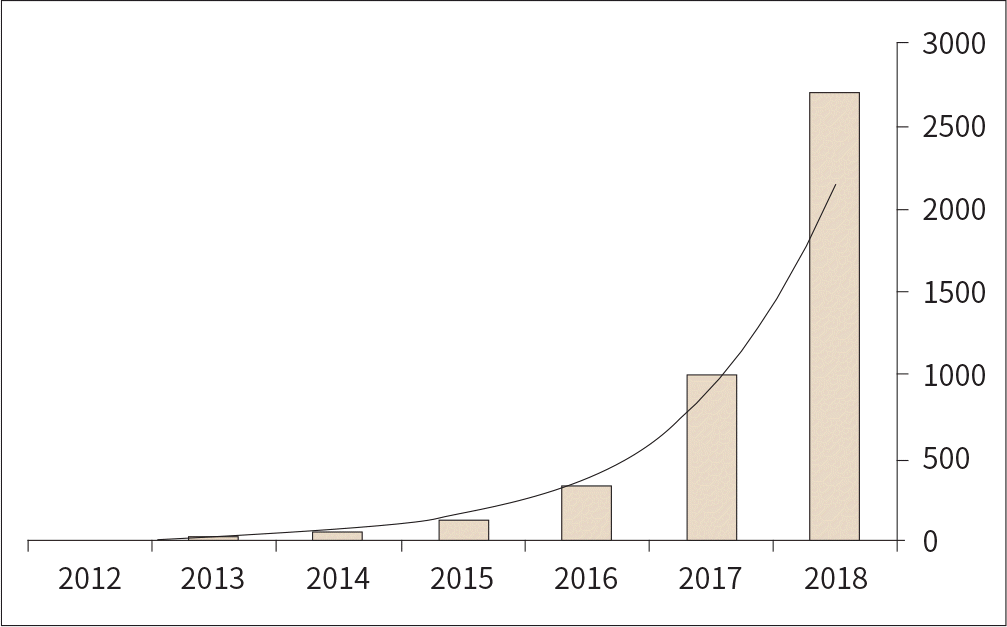
Fig. 3.
Relationship between the amount of noise in the dataset and the critical number of clean training examples needed to achieve high test accuracy. MNIST = Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology Adapted from Rolnick et al. arXiv preprint 2017;arXiv:1705.10694, with permission of author (7).
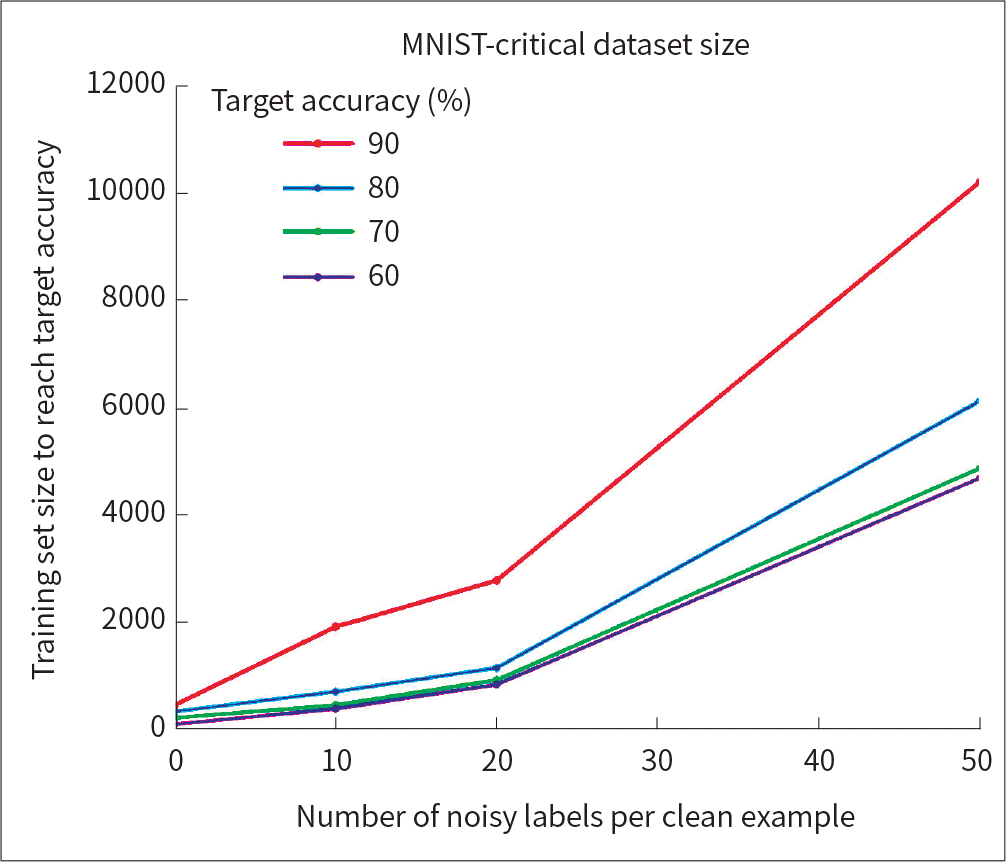
Fig. 4.
Correlation between ImageNet Top-1 one-crop accuracy and amount of operations. Adapted from Canziani et al. arXiv preprint 2016;arXiv:1605.07678, with permission of author (15).
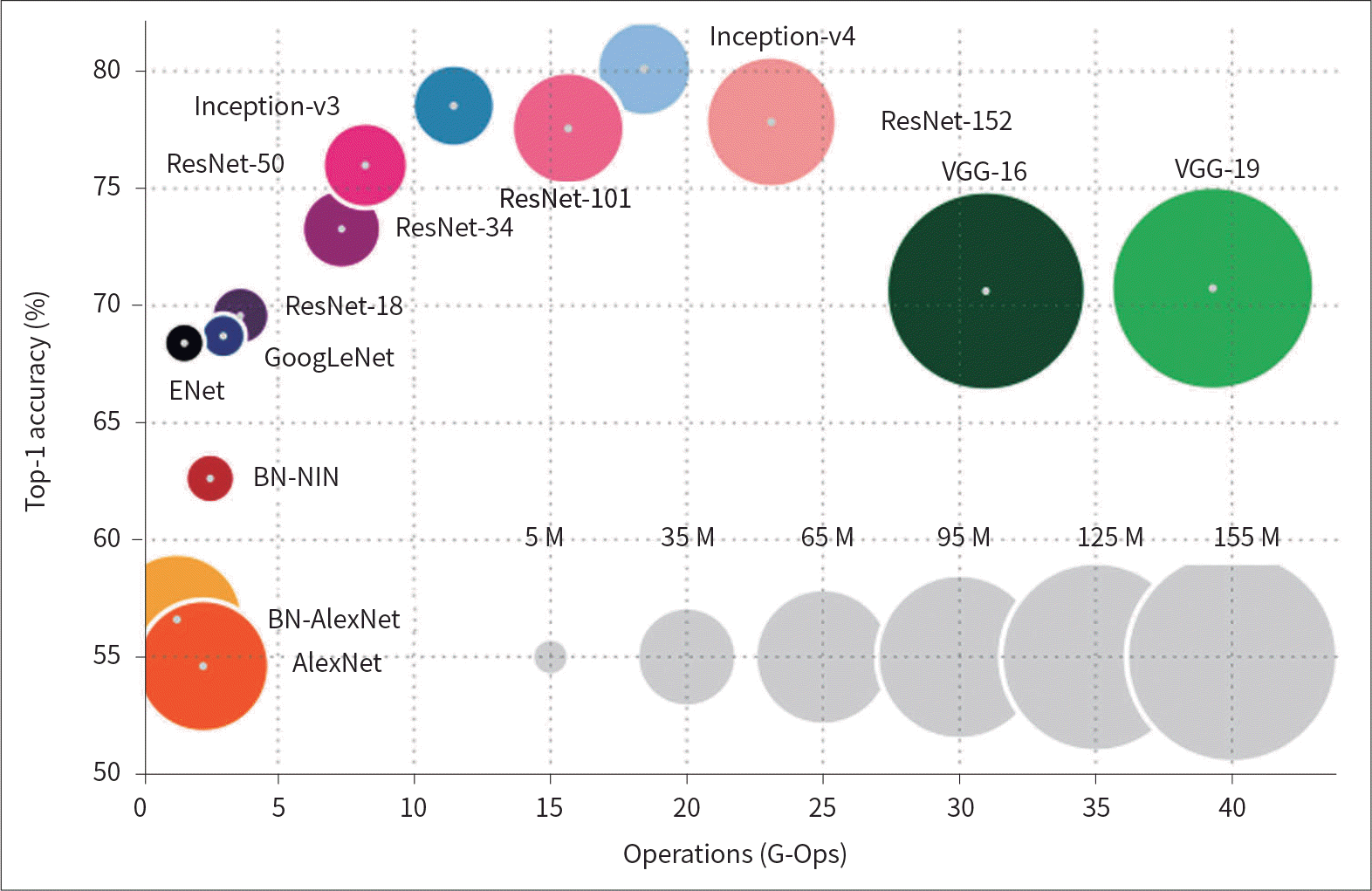
Table 1.
Latest important papers on deep learning in the field of medical imaging
∗Prospective assessment. Adapted from Eric Topol. Available from: URL: https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1051174567882907648, with permission of author (3).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download