Abstract
Objective
Methods
Figures and Tables
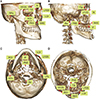 | Figure 1Cephalometric landmarks indicated on three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography images. A, 45° lateral view; B, 90° lateral view (clipping view); C, inferior view; D, superior view.RFZS, Right frontozygomatic suture; RPo, right porion; ROr, right orbitale; LOr, left orbitale; LFZS, left frontozygomatic suture; LPo, left porion.
See Table 2 for definitions of the other landmarks.
|
 | Figure 2The midsagittal plane (MSP) established by different reorientation methods. A, Superolateral view. B, Superior view. C, Frontal view.M1, The MSP perpendicular to the horizontal plane including the right orbitale, right porion, and left orbitale while passing through the crista galli and basion; M2, the MSP passing through the nasion, incisive foramen, and basion; M3, the MSP passing through the nasion, anterior nasal spine, and posterior nasal spine.
|
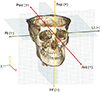 | Figure 3The three-dimensional coordinate systems used in this study.N, Nasion; Ant, anterior side; Post, posterior side; Rt, right side; Lt, left side; Sup, superior side; Inf, inferior side.
|
Table 3
The distances of the landmarks to the MSPs according to the RMs (mm)

MSP, Midsagittal plane; RM, reorientation method; SD, standard deviation; MidOr, midorbitale; MidFZS, midfrontozygomatic suture; MidPo, midporion.
*Group 1 consisted of 10 patients with skeletal Class I malocclusion and a menton (Me) deviation of less than 2 mm, group 2 included 11 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of less than 2 mm, group 3 consisted of nine patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of 2 to less than 4 mm, and group 4 included 13 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of more than 4 mm.
See Table 2 for definitions of the other landmarks.
Table 4
The MADs according to the RMs for the groups (mm)

Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
MAD, Mean absolute distance; RM, reorientation method.
*p < 0.05 by two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Greenhouse–Geisser; †p > 0.05 by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA.
‡Group 1 consisted of 10 patients with skeletal Class I malocclusion and a menton (Me) deviation of less than 2 mm, group 2 included 11 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of less than 2 mm, group 3 consisted of nine patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of 2 to less than 4 mm, and group 4 included 13 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of more than 4 mm.
Table 6
Landmarks showing significance in the difference in values of those coordinates among RMs in within-group comparisons (mm)

RM, Reorientation method; Δ X, difference value for the x coordinate; Δ Y, difference value for the y coordinate; Δ Z, difference value for the z coordinate; SD, standard deviation.
*p < 0.05.
†Group 1 consisted of 10 patients with skeletal Class I malocclusion and a menton (Me) deviation of less than 2 mm, group 2 included 11 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of less than 2 mm, group 3 consisted of nine patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of 2 to less than 4 mm, and group 4 included 13 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of more than 4 mm.
See Figure 1, Tables 2 and 3 for definitions of each landmark or measurement.
Table 7
Landmarks showing significance in the difference in values of those coordinates among RMs in between-group comparisons (mm)

*p < 0.05 by one-way analysis of variance.
†Group 1 consisted of 10 patients with skeletal Class I malocclusion and a menton (Me) deviation of less than 2 mm, group 2 included 11 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of less than 2 mm, group 3 consisted of nine patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of 2 to less than 4 mm, and group 4 included 13 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and a Me deviation of more than 4 mm.
See Tables 3 and 6 for definitions of each landmark or measurement.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download