Abstract
Purpose
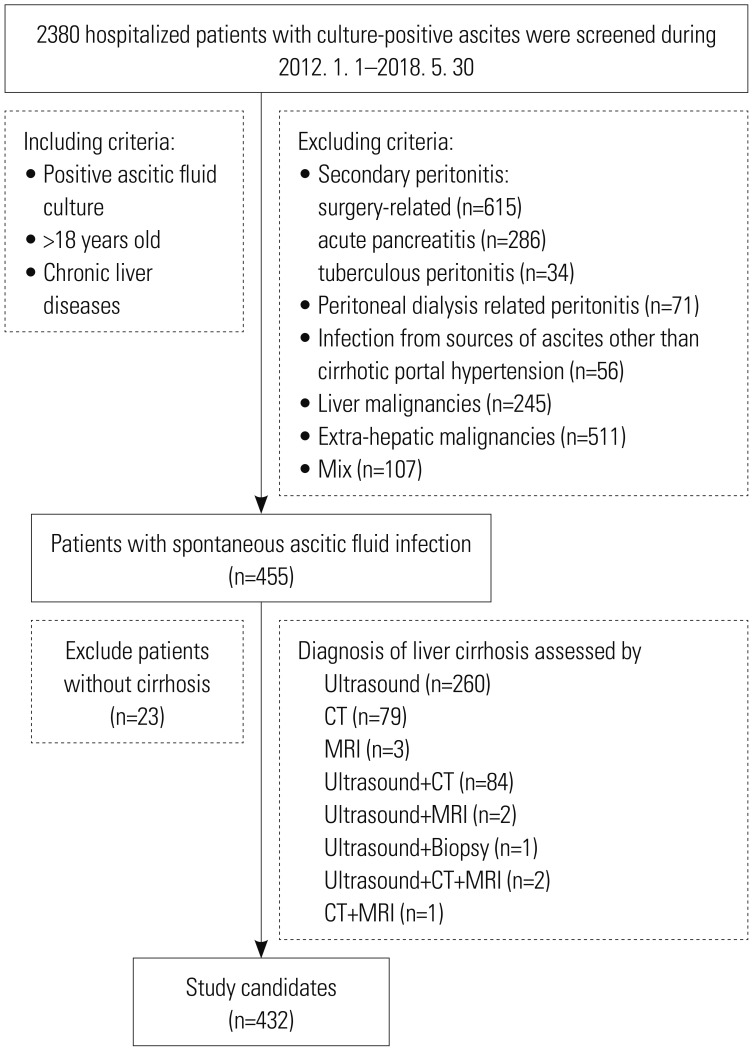
Materials and Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
Conceptualization: Jing Liu, Yanhang Gao, Xianbo Wang, and Xin Zheng.
Data curation: Jing Liu.
Formal analysis: Jing Liu.
Funding acquisition: Xin Zheng, Hai Li, and Jinjun Chen.
Investigation: Zhiping Qian, Jinjun Chen, Yan Huang, Zhongji Meng, Xiaobo Lu, Guohong Deng, Feng Liu, and Hai Li.
Methodology: Zhiguo Zhang.
Project administration: Jing Liu.
Resources: Zhiping Qian, Jinjun Chen, Yan Huang, Zhongji Meng, Xiaobo Lu, Guohong Deng, Feng Liu, and Hai Li.
Software: Zhiguo Zhang.
Supervision: Jing Liu and Xin Zheng.
Validation: Jing Liu and Xin Zheng.
Visualization: Jing Liu.
Writing—original draft: Jing Liu and Xin Zheng.
Writing—review & editing: Jing Liu and Xin Zheng.
Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
References
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 1
Supplementary Table 2
Supplementary Table 4
Fig. 2
Trends in microorganism and multidrug-resistant isolates distributions between 2012–2015 and 2016–2018. ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; FQR, fluoroquinolone-resistant; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PRSV, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus viridans.

Table 1
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Community-Acquired, Healthcare-Associated, and Nosocomial Culture-Positive Spontaneous Ascitic Infections
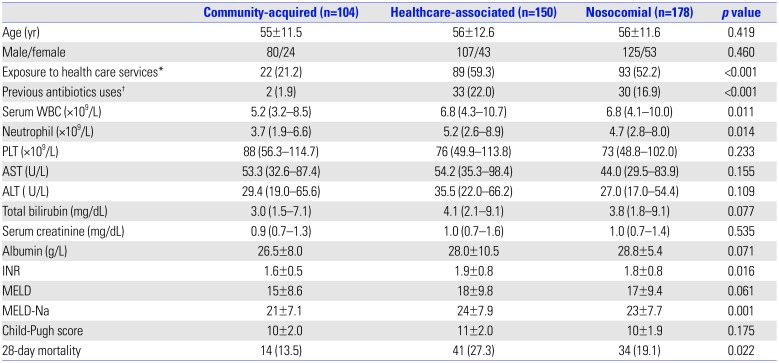
WBC, white blood cell; PLT, platelet; AST, aspartate transaminase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; MELD-Na, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Sodium.
Categorical variables: number (percentage). Continuous variables: means±SD, median and interquartile ranges.
*Health care services are defined as hospitalization or contact with the health care system (emergency department, nursing home, and clinic) within 2 weeks prior to admission. †Previous antibiotics are defined as any antibiotics used for more than 2 days during the 14 days before admission.
Table 2
Distributions of Resistance Microorganisms between Survivors and Non-Survivors
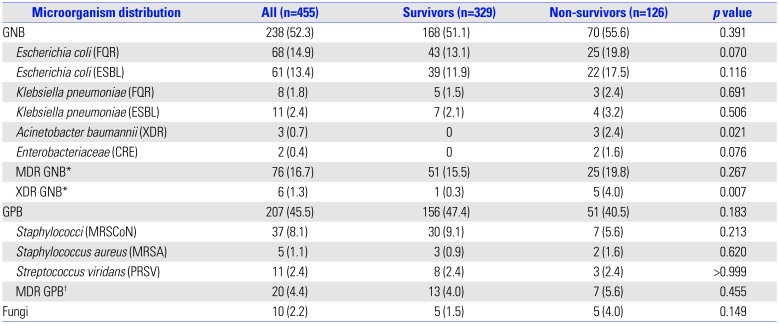
FQR, fluoroquinolone-resistant; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; XDR, extensively drug resistant; CRE, carbapenemase resistant Enterobacteriaceae; MRSCoN, methicillin resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PRSV, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus viridans; GNB, gram-negative bacteria; GPB, gram-positive bacteria; MDR GNB, multidrug resistant GNB; XDR GNB, extensively drug resistant GNB.
Categorical variables: number (percentage).
*MDR and XDR GNB including Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Acinetobacter spp. †MDR GPB including Enterococcus spp. and Staphylococcus aureus.
Table 3
In Vitro Susceptibility Rates (%) of Gram-Negative Isolates
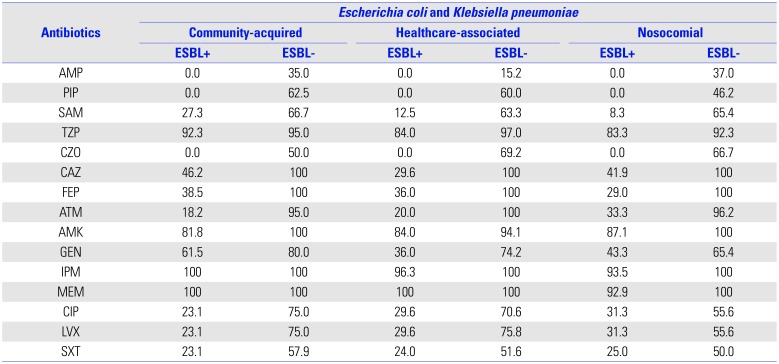
AMP, ampicillin; PIP, piperacillin; SAM, ampicillin/sulbactam; TZP, piperacillin/tazobactam; CZO, cefazolin; CAZ, ceftazidime; FEP, cefepime; ATM, aztreonam; AMK, amikacin; GEN, gentamicin; IPM, imipenem; MEM, meropenem; CIP, ciprofloxacin; LVX, levofloxacin; SXT, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase.
Table 4
In Vitro Susceptibility Rates (%) of Gram-Positive Isolates
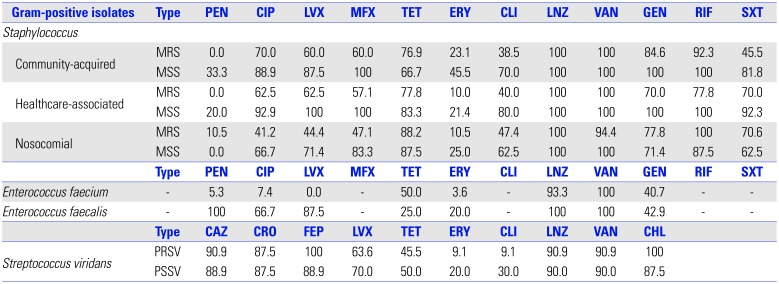
| Type | PEN | CIP | LVX | MFX | TET | ERY | CLI | LNZ | VAN | GEN | RIF | SXT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecium | - | 5.3 | 7.4 | 0.0 | - | 50.0 | 3.6 | - | 93.3 | 100 | 40.7 | - | - |
| Enterococcus faecalis | - | 100 | 66.7 | 87.5 | - | 25.0 | 20.0 | - | 100 | 100 | 42.9 | - | - |
| Type | CAZ | CRO | FEP | LVX | TET | ERY | CLI | LNZ | VAN | CHL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptococcus viridans | PRSV | 90.9 | 87.5 | 100 | 63.6 | 45.5 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 100 |
| PSSV | 88.9 | 87.5 | 88.9 | 70.0 | 50.0 | 20.0 | 30.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 87.5 |
PEN, penicillin; CIP, ciprofloxacin; LVX, levofloxacin; MFX, moxifloxacin; TET, tetracycline; ERY, erythromycin; CLI, clindamycin; LNZ, linezolid; VAN, vancomycin; GEN, gentamicin; RIF, rifampin; SXT, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim; CAZ, ceftazidime; CRO, ceftriaxone; FEP, cefepime; CHL, chloramphenicol; MRS, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus; MSS, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus; PRSV, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus viridans; PSSV, penicillin-sensitive Streptococcus viridans.
Table 5
Predictors of 28-Day Mortality in Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Cirrhotic Patients with Culture-Positive SAI
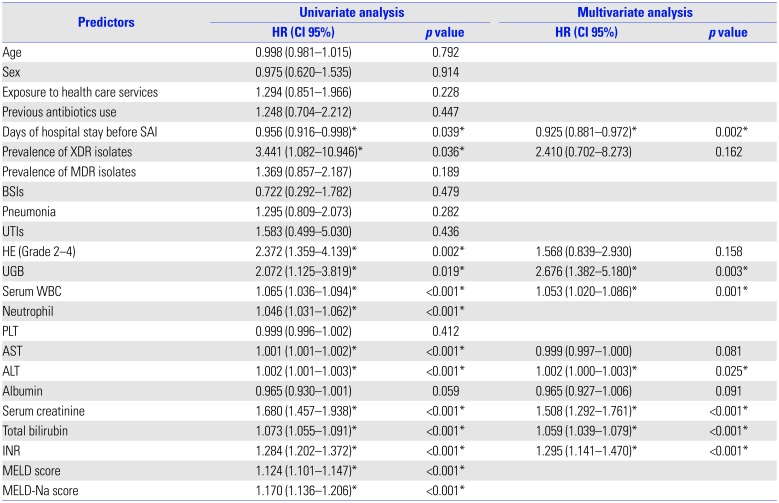
SAI, spontaneous ascitic infection; BSIs, blood stream infections; UTIs, urinary tract infections; HE (Grade 2–4), hepatic encephalopathy (Grade 2–4); UGB, upper gastrointestinal bleeding; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
MELD scores, MELD-Na scores and neutrophil were not included in the multivariate model to avoid potential collinearities.
*p-values <0.05 and corresponding HR are indicated.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download