Abstract
Figures and Tables
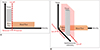 | Fig. 1Comparison of conventional clutter filter of color Doppler ultrasonography and advanced clutter filter of microvascular ultrasonography.
A. Conventional clutter filter of color Doppler ultrasonography cannot distinguish between tissues and low-velocity vessels using velocity information. B. Advanced clutter filter of microvascular ultrasonography makes it possible to extract low-velocity vessels by exploiting spatiotemporal coherence information.
|
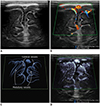 | Fig. 2Normal brain ultrasonography in 2-month-old boy.
A. Grayscale ultrasonography. B. Color Doppler ultrasonography shows leptomeningeal vessels covering gyri. C. Illustration indicates intracortical, subcortical, and medullary vessels, as seen on microvascular ultrasonography (D). Parameters on Doppler images: DR = dynamic range, F = filter, FA = frame average, G = gain, P = power
|
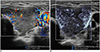 | Fig. 3Thyroid ultrasonography in 14-year-old girl with toxic Grave's disease.Microvascular ultrasonography image (B) shows status of vascularity better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography image (A).
|
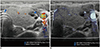 | Fig. 4Thyroid ultrasonography in 13-year-old girl with non-toxic simple goiter.Both color Doppler ultrasonography (A) and microvascular ultrasonography images (B) show scanty parenchymal vascularity of thyroid gland, which correlated with normal results of thyroid function tests (not shown here).
|
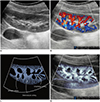 | Fig. 5Normal kidney ultrasonography in 10-year-old girl.
A. Grayscale ultrasonography. B. Color Doppler ultrasonography shows interlobar arteries and some arcuate and interlobular arteries. C. Illustration indicates interlobar, arcuate, and peripheral interlobular arteries filling renal cortex tightly, as seen on microvascular ultrasonography (D).
Microvascular ultrasonography also defines hypoechoic renal medulla clearly.
|
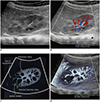 | Fig. 6Kidney ultrasonography in 5-month-old girl with acute pyelonephritis.
A. On grayscale ultrasonography, wedge-shaped, hyperechoic lesion is suspected at upper pole. B. Color Doppler ultrasonography shows area of hypoperfusion at upper pole. C. Illustration indicates area of hypoperfusion, interlobular arteries stretched by swollen medulla, and scanty interlobular arteries, as seen on microvascular ultrasonography (D).
|
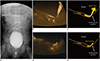 | Fig. 7Microvascular ultrasonography video clips and illustrations of 22-month-old boy with grade 2 vesicoureteral reflux confirmed on voiding cystourethrography.
A. Refluxed contrast media from urinary bladder in right ureter, renal pelvis, and calyces without dilatation (arrows). B, C. Normal urine flow from distal ureter to urinary bladder (B; Supplementary Movie 1). D, E. Reversed urine flow from ureterovesical junction to distal ureter (D; Supplementary Movie 2).
|
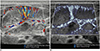 | Fig. 8Small bowel ultrasonography in 3-day-old boy with adenoviral enteritis.Microvascular ultrasonography image (B) shows vasa recta and vessels circumscribing bowel wall better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography image (A).
|
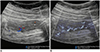 | Fig. 9Small bowel ultrasonography in 16-year-old girl with tuberculous enteritis.Microvascular ultrasonography image (B) shows transmural vessels better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography image (A).
|
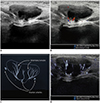 | Fig. 10Ovarian ultrasonography in 30-month-old girl with incarcerated left ovarian hernia.
A. Grayscale ultrasonography. B. Color Doppler ultrasonography shows ovarian arteries and veins close to hilum. D. Microvascular ultrasonography shows more arterioles traversing ovarian medulla to cortex, which are indicated on illustration (C).
|
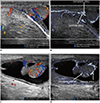 | Fig. 11Testicular ultrasonography longitudinal scan in 25-day-old boy with scrotal hydrocele.Microvascular ultrasonography images (B, D) show testicular, cremasteric, capsular, and centripetal arteries better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography images (A, C).
|
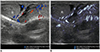 | Fig. 12Testicular ultrasonography transverse scan in 2-month-old boy with right inguinal hernia.Perfusion of right testis (R) is lesser than that of left testis (L) because vascular pedicle is compressed by right inguinal hernia (not shown here). Perfusion differences between testes are more pronounced on microvascular ultrasonography (B) than on color Doppler ultrasonography (A).
|
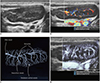 | Fig. 13Reactive cervical lymphadenopathy in 4-year-old boy.
A. Grayscale ultrasonography. B. Color Doppler ultrasonography shows hilar and paracortical vessels. C. Illustration indicates hilar, paracortical, and peripheral cortical vessels and paracortices, as seen on microvascular ultrasonography (D).
|
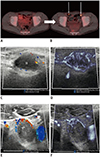 | Fig. 14Inguinal metastatic lymphadenopathies in 15-year-old boy with desmoplastic small round-cell tumor.
A, B. 18F-F-FDG positron emission tomography/CT scans performed at 2-month intervals. Increased 18F-F-FDG uptake (arrows) in bilateral inguinal lymph nodes on follow-up CT (B) suggests metastases. C, D. Right inguinal lymphadenopathy. E, F. Left inguinal lymphadenopathy. Microvascular ultrasonography (D, F) defines increased vascular structures better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography (C, E). CT = computed tomography, 18F-F-FDG = 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose
|
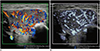 | Fig. 15Infantile hemangioma of right parotid gland in 1-month-old boy.Microvascular ultrasonography video clip (Supplementary Movie 4) (B) shows definition of margin and extent of mass better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography video clip (Supplementary Movie 3) (A).
|
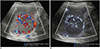 | Fig. 16Cavernous hemangioma of spleen in 10-year-old boy.Microvascular ultrasonography video clip (Supplementary Movie 6) (B) demonstrates small vessels within mass better compared to color Doppler ultrasonography video clip (Supplementary Movie 5) (A).
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download