INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and tissue preparations
Micro-CT-based evaluation of bone thickness
Histopathological analysis and immunohistochemistry of animal tissues
Immunofluorescence (IF) staining and confocal microscopy
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Bioinformatic analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Histopathological evidence of neo-osteogenesis in the eosinophilic CRSwNP model
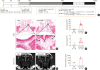 | Fig. 1Establishment of eosinophilic CRS with neo-osteogenesis murine model. (A) A schematic representation of the study protocol. (B) Representative images of decalcified tissue specimens showing histological evidence of neo-osteogenesis in mice. Insets in (B) show a magnified view of the outlined area (bottom). The rows of osteoblasts (arrowhead) at the rim of bone were noted. The white arrowhead indicates an osteoclast, while the black arrow indicates a Haversian canal. Original magnification ×2.5 (above) and insets ×40 (bottom). (C, D) The numbers of osteoblasts and osteoclasts per HPF were quantified in indicated groups. (E) Micro-CT evaluation of bony changes. Evidence of bone thickening (arrowhead) was found in the OVA/SEB-treated group. (F) Histo-morphometric analyses showed upregulation of bone thickness in the OVA/SEB-delivered group. All results are presented as mean ± SEM. Individual values are indicated by dots (C, D, F). Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney U test for pairwise comparisons (C, D, F).
OVA, ovalbumin; SEB, staphylococcal enterotoxin B; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; i.p., intraperitoneal; i.n., intranasal; HPF, high-powered field; CT, computed tomography; SEM, standard error of the mean.
*P < 0.01.
|
Increased RUNX2 expression in eosinophilic CRS with neo-osteogenesis
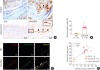 | Fig. 2OVA and SEB induced the expression of RUNX2 and osteonectin. (A) Representative photographs of immune-histochemical staining against RUNX2 (above) and osteonectin (bottom). Insets in (A) present a magnified view of the outlined area, and arrowheads denote representative positive cells (scale bar = 50 µm in above and scale bar = 20 µm in bottom). (B) The numbers of RUNX2-positive cells per HPF were counted in each group. (C) Co-localization of RUNX2 (red) and osteonectin (green) in nasal tissues revealed by immunofluorescence staining. Arrowheads indicate RUNX2 and osteonectin-double positive cells (yellow) (scale bar = 10 µm). (D) Relationship between bone thickness and RUNX2-positive cells. All results are presented as mean ± SEM. Individual values are indicated by dots (B, D). Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney U test for pairwise comparisons (B). Pearson's r values and the corresponding P-values were determined by Pearson's correlation test (D).
OVA, ovalbumin; SEB, staphylococcal enterotoxin B; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; HPF, high-powered field; SEM, standard error of the mean.
*P < 0.01.
|
Increased IL-13 expression in eosinophilic CRS with neo-osteogenesis
 | Fig. 3OVA and SEB upregulated the expression of IL-13 and showed positive correlations with RUNX2 downstream genes. (A) Representative images of immune-histochemical staining against IL-13 (original magnification ×400). Insets in (A) show a magnified view of the outlined area, and arrowheads denote IL-13-positive cells (scale bar = 50 µm). (B) The number of IL-13-positive cells per HPF was counted and compared to the control group. Correlation of the number of IL-13-positive cells and the number of RUNX2-positive cells (C) or the number of IL-13-positive cells and bone thickness (D) in each group of mice. (E) Relative mRNA expressions of IL13, RUNX2, and RUNX2 downstream genes (MMP9, COL1A1, and SPP1) in mucosal tissues from mice were compared. All results are presented as means ± SEM. Individual values are indicated by dots (B-E). Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney U test for pairwise comparisons (B, E). Pearson's r values and the corresponding P-values were determined by Pearson's correlation test (C, D).
OVA, ovalbumin; SEB, staphylococcal enterotoxin B; IL, interleukin; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; HPF, high-powered field; MMP9, matrix metallopeptidase 9; COL1A1, collagen type 1; SPP1, osteopontin; SEM, standard error of the mean; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
*P < 0.01.
|
Positive correlations between IL-13 and RUNX2 downstream genes in human CRS transcriptome
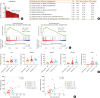 | Fig. 4IL-13 is upregulated in CRS patients and positively correlated with osteogenesis-related genes. (A) Distribution of IL13 mRNA levels in 26 human CRS nasal tissues (data set GSE23552). Based on the median value, the CRS patients with or without NPs were categorized into high and low groups. The number of CRS tissues are IL13 high group (n = 13) and IL13 low group (n = 13). (B) GSEA. osteogenesis-related gene sets were selected in the GO collection from MSigDB v6.2. The 8 gene sets which show a positive correlation with IL13 are presented (P < 0.05 and FDR < 0.25). (C) Representative enrichment plots of the GSEA analysis in the GSE23552 data set. (D) Relative mRNA levels of IL-13, RUNX2 and RUNX2 downstream genes in the nasal tissues obtained from the GSE23552 data set. (E) Correlation between IL13 and SPP1 or IL13 and MMP9. Spearman's correlation analysis was performed in each group of subjects. All results are presented as means ± SEM. Individual values are indicated by dots (D, E). Statistical significance was determined by Kruskal-Wallis tests (P < 0.01), followed by Mann-Whitney U test for pairwise comparisons (D). Spearman's r values and the corresponding P-values were determined by spearman's correlation test (E).
IL, interleukin; CRS, chronic rhinosinusitis; NP, nasal polyp; GSEA, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis; GO, Gene Ontology; FDR, false discovery rate; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; SPP1, osteopontin; MMP9, matrix metallopeptidase 9; SEM, standard error of the mean; ES, enrichment score; NES, normalized enrichment score; COL1A1, collagen type 1; CRSsNP, chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyp; CRSwNP, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp.
*P < 0.05; †P < 0.01.
|
RSV treatment diminished osteogenesis in eosinophilic CRS NP model
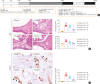 | Fig. 5Resveratrol suppresses the new bone formation in neo-osteogenesis murine model. (A) A schematic illustration of the study procedure. (B) Representative H&E photographs of nasal tissue specimens (left). The number of osteoblasts and bone thickness per HPF were quantified in specified groups and compared (scale bar = 50 µm). (C) Cells showing RUNX2 positivity per HPF were counted in designated groups and compared (scale bar = 20 µm). All results are presented as means ± SEM. Individual values are indicated by dots (B, C). Statistical significance was determined by Kruskal-Wallis tests (P < 0.01), followed by Mann-Whitney U test for pairwise comparisons (B, C).
H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; HPF, high-powered field; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; OVA, ovalbumin; SEB, staphylococcal enterotoxin B; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; i.p., intraperitoneal; i.n., intranasal.
Significant differences are denoted relative to group B (OVA/SEB-applied group) (*P < 0.05; †P < 0.01) or to group C (Resveratrol-treated group) (‡P < 0.01).
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download