Abstract
Purpose
To compare the accuracy of three intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation formulas (SRK/T, Barrett Universal II, and T2) in cataract surgery patients.
Methods
In total, 73 eyes of 73 patients who underwent uneventful cataract surgery were retrospectively reviewed. IOL power was determined using SRK/T, Barrett Universal II, and T2 preoperatively. The findings were compared with the actual refractive outcome to obtain the prediction error. The mean prediction error (ME) and mean absolute error (MAE) of each formula were compared. The MAE was defined as the difference between the postoperative spherical equivalence (SE) and the preoperatively predicted SE. The ME and MAE of each formula 3 months after surgery were compared with preoperatively predicted SE. Eyes were classified into subgroups based on axial length (AL) and average keratometry (K).
Results
The ME and MAE for the three formulas were SRK/T [−0.08 ± 0.45 diopters (D) and 0.35 ± 0.40 D, respectively], Barrett Universal II (−0.01 ± 0.44 D and 0.33 ± 0.30 D, respectively), and T2 (0.04 ± 0.45 D and −0.34 ± 0.30 D, respectively), but no statistically significant differences were detected. Similar results were obtained in groups with a long AL or a large average K. In groups with an AL ≥ 26 mm or with an average K ≥ 47 D, the Barrett Universal II formula yielded the smallest standard deviation and a ME closest to zero, but these differences were not statistically significant.
Conclusions
No significant differences were observed between the three formulas regarding ME or MAE. However, recent formulas such as the Barrett Universal II could provide certain benefits in predicting IOL power for patients with a long AL (> 26 mm) or larger average K. Further research with a larger sample size is recommended for more evaluation.
Figures and Tables
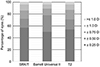 | Figure 1The Percentage of eyes of over the entire axial length range with a prediction error between ± 0.25 D, ± 0.50 D, ± 0.75 D and ± 1.00 D for each of the 3 formulas. All three formulas showed similar tendency regarding prediction error even though the differences were not statistically significant. D = diopters. |
 | Figure 2Mean error values three month after surgery shown for different keratometry values for three formulas. (A) Barrett Universal II showing smallest standard deviation and mean prediction error (ME) closest to zero in keratometry 47 diopters (D). (B) Mean error values three months after surgery shown for different axial lengths for three formulas. Barrett Universal II showing smallest standard deviation and ME closest to zero in axial lengths 26 mm. |
Table 2
Comparison between SRK/T, Barrett Universal II, and T2 formulas in mean prediction error and mean absolute error

Table 3
Comparison between SRK/T, Barrett Universal II, and T2 formulas in mean prediction error and mean absolute error according to keratometry value (Kavg ≥ 46 D or <46 D)

References
1. Abulafia A, Barrett GD, Rotenberg M, et al. Intraocular lens power calculation for eyes with an axial length greater than 26.0 mm: comparison of formulas and methods. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:548–556.


2. Narváez J, Zimmerman G, Stulting RD, Chang DH. Accuracy of intraocular lens power prediction using the Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, Holladay 2, and SRK/T formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2050–2053.

3. Németh J, Fekete O, Pesztenlehrer N. Optical and ultrasound measurement of axial length and anterior chamber depth for intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:85–88.


4. Olsen T, Olesen H, Thim K, Corydon L. Prediction of postoperative intraocular lens chamber depth. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:587–590.

5. Yi CH, Choi SH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Accuracy of the Haigis formula based on axial length and anterior chamber depth. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:175–181.

6. Srivannaboon S, Chirapapaisan C, Chirapapaisan N, et al. Accuracy of Holladay 2 formula using IOLMaster parameters in the absence of lens thickness value. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:2563–2567.

7. Melles RB, Holladay JT, Chang WJ. Accuracy of intraocular lens calculation formulas. Ophthalmology. 2018; 125:169–178.


8. Kane JX, Van Heerden A, Atik A, Petsoglou C. Intraocular lens power formula accuracy: comparison of 7 formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016; 42:1490–1500.


9. Sheard RM, Smith GT, Cooke DL. Improving the prediction accuracy of the SRK/T formula: the T2 formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1829–1834.


10. Patel RP, Pandit RT. Comparison of anterior chamber depth measurements from the Galilei Dual Scheimpflug Analyzer with IOLMaster. J Ophthalmol. 2012; 2012:430249.

11. Kim SI, Kang SJ, Oh TH, et al. Accuracy of ocular biometry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients with AL-Scan®. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1688–1693.

12. Shin JA, Hwang KY, Kim MS. Refractive eerror according to the anterior chamber depth and corneal refractive power in short eyes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:65–71.

13. Maeng HS, Ryu EH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Effects of anterior chamber depth and axial length on refractive error after intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:195–202.

14. Hoffer KJ. The hoffer Q formula: a comparison of theoretic and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:700–712.


15. Donoso R, Mura J, López M, Papic A. Emmetropization at cataract surgery. Looking for the best IOL power calculation formula according to the eye length. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2003; 78:477–480.

16. Oh JJ, Choi JS. Accuracy of intraocular lens power calculations according to corneal curvature in short eyes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:826–832.

17. Eleftheriadis H. IOLMaster biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–963.







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download