1. Ghazanfarpour M, Abdolahian S, Zare M, Shahsavari S. Association between anthropometric indices and quality of life in menopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2013; 29:917–920. PMID:
23895298.

2. Ghazanfarpour M, Kaviani M, Abdolahian S, Bonakchi H, Najmabadi Khadijeh M, Naghavi M, et al. The relationship between women's attitude towards menopause and menopausal symptoms among postmenopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2015; 31:860–865. PMID:
26425992.

3. Huang AJ, Moore EE, Boyko EJ, Scholes D, Lin F, Vittinghoff E, et al. Vaginal symptoms in postmenopausal women: self-reported severity, natural history, and risk factors. Menopause. 2010; 17:121–126. PMID:
19574936.
4. Weber MA, Limpens J, Roovers JP. Assessment of vaginal atrophy: a review. Int Urogynecol J. 2015; 26:15–28. PMID:
25047897.

5. Tersigni C, Di Simone N, Tempestilli E, Cianfrini F, Russo R, Moruzzi MC, et al. Non-hormonal treatment of vulvo-vaginal atrophy-related symptoms in post-menopausal women. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2015; 35:835–838. PMID:
25968636.

6. Naumova I, Castelo-Branco C. Current treatment options for postmenopausal vaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2018; 10:387–395. PMID:
30104904.

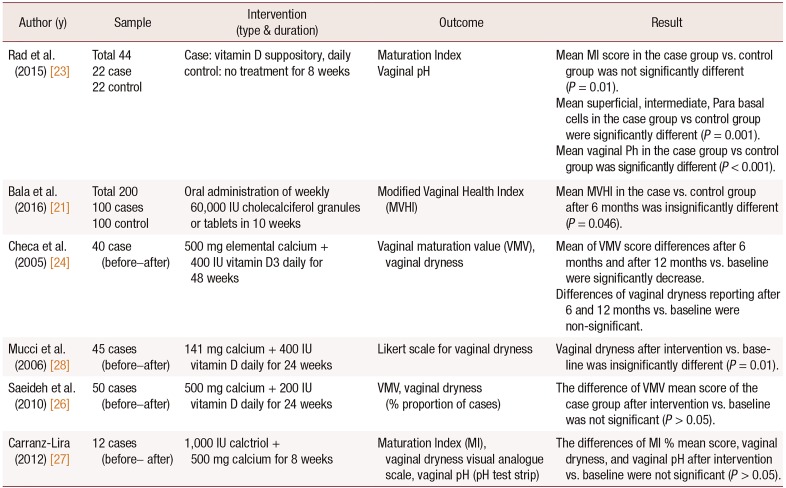
7. Yildirim B, Kaleli B, Düzcan E, Topuz O. The effects of postmenopausal Vitamin D treatment on vaginal atrophy. Maturitas. 2004; 49:334–337. PMID:
15531130.

8. Palma F, Volpe A, Villa P, Cagnacci A. Vaginal atrophy of women in postmenopause. Results from a multicentric observational study: The AGATA study. Maturitas. 2016; 83:40–44. PMID:
26421474.

9. Ballagh SA. Vaginal hormone therapy for urogenital and menopausal symptoms. Semin Reprod Med. 2005; 23:126–140. PMID:
15852198.

10. Dessie SG, Armstrong K, Modest AM, Hacker MR, Hota LS. Effect of vaginal estrogen on pessary use. Int Urogynecol J. 2016; 27:1423–1429. PMID:
26992727.

11. Lynch C. Vaginal estrogen therapy for the treatment of atrophic vaginitis. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2009; 18:1595–1606. PMID:
19788364.

12. Gambacciani M, Levancini M. Hormone replacement therapy and the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Prz Menopauzalny. 2014; 13:213–220. PMID:
26327857.
13. Castelo-Branco C, Cancelo MJ, Villero J, Nohales F, Juliá MD. Management of post-menopausal vaginal atrophy and atrophic vaginitis. Maturitas. 2005; 52 Suppl 1:S46–S52. PMID:
16139449.

14. Parnan emamverdikhan A, Golmakani N, SharifiSistani N, Taghi Shakeri M, Hasanzade Mofrad M, Sajadi Tabassi A. Comparing two treatment methods of vitamin E suppository and conjugated estrogen vaginal cream on the quality of life in menopausal women with vaginal atrophy. J Midwifery Reprod Health. 2014; 2:253–261.
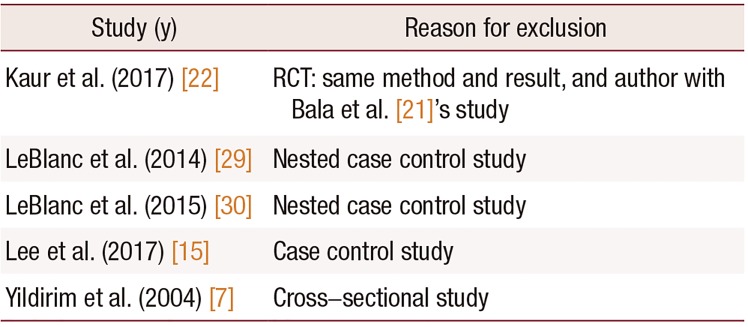
15. Lee A, Lee MR, Lee HH, Kim YS, Kim JM, Enkhbold T, et al. Vitamin D proliferates vaginal epithelium through RhoA expression in postmenopausal atrophic vagina tissue. Mol Cells. 2017; 40:677–684. PMID:
28843271.

16. Welsh J. Cellular and molecular effects of vitamin D on carcinogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012; 523:107–114. PMID:
22085499.

17. Irwýng MF, Thomas BF. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1999.
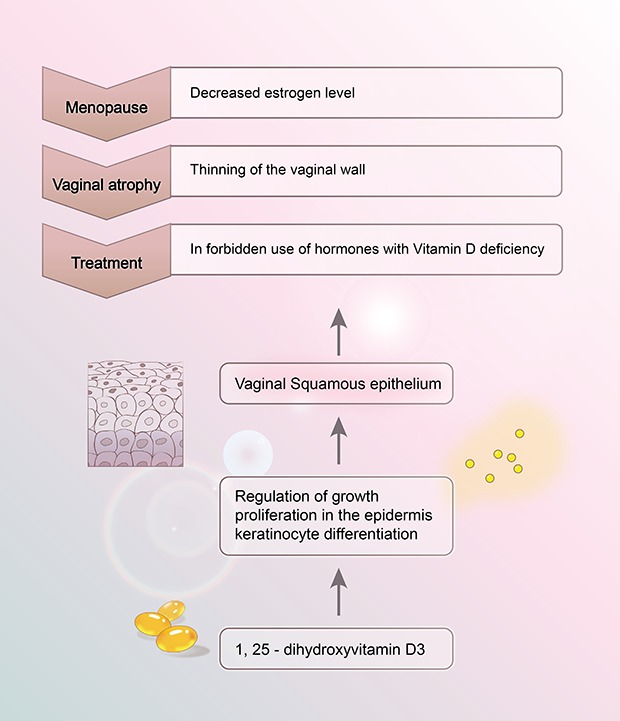
18. Kim TH, Lee HH, Park J. Immunohistochemical detection of the 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D receptor in the human vagina. Iran J Reprod Med. 2014; 12:805–810. PMID:
25709637.
19. Pike JW, Meyer MB. The vitamin D receptor: new paradigms for the regulation of gene expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3). Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2010; 39:255–269. PMID:
20511050.

20. Riazi H, Alaei S, Emamhadi M, Nazparvar B, Salmani F. The comparison of spiritual health and self-esteem in women with and without sexual violence. Electron Physician. 2017; 9:5705–5711. PMID:
29403609.

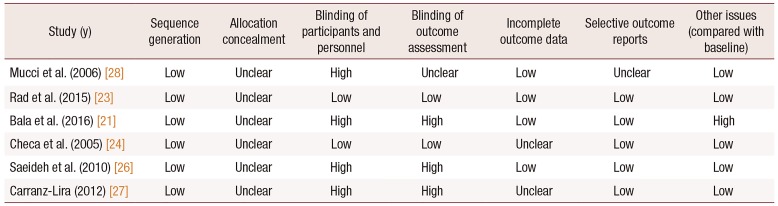
21. Bala R, Kaur H, Nagpal M. Authenticity of vitamin D in modified vaginal health index in geriatric subjects. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016; 5:4119–4122.

22. Kaur H, Bala R, Nagpal M. Role of Vitamin D in urogenital health of geriatric participants. J Midlife Health. 2017; 8:28–35. PMID:
28458477.
23. Rad P, Tadayon M, Abbaspour M, Latifi SM, Rashidi I, Delaviz H. The effect of vitamin D on vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2015; 20:211–215. PMID:
25878698.
24. Checa MA, Garrido A, Prat M, Conangla M, Rueda C, Carreras R. A comparison of raloxifene and calcium plus vitamin D on vaginal atrophy after discontinuation of long-standing postmenopausal hormone therapy in osteoporotic women. A randomized, masked-evaluator, one-year, prospective study. Maturitas. 2005; 52:70–77. PMID:
16143228.
25. Zareai M. Effect of vitamin E on the vaginal atrophy of postmenopausal women. Value Health. 2014; 17:A750.

26. Saeideh Z, Raziyeh M, Soghrat F. Comparing the effects of continuous hormone replacement therapy and tibolone on the genital tract of menopausal women; a randomized controlled trial. J Reprod Infertil. 2010; 11:183–187. PMID:
23926488.
27. Carranza-Lira S, Amador-Pérez C, Macgregor-Gooch AL, Estrada-Moscoso I. [Changes in maturation index and vaginal dryness in postmenopausal women who use or not calcitriol]. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2012; 50:537–540. Spanish. PMID:
23282268.
28. Mucci M, Carraro C, Mancino P, Monti M, Papadia LS, Volpini G, et al. Soy isoflavones, lactobacilli, Magnolia bark extract, vitamin D3 and calcium. Controlled clinical study in menopause. Minerva Ginecol. 2006; 58:323–334. PMID:
16957676.
29. LeBlanc ES, Desai M, Perrin N, Wactawski-Wende J, Manson JE, Cauley JA, et al. Vitamin D levels and menopause-related symptoms. Menopause. 2014; 21:1197–1203. PMID:
24736200.

30. LeBlanc ES, Hedlin H, Qin F, Desai M, Wactawski-Wende J, Perrin N, et al. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation do not influence menopause-related symptoms: Results of the Women's Health Initiative Trial. Maturitas. 2015; 81:377–383. PMID:
26044075.

31. Avenell A, Gillespie WJ, Gillespie LD, O'Connell D. Vitamin D and vitamin D analogues for preventing fractures associated with involutional and post-menopausal osteoporosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009; (2):CD000227. PMID:
19370554.

32. Kennel KA, Drake MT, Hurley DL. Vitamin D deficiency in adults: when to test and how to treat. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010; 85:752–757. quiz 757-8. PMID:
20675513.

33. Bolland MJ, Avenell A, Baron JA, Grey A, MacLennan GS, Gamble GD, et al. Effect of calcium supplements on risk of myocardial infarction and cardiovascular events: meta-analysis. BMJ. 2010; 341:c3691. PMID:
20671013.

34. Bolland MJ, Grey A, Avenell A, Gamble GD, Reid IR. Calcium supplements with or without vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular events: reanalysis of the Women's Health Initiative limited access dataset and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2011; 342:d2040. PMID:
21505219.

35. Bolland MJ, Grey A, Gamble GD, Reid IR. Calcium and vitamin D supplements and health outcomes: a reanalysis of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) limited-access data set. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011; 94:1144–1149. PMID:
21880848.

36. Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Shao A, Dawson-Hughes B, Hathcock J, Giovannucci E, Willett WC. Benefit-risk assessment of vitamin D supplementation. Osteoporos Int. 2010; 21:1121–1132. PMID:
19957164.

37. Zeyneloglu HB, Oktem M, Haberal NA, Esinler I, Kuscu E. The effect of raloxifene in association with vitamin D on vaginal maturation index and urogenital symptoms in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Fertil Steril. 2007; 88:530–532. PMID:
17336964.

38. Avenell A, Mak JC, O'Connell D. Vitamin D and vitamin D analogues for preventing fractures in post-menopausal women and older men. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; (4):CD000227. PMID:
24729336.

39. Purdue-Smithe AC, Whitcomb BW, Szegda KL, Boutot ME, Manson JE, Hankinson SE, et al. Vitamin D and calcium intake and risk of early menopause. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017; 105:1493–1501. PMID:
28490509.

40. Ghazanfarpour M, Sadeghi R, Abdolahian S, Latifnejad Roudsari R. The efficacy of Iranian herbal medicines in alleviating hot flashes: a systematic review. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd). 2016; 14:155–166. PMID:
27294213.

41. Chen MN, Lin CC, Liu CF. Efficacy of phytoestrogens for menopausal symptoms: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Climacteric. 2015; 18:260–269. PMID:
25263312.

42. Tadir Y, Gaspar A, Lev-Sagie A, Alexiades M, Alinsod R, Bader A, et al. Light and energy based therapeutics for genitourinary syndrome of menopause: consensus and controversies. Lasers Surg Med. 2017; 49:137–159. PMID:
28220946.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download